By David Snowball
Dear friends,
Welcome to the end of a long, odd month. The market bounced. The pope took a long victory lap around St. Peter’s Square in his Popemobile before giving up the red shoes for life. King Richard III was discovered after 500 years buried under a parking lot with evidence of an ignominious wound in his nether regions. At about the same time, French scientists discovered the Richard the Lionheart’s heart had been embalmed with daisies, myrtle, mint and frankincense and stored in a lead box. A series of named storms (Nemo? Really? Q?) wacked the Northeast.

And I, briefly, had fantasies of enormous wealth. My family discovered a long forgotten stock certificate issued around the time of the First World War in my grandfather’s name. After some poking about, it appeared that a chain of mergers and acquisitions led from a small Ohio bank to Fifth Third Bank, to whom I sent a scan of the stock certificate. While I waited for them to marvel at its antiquity and authenticity, I reviewed my lessons in the power of compounding. $100 in 1914, growing at 5% per year, would be worth $13,000 now. Cool. But, growing at 10% per year – the amount long-term stock investors are guaranteed, right? – it would have grown to $13,000,000. In the midst of my reverie about Chateau Snowball, Fifth Third wrote back with modestly deflating news: there was no evidence that the stock hadn’t been redeemed. There was also no evidence that it had been, but after 90 years presumption appears to shift in the bank’s favor. (Who’d have guessed?)
It looks like I better keep my day job. (Which, happily enough, is an immensely fulfilling one.)
Longleaf Global and its brethren
Two bits of news lay behind this story. First, Longleaf freakishly closed its new Longleaf Partners Global Fund (LLGFX) after just three weeks. Given that Longleaf hadn’t launched a fund in 15 years, it seemed odd that this one was so poorly-planned that they’d need to immediately close the door.
 At around the same time, I received a cheerful note from Tom Pinto, a long-time correspondent of ours and vice president at Mount & Nadler. Mount & Nadler (presided over, these last 33 years, by the redoubtable Hedda Nadler) does public relations for mutual funds and other money management folks. They’ve arranged some really productive conversations (with, for example, David Winters and Bruce Berkowitz) over the years and I tend to take their notes seriously. This one celebrated an entirely remarkable achievement for Tweedy Browne Global Value (TBGVX):
At around the same time, I received a cheerful note from Tom Pinto, a long-time correspondent of ours and vice president at Mount & Nadler. Mount & Nadler (presided over, these last 33 years, by the redoubtable Hedda Nadler) does public relations for mutual funds and other money management folks. They’ve arranged some really productive conversations (with, for example, David Winters and Bruce Berkowitz) over the years and I tend to take their notes seriously. This one celebrated an entirely remarkable achievement for Tweedy Browne Global Value (TBGVX):
Incredibly, when measured on a rolling 10-year basis since its inception through 11/30/12 using monthly returns, the fund is batting 1000, having outperformed its benchmark – MSCI EAFE — in 115 out of 115 possible 10-year holding periods over the last 19 plus years it has been in existence. It also outperformed its benchmark in 91% of the rolling five-year periods and 82% of the rolling three-year periods.
That one note combined three of my favorite things: (1) consistency in performance, (2) Tweedy, Browne and (3) Hedda.
Why consistency? It helps investors fight their worst enemy: themselves. Very streaky funds have very streaky investors, folks who buy and sell excessively and, in most cases, poorly. Morningstar has documented a regrettably clear pattern of investors earning less –sometimes dramatically less – than their funds, because of their ill-time actions. Steady funds tend to have steady investors; in Tweedy’s case, “investor returns” are close to and occasionally higher than the fund’s returns.
Why Tweedy? It’s one of those grand old firms – like Dodge & Cox and Northern – that started a century or more ago and that has been quietly serving “old wealth” for much of that time. Tweedy, founded in 1920 as a brokerage, counts Benjamin Graham, Walter Schloss and Warren Buffett among its clients. They’ve only got three funds (though one does come in two flavors: currency hedged and not) and they pour their own money into them. The firm’s website notes:
As of December 31, 2012, the current Managing Directors and retired principals and their families, as well as employees of Tweedy, Browne had more than $759.5 million in portfolios combined with or similar to client portfolios, including approximately $101.9 million in the Global Value Fund and $57.9 million in the Value Fund, $6.8 million in the Worldwide High Dividend Yield Value Fund and $3.7 million in the Global Value Fund II — Currency Unhedged.
Value (low risk, four stars) and Global Value (low risk, five stars) launched in 1993. The one with the long name (low risk, five stars) launched 14 years later, in 2007. Our profile of the fund, Tweedy Browne Worldwide High Dividend Yield Value (TBHDX), appeared as soon as it was launched. At that point, Global Value was rated by Morningstar as a two-star fund. Nonetheless, I plowed in with the argument that it represented a compelling opportunity:
They are really good stock-pickers. I know, I know: “gee, Dave, can’t you read? Two blinkin’ stars.” Three things to remember. First, the validity of Morningstar’s peer ratings depend on the validity of their peer group assignment. In the case of Global Value, they’re categorized as small-mid foreign value (which has been on something of a tear in recent years), despite the fact that 60% of their portfolio is in large cap stocks.
Second, much of the underperformance for Global Value is attributable to their currency hedging.
Third, they provide strong absolute returns even when they have weak relative ones. In the case of Global Value they have churned out returns around 17-18% over the trailing three- and five-year periods. Combine that with uniformly “low” Morningstar risk scores for both funds and you get an awfully compelling risk/return profile.
Bottom Line: there’s a lot to be said, especially in uncertain times, for picking cautious, experienced managers and giving them broad latitude. Worldwide High Dividend Yield has both of those attributes and it’s likely to be a remarkably rewarding instrument for folks who like to sleep well at night.
 Why Hedda? I’ve never had the pleasure of meeting Hedda in person, but our long phone conversations over the years make it clear that she’s smart, funny, and generous and has an incredible institutional memory. When I think of Hedda, the picture that pops into mind is Edna Mode from The Incredibles, darling.
Why Hedda? I’ve never had the pleasure of meeting Hedda in person, but our long phone conversations over the years make it clear that she’s smart, funny, and generous and has an incredible institutional memory. When I think of Hedda, the picture that pops into mind is Edna Mode from The Incredibles, darling.
The Observer’s specialty are new and small funds. The problem in covering Tweedy is that the next new fund is apt to launch around about the time that you folks start receiving copies of the Observer by direct neural implants. I had similar enthusiasm for other long-interval launches, including Dodge and Cox Global (“Let’s be blunt about this. If this fund fails, it’s pretty much time for us to admit that the efficient market folks are right and give up on active management.”) and Oakmark Global Select (“both of the managers are talented, experienced and disciplined. Investors willing to take the risk are getting access to a lot of talent and a unique vehicle”).
That led to the question: what happens when funds that never launch new funds, launch new funds?
With the help of the folks on the Observer’s discussion board and, most especially, Charles Boccadoro, we combed through hundreds of records and tracked down all of the long-interval launches that we could. “Long-interval launches” were those where a firm hadn’t launched in anew fund in 10 years or more. (Dodge & Cox – with five fund launches in 81 years – was close enough, as was FMI with a launch after nine-and-a-fraction years.) We were able to identify 17 funds, either retail or nominally institutional but with low minimum shares, that qualified.
