Dear friends,
Occasionally Facebook produces finds that I’m at a loss to explain. Ecce:

(Thanks to Nina K., a really first-rate writer and first-rate property/insurance lawyer in the Bay State for sharing Mr. Takei’s post with us. Now if I could just get her to restrain the impulse to blurt out, incredulous, “you really find this stuff interesting?”)
Let’s see. Should I be more curious about the fact that Mr. Takei (iconically Ensign Sulu on Star Trek) manages just a basso profundo “oh myyy” on his post or the fact that he was recently lounging in a waiting room at the University of Iowa Hospitals, a bit west of here? Perhaps it would be better to let his friends weigh in?
Chip’s vote was to simply swipe her favorite image from the thread, one labeled “a real hedge fund.”

Which is to say, a market that tacks on 29% in a year makes it easy to think of investing as fun and funny again.
Now if only that popular sentiment could be reconciled with the fact that a bunch of very disciplined, very successful managers are quietly selling down their stocks and building their cash reserves again.
 Here’s today’s “know your Morningstar!” quiz.
Here’s today’s “know your Morningstar!” quiz.
Here are the total return charts for two short-term bond funds. One is the sole Morningstar Gold Medalist in the group, representing “one of the industry’s best managers, and one of the category’s best funds.” The other is a lowly one-star fund unworthy of Morningstar’s notice
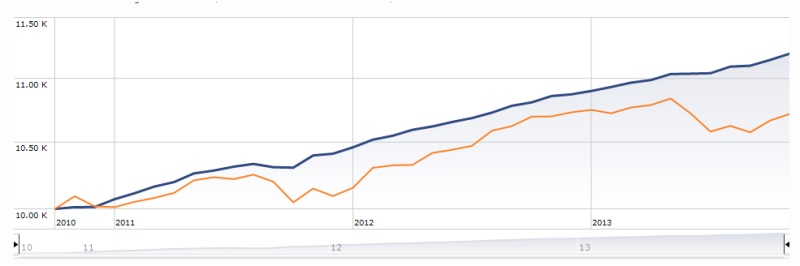
Question: do you …know your Morningstar!? Which is the golden child? Is it blue or orange?
Would it help to know that one of these funds is managed by a multi-trillion dollar titan and the other by a small, distinctive boutique? Or that one of the funds invests quite conventionally and fits neatly into a style-box while the other is one-of-a-kind?
If you know your Morningstar, you’ll know that “small, distinctive and hard to pigeonhole” is pretty much the kiss of death. The orange (or gold) line represents PIMCO Low Duration, “D” shares (PLDDX). It’s a $24 billion “juggernaut” (Morningstar’s term) that’s earned four stars and a Gold designation. It tends to be in the top quarter of the short-term bond group, though not at its top, and is a bit riskier than average.
The blue line represents RiverPark Short Term High Yield (RPHYX), an absolutely first-rate cash management fund about which we’ve written a lot. And which Morningstar just designated as a one-star fund. Why so? Because Morningstar classifies it as a “high yield bond” fund and benchmarks it against an investment class that has outperformed the stock market over the past 15 years but with the highest volatility in the fixed-income universe. To be clear: there is essentially no overlap between RiverPark’s portfolio and the average high-yield bond funds and they have entirely different strategies, objectives and risk profiles. Which is to say, Morningstar has managed a classic “walnuts to lug nuts” comparison.
Here’s the defense Morningstar might reasonably make: “we had to put it somewhere. It says ‘high yield.’ We put it there.”
Here’s our response: “that’s a sad and self-damning answer. Yes, you had to put it somewhere. But having put it in a place that you know is wildly inappropriate, you also need to accept the responsibility – to your readers, to RiverPark’s investors and to yourselves – to address your decision. You’ve got the world’s biggest and best supported corps of analysts in the world. Use them! Don’t ignore the funds that do well outside of the comfortable framework of style boxes, categories and corporate investing! If the algorithms produce palpably misleading ratings, speak up.”
But, of course, they didn’t.
