Dear friends,
I’m intrigued by the number of times that really experienced managers have made one of two rueful observations to me:
“I make all my money in bear markets, I just don’t know it at the time”
“I add most of my value when the market’s in panic.”
With the market down 6.2% in May, Morningstar’s surrogate for high-quality domestic companies down by nearly 9% and only one equity sector posting a gain (utilities were up by 0.1%), presumably a lot of investment managers are gleefully earning much of the $10 billion in fees that the industry will collect this year.
Long-Short Funds and the Long, Hot Summer
The investment industry seems to think you need a long-short fund, given the number of long-short equity funds that they’ve rolled-out in recent years. They are now 70 long-short funds (a category distinct from market neutral and bear market funds, and from funds that occasionally short as a hedging strategy). With impeccable timing, 36 were launched after we passed the last bear market bottom in March 2009.
Long-short fund launches, by year
| 2011 – 12 | 13 funds |
| 2010 | 16 funds |
| 2009 | 7 funds |
| Pre-2009 | 34 funds |
The idea of a long-short fund is unambiguously appealing and is actually modeled after the very first hedge fund, A. W. Jones’s 1949 hedged fund. Much is made of the fact that hedge funds have lost both their final “d” and their original rationale. Mr. Jones reasoned that we could not reliably predict short-term market movements, but we could position ourselves to take advantage of them (or at least to minimize their damage). He called for investing in net-long in the stock market, since it was our most reliable engine of “real” returns, but of hedging that exposure by betting against the least rational slices of the market. If the market rose, your fund rose because it was net-long and invested in unusually attractive firms. If the market wandered sideways, your fund might drift upward as individual instances of irrational pricing (the folks you shorted) corrected. And if the market fell, ideally the stocks you shorted would fall the most and would offer a disproportionately large cushion. A 30% short exposure in really mispriced stocks might, hypothetically, buffer 50% of a market slide.
Unfortunately, most long-short funds aren’t able to clear even the simplest performance hurdle, the returns of a conservative short-term bond index fund. Here are the numbers:
| Number that outperformed a short-term bond index fund (up 3%) in 2011 |
11 of 59 |
| Number that outperformed a short-term bond index fund from May 2011 – May 2012 |
6 of 62 |
| Number that outperformed a short-term bond index over three years, May 2010 – May 2012 |
21 of 32 |
| Number that outperformed a short-term bond index over five years, May 2008 – May 2012 |
1 of 22 |
| Number in the red over the past five years |
13 of 22 |
| Number that outperformed a short-term bond index fund in 2008 |
0 of 25 |
In general, over the past five years, you’d have been much better off buying the Vanguard Short-Term Bond Index (VBISX), pocketing your 4.6% and going to bed rather than surrendering to the seductive logic and the industry’s most-sophisticated strategies.
Indeed, there is only one long-short fund that’s unambiguously worth owning: Robeco Long/Short Equity (BPLSX). But it had a $100,000 investment minimum. And it closed to new investors in July, 2010.
Nonetheless, the idea behind long/short investing makes sense. In consequence of that, the Observer has begun a summer-long series of profiles of long-short funds that hold promise, some few that have substantial track records as mutual funds and rather more with short fund records but longer pedigrees as separate accounts or hedge funds. Our hope is to identify one or two interesting options for you that might help you weather the turbulence that’s inevitably ahead for us all.
This month we begin by renewing the 2009 profile of a distinguished fund, Wasatch Long/ Short (FMLSX) and bringing a really promising newcomer, Aston / River Road Long- Short (ARLSX) onto your radar.
Our plans for the months ahead include profiles of Aston/MD Sass Enhanced Equity (AMBEX), RiverPark Long/Short Opportunity (RLSFX), RiverPark/Gargoyle Hedged Value (RGHVX), James Long-Short (JAZZX), and Paladin Long Short (PALFX). If we’ve missed someone that you think of a crazy-great, drop me a line. I’m open to new ideas.
