It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!
Big changes from a week ago based on whether the debt-ceiling deal will pass which it did ! The bulls went from 29% to 40% in one week.AAII Sentiment Survey, 6/7/23
Vow! Bullish became the top sentiment (44.5%; above average) & bearish became the bottom sentiment (24.3%; below average); neutral remained the middle sentiment (31.2%; near average)
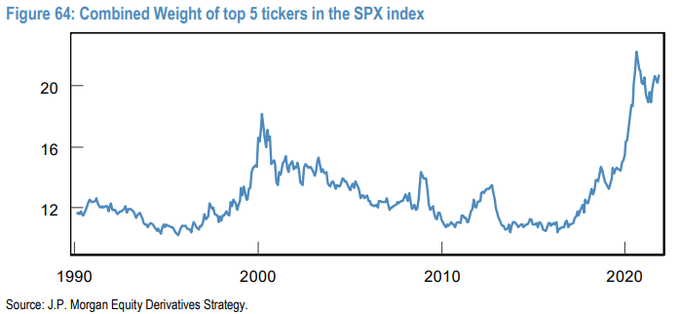
Not responsive to your specific question, but I have spent a few hours the last few weeks comparing RSP vs IVV and IVE, also VONE vs VONV, also the gaming value outliers SCHD and DIVO and CAPE.Anyone know if the concentration of holdings in a relative few companies is historically significant? I know the index is cap weighted but is todays concentration out of the ordinary? Thanks for your replies.
Crash, I understand. I am retired and focused on preserving principal, while making a decent TR with CD interest payments. After I retired, I focused on making 4 to 6% TR, but CDs paid nothing, and so I chose to focus on low risk bond oefs. Loved those years with PIMIX from which I collected monthly income payments that were very predictable and dependable. I had several other bond oefs that I did well with--SEMMX, VCFIX, NVHAX, etc. When the FEDs got serious about raising interest rates, bond oefs got less appealing to me, but CDs became attractive alternatives. I have no idea how long I can ride the CD gravy train, but for now, I will enjoy the stress free 5% returns during my "golden years". I keep watching Floating Rate Bank Loan funds, which I played with for a few years, and keep wondering when they will start benefiting from the rising interest rate period.DT: Good on ya. Can't tie up my $$$ for very long like that. Of course, I'm investing, and that's long-term. What you're doing with CDs, I'n doing with bond OEFs.

Banks have many reasons to worry. Rising interest rates have devalued other assets on their balance sheets, especially government bonds, leaving them vulnerable to bank runs. In recent months, Silicon Valley Bank, First Republic, and Signature all collapsed. Regional institutions like these account for nearly 70 percent of all commercial-property bank loans. Pushing down the valuation of office buildings or taking possession of foreclosed properties would further weaken their balance sheets.
Municipal governments have even more to worry about. Property taxes underpin city budgets. In New York City, such taxes generate approximately 40 percent of revenue. Commercial property—mostly offices—contributes about 40 percent of these taxes, or 16 percent of the city’s total tax revenue. In San Francisco, property taxes contribute a lower share, but offices and retail appear to be in an even worse state.
Empty offices also contribute to lower retail sales and public-transport usage. In New York City, weekday subway trips are 65 percent of their 2019 level—though they’re trending up—and public-transport revenue has declined by $2.4 billion. Meanwhile, more than 40,000 retail-sector jobs lost since 2019 have yet to return. A recent study by an NYU professor named Arpit Gupta and others estimate a 6.5 percent “fiscal hole” in the city’s budget due to declining office and retail valuations. Such a hole “would need to be plugged by raising tax rates or cutting government spending.”
Post-pandemic, kids are back in school, retirees are back on cruise ships, and physical stores are doing better than expected. But offices are struggling perhaps more than most casual observers realize, and the consequences for landlords, banks, municipal governments, and even individual portfolios will be far-reaching. In some cases, they will be catastrophic. But this crisis, like all crises, also represents an opportunity to reconsider many of our assumptions about work and cities.
During the first three months of 2023, U.S. office vacancy topped 20 percent for the first time in decades. In San Francisco, Dallas, and Houston, vacancy rates are as high as 25 percent. These figures understate the severity of the crisis because they only cover spaces that are no longer leased. Most office leases were signed before the pandemic and have yet to come up for renewal. Actual office use points to a further decrease in demand. Attendance in the 10 largest business districts is still below 50 percent of its pre-COVID level, as white-collar employees spend an estimated 28 percent of their workdays at home.
With a third of all office leases expiring by 2026, we can expect higher vacancies, significantly lower rents, or both. And while we wrestle with the effects of distributed work, artificial intelligence could drive office demand even lower. Some pundits point out that the most expensive offices are still doing okay and that others could be saved by introducing new amenities and services. But landlords can’t very well lease all empty retail stores to Louis Vuitton and Apple. There’s simply not enough demand for such space, and new features make buildings even more expensive to build and operate.
With such grim prospects, some landlords are threatening to “give the keys back to the bank.” Over the past few months, the property giants RXR, Columbia Property Trust, Brookfield Asset Management, and others have collectively defaulted on billions in commercial-property loans. Such defaults are partly an indication of real struggles and partly a game of chicken. Most commercial loans were issued before the pandemic, when offices were full and interest rates were low.
The current landscape is drastically different: high vacancy rates, doubled interest rates, and nearly $1.5 trillion in loans due for repayment by 2025. By defaulting now, landlords leverage their remaining influence to advocate for loan extensions or a bailout. As John Maynard Keynes observed, when you owe your banker $1,000, you are at his mercy, but when you owe him $1 million, “the position is reversed.”
© 2015 Mutual Fund Observer. All rights reserved.
© 2015 Mutual Fund Observer. All rights reserved. Powered by Vanilla