The problem is straightforward: Morningstar’s ratings are most reliable when you least need them. For funds with conventional, straightforward, style-pure disciplines – index funds and closet index funds – the star ratings probably produce a fair snapshot across the funds. But really, how hard is it – even absent Morningstar’s imprimatur – to find the most solid offering among a gaggle of long-only, domestic large cap, growth-at-a-reasonable price funds? You’ll get 90% of the way there with three numbers: five year returns, five year volatility and expense ratio. Look for ones where the first is higher and the second two are lower.
When funds try not to follow the herd, when the manager appears to have a brain and to be using it to pursue different possibilities, is when the ratings system is most prone to misleading readers. That’s when you need to hear an expert’s analysis.
So why, then, deploy your analysts to write endless prose about domestic large cap funds? Because that’s where the money is.
Morningstar ETF Invest: Rather less useful content than I’d imagined
Morningstar hosted their ETF-focused conference in Chicago at the beginning of October. The folks report that the gathering has tripled in size over the last couple years, turned away potential registrants and will soon need to move to a new space. After three days there, though, I came away with few strong reactions. I was struck by the decision of one keynote speaker to refer to active fixed-income managers as “the enemy” (no, dude, check the mirror) and the apparent anxiety around Fidelity’s decision to enter the ETF market (“Fidelity is coming. We know they’re coming. It’s only a matter of time,” warned one).
My greatest bewilderment was at the industry’s apparent insistence on damaging themselves as quickly and thoroughly as possible. ETFs really have, at most, three advantages: they’re cheap, transparent and liquid. The vogue seems to be for frittering that away. More and more advisors are being persuaded to purchase the services of managed portfolio advisors who, for a fee, promise to custom-package (and trade) dozens of ETFs. I spoke with representatives of a couple index providers, including FTSE, who corroborated Morningstar’s assertion that there are likely two million separate security indexes in operation with more being created daily. And many of the exchange-traded products rely in derivatives to try to capture the movements of those 2,000,000. On whole, it feels like a systematic attempt to capture the most troubling features of the mutual fund industry – all while preening about your Olympian superiority to the mutual fund industry.
Odd.
The most interesting presentation at the conference was made by Austan Goolsbee, a University of Chicago economist and former chief of the President’s Council of Economic Advisers, who addressed a luncheon crowd. It was a thoroughly unexpected performance: there’s a strong overtone of Jon Stewart from The Daily Show, an almost antic energy. The presentation was one-third Goolsbee family anecdotes (“when I’d complain about a problem, gramma would say ‘80% of us don’t care. . . and the other 20% are glad about it'”), one-third White House anecdotes and one-third economic arguments.
The short version:
- The next 12-18 months will be tough because the old drivers of recovery aren’t available this time. Over the last century, house prices appreciated by 40 basis points annually for the first 90 years. From 2000-08, it appreciated 1350 bps annually. In the future, 40 bps is likely about right which means that a recovery in the housing industry won’t be lifting all boats any time soon.
- We’ll know the economy is recovering when 25 year olds start moving out of their parents’ basements, renting little apartments, buying futons and cheap pots and pans. (Technically, an uptick in household formation. Since the beginning of the recession, the US population has grown by 10 million but the number of households has remained flat.) One optimistic measure that Goolsbee did not mention but which seems comparable: the number of Americans choosing to quit their jobs (presumably for something better) is rising.
- The shutdown is probably a good thing, since it will derail efforts to create an unnecessary crisis around the debt ceiling.
- In the longer term, the US will recover and grow at 3.5% annually, driven by a population that’s growing (we’ll likely peak around 400 million while Japan, Western Europe and Russia contract), the world’s most productive workforce and relatively light taxation. While Social Security faces challenges, they’re manageable. Given the slow rolling crisis in higher education and the near collapse of new business launches over the past decade, I’m actually somewhere between skeptical and queasy on this one.
- The Chinese economic numbers can’t be trusted at all. The US reports quarterly economic data after a 30 day lag and frequently revises the numbers 30 days after that. China reports their quarterly numbers one day after the end of the quarter and has never revised any of the numbers. A better measure of Chinese activity is derivable from FedEx volume (it’s way down) since China is so export driven.
One highlight was his report of a headline from The Onion: “recession-plagued nation demands a new bubble to invest in … so we can get the economy going again. We need a concrete way to create illusory wealth in the near future.”