FBR reaps what it sowed
FBR & Co. filed an interesting Regulation FD Disclosure with the SEC on May 30, 2012. Here’s the text of the filing:
FBR & Co. (the “Company”) disclosed today that it has been working with outside advisors who are assisting the Company in its evaluation of strategic alternatives for its asset management business, including the sale of all or a portion of the business.
There can be no assurance that this process will result in any specific action or transaction. The Company does not intend to further publicly comment on this initiative unless the Company executes definitive deal documentation providing for a specific transaction approved by its Board of Directors.
FBR has been financially troubled for years, a fact highlighted by their decision in 2009 to squeeze out their most successful portfolio manager, Chuck Akre and his team. In 1997, Mr. Akre became of founding manager of FBR Small Cap Growth – Value fund, which became FBR Small Cap Value, the FBR Small Cap, and finally FBR Focus (FBRVX). Merely saying that he was “brilliant” underestimates his stewardship of the fund. Under his watch (December 1996 – August 2009), Mr. Akre turned $10,000 invested in the fund at inception to $44,000. His average peer would have yielded $18,000. Put another way: he added $34,000 to the value of your opening portfolio while the average midcap manager added $8,000. Uhh: he added four times as much?
In recognition of which, FBR through the Board of Trustees whose sole responsibility is safeguarding the interests of the fund’s shareholders, offered to renew his management contract in 2009 – as long as he accepted a 50% pay cut. Mr. Akre predictably left with his analyst team and launched his own fund, Akre Focus (AKREX). In a singularly classy move, FBR waited until Mr. Akre was out of town on a research trip and made his analysts an offer they couldn’t refuse. Akre got a phone call from his analysts, letting him know that they’d resigned so that they could return to run FBR Focus.
Why? At base, FBR was in financial trouble and almost all of their funds were running at a loss. The question became how to maximize the revenue produced by their most viable asset, FBR Focus and the associated separate accounts which accounted for more than a billion of assets under management. FBR seems to have made a calculated bet that by slashing the portion of fund fees going to Mr. Akre’s firm would increase their own revenues dramatically. Even if a few hundred million followed Mr. Akre out the door, they’d still make money on the deal.
Why, exactly, the Board of Trustees found this in the best interests of the Focus shareholders (as opposed to FBR’s corporate interests) has never been explained.
How did FBR’s bet play out? Here’s your clue: they’re trying to sell their mutual fund unit (see above). FBR Focus’s assets have dropped by a hundred million or so, while Akre Focus has drawn nearly a billion in new assets. FBR & Co’s first quarter revenues were $39 million in 2012, down from $50 million in 2011. Ironically, FBR’s 10 funds – in particular, David Ellison’s duo – are uniformly solid performers which have simply not caught investors’ attention. (Credit Bryan Switzky of the Washington Business Journal for first writing about the FD filing, “FBR & Co. exploring sale of its asset management business,” and MFWire for highlighting his story.)
Speaking of Fund Trustees
An entirely unremarkable little fund, Autopilot Managed Growth Fund (AUTOX), gave up the ghost in May. Why? Same as always:
The Board of Trustees of the Autopilot Managed Growth Fund (the “Fund”), a separate series of the Northern Lights Fund Trust, has concluded that it is in the best interests of the Fund and its shareholders that the Fund cease operations. The Board has determined to close the Fund, and redeem all outstanding shares, on June 15, 2012.
Wow. That’s a solemn responsibility, weighing the fate of an entire enterprise and acting selflessly to protect your fellow shareholders.
Sure would be nice if Trustees actually did all that stuff, but the evidence suggests that it’s damned unlikely. Here’s the profile for Autopilot’s Board, from the fund’s most recent Statement of Additional Information.
| Name of Trustee (names in the original, just initials here) | Number of Portfolios in Fund Complex Overseen by Trustee | Total Compensation Paid to Directors | Aggregate Dollar Range of Equity Securities in All Registered Investment Companies Overseen by Trustee in Family of Investment Companies |
| LMB |
95 |
$65,000 |
None |
| AJH |
95 |
$77,500 |
None |
| GL |
95 |
$65,000 |
None |
| MT |
95 |
$65,000 |
None |
| MM |
95 |
none |
None |
A footnote adds that each Trustee oversees between two and 14 other funds.
