It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!
https://www.propublica.org/article/lord-of-the-roths-how-tech-mogul-peter-thiel-turned-a-retirement-account-for-the-middle-class-into-a-5-billion-dollar-tax-free-piggy-bankUsing stock deals unavailable to most people, Thiel has taken a retirement account worth less than $2,000 in 1999 and spun it into a $5 billion windfall. To put that into perspective, here’s how much the average Roth was worth at the end of 2018: $39,108.
Which seems to bring us back to the thread AMG to Acquire Parnassus Funds:-Easterly, an asset management holding company that owns stakes in third-party investment management businesses and assists them with strategic growth, announced today it has acquired an equity interest in James Alpha Advisors, LLC, a boutique asset management firm specializing in Global REITs and liquid alternative portfolio solutions for institutional and individual investors. ...
As a result of the investment, Easterly has assumed operational control of the firm. ...
[Darrell Crate, Easterly’s Managing Principal] helped to build an asset management powerhouse as Chief Financial Officer of Affiliated Managers Group (NYSE: AMG), established Easterly in 2009...
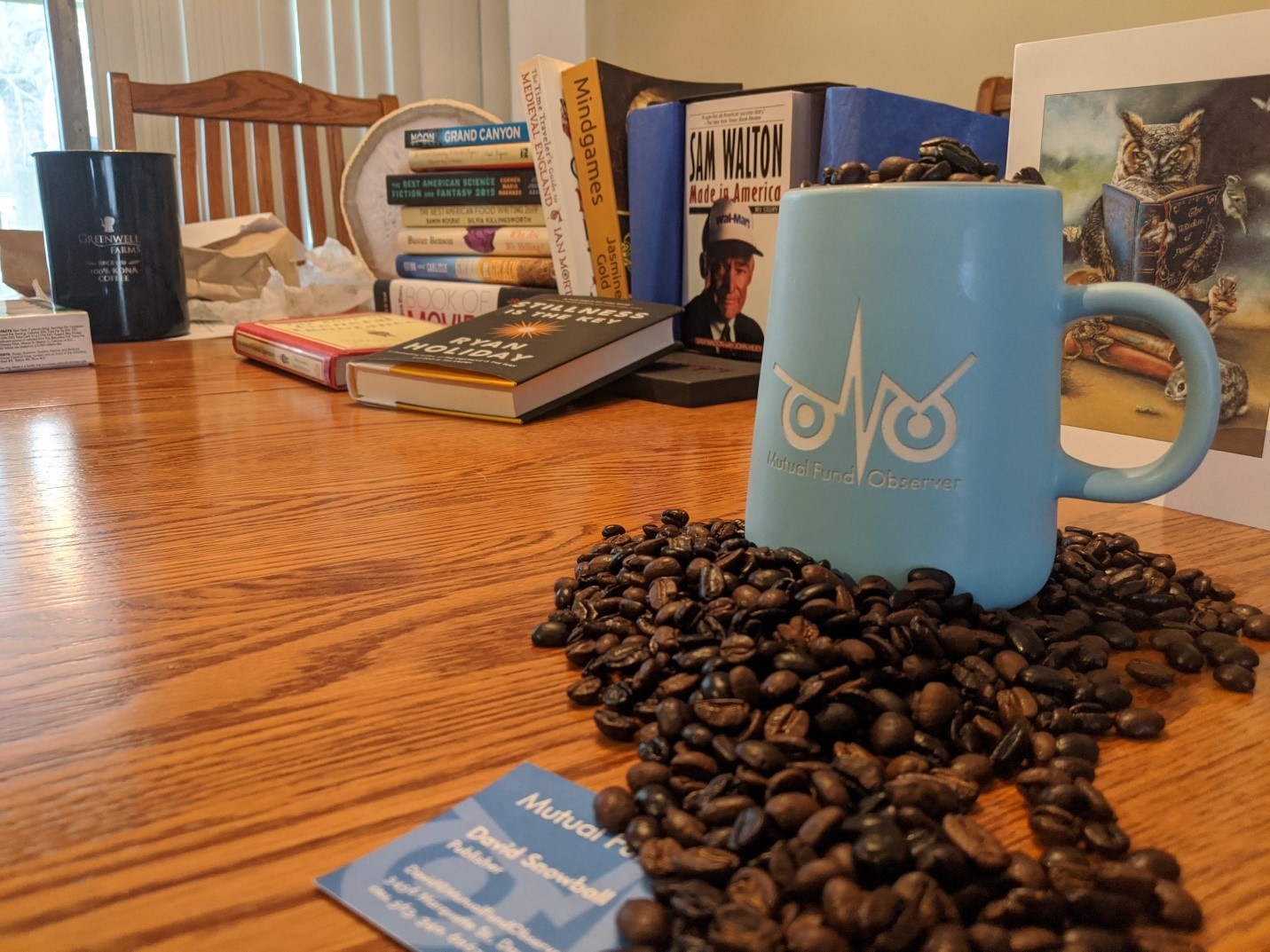

IMHO the answers are: no (it doesn't mean this) and yes (it is supposed to mean this).>> The Ulcer Index is about half of the S&P 500 meaning half as risky.
Is that what UI means / is supposed to mean?
If drawdown A is twice that of drawdown B, it is already being penalized twice as much by simply using its magnitude. Squaring that figure distorts this. And what is magical about squaring, as opposed to, say cubing, or taking the retracements to the 1.5 power? (These are all positive numbers we're using.) Why is squaring the appropriate "penalty"?A better method [than merely summing] is to add the squares of the retracements, in order to penalize large retracements proportionately more than small ones.
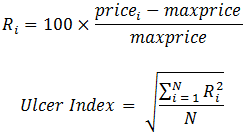


@davidrmoran,my 'petty' proofing and query had only to do with whether the quote posted as from the WSJ was actually from the WSJ, given the 'typo'; no one here is served by inexactness, of which there is enough, much less suspect or sketchy origin …
© 2015 Mutual Fund Observer. All rights reserved.
© 2015 Mutual Fund Observer. All rights reserved. Powered by Vanilla