We looked at two measures: how did they do, compared to their Morningstar peers, in their first full year (so, if they launched in October 2009, we looked at 2010) and how have they done since launch?
|
Fund
|
Ticker
|
Launch
|
Years since the last launch
|
First full year vs peers
|
Cumulative (not annual!) return since inception vs peers
|
|
Acadian Emerging Markets Debt
|
AEMDX
|
12/10
|
17
|
(2.1) vs 2.0
|
22.7 vs 20.0
|
|
Advance Capital I Core Equity
|
ADCEX
|
01/08
|
15
|
33.2 vs 24.1
|
17.8 vs 9.7
|
|
API Master Allocation A
|
APIFX
|
03/09
|
12
|
19.9 vs 4.1
|
103.1 vs 89.1
|
|
Assad Wise Capital
|
WISEX
|
04/10
|
10
|
0.9 vs 1.7
|
7.4 vs 8.4
|
|
Dodge & Cox Global
|
DODWX
|
05/08
|
7
|
(44.5) vs (38.3)
|
85.5 v 68.4
|
|
Fairholme Allocation
|
FAAFX
|
12/10
|
11
|
(14.0) vs (4.0)
|
5.0 vs 21.1
|
|
FMI International
|
FMIJX
|
12/10
|
9
|
(1.8) vs (14.0)
|
23.8 vs 4.6
|
|
FPA International Value
|
FPIVX
|
12/11
|
18
|
20.6 vs 10.3
|
27.8 vs 18.8
|
|
Heartland International Value
|
HINVX
|
10/10
|
14
|
(22.0) vs (16.0)
|
9.3 vs 16.3
|
|
Jensen Quality Value
|
JNVIX
|
03/10
|
18
|
2.4 vs (3.8)
|
23.7 vs 36.4
|
|
LKCM Small-Mid Cap
|
LKSMX
|
04/11
|
14
|
9.3 vs 14.1
|
0.8 vs 5.0
|
|
Mairs & Power Small Cap
|
MSCFX
|
08/11
|
50
|
34.9 vs 13.7
|
59.4 vs 31.1
|
|
Oakmark Global Select
|
OAKWX
|
10/06
|
11
|
11.7 vs 12.5
|
54.8 vs 20.5
|
|
Pear Tree Polaris Foreign Value Small Cap
|
QUSIX
|
05/08
|
10
|
83.4 vs 44.1
|
26.3 vs 0.8
|
|
Thomas White Emerging Markets
|
TWEMX
|
06/10
|
11
|
(17.9) vs (19.9)
|
26.1 vs 16.5
|
|
Torray Resolute
|
TOREX
|
12/10
|
20
|
2.2 vs (2.5)
|
29.0 vs 18.4
|
|
Tweedy, Browne Worldwide High Dividend Yield Value
|
TBHDX
|
09/07
|
14
|
(13) vs (17.7)
|
18.2 vs 1.5
|
|
|
Ticker
|
First full year
|
Since launch
|
|
Acadian
|
AEMDX
|
L
|
W
|
|
Advance Capital
|
ADCEX
|
W
|
W
|
|
API
|
APIFX
|
W
|
W
|
|
Assad
|
WISEX
|
L
|
L
|
|
Dodge & Cox
|
DODWX
|
L
|
W
|
|
Fairholme
|
FAAFX
|
L
|
L
|
|
FMI
|
FMIJX
|
W
|
W
|
|
FPA
|
FPIVX
|
W
|
W
|
|
Heartland
|
HINVX
|
W
|
L
|
|
Jensen
|
JNVIX
|
W
|
L
|
|
LKCM
|
LKSMX
|
L
|
L
|
|
Mairs & Power
|
MSCFX
|
W
|
W
|
|
Oakmark
|
OAKWX
|
L
|
W
|
|
Pear Tree
|
QUSIX
|
W
|
W
|
|
Thomas White
|
TWEMX
|
W
|
W
|
|
Torray
|
TOREX
|
W
|
W
|
|
Tweedy, Browne
|
TBHDX
|
W
|
W
|
|
Batting average
|
|
.647
|
.705
|
While this isn’t a sure thing, there are good explanations for the success. At base, these are firms that are not responding to market pressures and that have extremely coherent disciplines. The fact that they choose to launch after a decade or more speaks to a combination of factors: they see something important and they’re willing to put their reputation on the line. Those are powerful motivators driving highly talented folks.
What might be the next funds to track? Two come to mind. Longleaf Global launched 15 years after Longleaf International (LLINX) and would warrant serious consideration when it reopens. And BBH Global Core Select will be opening in the next month, 15 years after BBH Core Select (BBTRX and BBTEX). Core Select has been wildly successful and has just closed to new investors. Global Core Select will use the same team and the same strategy.
(Thanks to my collaborators on this piece: Mike M, Andrei, Charles and MourningStars.)
The Phrase, “Oh, that can’t be good” comes to mind

I read a lot of fund reports – annual, semi-annual and monthly. I read most of them to find up what’s going on with the fund. I read a few because I want to find up what’s going on with the world. One of the managers whose opinion I take seriously is Steven Romick, of FPA Crescent (FPACX).
They wanted to make two points. One: you were exactly right to notice that one paragraph in the Annual Report. It was, they report, written with exceeding care and intention. They believe that it warrants re-reading, perhaps several times. For those who have not read the passage in question:
Opportunity: When thinking about closing, we also think about the investing environment —both the current opportunity set and our expectations for future opportunities. Currently, we find limited prospects. However, we believe the future opportunity set will be substantial. As we have oft discussed, we are managing capital in the face of Central Bankers’ “grand experiment” that we do not believe will end well, fomenting volatility and creating opportunity. We continue to maintain a more defensive posture until the fallout. Though underperformance might be the price we pay in the interim should the market continue to rise, we believe in focusing on the preservation of capital before considering the return on it. The imbalances that we see, coupled with the current positioning of our Fund, give us confidence that over the long term, we will be able to invest our increased asset base in compelling absolute value opportunities.
Fund flows: We are sensitive to the negative impact that substantial asset flows (in or out) can have on the management and performance of a portfolio. At present, asset flows are not material relative to the size of the Fund, so we believe that the portfolio is not harmed. However, while members of the Investment Committee will continue to be available to existing clients, we have restricted discussions with new relationships so that our attention can be on investment management rather than asset gathering.
For now, we are satisfied with the team’s capabilities, the Fund’s positioning, and the impact of asset flows. As fellow shareholders, should anything cause us to doubt the likelihood of meeting our stated objectives we will close the Fund as we did before, and/or return capital to our shareholders.
What might be the sound bites in that paragraph? “We think about future opportunities. They will be substantial. For now we’ll focus on the preservation of capital. Soon enough, there will be billions of dollars’ worth of compelling absolute value opportunities.” In the interim, they know that they’re both growing and underperforming. They’ve cut off talk with potential new clients to limit the first and are talking with the rest of us so that we understand the second.