How is it that Autopilot became 1% of a Trustee’s responsibilities? Simple: funds buy access to prepackaged Boards of Trustees as part of the same arrangement that provides the rest of their “back office” services. The ability of a fund to bundle all of those services can dramatically reduce the cost of operation and dramatically increase the feasibility of launching an interesting new product.
So, “LMB” is overseeing the interests of the shareholders in 109 mutual funds, for which he’s paid $65,000. Frankly, for LMB and his brethren, as with the FBR Board of Trustees (see above), this is a well-paid, part-time job. His commitment to the funds and their shareholders might be reflected by the fact that he’s willing to pretend to have time to understand 100 funds or by the fact that not one of those hundred has received a dollar of his own money.
It is, in either case, evidence of a broken system.
Trust But Verify . . .
Over and over again.
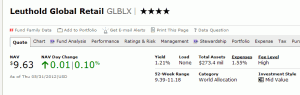
Large databases are tricky creatures, and few are larger or trickier than Morningstar’s. I’ve been wondering, lately, whether there are better choices than Leuthold Global (GLBLX) for part of my non-retirement portfolio. Leuthold’s fees tend to be high, Mr. Leuthold is stepping away from active management and the fund might be a bit stock-heavy for my purposes. I set up a watchlist of plausible alternatives through Morningstar to see what I might find.
What I expected to find was the same data on each page, as was the case with Leuthold Global itself.
 |
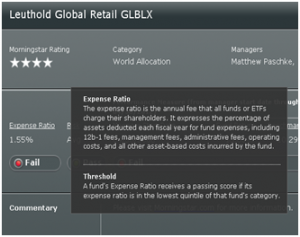 |
What I found was that Morningstar inconsistently reports the expense ratios for five of seven funds, with different parts of the site offering different expenses for the same fund. Below is the comparison of the expense ratio reported on a fund’s profile page at Morningstar and at Morningstar’s Fund Spy page.
|
Profiled e.r. |
Fund Spy e.r. |
|
| Leuthold Global |
1.55% |
1.55% |
| PIMCO All Asset, A |
1.38 |
0.76 |
| PIMCO All Asset, D |
1.28 |
0.56 |
| Northern Global Tact Alloc |
0.68 |
0.25 |
| Vanguard STAR |
0.34 |
0.00 |
| FPA Crescent |
1.18 |
1.18 |
| Price Spectrum Income |
0.69 |
0.00 |
I called and asked about the discrepancy. The best explanation that Morningstar’s rep had was that Fund Spy updated monthly and the profile daily. When I asked how that might explain a 50% discrepancy in expenses, which don’t vary month-to-month, the answer was an honest: “I don’t know.”
The same problem appeared when I began looking at portfolio turnover data, occasioned by the question “does any SCV fund have a lower turnover than Huber Small Cap?” Morningstar’s database reported 15 such funds, but when I clicked on the linked profile for each fund, I noticed errors in almost half of the reports.
|
Profiled turnover |
Fund Screener turnover |
|
| Allianz NFJ Small Cap Value (PCVAX) |
26 |
9 |
| Consulting Group SCV (TSVUX) |
38 |
9 |
| Hotchkis and Wiley SCV (HWSIX) |
54 |
11 |
| JHFunds 2 SCV (JSCNX) |
15 |
9 |
| Northern Small Cap Value (NOSGX) |
21 |
6 |
| Queens Road Small Cal (QRSVX) |
38 |
9 |
| Robeco SCV I (BPSCX) |
38 |
6 |
| Bridgeway Omni SCV (BOSVX) |
n/a |
Registers as <12% |
Just to be clear: these sorts of errors, while annoying, might well be entirely unavoidable. Morningstar’s database is enormous – they track 375,000 investment products each day – and incredibly complex. Even if they get 99.99% accuracy, they’re going to create thousands of errors.