One of the great things about having Messrs Studzinski and Boccadoro contributing to the Observer is that they’re keen, experienced observers and very good writers. The other great thing about it is that I no longer have to bear the label, “the cranky one.” In the following essay, Ed Studzinkski takes on one of the beloved touchstones of shareholder-friendly management: “skin in the game.” Further down, Charles Boccadoro casts a skeptical eye, in a data-rich piece, on the likelihood that an investor’s going to avoid permanent loss of capital.
Skin in the Game, Part Two
The trouble with our times is that the future is not what it used to be.
Paul Valery
Nassim Nicholas Taleb, the author of The Black Swan as well as Antifragile: Things That Gain from Disorder, has recently been giving a series of interviews in which he argues that current investment industry compensation practices lead to subtle conflicts of interest, that end up inuring to the disadvantage of individual investors. Nowhere is this more apparent than when one looks at the mutual fund complexes that have become asset gatherers rather than investment managers.
By way of full disclosure I have to tell you that I am an admirer of Mr. Taleb’s. I was not always the most popular boy in the classroom as I was always worrying about the need to consider the potential for “Black Swan” or outlier events. Unfortunately all one has to have is one investment massacre like the 2008-2009 period. This gave investors a lost decade of investment returns and a potentially permanent loss of capital if they panicked and liquidated their investments. To have a more in-depth appreciation of the concept and its implications, I commend those of you with the time to a careful study of the data that the Mutual Fund Observer has compiled and begun releasing regularly. You should pay particular attention to a number called the “Maximum Drawdown.” There you will see that as a result of that dark period, looking back five years it is a rarity to find a domestic fund manager who did not lose 35-50% of his or her investors’ money. The same is to be said for global and international fund managers who likewise did not distinguish themselves, losing 50-65% of investors’ capital, assuming the investors panicked and liquidated their investments, and many did.
A number of investment managers that I know are not fans of Mr. Taleb’s work, primarily because he has a habit of bringing attention to inconvenient truths. In Fooled by Randomness, he made the case that given the large number of people who had come into the investment management business in recent years, there were a number who had to have generated good records randomly. They were what he calls “spurious winners.” I would argue that the maximum drawdown numbers referred to above confirm that thesis.
How then to avoid the spurious winner? Taleb argues that the hedge fund industry serves as a model, by truly having managers with “skin in the game.” In his experience a hedge fund manager typically has twenty to fifty times the exposure of his next biggest client. That of necessity makes them both more careful and as well as aware of the consequences if they have underinvested in the necessary talent to remain competitive. Taleb quite definitively states, “You don’t get that with fund managers.”
I suspect the counterargument I am going to hear is that fund managers are now required to disclose, by means of reporting within various ranges, the amount of money they have invested in the fund they are managing. Just go to the Statement of Additional Information, which is usually found on a fund website. And if the SAI shows that the manager has more than $1 million invested in his or her fund, then that is supposed to be a good sign concerning alignment of interests. Like the old Hertz commercial, the real rather than apparent answer is “not exactly.”
The gold standard in this regard has been set by Longleaf Partners with their funds. Their employees are required to limit their publicly offered equity investments to funds advised by Southeastern Asset Management, Longleaf’s advisor, unless granted a compliance exception. Their trustees also must obtain permission before making a publicly offered equity investment. That is rather unique in the fund industry, since what you usually see in the marketing brochures or periodic fund reports is something like “the employees and families of blah-blah have more than $X million invested in our funds.” If you are lucky this may work out to be one percent of assets under management in the firm, hardly hedge-fund like metrics. At the same time, you often find trustees of the fund with de minimis investments.
The comparison becomes worse when you look at a fund with $9 billion in assets and the “normal” one percent investment management fee, which generates $90 million in revenue. The fund manager may tell you that his largest equity investment is in the fund and is more than $1 million. But if his annual compensation runs somewhere between $1million and $10 million, and this is Taleb’s strongest point, the fund manager does not have a true disincentive for losing money. The situation becomes even more blurred where compliance policy allows investment in ETF’s or open-ended mutual funds, which in today’s world will often allow a fund manager to construct his own personal market neutral or hedged portfolio, to offset his investment in the fund he is managing.
