Originally published in November 1, 2013 Commentary
The father of value investing, Benjamin Graham, employed the concept of “Margin of Safety” to minimize risk of permanent loss. His great student, Warren Buffett, puts it like this: “Rule No. 1: never lose money; rule No. 2: don’t forget rule No. 1.”
Zachary Wydra, portfolio manager of the 5-star Beck Mack & Oliver Partners (BMPEX) fund, actually cited Mr. Buffett’s quote during the recent MFO conference call.
But a look at Berkshire Hathaway, one of the great stocks of all time, shows it dropped 46% between December 2007 and February of 2009. And, further back, it dropped about the same between June 1998 and February 2002. So, is Mr. Buffett not following his own rule? Similarly, a look at BMPEX shows an even steeper decline in 2009 at -54%, slightly worse than the SP500.
The distinction, of course, is that drawdown does not necessarily mean loss, unless one sells at what is only a temporary loss in valuation – as opposed to an unrecoverable loss, like experienced by Enron shareholders. Since its 2009 drawdown, BMPEX is in fact up an enviable 161%, beating the SP500 by 9%.
Robert Arnott, founder of Research Associates, summarizes as follows: “Temporary losses of value are frequent; at times they can become so frightening that they become permanent—for those that sell.” Distinguishing between temporary drawdown and permanent loss of capital (aka “the ultimate risk”) is singularly the most important, if unnerving, aspect of successful value investing.
Mr. Wydra explains his strategy is to target stocks that have an upside potential over the next three years of at least 50% and will not lose value over that time. Translation: “loss,” as far as BMPEX is concerned, equates to no drawdown over a three year period. A very practical goal indeed, since any longer period would likely not be tolerated by risk adverse investors.
And yet, it is very, very hard to do, perhaps even impossible for any fund that is primarily long equities.
Here is downside SP500 total return performance looking back about 52 years:
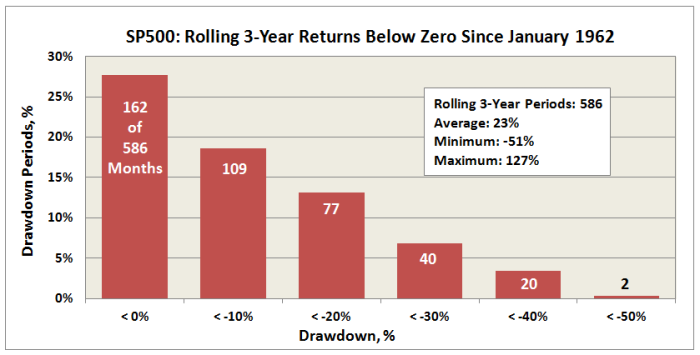
It says that 3-year returns fall below zero over nearly 30% of the time….and fall below 20% nearly half of that time. If we compare returns against consumer price index (CPI), the result is even worse. But for simplicity (and Pete’s) sake, we will not. Fact is, over this time frame, one would need to have invested in the SP500 for nearly 12 years continuously to guarantee a positive return. 12 years!
How many equity or asset allocation funds have not experienced a drawdown over any three year period? Very few. In the last 20 years, only four, or about 1-in-1000. Gabelli ABC (GABCX) and Merger (MERFX), both in the market neutral category and both focused on merger arbitrage strategies. Along with Permanent Portfolio (PRPFX) and Midas Perpetual Portfolio (MPREX), both in the conservative allocation category and both with large a percentage of their portfolios in gold. None of these four beat the SP500. (Although three beat bonds and GABCX did so with especially low volatility.)
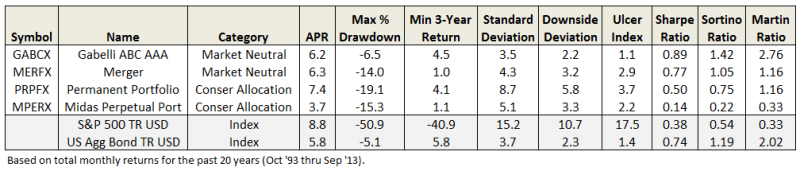
So, while delivering equity-like returns without incurring a “loss” over a three year period may simply prove too high a goal to come true, it is what we wish was true.
29Oct2013/Charles