One responsibility lies with Morningstar to clear up, as soon as is practical, the errors that they’ve learned of. A greater responsibility lies with data users to double-check the accuracy of the data upon which they’re basing their decisions or forming their judgments. It’s a hassle but until data providers become perfectly reliable, it’s an essential discipline.
A mid-month update:
The folks at Morningstar looked into these problems quite quickly. The short version is this: fund filings often contain multiple versions of what’s apparently the same data point. There are, for example, a couple different turnover ratios and up to four expense ratios. Different functions, developed by different folks at different times, might inadvertently choose to pull stats from different places. Both stats are correct but also inconsistent. If they aren’t flagged so that readers can understand the differences, they can also be misleading.
Morningstar is interested in providing consistent, system-wide data. Once they recognized the inconsistency, they moved quickly to reconcile it. As of June 19, the data had been reconciled. Thanks to the Wizards on West Wacker for their quick work. We’ll have a slightly more complete update in our July issue.
Proof that Time Travel is Possible: The SEC’s Current Filings
Each day, the Securities and Exchange Commission posts all of their current filings on their website. For example, when a fund company files a new prospectus or a quarterly portfolio list, it appears at the SEC. Each filing contains a date. In theory, the page for May 22 will contain filings all of which are dated May 22.
How hard could that be?
Here’s a clue: of 187 entries for May 22, 25 were actually documents filed on May 22nd. That’s 13.3%. What are the other 86.7% of postings? 137 of them are filings originally made on other days or in other years. 25 of them are duplicate filings that are dated May 22.
I’ve regularly noted the agency’s whimsical programming. This month I filed two written inquiries with them, asking why this happens. The first query provoked no response for about 10 days, so I filed the second. That provoked a voicemail message from an SEC attorney. The essence of her answer:
- I don’t know
- Other parts of the agency aren’t returning our phone calls
- But maybe they’ll contact you?
Uhh … no, not so far. Which leads me to the only possible conclusion: time vortex centered on the SEC headquarters. To those of us outside the SEC, it was May 22, 2012. To those inside the agency, all the dates in recent history had actually converged and so it was possible that all 15 dates recorded on the May 22 page were occurring simultaneously.

And now a word from Chip, MFO’s technical director: “dear God, guys, hire a programmer. It’s not that blinkin’ hard.”
Launch Alert 1: Rocky Peak Small Cap Value
 On April 2, Rocky Peak Capital Management launched Rocky Peak Small Cap Value (RPCSX). Rocky Peak was founded in 2011 by Tom Kerr, a Partner at Reed Conner Birdwell and long-time co-manager of CNI Charter RCB Small Cap Value fund. He did well enough with that fund that Litman Gregory selected him as one of the managers of their Masters Smaller Companies fund (MSSFX).
On April 2, Rocky Peak Capital Management launched Rocky Peak Small Cap Value (RPCSX). Rocky Peak was founded in 2011 by Tom Kerr, a Partner at Reed Conner Birdwell and long-time co-manager of CNI Charter RCB Small Cap Value fund. He did well enough with that fund that Litman Gregory selected him as one of the managers of their Masters Smaller Companies fund (MSSFX).
While RPCSX doesn’t have enough of a track record to yet warrant a full profile, the manager’s experience and track record warrant adding it to a watch-list. His plan is to hold 35-40 small cap stocks, many that pay dividends, and to keep risk-management in the forefront of his discipline. Among the more interesting notes that came out of our hour-long conversation was (1) his interest in monitoring the quality of the boards of directors which should be reflected in both capital allocation and management compensation decisions and (2) his contention that there are three distinct sub-sets of the small cap universe which require different valuation strategies. “Quality value” companies often have decades of profitable operating history and would be attractive at a modest discount to fair value. “Contrarian value” companies, which he describes as “Third Avenue-type companies” are often great companies undergoing “corporate events” and might require a considerably greater discount. “Smaller unknown value” stocks are microcap stocks with no more than one analyst covering them, but also really good companies (e.g. Federated Investors or Duff & Phelps). I’ll follow it for a bit.