Point two: they’ve closed Crescent before. They’ll do it again if they don’t anticipate the opportunity to find good uses for new cash.
Artisan goes public. Now what?
Artisan Partners are one on my favorite investment management firms. Their policies are consistently shareholder friendly, their management teams are stable and disciplined, and their funds are consistently top-notch.
And now you’ll be able to own a piece of the action. Artisan will offer shares to the public, with the proceeds used to resolve some debt and make it possible for some of the younger partners to gain an equity stake in the firm. Three questions arise:
- Is this good for the investors in Artisan’s funds?
- Should you consider buying the stock?
- And would it all work a bit better with Godiva chocolate?
What happens now with the Artisan funds?
The concern is that Artisan is gaining a fiduciary responsibility to a large set of outside shareholders. Their obligation to those shareholders is to increase Artisan’s earnings which, with other fund companies, has translated to (1) gather assets and (2) gather attention. There’s only been one academic study on the difference in performance between publicly-owned and privately-held fund companies, and that study looked only at Canadian firms. That study found:
… publicly-traded management companies invest in riskier assets and charge higher management fees relative to the funds managed by private management companies. At the same time, however, the risk-adjusted returns of the mutual funds managed by publicly-traded management companies do not appear to outperform those of the mutual funds managed by private management companies. This finding is consistent with both the risk reduction and agency cost arguments that have been made in the literature. (M K Berkowitz, Ownership, Risk and Performance of Mutual Fund Management Companies, 2001)
The only other serious investigation that I know of was undertaken by Bill Bernstein, and reported in his book The Investor’s Manifesto. Bernstein’s opinion of the financial services industry in general and of actively-managed funds in particular is akin to his opinions on astrology and reading goat entrails. Think I’m kidding? Here’s Bill:
The prudent investor treats almost the entirety of the financial industrial landscape as an urban combat zone. This means any stock broker or full-service brokerage firm, any newsletter, any advisor who purchases individual securities, any hedge fund. Most mutual fund companies spew more toxic waste into the investment environment than a third-world refinery. Most financial advisors cannot invest their way out a paper bag. Who can you trust? Almost no one.
Bill looked at the performance of 18 fund companies, five of which were not publicly-traded. In particular, he looked at the average star ratings for their funds (admittedly an imperfect measure, but among the best we’ve got). The privately-held firms placed 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 6th and 9th in performance. The lowest positions were all public firms with a record of peddling bloated, undistinguished funds to an indolent public. His recommendation is categorical: “Do not invest with any mutual fund family that is owned by a publicly traded parent company.”
While the conflicts between the interests of the firm’s stockholders and the funds’ shareholders are real and serious, it’s also true that a number of public firms – the Affiliated Managers Group and T. Rowe Price, notably – have continued offered solid funds and reasonable prices. While it’s possible that Artisan will suddenly veer off the path that’s made them so admirable, that’s neither necessary nor immediately probable.
So, should you buy the stock instead of the funds?
In investor mythology, the fund companies’ stock always seems the better bet than the fund company’s funds. That seems, broadly speaking, true. Fund company stock has broadly outperformed the stock market and the financial sector stocks over time. I’ve gathered a listing of all of the publicly-traded mutual fund companies that I can identify, excluding only those instances where the funds are a tiny slice of a huge financial empire.
Here’s the performance of the companies’ stock, for various periods through February, 2013.
|
|
|
3 year
|
5 year
|
10 year
|
|
Affiliated Managers Group
|
AMG
|
27.1
|
7.8
|
17.7
|
|
AllianceBernstein
|
AB
|
-1.6
|
-14.6
|
4.9
|
|
BlackRock
|
BLK
|
5.5
|
5.5
|
20.6
|
|
Calamos
|
CLMS
|
-2.7
|
-8.7
|
—
|
|
Cohen & Steers
|
CNS
|
21.7
|
9.0
|
—
|
|
Diamond Hill
|
DHIL
|
16.4
|
9.1
|
39.3
|
|
Eaton Vance
|
EV
|
11.3
|
4.3
|
13.2
|
|
Federated Investors
|
FII
|
3.4
|
-5.0
|
3.8
|
|
Franklin Resources
|
BEN
|
13.8
|
8.6
|
17.2
|
|
GAMCO Investors
|
GBL
|
10.6
|
1.5
|
8.8
|
|
Hennessy Advisors
|
HNNA
|
41.5
|
3.0
|
9.8
|
|
Invesco
|
IVZ
|
12.7
|
1.4
|
13.3
|
|
Janus Capital Group
|
JNS
|
-8.0
|
-17.8
|
-1.6
|
|
Legg Mason
|
LM
|
4.3
|
-15.4
|
0.4
|
|
Manning & Napier
|
MN
|
—
|
—
|
—
|
|
Northern Trust
|
NTRS
|
2.1
|
-3.8
|
7.2
|
|
State Street Corp
|
STT
|
9.3
|
-6.4
|
5.7
|
|
T. Rowe Price Group
|
TROW
|
14.7
|
7.6
|
20.3
|
|
US Global Investors
|
GROW
|
-22.2
|
-21.8
|
15.9
|
|
Waddell & Reed
|
WDR
|
10.9
|
6.1
|
11.4
|
|
Westwood Holdings
|
WHG
|
7.1
|
7.0
|
15.3
|
|
|
Average:
|
8.9
|
-1.1
|
12.4
|
|
Vanguard Total Stock
|
|
13.8
|
4.8
|
9.1
|
|
Financials
|
|
6.6
|
6.8
|
5.4
|
|
Morningstar (just for fun)
|
|
16.3
|
1.1
|
—
|
Several of the largest fund companies – Capital Group Companies, Fidelity Management & Research, and Vanguard – are all private. Vanguard alone is owned by its fund shareholders.
Several high visibility firms – Janus and U.S. Global Investors – have had miserable performance and several others are extremely volatile. The chart for Hennessy Advisors, for example, shows a 90% decline in value during the financial crisis, flat performance for three years, then a freakish 90% rise in the past three months.
On whole, you’d have to conclude that “buy the company, not the funds” is no path to easy money.
Have They Even Considered Using Godiva as a Sub-advisor?
Artisan’s upcoming IPO has been priced at $27-29 a share, which would give Artisan a fully-diluted market value of about $1.8 billion. That’s roughly the same as the market capitalizations for Cheesecake Factory, Inc. (CAKE) or for Janus Capital Group (JNS).
So, for $1.8 billion you could buy all of Artisan or at least all of the publicly-available stock for CAKE or JNS. The question for all of you with $1.8 billion burning a hole in your pockets is “which one?” While an efficient market investor might shrug and suggest a screening process that begins with the words “Eenie” and “Meenie,” we know that you depend on us for better.