Is there a solution? Yes, a fairly easy one – adopt as an industry standard through government regulation the requirement that all employees in the investment firm are required to limit their publicly offered equity investments to the funds in the complex. To give credit where credit is due, just as we have a Volcker rule, we can call it the “Southeastern Asset Management” rule. If that should prove too restrictive, I would suggest as an alternative that the SEC add another band of investment ranges above the current $1 million limit, at perhaps $5 million. That at least would give a truer picture for the investor, especially given the money flows now gushing into a number of firms, which often make a $1 million investment not material to the fund manager. Such disclosure will do a better job of attuning investment professionals to what should be their real concern – managing risk with a view towards the potential downside, rather than ignoring risk with other people’s money.
Postscript:
What does it say when such well known value managers as Tweedy, Browne and First Pacific Advisors are letting cash positions rise in their portfolios as they sell and don’t replace securities that have reached their target valuations? Probably the same thing as when one of the people I consider to be one of the outstanding money managers of our time, Seth Klarman at Baupost Partners, announces that he will be returning some capital to his partnership investors at year end. Stay tuned.
So, if it’s “the best,” why can’t people just agree on what it is?
Last month David pointed out how little overlap he found between three popular mutual fund lists: Kiplinger 25, Money 70, and Morningstar’s Fantastic 51. David mused: “You’d think that if all of these publications shared the same sensible goal – good risk-adjusted returns and shareholder-friendly practices – they’d also be stumbling across the same funds. You’d be wrong.”
He found only one fund, Dodge & Cox International Fund DODFX, on all three lists. Just one! Although just one is a statistically better outcome than randomly picking three such lists from the 6600 or so mutual funds and 1000 ETFs, it does seem surprisingly small.
Opening up the field a little, by replacing the Fantastic 51 with a list of 232 funds formed from Morningstar’s current “Gold-Rated Funds” and “Favorite ETFs,” the overlap does not improve much. Just two funds appear in all three publications: DODFX and Habor Bond Institutional HABDX. Just two!
While perhaps not directly comparable, the table below provides a quick summary of the criteria used by each publication. Money 70 criteria actually include Morningstar’s so-called stewardship grade, which must be one of the least maintained measures. For example, Morningstar awarded Bruce Berkowitz Fund Manager of the Decade, but it never published a stewardship grade for Fairholme.
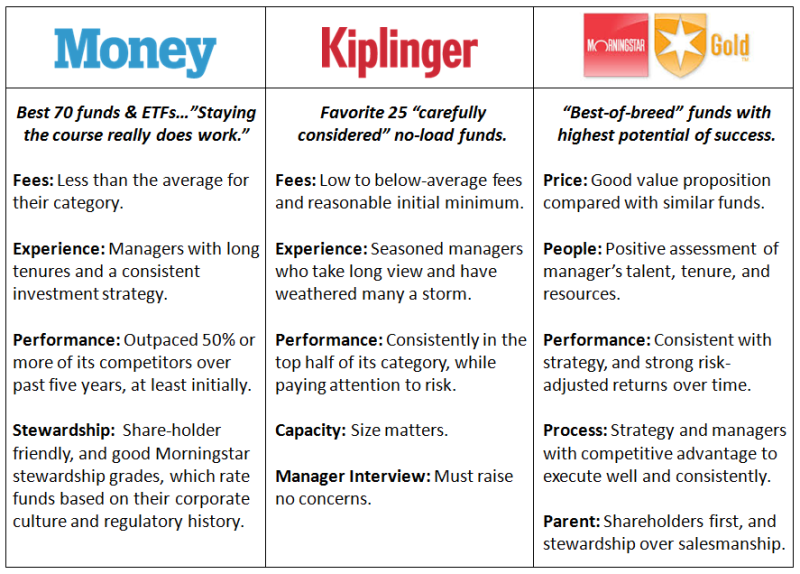
Overall, however, the criteria seem quite similar, or as David described “good risk-adjusted returns and shareholder-friendly practices.” Add in experienced managers for good measure and one would expect the lists to overlap pretty well. But again, they don’t.