The fund has a $10,000 investment minimum and 1.50% expense ratio, after waivers.
Launch Alert 2: T. Rowe Price Emerging-Markets Corporate Bond Fund
On May 24, T. Rowe Price launched Emerging Markets Corporate Bond (TRECX), which will be managed by Michael Conelius, who also manages T. Rowe Price Emerging Markets Bond (PREMX). PREMX has a substantial EM corporate bond stake, so it’s not a new area for him. The argument is that, in a low-yield world, these bonds offer a relatively low-risk way to gain exposure to financially sound, quickly growing firms. The manager will mostly invest in dollar-denominated bonds as a way to hedge currency risks and will pursue theme-based investing (“rise of the Brazilian middle class”) in the same way many e.m. stock funds do. The fund has a $2500 investment minimum, reduced to $1000 for IRAs and will charge a 1.15% expense ratio, after waivers. That’s just above the emerging-markets bond category average of 1.11%, which is a great deal on a fund with no assets yet.
Launch Alert 3: PIMCO Short Asset Investment Fund
On May 31, PIMCO launched this fund has an alternative to a money-market fund. PIMCO presents the fund as “a choice for conservative investors” which will offer “higher income potential than traditional cash investments.” Here’s their argument:
Yields remain compressed, making it difficult for investors to obtain high-quality income without taking on excess risk. PIMCO Short Asset Investment Fund offers higher income potential than traditional cash investments by drawing on multiple high-quality fixed income opportunity sets and PIMCO’s expertise.
The manager, Jerome Schneider, has access to a variety of higher-quality fixed-income products as well as limited access to derivatives. He’s “head of [their] short-term funding desk and is responsible for supervising all of PIMCO’s short-term investment strategies.” The “D” class shares trade under the symbol PAIUX, have a $1000 minimum, and expenses of 0.59% after waivers. “D” shares are generally available no-load/NTF at a variety of brokerages.
Four Funds and Why They’re Really Worth Your While
Each month, the Observer profiles between two and four mutual funds that you likely have not heard about, but really should have. Our “Most intriguing new funds: good ideas, great managers” do not yet have a long track record, but which have other virtues which warrant your attention. They might come from a great boutique or be offered by a top-tier manager who has struck out on his own. The “most intriguing new funds” aren’t all worthy of your “gotta buy” list, but all of them are going to be fundamentally intriguing possibilities that warrant some thought. Two intriguing newer funds are:
Aston / River Road Long-Short (ARLSX). There are few successful, time-tested long-short funds available to retail investors. Among the crop of newer offerings, few are more sensibly-constructed, less expensive or more carefully managed that ARLSX seems to be. It deserves attention.
Osterweis Strategic Investment (OSTVX). For folks who remain anxious about the prospects of a static allocation in a dynamic world, OSTVX combines the virtues of two highly-flexible Osterweis funds in a single package. The fund remains a very credible choice along with stalwarts such as PIMCO All-Asset (PASDX) and FPA Crescent (FPACX). This is an update to our May 2011 profile. We’ve changed styles in presenting our updates. We’ve placed the new commentary in a text box but we’ve also preserved all of the original commentary, which often provides a fuller discussion of strategies and the fund’s competitive universe. Feel free to weigh-in on whether this style works for you.
The “stars in the shadows” are all time-tested funds, many of which have everything except shareholders.
Huber Small Cap Value (HUSIX). Huber Small Cap is not only the best small-cap value fund of the past three years, it’s the extension of a long-practice, intensive and successful discipline with a documented public record. For investors who understand that even great funds have scary stretches and are able to tolerate “being early” as a condition of long-term outperformance, HUSIX justifies as close a look as any fund launched in the past several years.
Wasatch Long Short (FMLSX). For folks interested in access to a volatility-controlled equity fund, the case for FMLSX was – and is – remarkably compelling. There’s only one demonstrably better fund in its class (BPLSX) and you can’t get into it. FMLSX is near the top of the “A” list for those you can consider. This is an update to our 2009 profile.