Herewith, our comprehensive comparison of Artisan, Cheesecake Factory and Janus:
|
|
Artisan Partners
|
Cheesecake Factory
|
Janus Capital
|
|
No. of four- and five-star funds or cheesecake flavors
|
7 (of 11)
|
33
|
17 (of 41)
|
|
No. of one- and two-star funds or number of restaurants in Iowa
|
1
|
1
|
8
|
|
Number of closed funds or entrees with over 3000 calories and four days’ worth of saturated fat
|
5 (Intl Small Cap, Intl Value, Mid Cap, Mid Cap Value, Small Cap Value)
|
1 (Bistro Shrimp
Pasta, 3,120 calories, 89 grams of saturated fat)
|
1 (Perkins Small Cap Value)
|
|
Assets under management or calories in a child’s portion of pasta with Alfredo sauce
|
$75 billion
|
1,810
|
$157 billion
|
|
Average assets under management per fund or number of Facebook likes
|
$3 billion
|
3.4 million
|
$1.9 billion
|
Jeez, that’s a tough call. Brilliant management or chocolate? Brilliant management or chocolate? Oh heck, who am I kidding:

USA Today launches a new portfolio tracker
In February, USA Today announced a partnership with SigFig (whose logo is a living piggy bank) to create a new and powerful portfolio tracker. Always game for a new experience, I signed up (it’s free, which helps). I allowed it to import my Scottrade portfolio and then to run an analysis on it.
Two pieces of good news. First, it made one sensible fund recommendation: that I sell Northern Global Tactical Asset Allocation (BBALX) and replace it with Buffalo Flexible Income (BUFBX). BBALX is a fund of index funds which represents a sort of “best ideas” approach from Northern’s investment policy committee. It has low expenses and I like the fact that it’s using index funds, which decreases complexity and increases predictability. That said, the Buffalo fund is very solid and has certainly outperformed Northern over the past several years. A FundAlarm profile of the fund, then called Buffalo Balanced, concluded:
This is clearly not a mild-mannered fund in the mold of Mairs & Power or Bridgeway. It takes more risks but is managed by an immensely experienced professional who has a pretty clearly-defined discipline. That has paid off, and likely will continue to pay off.
So, that’s sensible.
Second bit of good news, the outputs are pretty:
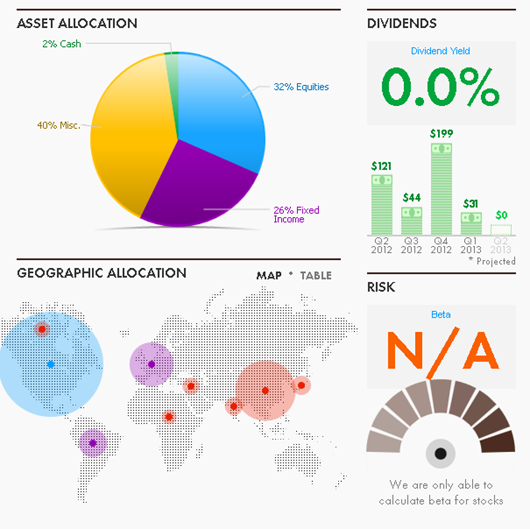
Now the bad news: the recommendations completely missed the problem. Scottrade holds five funds for me. They are RiverPark Short-Term High Yield (RPHYX), one of two cash-management accounts, Northern and three emerging markets funds. Any reasonable analyst would have said: “Snowball, what are you thinking? You’ve got over two-thirds of your money in the emerging markets, virtually no U.S. stocks and a slug of very odd bonds. This is wrong, wrong, wrong!”
None of which USAToday/SigFig noticed. They were unable even to categorize 40% of the portfolio, saw only 2% cash (it’s actually about 10%), saw no dividends (Morningstar calculates it at 2.4%) and had no apparent concern about my wild asset allocation skew.
Bottom line: look if you like, but look very skeptically at these outputs. This system might work for a very conventional portfolio, but even that isn’t yet proven.
Fidelity spirals (and not upward)
Investors pulled nearly $36 billion from Fidelity’s funds in 2012. That’s from Fido’s recently-released 2012 annual report. Their once-vaunted stock funds (a) had a really strong year in terms of performance and (b) bled $24 billion in assets regardless (Fidelity Sees More Fund Outflows, 02/15/13). The company’s operating income of $2.3 billion fell 29% compared with 2011.
The most troubling sign of Fidelity’s long-term malaise comes from a January announcement. Reuters reported that Fido’s target-date retirement funds were steadily losing market share to Vanguard. As a result, they needed to act to strengthen them.
Fidelity Investments’ target-date funds will start 2013 with more stock-picking firepower, as star money managers Will Danoff and Joel Tillinghast pick up new assignments to protect a No. 1 position under fire from rival Vanguard Group.
Why is that bad? Because Tillinghast and Danoff seem to be all that they have left. Danoff has been running Contrafund since 1990 and was moved in Fidelity Advisor New Insights in 2003 to beef up the Fidelity Advisor funds and now Fidelity Series Opportunistic Insights in 2012 to beef up the funds used by the target-date series. Even before the first dollar goes to Opportunistic Insights, Danoff was managing $107 billion in equity investments. Tillinghast has been running Low-Priced Stock, a $35 billion former small cap fund, since 1989 and now adds Fidelity Series Intrinsic Opportunities Fund. This feels a lot like a major league ball team staking their playoff chances on two 39-year-old power hitters; the old guys have a world of talent but you have to ask, what’s happened to the farm system?
One more slap at Morningstar’s new ratings
There was a long, healthy, and not altogether negative discussion of Morningstar’s analyst ratings on the Observer’s discussion board. For those trying to think through the weight to give a “Gold” analyst rating, it’s a really worthwhile use of your time. Three concerns emerge:
- There may be a positivity bias in the ratings. It’s clear that the ratings are vastly skewed, so that negative assessments are few and far between. Some writers speculate that Morningstar’s corporate interests (drawing advertising, for example) might create pressure in that direction.
- There’s no clear relationship between the five pillars and the ultimate rating. Morningstar’s analysts look at five factors (people, price, process, parent, performance – side note, be skeptical of any system designed for alliteration) and assign a positive, neutral or negative judgment to each. Some writers express bewilderment that one fund with a single “positive” might be silver while another with two positives might be “neutral.”
- There’s no evidence, yet, that the ratings have predictive validity. The anonymous author of the Wall Street Rant blog produced a fairly close look at the 2012 performance of the newly-rated funds. Here’s the visual summary of Ranter’s research:
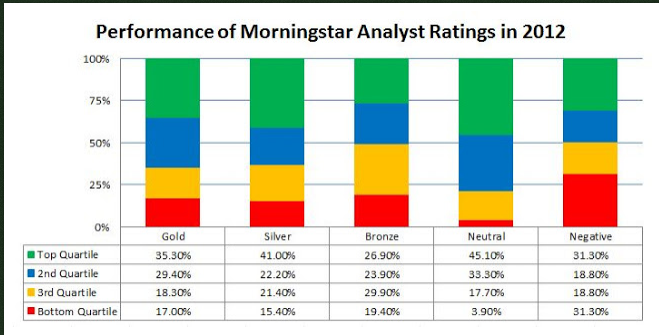
In short, “Not much really stands out after the first year. While there was a slight positive result for Gold and Silver rated funds, Neutral rated funds did even better.” The complete analysis is in a post entitled Performance of Morningstar’s New Analyst Ratings For Mutual Funds in 2012 (02/17/2013)
My own view is in accord with what Morningstar says about their ratings (use them as one element of your due diligence in assessing a fund) but, in practice, Morningstar’s functional monopoly in the fund ratings business means that these function as marketing tools far more than as analytic ones.