How do the “forward-looking” recommendations in each of these lists fare against Morningstar’s purely quantitative “backward-looking” performance rating system? Not as well as you might think. There are just seven 5-star funds on Money’s list, or 1-in-10. Kiplinger does the best with six, from a percentage perspective, or almost 1-in-4. (They must have peeked.) Morningstar’s own list includes 44 5-star funds, or about 1-in-5. So, as well intentioned and “forward looking” as these analysts certainly try to be, only a small minority of their “best funds” have delivered top-tier returns.
On the other hand, they each do better than picking funds arbitrarily, if not unwittingly, since Morningstar assigns 5 stars to only about 1-in-17 funds. Neither of the two over-lapping funds that appear on all three lists, DODFX and HABDX, have 5 stars. But both have a commendable 4 stars, and certainly, that’s good enough.
Lowering expectations a bit, how many funds appear on at least two of these lists? The answer: 38, excluding the two trifectas. Vanguard dominates with 14. T. Rowe Price and American Funds each have 4. Fidelity has just one. Most have 4 stars, a few have 3, like SLASX, probably the scariest.
But there is no Artisan. There is no Tweedy. There is no Matthews. There is no TCW or Doubleline. There are no PIMCO bond funds. (Can you believe?) There is no Yacktman. Or Arke. Or Sequoia. There are no funds less than five years old. In short, there’s a lot missing.
There are, however, nine 5-star funds among the 38, or just about 1-in-4. That’s not bad. Interestingly, not one is a fixed income fund, which is probably a sign of the times. Here’s how they stack-up in MFO’s own “backward looking” ratings system, updated through September:
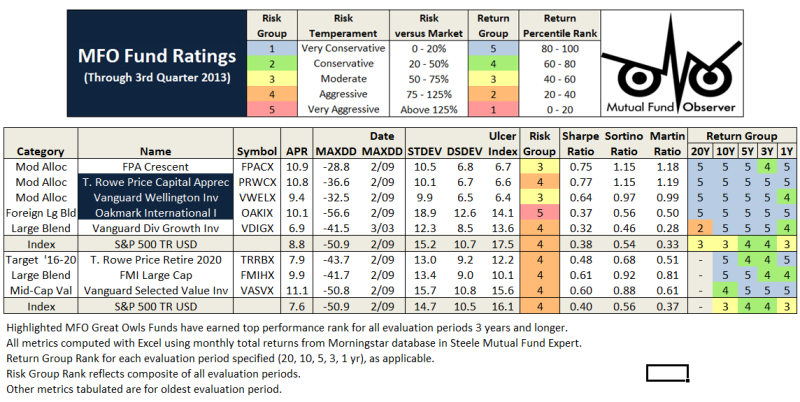
Four are moderate allocation funds: FPACX, PRWCX, VWELX, and TRRBX. Three are Vanguard funds: VWELX, VDIGX, and VASVX. One FMI fund FMIHX and one Oakmark fund OAKIX. Hard to argue with any of these funds, especially the three Great Owls: PRWCX, VWELX, and OAKIX.
These lists of “best funds” are probably not a bad place to start, especially for those new to mutual funds. They tend to expose investors to many perfectly acceptable, if more mainstream, funds with desirable characteristics: lower fees, experienced teams, defensible, if not superior, past performance.
They probably do not stress downside potential enough, so any selection needs to also take risk tolerance and investment time-frame into account. And, incredulously, Morningstar continues to give Gold ratings to loaded funds, about 1-in-7 actually.
The lists produce surprisingly little overlap, perhaps simply because there are a lot of funds available that satisfy the broad screening criteria. But within the little bit of overlap, one can find some very satisfying funds.
Money 70 and Kiplinger 25 are free and online. Morningstar’s rated funds are available for a premium subscription. (Cheapest path may be to subscribe for just one month each year at $22 while performing an annual portfolio review.)
As for a list of smaller, less well known mutual funds with great managers and intriguing strategies? Well, of course, that’s the niche MFO aspires to cover.
23Oct2013/Charles
The Great Owl search engine has arrived
Great Owls are the designation that my colleague Charles Boccadoro gives to those funds which are first in the top 20% of their peer group for every trailing period of three years or more. Because we know that “risk” is often more durable and a better predictor of investor actions than “return” is, we’ve compiled a wide variety of risk measures for each of the Great Owl funds.