The Best of the Web: Retirement Income Calculators
Our fourth “Best of the Web” feature focuses on retirement income calculators. These are software programs, some quite primitive and a couple that are really smooth, that help answer two questions that most of us have been afraid to ask:
- How much income will a continuation of my current efforts generate?
and
- Will it be enough?
 The ugly reality is that for most Americans, the answers are “not much” and “no.” Tom Ashbrook, host of NPR’s On Point, describes most of us as “flying naked” toward retirement. His May 29 program entitled “Is the 401(k) Working?” featured Teresa Ghilarducci, an economics professor at The New School of Social Research, nationally-recognized expert in retirement security and author of When I’m Sixty-Four: The Plot against Pensions and the Plan to Save Them (Princeton UP, 2008). Based on her analysis of the most recent data, it “doesn’t look good at all” with “a lot of middle-class working Americans [becoming] ‘poor’ or ‘near-poor’ at retirement.”
The ugly reality is that for most Americans, the answers are “not much” and “no.” Tom Ashbrook, host of NPR’s On Point, describes most of us as “flying naked” toward retirement. His May 29 program entitled “Is the 401(k) Working?” featured Teresa Ghilarducci, an economics professor at The New School of Social Research, nationally-recognized expert in retirement security and author of When I’m Sixty-Four: The Plot against Pensions and the Plan to Save Them (Princeton UP, 2008). Based on her analysis of the most recent data, it “doesn’t look good at all” with “a lot of middle-class working Americans [becoming] ‘poor’ or ‘near-poor’ at retirement.”
Her data looks at the investments of folks from 50-64 and finds that most, 52%, have nothing (as in: zero, zip, zilch, nada, the piggy bank is empty). In the top quarter of wage earners, folks with incomes above $75,000, one quarter of those in their 50s and 60s have no retirement savings. Among the bottom quarter, 77% have nothing and the average account value for those who have been saving is $10,000.
The best strategy is neither playing the lottery nor pretending that it won’t happen. The best strategy is a realistic assessment now, when you still have the opportunity to change your habits or your plans. The challenge is finding a guide that you can rely upon. Certainly a good fee-only financial planner would be an excellent choice but many folks would prefer to turn to the web answers. And so this month we trying to ferret out the best free, freely-available retirement income calculators on the web.
MFO at MIC

I’m pleased to report that I’ll be attending The Morningstar Investment Conference on behalf of the Observer. This will be my first time in attendance. I’ve got a couple meetings already scheduled and am looking forward to meeting some of the folks who I’ve only known through years of phone conversations and emails.
I’m hopeful of meeting Joan Rivers – I presume she’ll be doing commentary on the arrival of fashionistas Steve Romick, Will Danoff & Brian Rogers – and am very much looking forward to hearing from Jeremy Grantham in Friday’s keynote. If folks have other suggestions for really good uses of my time, I’d like to hear from you. Too, if you’d like to talk with me about the Observer and potential story leads, I’d be pleased to spend the time with you.
 There’s a cheerful internal debate here about what I should wear. Junior favors an old-school image for me: gray fedora with a press card in the hatband, flash camera and spiral notebook. (Imagine a sort of balding Clark Kent.) Chip, whose PhotoShop skills are so refined that she once made George W. look downright studious, just smiles and assures me that it doesn’t matter what I wear. (Why does a smile and the phrase “Wear what you like and I’ll take care of everything” make me so apprehensive? Hmmm…)
There’s a cheerful internal debate here about what I should wear. Junior favors an old-school image for me: gray fedora with a press card in the hatband, flash camera and spiral notebook. (Imagine a sort of balding Clark Kent.) Chip, whose PhotoShop skills are so refined that she once made George W. look downright studious, just smiles and assures me that it doesn’t matter what I wear. (Why does a smile and the phrase “Wear what you like and I’ll take care of everything” make me so apprehensive? Hmmm…)
Perhaps the better course is just to drop me a quick note if you’re going to be around and would like to chat.