Five-star and Gold is surely a lot better than one-star and negative, but it’s not nearly as good as a careful, time-consuming inquiry into what the manager does, what the risks look like, and whether this makes even marginal sense in your own portfolio.
Introducing: The Elevator Talk
 The Elevator Talk is a new feature which began in February. Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
The Elevator Talk is a new feature which began in February. Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Elevator Talk #2: Dale Harvey, Poplar Forest Partners (PFPFX and IPFPX)
 Mr. Harvey manages the Poplar Forest Partners (PFPFX and IPFPX), which launched on December 31, 2009. For 16 years, Dale co-managed several of the flagship American Funds including Investment Company of America (AIVSX), Washington Mutual (AWSHX) and American Mutual (AMRMX). Some managers start their own firms in order to get rich. Others because asset bloat was making them crazy. A passage from an internal survey that Dale completed, quoted by Morningstar, gives you some idea of his motivation:
Mr. Harvey manages the Poplar Forest Partners (PFPFX and IPFPX), which launched on December 31, 2009. For 16 years, Dale co-managed several of the flagship American Funds including Investment Company of America (AIVSX), Washington Mutual (AWSHX) and American Mutual (AMRMX). Some managers start their own firms in order to get rich. Others because asset bloat was making them crazy. A passage from an internal survey that Dale completed, quoted by Morningstar, gives you some idea of his motivation:
Counselor Dale Harvey remarked that Capital should “[c]lose all the funds. Don’t just close the biggest or fastest growing. Doing that would simply shift the burden on to other funds. Keep them shut until we figure out the new unit structure and relieve the pressure of PCs managing $20 billion.”
Many of his first investors were former colleagues at the American Funds.
Dale offers these 152 words on why folks should check in:
This is a once-in-a-generation opportunity to invest with a successful American Funds manager who went out on his own. The last was the late Howard Schow, who left to launch the Primecap Funds.
The real reason to leave is about size, the funds just kept taking in money. There came a point where it was a real impediment to performance. That will never be the case at Poplar Forest. Everyone here invests heavily in our funds, so our interests are directly aligned with yours.
From a process perspective, we’re defined by a contrarian value perspective with a long-term time horizon. This is a high conviction portfolio with no second choices or fillers. Because we’re contrarian, we’ll sometimes be out of step with the market as we were in 2011. But we’ve always known that the best time to invest in a four- or five-star fund is when it only has two stars.
The fund’s minimum initial investment is $25,000 for retail shares, reduced to $5,000 for IRAs. They maintain a minimal website for the fund and a substantially more informative site for their investment firm, Poplar Forest LLC. Dale’s most-recent discussion of the fund appears in his 2012 Annual Review.
Conference Call Highlights
On February 19th, about 50 people phoned-in to listen to our conversation with Andrew Foster, manager of Seafarer Overseas Growth and Income Fund (SFGIX and SIGIX). The fund has an exceptional first year: it gathered $35 million in asset and returned 18% while the MSCI emerging market index made 3.8%. The fund has about 70% of its assets in Asia, with the rest pretty much evenly split between Latin America and Emerging Europe. Their growth has allowed them to institute two sets of expense ratio reductions, one formal and one voluntary.
For folks interested but unable to join us, here’s the complete audio of the hour-long conversation.
The SFGIX conference call
When you click on the link, the file will load in your browser and will begin playing after it’s partially loaded. If the file downloads, instead, you may have to double-click to play it.
Among the highlights of the call, for me:
- China has changed. Andrew offered a rich discussion about his decision to launch the fund. The short version: early in his career, he concluded that emergent China was “the world’s most under-rated opportunity” and he really wanted to be there. By late 2009, he noticed that China was structurally slowing. That is, it was slow because of features that had no “easy or obvious” solution, rather than just slowly as part of a cycle. He concluded that “China will never be the same.” Long reflection and investigation led him to begin focusing on other markets, many of which were new to him, that had many of the same characteristics that made China exciting and profitable a decade earlier. Given Matthews’ exclusive and principled focus on Asia, he concluded that the only way to pursue those opportunities was to leave Matthews and launch Seafarer.
- It’s time to be a bit cautious. As markets have become a bit stretched – prices are up 30% since the recent trough but fundamentals have not much changed – he’s moved at the margins from smaller names to larger, steadier firms.
- There are still better opportunities in equities than fixed income; hence he’s about 90% in equities.
- Income has important roles to play in his portfolio. (1) It serves as a check on the quality of a firm’s business model. At base, you can’t pay dividends if you’re not generating substantial, sustained free cash flow and generating that flow is a sign of a healthy business. (2) It serves as a common metric across various markets, each of which has its own accounting schemes and regimes. (3) It provides as least a bit of a buffer in rough markets. Andrew likened it to a sea anchor, which won’t immediately stop a ship caught in a gale but will slow it, steady it and eventually stop it.
Bottom-line: the valuations on emerging equities look good if you’ve got a three-to-five year time horizon, fixed-income globally strikes him as stretched, he expects to remain fully invested, reasonably cautious and reasonably concentrated.
Conference Call Upcoming: Cook and Bynum, March 5th
Cook and Bynum (COBYX) is an intriguing fund. COBYX holds only seven holdings and a 33% cash stake. Since two-thirds of the fund is in the stock market, you might reasonably expect to harvest two-thirds of the market’s gains but suffer through just two-thirds of its volatility. Cook and Bynum has done far better. Since launch they’ve captured nearly 100% of the market’s gains with only one third of its volatility. In the past twelve months, Morningstar estimates that they’ve captured just 7% of the market’s downside.
We’ll have a chance to hear from Richard and Dowe (Cook and Bynum, respectively) about their approach to high-conviction investing and their amazing research efforts. To help facilitate the discussion, they prepared a short document that walks through their strategy with you. You can download that document here.
Our conference call will be Tuesday, March 5, from 7:00 – 8:00 Eastern.
How can you join in?
 If you’d like to join in, just click on register and you’ll be taken to the Chorus Call site. In exchange for your name and email, you’ll receive a toll-free number, a PIN and instructions on joining the call. If you register, I’ll send you a reminder email on the morning of the call.
If you’d like to join in, just click on register and you’ll be taken to the Chorus Call site. In exchange for your name and email, you’ll receive a toll-free number, a PIN and instructions on joining the call. If you register, I’ll send you a reminder email on the morning of the call.
Remember: registering for one call does not automatically register you for another. You need to click each separately. Likewise, registering for the conference call mailing list doesn’t register you for a call; it just lets you know when an opportunity comes up.
This will be the first of three conversations with distinguished managers who defy that trend through their commitment to a singular discipline: buy only the best. In the months ahead, we plan to talk with David Rolfe of RiverPark/Wedgewood Fund (RWGFX) and Stephen Dodson of Bretton Fund (BRTNX).
