Originally published in December 1, 2013 Commentary
 Roy Weitz first published the legacy Three Alarm fund list in 1996. He wanted to help investors decide when to sell mutual funds. Being on the list was not an automatic sell, but a warning signal to look further and see why.
Roy Weitz first published the legacy Three Alarm fund list in 1996. He wanted to help investors decide when to sell mutual funds. Being on the list was not an automatic sell, but a warning signal to look further and see why.
“I liken the list to the tired old analogy of the smoke detector. If it goes off, your house could be on fire. But it could also be cobwebs in the smoke detector, in which case you just change the batteries and go back to sleep,” he explained in a 2002 interview.
Funds made the list if they trailed their benchmarks for the past 1, 3, and 5 year periods. At the time, he grouped funds into only five equity (large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap, balanced, and international) and six specialty “benchmark categories.” Instead of pure indices, he used actual funds, like Vanguard 500 Index Fund VFINX, as benchmarks. Occasionally, the list would catch some heat because “mis-categorization” resulted in an “unfair” rating. Some things never change.
At the end of the day, however, Mr. Weitz wanted “to highlight the most serious underperformers.” In that spirit, MFO will resurrect the Three Alarm fund list, which will be updated quarterly along with the Great Owl ratings. Like the original methodology, inclusion on the list will be based entirely on absolute, not risk-adjusted, returns over the past 1, 3, and 5 year periods.
Since 1996, many more fund categories exist. Today Morningstar assigns over 90 categories across more than 7500 unique funds, excluding money market, bear, trading, volatility, and specialized commodity. MFO will rate the new Three Alarm funds using the Morningstar categories. We acknowledge that “mis-categorization” may occasionally skew the ratings, but probably much less than if we tried to distill all rated funds into just 11 or so categories.
For more than two-thirds of the categories, one can easily identify a reasonable “benchmark” or reference fund, thanks in part to the proliferation of ETFs. Below is a sample of these funds, sorted first by broad investment Type (FI – Fixed Income, AA – Asset Allocation, EQ – Equity), then Category:
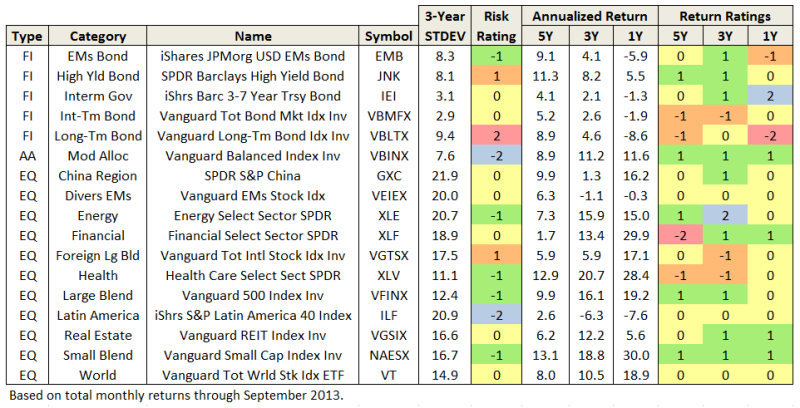
Values in the table include the 3-year annualized standard deviation percentage (STDEV), as well as annualized return percentages (APR) for the past 1, 3, and 5 year periods.
A Return Rating is assigned based how well a fund performs against other funds in the same category during the same time periods. Following the original Three Alarm nomenclature, best performing funds rate a “2” (highlighted in blue) and the worst rate a “-2” (red).
As expected, most of the reference funds rate mid range “0” or slightly better. None produce top or bottom tier returns across all evaluation periods. The same is true for all 60 plus category reference funds. Selecting reference funds in the other 30 categories remains difficult because of their diversity.
To “keep it simple” MFO will include funds on the Three Alarm list if they have the worst returns in their categories across all three evaluation periods. More precisely, Three Alarm Funds have absolute returns in the bottom quintile of their categories during the past 1, 3, and 5 years. Most likely, these funds have also under-performed their “benchmarks” over the same three periods.
There are currently 316 funds on the list, or fewer than 6% of all funds rated. Here are the Three Alarm Funds in the balanced category, sorted by 3 year annualized return:
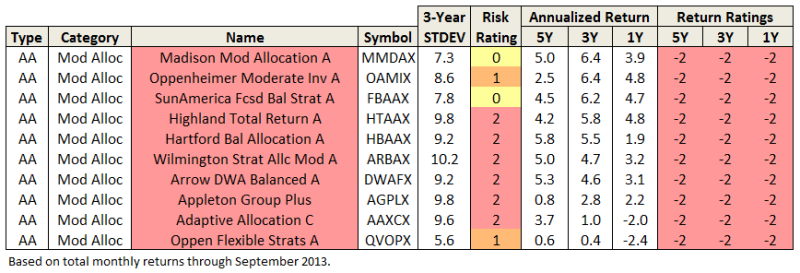
Like in the original Three Alarm list, a fund’s Risk Rating is assigned based a “potential bad year” relative to other funds in the same category. A Risk Rating of “2” (highlighted in red) goes to the highest risk funds, while “-2” (blue) goes to the lowest risk funds. (Caution: This rating measures a fund’s risk relative to other funds in same category, so a fund in a high volatility category like energy can have high absolute risk relative to market, even if it has a low risk rating in its category.)
“Risk” in this case is based on the 3 year standard deviation and return values. Specifically, two standard deviations are subtracted from the return value. The result is then compared with other funds in the category to assign a rating. The rating is a little more sensitive to downside than the original measure as investors have experienced two 50% drawdowns since the Three Alarm system was first published.
While never quite as popular as the Three Alarm list, Mr. Weitz also published an Honor Roll list. In the redux system, Honor Roll funds have returns in the top quintile of their categories in the past 1, 3, and 5 years. There are currently 339 such funds.
The Three Alarm, Honor Roll, and Reference funds can all be found here.
06Nov2013/Charles