Briefly noted . . .
Dreyfus has added Vulcan Value Partners as a sixth subadvisor for Dreyfus Select Managers Small Cap Value (DMVAX). Good move! Our profile described Vulcan Value Partners Small Cap fund as “a solid, sensible, profitable vehicle.” Manager C.T. Fitzpatrick spent 17 years managing with Longleaf Partners before founding the Vulcan Value Partners.
First Eagle has launched First Eagle Global Income Builder (FEBAX) in hopes that it will provide “a meaningful but sustainable income stream across all market environments.” Like me, they’re hopeful of avoiding “permanent impairment of capital.” The management team overlaps their four-star High Yield Fund team. The fund had $11 million on opening day and charges 1.3%, after waivers, for its “A” shares.
Vanguard Gets Busy
In the past four weeks, Vanguard:
Closed Vanguard High-Yield Corporate (VWEHX), closed to new investors. The fund, subadvised by Wellington, sucked in $1.5 billion in new assets this year. T. Rowe Price closed its High Yield (PRHYX) fund in April after a similar in-rush.
Eliminated the redemption fee on 33 mutual funds
Cut the expense ratios for 15 fixed-income, diversified-equity, and sector funds and ETFs.
Invented a calorie-free chocolate fudge brownie.
Osterweis, too
Osterweis Strategic Income (OSTIX) has added another fee breakpoint. The fund will charge 0.65% on assets over $2.5 billion. Given that the fund is a $2.3 billion, that’s worthwhile. It’s a distinctly untraditional bond fund and well-managed. Because its portfolio is so distinctive (lots of short-term, higher-yielding debt), its peer rankings are largely irrelevant.
At Least They’re Not in Jail
Former Seligman Communications and Information comanager Reema Shah pled guilty to securities fraud and is barred from the securities industry for life. She traded inside information with a Yahoo executive, which netted a few hundred thousand for her fund.
Authorities in Hong Kong have declined to pursue prosecution of George Stairs, former Fidelity International Value (FIVLX) manager. Even Fido agrees that Mr. Stairs “did knowingly trade on non-public sensitive information.” Stairs ran the fund, largely into the ground, from 2006-11.
Farewells
Henry Berghoef, long-time co-manager of Oakmark Select (OAKLX), plans to retire at the end of July.
Andrew Engel, who helped manage Leuthold’s flagship Core Investment(LCORX) and Asset Allocation(LAALX) funds, died on May 9, at the age of 52. He left behind a wife, four children and many friends.
David Williams, who managed Columbia Value & Restructuring (EVRAX, which started life as Excelsior Value & Restructuring), has retired after 20 years at the helm. The fund was one of the first to look beyond simple “value” and “growth” categories and into other structural elements in constructing its portfolio.
Closings
Delaware Select Growth (DVEAX) will close to new investors at the beginning of June, 2012.
Franklin Double Tax-Free Income (FPRTX) will soft-close in mid-June then hard-close at the beginning of August.
Goldman Sachs Mid Cap Value (GCMAX) will close to new investors at the end of July. Over the past five years the fund has been solidly . .. uh, “okay.” You could do worse. It doesn’t suck often. Not clear why, exactly, that justifies $8 billion in assets.
Old Wine, New Bottles
Artisan Growth Opportunities (ARTRX) is being renamed Artisan Global Opportunities. The fund is also pretty global and the management team is talented and remaining, so it’s mostly a branding issue.
BlackRock Multi-Sector Bond Portfolio (BMSAX) becomes BlackRock Secured Credit Portfolio in June. It also gets a new mandate (investing in “secured” instruments such as bank loans) and a new management team. Presumably BlackRock is annoyed that the fund isn’t drawing enough assets (just $55 million after two years). Its performance has been solid and it’s relatively new, so the problem mostly comes down to avarice.