Observer Fund Profiles
Each month the Observer provides in-depth profiles of between two and four funds. Our “Most Intriguing New Funds” are funds launched within the past couple years that most frequently feature experienced managers leading innovative newer funds. “Stars in the Shadows” are older funds that have attracted far less attention than they deserve. This month’s lineup features:
Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX/SIGIX): The evidence is clear and consistent. It’s not just different. It’s better.
Funds in Registration
New mutual funds must be registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission before they can be offered for sale to the public. The SEC has a 75-day window during which to call for revisions of a prospectus; fund companies sometimes use that same time to tweak a fund’s fee structure or operating details. Every day we scour new SEC filings to see what opportunities might be about to present themselves. Many of the proposed funds offer nothing new, distinctive or interesting. Some are downright horrors of Dilbertesque babble (see “Synthetic Reverse Convertibles,” below).
Funds in registration this month won’t be available for sale until, typically, the beginning of May 2013. We found a dozen funds in the pipeline, notably:
Grandeur Peak Emerging Markets Opportunities Fund will seek long-term growth of capital by investing in small and micro-cap companies domiciled in emerging or frontier markets. They’re willing to consider common stock, preferred and convertible shares. The most reassuring thing about it is the Grandeur Peak’s founders, Robert Gardiner & Blake Walker, are running the fund and have been successfully navigating these waters since their days at Wasatch. The minimum initial investment is $2,000, reduced to $1,000 for accounts with an automatic investing plan and $100 for UGMA/UTMA or a Coverdell Education Savings Accounts. Expenses not yet set.
Matthews Emerging Asia Fund will pursue long-term capital appreciation by investing in common and preferred stock and convertible securities of companies that have “substantial ties” to the countries of Asia, except Japan. Under normal conditions, you might expect to see companies from Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Pakistan, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Vietnam. They’ll run an all-cap portfolio which might invest in micro-cap stocks. Taizo Ishida, who serves on the management team of two other funds (Growth and Japan), will be in charge. The minimum initial investment in the fund is $2500, reduced to $500 for IRAs and Coverdell accounts. Expenses for both Investor and Institutional shares are capped at 1.90%.
Details on these funds and the list of all of the funds in registration are available at the Observer’s Funds in Registration page or by clicking “Funds” on the menu atop each page.
Manager Changes
On a related note, we also tracked down 31 fund manager changes, including the blockbuster departure of Kris Jenner from T. Rowe Price Health Sciences (PRHSX) and the departure, after nearly 20 years, of Patrick Rogers from Gateway Fund (GATEX).
There was also a change on a slew of Vanguard funds, though I see no explanation at Vanguard for most of them. The affected funds are a dozen Target Retirement Date funds plus
- Diversified Equity
- Extended Duration Treasury Index
- FTSE All-World ex-US Small Index
- Global ex-US Real Estate
- Long-Term Bond Index
- Long-Term Government Bond Index
- Short-Term Bond Index
- STAR
- Tax-Managed Growth & Income
- Tax-Managed International
Vanguard did note that five senior executives were being moved around (including to and from Australia) and, at the end of that announcement, nonchalantly mentioned that “Along with these leadership changes, 15 equity funds, 11 fixed income funds, two balanced funds, and Vanguard Target Retirement Funds will have new portfolio managers rotate onto their teams.” The folks being moved did actually manage the funds affected so the cause is undetermined.
Snowball and the fine art of Jaffe-casting
Despite the suspicion that I have a face made for radio but a voice made for print, Chuck Jaffe invited me to appear as a guest on the February 28 broadcast of MoneyLife with Chuck Jaffe. (Ted tells me that I appear at the 34:10 mark and that you can just move the slider there if you’d like.) We chatted amiably for a bit under 20 minutes, about what to look for and what to avoid in the fund world. I ended up doing capsule critiques of five funds that his listeners had questions about:
WisdomTree Emerging Markets Equity Income (DDEM) for Rick in York, Pa. Certainly more attractive than the Vanguard index, despite high expenses. High dividend-yield stocks. Broader market cap diversification, lower beta – 0.8
Fidelity Total Emerging Markets (FTEMX), also for Rick. I own it. Why? Not because it’s good but because it looks better than the alternatives in my 403(b). Broad and deep management team but, frankly, First Trust/Aberdeen Emerging Opportunity (FEO) is vastly better.
Fidelity Emerging Markets (FEMKX) for Jim in Princeton, NJ. Good news, Jim. They don’t charge much. Bad news: they haven’t really earned what they do charge. Good news: they got a new manager in October. Sammy Simnegar. Bad news: he’s not been very consistent, trades a lot, and is likely to tank tax efficiency in repositioning. Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX) is vastly better.
Nile Pan Africa (NAFAX) for Bruce in Easton, Pa. This fund will be getting its first Morningstar star rating this year. Ignore it! It’s a narrow fund being compared to globally-diversified ones. 75% of its money is in two countries, Nigeria and South Africa. If this were called the Nile Nigeria and South Africa Fund, would you even glance at it?
EP Asia Small Companies (EPASX), also for Bruce. Two problems, putting aside the question of whether you want to be investing in small Asian companies. First, the manager’s record at his China fund is mediocre. Second, he doesn’t actually seem to be investing in small companies. Morningstar places them at just 10% of the portfolio. I’d be more prone to trust Matthews.
I was saddened to learn that Chuck has lost the sponsor for his show. His listenership is large, engaged and growing. And his expenses are really pretty modest (uhhh … rather more than the Observer’s, rather less than the Pennysaver paper that keeps getting tossed on your porch). If any of you want to become even a part-sponsor of a fairly high-visibility show/podcast, you should drop Chuck a line. Heck, he could even help you launch your own line of podcasts.
Briefly Noted ….
Kris Jenner’s curious departure
Kris Jenner, long-time manager of T. Rowe Price Health Sciences (PRHSX) left rather abruptly on February 15th. The fund carries a Gold rating and five stars from Morningstar (but see the discussion, above, about what that might mean) and Jenner was a finalist for Morningstar’s Domestic Manager of the Year award in 2011. A doctor by training, Price long touted Jenner’s special expertise as one source of the fund’s competitive advantage.
So, what’s up? No one who’s talking knows, and no one who knows is talking. The best coverage of his departure comes from Bloomberg, which makes four notes that many others skip:
- Jenner left with two of his (presumably) top analysts from his former team of eight,
- he reached out to lots of his contacts in the industry after he left,
- he’s being represented by a public relations firms, Burns McClennan, Inc. and
- he’s being coy as part of his p.r. campaign: “We cannot share our plans with you at this time, in part due to regulatory and reporting requirements.”
Price seems a bit offended at the breach of collegiality. “They are leaving to pursue other opportunities,” Price spokesman Brian Lewbart told The Baltimore Sun. “They didn’t share what they are.”
My guess would be that some combination of the desire to be fabulously rich and the desire to facilitate medical innovation might well lead him to found something like a biotech venture capital firm or business development company. Regardless, it seems certain that the mutual fund world has seen the last of one of its brighter stars.
FPA announces conversion to a pure no-load fund family
Effective April 1, 2013, all of the FPA Funds will be available as no-load funds. This change will affect FPA Capital (FPPTX), New Income (FPNIX), Paramount (FPRAX) and Perennial Funds (FPPFX), since these funds are currently structured as front-load mutual funds. FPA Capital Fund will remain closed to new investors. This also means that shareholders of FPA Crescent Fund (FPACX) and International Value Fund (FPIVX) will now be able to exchange into the other FPA Funds without incurring a sales charge.
