It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!
For a few months, I've been promising myself to make a post on being careful about what numbers do and don't represent (i.e. look behind the numbers). Figures like ERs, duration, performance. One of these days.I own PRIDX. ... It fell hard with coronavirus. But it's coming back, down -13% now, ytd. Down to 3 stars, but still with a silver decoration. ... Top 15% among peers, ytd. Not a great showing compared to peers LAST year, but still very good indeed.
For example a portfolio of 100% PRWCX would have a "Safe Withdrawal Rate" of 10% and a "Safe Perpetual Withdrawal Rate" of 5.6%. The rule of thumb for a Safe Perpetual Withdrawal Rate is 4% according to the Trinity Study (linked below).
The manufacturing sector hasn't completely rolled over yet, but the services sector simply ceased to exist starting late last month.....The message is clear: Main Street isn't just hurting, it is disappearing in a very literal sense. As Atlanta Fed boss Raphael Bostic warned earlier this month, "May is going to loom large, in terms of the transition of concern from this being a liquidity issue… to this perhaps translating and transferring into a solvency issue, and whether companies can exist at all."
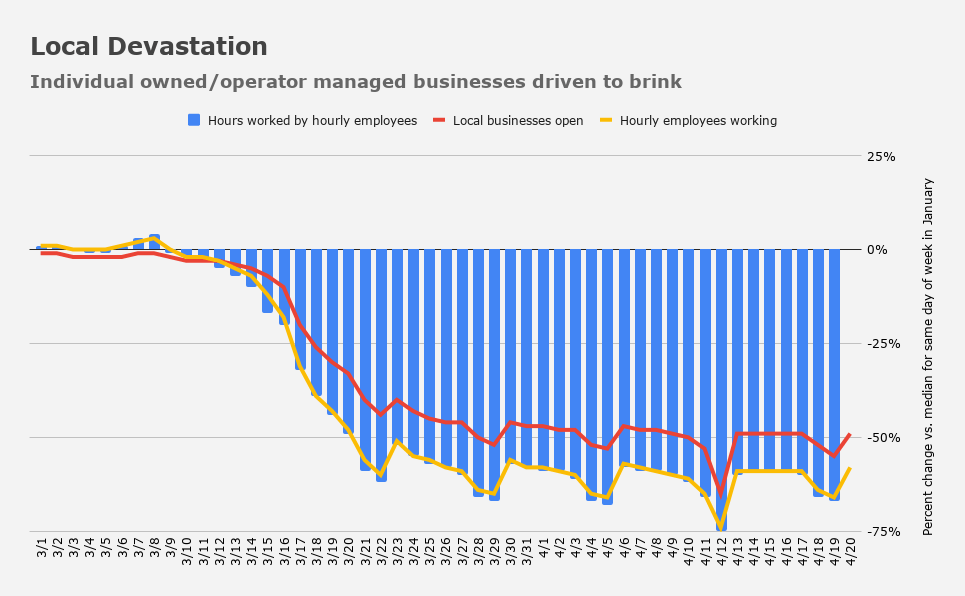
.(...from Homebase, a scheduling and time tracking tool used by more than 100,000 local businesses covering 1 million hourly employees.)