Likewise BlackRock Mid-Cap Value Equity (BMCAX) will be revamped into BlackRock Flexible Equity at the end of July. After its rebirth, the fund will become all-cap, able to invest across the valuation spectrum and able to invest large chunks into bonds, commodities and cash. The current version of the fund has been consistently bad at everything except gathering assets, so it makes sense to change managers. The eclectic new portfolio may reflect its new manager’s background in the hedge fund world.
Buffalo Science & Technology (BUFTX) will be renamed Buffalo Discovery, effective June 29, 2012.
Goldman Sachs Ultra-Short Duration Government (GSARX) is about to become Goldman Sachs High Quality Floating Rate and its mandate has been rewritten to focus on foreign and domestic floating-rate government debt.
Invesco Small Companies (ATIAX) will be renamed Invesco Select Companies at the beginning of August.
Nuveen is reorganizing Nuveen Large Cap Value (FASKX) into Dividend Value (FFEIX), pending shareholder approval of course, next autumn. The recently-despatched management team managed to parlay high risk and low returns into a consistently dismal record so shareholders are apt to agree.
Perritt Emerging Opportunities (PREOX) has been renamed Perritt Ultra MicroCap. The fund’s greatest distinction is that it invests in smaller stocks, on whole, than any other fund and their original name didn’t capture that reality. The fund is a poster child for “erratic,” finishing either in the top 10% or the bottom 10% of small cap funds almost every year. Its performance roughly parallels that of Bridgeway’s two “ultra-small company” funds.
Nuveen Tradewinds Global All-Cap (NWGAX) and Nuveen Tradewinds Value Opportunities (NVOAX) have reopened to new investors after the fund’s manager and a third of assets left.
Off to the Dustbin of History
AllianceBernstein Greater China ’97 (GCHAX) will be liquidated in early June. It’s the old story: high expenses, low returns, no assets.
Leuthold Hedged Equity will liquidate in June 2012, just short of its third anniversary. The fund drew $4.7 million between two share clases and the Board of Trustees determined it was in the best interests of shareholders to liquidate. Given the fund’s consistent losses – it turned $10,000 into $7900 – and high expenses, they’re likely right. The most interesting feature of the fund is that the Institutional share class investors were asked to pony up $1 million to get in, and were then charged higher fees than were retail class investors.
Lord Abbett Large Cap (LALAX) mergers into Lord Abbett Fundamental Equity (LDFVX) on June 15.
Oppenheimer plans to merge Oppenheimer Champion Income (OPCHX) and Oppenheimer Fixed Income Active Allocation (OAFAX) funds will merge into Oppenheimer Global Strategic Income (OPSIX) later this year. That’s the final chapter in the saga of two funds that imploded (think: down 80%) in 2008, then saw their management teams canned in 2009. The decision still seems odd: OPCHX has a half-billion in assets and OAFAX is a small, entirely solid fund-of-funds.
In closing . . .
Thanks to all the folks who’ve provided financial support for the Observer this month. In addition to a handful of friends who provided cash contributions, either via PayPal or by check, readers purchased almost 210 items through the Observer’s Amazon link. Thanks! If you have questions about how to use or share the link, or if you’re just not sure that you’re doing it right, drop me a line.
It’s been a tough month, but it could be worse. You could have made a leveraged bet on the rise of Latin American markets (down 25% in May). For folks looking for sanity and stability, though, we’ll continue in July our summer-long series of long-short funds, but we’ll also update the profiles of RiverPark Short-Term High Yield (RPHYX), a fund in which both Chip and I invest, and ING Corporate Leaders (LEXCX), the ghost ship of the fund world. It’s a fund whose motto is “No manager? No problem!” We’re hoping to have a first profile of Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX) and Conestoga Small Cap (CCASX).
Until then, take care and keep cool!





 RiverPark/Gargoyle Hedged Value Fund pursued a covered call strategy. Here’s how Gargoyle describes their investment strategy:
RiverPark/Gargoyle Hedged Value Fund pursued a covered call strategy. Here’s how Gargoyle describes their investment strategy: Lipper: Your Best Small Fund Company is . . .
Lipper: Your Best Small Fund Company is . . .