And apologies to FPA: in the first version of our February issue, we misidentified the role Victor Liu will play on FPA’s International Value team. Mr. Liu, who spent eight years with Causeway Capital Management as Vice President and Research Analyst, will serve in a similar capacity as FPA and will report to Pierre Py, portfolio manager of FPA International Value Fund [FPIVX].
Morningstar tracks down experienced managers in new funds
Morningstar recently “gassed up the Premium Fund Screener tool and set it to find funds incepted since 2010 that have Analyst Ratings of Gold, Silver, or Bronze” (Young Funds, Old Pros, 02/20/2013). Setting aside the unfortunate notion of “gassing up” one’s software and the voguish “incepted,” here are editor Adam Zoll’s picks for new funds headed by highly experienced managers.
Royce Special Equity Multi-Cap (RSMCX), managed by Charlie Dreifus. Dreifus has a great long-term record with the small cap Royce Special Equity fund. This would be an all-cap application of that same discipline. I’ll note, in passing, the Special hasn’t been quite as special in the past decade as in the one preceding it and Dreifus, in his mid60s, is closer to the conclusion of his career than its launch.
PIMCO Inflation Response Multi-Asset (PZRMX) , managed by Mihir Worah who also manages PIMCO Real Return (PRTNX), Commodity Real Return Strategy (PCRAX) and Real Estate Real Return Strategy (PETAX). The fund combines five inflation-linked assets (TIPS, commodities, emerging market currencies, REITs and gold) to preserve purchasing power in times of rising inflation. PIMCO’s reputation is such that after six months of meager performance, the fund is moving toward a quarter billion in assets.
Ariel Discovery (ARDFX), managed by David Maley. As I’ve noted before, Morningstar really likes the Ariel family of funds. Maley has no prior experience in managing a mutual fund, though he has been managing the Ariel Micro-Cap Value separate accounts for a decade. So far ARDFX has pretty consistently trailed its small-value peer group as well as most of the micro-cap funds (Aegis, Bridgeway, Wasatch) that I follow.
Rebalancing matters.
In investigating the closure of Vanguard Wellington, I came across an interesting argument that the simple act of annual rebalancing can substantially boost returns. It’s reflected in the difference in the first two columns. The first column is what you’d have earned with a 65/35 portfolio purchased in 2002 and never rebalanced. Column 2 shows the effect of rebalancing. (Column 3 is the ad for the mostly-closed Wellington fund.)
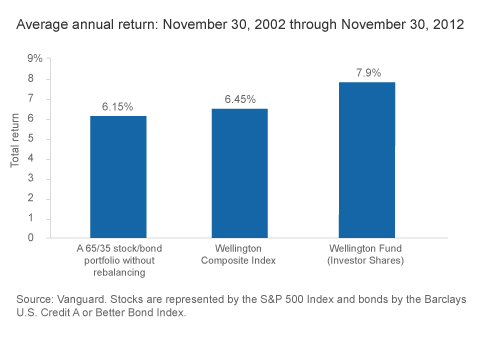
How big is the difference? A $10,000 investment in 2002, split 65/35 and never again touched, would have grown to $18,500. A rebalanced portfolio, which would have triggered some additional taxes unless it was in an IRA, would end a bit over $19,000. Not bad for 10 minutes a year.
On a completely unrelated note, here’s one really striking fund in registration: NYSE Arca U.S. Equity Synthetic Reverse Convertible Index Fund? Really? Two questions: (1) what on earth is that? And (2) why does it strike anyone as “just what the doctor ordered”?
Small Wins for Investors
Vanguard has dropped the expense ratios on three funds, while boosting them on two.
|
Vanguard fund
|
Share class
|
Former
expense ratio
|
Current
expense ratio*
|
|
High Dividend Yield Index Fund
|
ETF
|
0.13%
|
0.10%
|
|
High Dividend Yield Index Fund
|
Investor
|
0.25%
|
0.20%
|
|
International Explorer™ Fund
|
Investor
|
0.42%
|
0.43%
|
|
Mid-Cap Growth Fund
|
Investor
|
0.53%
|
0.54%
|
|
Selected Value Fund
|
Investor
|
0.45%
|
0.38%
|
Not much else to celebrate this month.
Closings
Fidelity closed Fidelity Small Cap Value Fund (FCPVX) on March 1, 2013. This is the second of Charles L. Myers’ funds to close this year. Just one month ago they closed Fidelity Small Cap Discovery (FSCRX). Between them they have ten stars and $8 billion in assets.
Huber Small Cap Value (HUSIX and HUSEX) is getting close to closing. Huber is about the best small cap value fund still open and available to retail investors. Its returns are in the top 1% of its peer group for the past one, three and five years. It has a five-star rating from Morningstar. It’s a Lipper Leader for Total Returns, Consistency of Returns and Tax Efficiency.
“Effectively managing capacity of our strategies is one of the core tenets at Huber Capital Management, and we believe it is important in both small and large cap. Our small cap strategy has a capacity of approximately $1 billion in assets and our large cap/equity income strategy has a capacity of between $10 – $15 billion. As of 2/22/13, small cap strategy assets were over $810 mm and large cap/equity income strategy assets were over $1 billion. We are committed to closing our strategies in such a way as to maintain our ability to effectuate our process on behalf of investors who have been with us the longest.”
Vanguard has partially closed to giant funds. The $68 billion Vanguard Wellington Fund (VWELX, VWENX) and the $39 billion Vanguard Intermediate-Term Tax-Exempt Fund (VWITX) closed to new institutional and advisor accounts on February 28th. Reportedly individual investors will be able to buy-in, but I wasn’t able to confirm that with Vanguard.
RS Global Natural Resources Fund (RSNRX) will close on March 15, 2013. It’s been consistently near the top of the performance charts, has probably improved with age and is dragging about $4.5 billion around.
Old Wine in New Bottles
Effective February 20, 2013, Frontegra SAM Global Equity Fund (FSGLX) became Frontegra RobecoSAM Global Equity Fund. That’s because the sub-adviser of this undistinguished institutional fund went from being SAM to RobecoSAM USA.
PL Growth LT Fund has been renamed PL Growth Fund and MFS took over as the sub-advisor. PL is Pacific Life and these are likely sold through the firm’s agents.
A peculiarly odd announcement from the folks at New Path Tactical Allocation Fund (GTAAX): “During the period from February 28, 2013 to April 29, 2013, the investment objective of Fund will be to seek capital appreciation and income.” With turnover well north of 400% and returns well south of “awful,” there are more sensible things for New Path to seek than a revised objective.
The board of the Touchstone funds apparently had a rollicking meeting in February, where they approved nine major changes. They approved reorganizing Touchstone Focused Equity Fund into the Touchstone Focused Fund. Touchstone Micro Cap Value Fund will, at the end of April, become Touchstone Small Cap Growth Fund. Sensibly, the strategy changes from investing in micro-caps to investing in small caps. Oddly, the objective changes from “capital appreciation” to “long-term capital growth.” The difference is, to an outsider, indiscernible.