Up until now, we’ve been limited to publishing the Great Owls as a .pdf while working on a search engine for them. We’re pleased to announce the launch of the Great Owl Search, 1.0. We expect in the months ahead to widen the engine’s function and to better integrate it into the site. We hope you like it.
For JJ and other fans of FundAlarm’s Three-Alarm and Most Alarming fund lists, we’re working to create a predefined search that will allow you to quickly and reliable identify the most gruesome investments in the fund world. More soon!
Who do you trust for fund information?
The short answer is: not fund companies. On October 22, the WSJ’s Karen Damato hosted an online poll entitled Poll: The Best Source of Mutual-Fund Information?
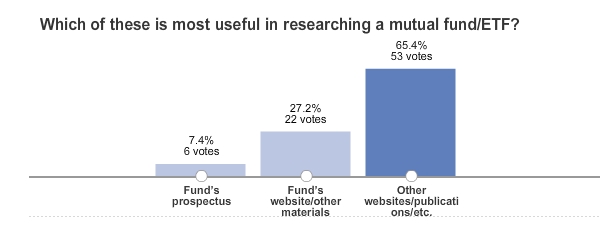
Representing, as I do, Column Three, I should be cheered. Teaching, as I do, Journalism 215: News Literacy, I felt compelled to admit that the results were somewhere between empty (the margin of error is 10.89, so it’s “somewhere between 16% and 38% think it’s the fund company’s website and marketing materials”) and discouraging (the country’s leading financial newspaper managed to engage the interest of precisely 81 of its readers on this question).
Nina Eisenman, President of Eisenman Associates which oversees strategic communications for corporations, and sometime contributor to the Observer
Asking which of the 3 choices individual investors find “most useful” generates data that creates an impression that they don’t use the other two at all when, in fact, they may use all 3 to varying degrees. It’s also a broad question. Are investors responding based on what’s most useful to them in conducting their initial research or due diligence? For example, I may read about a fund in the Mutual Fund Observer (“other website”) and decide to check it out but I would (hopefully) look at the fund’s website, read the manager’s letters and the fund prospectus before I actually put money in.
When I surveyed financial advisors and RIAs on the same topic, but gave them an option to rate the importance of various sources of information they use, the vast majority used mutual funds’ own websites to some extent as part of their due diligence research. [especially for] fund-specific information (including the fund prospectus which is generally available on the website) that can help investors make educated investment decisions.
Both Nina’s own research and the results of a comparable Advisor Perspectives poll can be found at FundSites, her portal for addressing the challenges and practices of small- to medium sizes fund company websites.
The difference between “departures” and “succession planning”
Three firms this month announced the decisions of superb managers to move on. Happily for their investors, the departures are long-dated and seem to be surrounded by a careful succession planning process.
Mitch Milias will be retiring at the end of 2013
Primecap Management was founded by three American Funds veterans. That generation is passing. Howard Schow has passed away at age 84 in April 2012. Vanguard observer Dan Weiner wrote at the time that “To say that he was one of the best, and least-known investors would be a vast understatement.” The second of the triumvirate, Mitch Milias, retires in two months at 71. That leaves Theo Kolokotrones who, at 68, is likely in the latter half of his investing career. Milias has served as comanager of four Gold-rated funds: Vanguard Primecap (VPMCX) Vanguard Primecap Core (VPCCX), Primecap Odyssey Growth (POGRX), and Primecap Odyssey Stock (POSKX).
Neil Woodford will depart Invesco in April, 2014
British fund manager Neil Woodford is leaving after 25 years of managing Invesco Perpetual High Income Fund and the Invesco Perpetual Income Fund. Mr. Woodford apparently is the best known manager in England and described as a “hero” in the media for his resolute style. He’s decided to set up his own English fund company. In making the move he reports:
My decision to leave is a personal one based on my views about where I see long-term opportunities in the fund management industry. My intention is to establish a new fund management business serving institutional and retail clients as soon as possible after 29th April 2014.
His investors seem somehow less sanguine: they pulled over £1 billion in the two weeks after his announcement. Invesco’s British president describes that reaction as “calm.”
Given Mr. Woodford’s reputation and the global nature of the securities market, I would surely flag 1 May 2014 as a day to peer across the Atlantic to see what “long-term opportunities” he’s pursuing.