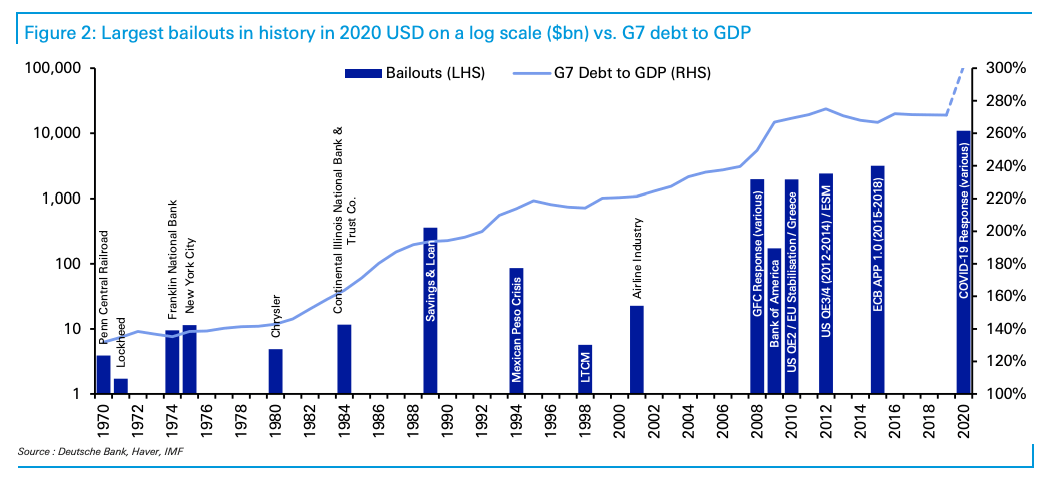
Deutsche Bank rolled up the fiscal and monetary support programs announced and implemented in the US and Europe into a single "bailout" figure. The sheer size of the COVID-19 response necessitated a log scale (on the left axis) in order to help "better identify the earlier bailouts and get a rough feel visually for the numbers," as the bank put it. ....."Obviously we won’t know how much will be used until much further down the road," the bank cautioned, in the course of presenting the numbers and accompanying visuals.
https://seekingalpha.com/article/4340027-dystopia-now
....policymakers have been deliberately suppressing volatility, compressing risk premia, tamping down credit spreads and keeping the market wide-open for borrowers for the better part of a decade....
Deutsche Bank's George Saravelos.....At the extreme, central banks could become permanent command economy agents administering equity and credit prices, aggressively subduing financial shocks. With unlimited capacity to print money, central banks have unlimited capacity to intervene in asset markets too. Put simply, a central bank that pegs bond, credit and equity markets is highly likely to stabilize portfolio flows as well.
This has been settled law for decades now. Here's a CNBC page discussing whether rewards are taxable.I believe that, unlike many cash back cards, Fido credit card now sends the tax form for these 2%, so it is not 2% cash back (no taxes, just cash return), but 2% minus taxes.
The Trinity Study:First, I wanted to see how this was working with recent stock market returns. The original study was only covering years up to 1995. I wanted to have more recent data. I wanted to make sure that the results were holding with more recent stock market behavior. So this simulation will cover returns until the end of 2019!
Secondly, the original study was only covering up to thirty years of retirement. I wanted to be sure that the portfolio can sustain withdrawals for much more extended periods. For people retiring early, I think that 50 years is not unreasonable.
I don't subscribe but for some reason the link worked for me.....The economists Milton Friedman and Anna Jacobson Schwartz demonstrated in “A Monetary History of the United States” that a collapse in the quantity of money was the main cause of the Great Depression. Hoping to avoid a repeat, the Federal Reserve in recent weeks has poured money into the economy at the fastest rate in the past 200 years. Unfortunately, this overreaction could turn out just as poorly; history suggests the U.S. will soon see an inflation boom.
Excluding the years immediately after the Revolutionary War, the past few weeks have seen by far the highest rate of monetary expansion in U.S. history. The Fed might defend itself by saying that its “shock and awe” tactics have given financial markets confidence that the coronavirus won’t cause a long and deep recession. And its massive bond purchases—more than $500 billion between March 11 and April 1—surely won’t continue at the same rate for the rest of the year.
It’s reasonable to assume that by spring 2021 the quantity of money will have increased by 15% and possibly by as much as 20%. That wouldn’t quite match the peak rates of expansion seen during and immediately after the two world wars of the 20th century, but it could surpass peacetime records, outpacing the previous peaks in the inflationary 1970s.
As in wartime, federal expenditures are rising sharply while tax revenues are being hit by the lockdown. Both World War I and World War II—and, indeed, the Vietnam War—were followed by nasty bouts of inflation.
Mr. Congdon CBE is chairman of the Institute of International Monetary Research at the University of Buckingham, England.
© 2015 Mutual Fund Observer. All rights reserved.
© 2015 Mutual Fund Observer. All rights reserved. Powered by Vanilla