Effective May 1, 2013, Western Asset High Income Fund (SHIAX) will be renamed Western Asset Short Duration High Income Fund. The fund’s mandate will be changed to allow investing in shorter duration high yield securities as well as adjustable-rate bank loans, among others. The sales load has been reduced to 2.25% and, in May, the expense ratio will also drop.
Off to the Dustbin of History
Guggenheim, after growing briskly through acquisitions, seems to be cleaning out some clutter. Between the end of March and beginning of May, the following funds are slated for execution:
- Guggenheim Large Cap Concentrated Growth (GIQIX)
- Small Cap Growth (SSCAX)
- Large Cap Value Institutional (SLCIX)
- Global Managed Futures Strategy (GISQX)
- All-Asset Aggressive Strategy (RYGGX)
- All-Asset Moderate Strategy (RYMOX)
- All-Asset Conservative Strategy (RYEOX)
Guggenheim is also bumping off nine of their ETFs. They are the ABC High Dividend, MSCI EAFE Equal Weight, S&P MidCap 400 Equal Weight, S&P SmallCap 600 Equal Weight, Airline, 2x S&P 500, Inverse 2x S&P 500, Wilshire 5000 Total Market, and Wilshire 4500 Completion ETFs.
Legg Mason Capital Management All Cap (SPAAX) will merge with ClearBridge Large Cap Value (SINAX) in mid-July. Good news there, since the ClearBridge fund is a lot cheaper.
Shelton California Insured Intermediate (CATFX) is expected to cease operations, liquidate its assets and distribute the proceeds by mid-March. The fund evolved from “mediocre” to “bad” over the years and had only $4 million in assets.
The Board of Trustees of Sterling Capital approved the liquidation of the $7 million Sterling Capital Strategic Allocation Equity (BCAAX) at the end of April.
Back to the aforementioned Touchstone board meeting. The board approved one merger and a series of executions. The merge occurs when Touchstone Short Duration Fixed Income (TSDYX), a no-load, will merge into Touchstone Ultra Short Duration Fixed Income (TSDAX), a low-load one. The dead walking are:
- Touchstone Global Equity (TGEAX)
- Touchstone Large Cap Relative Value (TRVAX)
- Touchstone Market Neutral Equity (TSEAX) – more “reverse” than “neutral”
- Touchstone International Equity (TIEAX)
- Touchstone Emerging Growth (TGFAX)
- Touchstone U.S. Long/Short (TUSAX). This used to be the Old Mutual Analytic U.S. Long/Short which, prior to 2006, didn’t short stocks.
The “walking” part ends on or about March 26, 2013.
In Closing . . .
 Here’s an unexpectedly important announcement: we are not spam! You can tell because spam is pink, glisteny goodness. We are not. I mention that because there’s a good chance that if you signed up to be notified about our monthly update or our conference calls, and haven’t been receiving our mail, it’s because we’ve been trapped by your spam filter. Please check your spam folder. If you see us there, just click on the “not spam” icon and things will improve.
Here’s an unexpectedly important announcement: we are not spam! You can tell because spam is pink, glisteny goodness. We are not. I mention that because there’s a good chance that if you signed up to be notified about our monthly update or our conference calls, and haven’t been receiving our mail, it’s because we’ve been trapped by your spam filter. Please check your spam folder. If you see us there, just click on the “not spam” icon and things will improve.
It’s also the case that if you want to stop receiving our monthly emails, you should use the “unsubscribe” button and we’ll go away. If you click on the “that’s spam” button instead (two or three people a month do that, for reasons unclear to me), it makes Mail Chimp anxious. Please don’t.
In April, the Observer celebrates its second anniversary. It wouldn’t be worthwhile without your readership and your thoughtful feedback. And it wouldn’t be possible without your support, either directly or by using our Amazon link. The Amazon system is amazingly simple and painless. If you set our link as your default bookmark for Amazon (or, as I do, use Amazon as your homepage), the Observer receives a rebate from Amazon equivalent to 6% or more of the amount of your purchase. It doesn’t change your cost by a penny since the money comes from Amazon’s marketing budget. While 6% of the $11 you’ll pay for Bill Bernstein’s The Investor’s Manifesto (or 6% of a pound of coffee beans or Little League bat) seems trivial, it adds up to about 75% of our income. Thanks for both!
In April, we’re going to look at closed-end s (CEFs) as an alternative to “regular” (or open-ended) mutual s and ETFs. We’ve had a chance to talk with some folks whose professional work centered on trading CEFs. We’ll talk through Morningstar’s recent CEF studies, a bit of what the academic literature says and the insights of the folks we’ve interviewed, and we’ll provide a couple intriguing possibilities. That will be on top of – not in place of – our regular features.
See you then!








 At around the same time, I received a cheerful note from Tom Pinto, a long-time correspondent of ours and vice president at Mount & Nadler. Mount & Nadler (presided over, these last 33 years, by the redoubtable Hedda Nadler) does public relations for mutual funds and other money management folks. They’ve arranged some really productive conversations (with, for example, David Winters and Bruce Berkowitz) over the years and I tend to take their notes seriously. This one celebrated an entirely remarkable achievement for Tweedy Browne Global Value (TBGVX):
At around the same time, I received a cheerful note from Tom Pinto, a long-time correspondent of ours and vice president at Mount & Nadler. Mount & Nadler (presided over, these last 33 years, by the redoubtable Hedda Nadler) does public relations for mutual funds and other money management folks. They’ve arranged some really productive conversations (with, for example, David Winters and Bruce Berkowitz) over the years and I tend to take their notes seriously. This one celebrated an entirely remarkable achievement for Tweedy Browne Global Value (TBGVX): Why Hedda? I’ve never had the pleasure of meeting Hedda in person, but our long phone conversations over the years make it clear that she’s smart, funny, and generous and has an incredible institutional memory. When I think of Hedda, the picture that pops into mind is Edna Mode from The Incredibles, darling.
Why Hedda? I’ve never had the pleasure of meeting Hedda in person, but our long phone conversations over the years make it clear that she’s smart, funny, and generous and has an incredible institutional memory. When I think of Hedda, the picture that pops into mind is Edna Mode from The Incredibles, darling. 



 The Elevator Talk is a new feature which began in February. Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
The Elevator Talk is a new feature which began in February. Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.


 Here’s an unexpectedly important announcement: we are not spam! You can tell because spam is pink, glisteny goodness. We are not. I mention that because there’s a good chance that if you signed up to be notified about our monthly update or our conference calls, and haven’t been receiving our mail, it’s because we’ve been trapped by your spam filter. Please check your spam folder. If you see us there, just click on the “not spam” icon and things will improve.
Here’s an unexpectedly important announcement: we are not spam! You can tell because spam is pink, glisteny goodness. We are not. I mention that because there’s a good chance that if you signed up to be notified about our monthly update or our conference calls, and haven’t been receiving our mail, it’s because we’ve been trapped by your spam filter. Please check your spam folder. If you see us there, just click on the “not spam” icon and things will improve.