Scott Satterwhite will be retiring at the end of September, 2016
Scott Satterwhite joined Artisan from Wachovia Securities in 1997 and was the sole manager of Artisan Small Cap Value (ARTVX) from its launch. ARTVX is also the longest-tenured fund in my non-retirement portfolio; I moved my Artisan Small Cap (ARTSX) investment into Satterwhite’s fund almost as soon as it launched and I’ve never had reason to question that decision. Mr. Satterwhite then extended his discipline into Artisan Mid Cap Value (ARTQX) and the large cap Artisan Value (ARTLX). All are, as is typical of Artisan, superb.
Artisan has a really strong internal culture and focus on creating coherent, self-sustaining investment teams. Three years after launch, Satterwhite’s long-time analyst Jim Kieffer became a co-manager. George Sertl was added six years after that and Dan Kane six years later. Mr. Kane is now described as “the informal lead manager” with Satterwhite on ARTVX. This is probably one of the two most significant manager changes in Artisan’s history (the retirement of its founder was the other) but the firm seems exceptionally well-positioned both to attract additional talent and to manage the required three year transition.
Observer Fund Profiles:
Each month the Observer provides in-depth profiles of between two and four funds. Our “Most Intriguing New Funds” are funds launched within the past couple years that most frequently feature experienced managers leading innovative newer funds. “Stars in the Shadows” are older funds that have attracted far less attention than they deserve.
T. Rowe Price Global Allocation (RPGAX): T. Rowe is getting bold, cautiously. Their newest and most innovative fund offers a changing mix of global assets, including structural exposure to a single hedge fund, is also broadly diversified, low-cost and run by the team responsible for their Spectrum and Personal Strategy Funds. So far, so good!
Oops! The fund profile is slightly delayed. Please check back tomorrow.
Elevator Talk: Jeffrey K. Ringdahl of American Beacon Flexible Bond (AFXAX)
 Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
 In a fundamentally hostile environment, investors need to have a flexible approach to income investing. Some funds express that flexibility by investing in emerging market bonds, financial derivatives such as options, or illiquid securities (think: “lease payments from the apartment complex we just bought”).
In a fundamentally hostile environment, investors need to have a flexible approach to income investing. Some funds express that flexibility by investing in emerging market bonds, financial derivatives such as options, or illiquid securities (think: “lease payments from the apartment complex we just bought”).
American Beacon’s decision was to target “positive total return regardless of market conditions” in their version. Beacon, like Harbor, positions itself as “a manager of managers” and assembles teams of institutional sub-advisors to manage the actual portfolio. In this case, they’ve paired Brandywine Global, GAM and PIMCO and have given the managers extraordinarily leeway in pursuing the fund’s objective. One measure of that flexibility is the fund’s duration, a measure of interest rate sensitivity. They project a duration of anything from negative five years (effectively shorting the market) to plus eight years (generally the preferred spot for long-term owners of bond funds). Since inception the fund has noticeably outrun its “nontraditional bond” peers with reasonable volatility.
Jeff Ringdahl is American Beacon’s Chief Operating Officer and one of the primary architects of the Flexible Bond Strategy. He’s worked with a bunch of “A” tier management firms including Touchstone Investments, Fidelity and State Street Global Advisors. Here are his 245 words (I know, he overshot) on why you should consider a flexible bond strategy:
In building an alternative to a traditional bond fund, our goal was to stay true to what we consider the three tenets of traditional bond investing: current income, principal preservation and equity diversification. However, we also sought to protect against unstable interest rates and credit spreads.
The word “unconstrained” is often used to describe similar strategies, but we believe “flexible” is a better descriptor for our approach. Many investors associate the word “unconstrained” with higher risk. We implemented important risk constraints which help to create a lower risk profile. Our multi-manager structure is a key distinguishing characteristic because of its built-in risk management. Unconstrained or flexible bond funds feature a great degree of investment flexibility. While investment managers may deliver compelling risk-adjusted performance by using this enhanced flexibility, there may be an increased possibility of underperformance because there are fewer risk controls imposed by many of our peer funds. In our opinion, if you would ever want to diversify your managers you would do so where the manager had the greatest latitude. We think that this product style is uniquely designed for multi-manager diversification.
Flexible bond investing allows asset managers the ability to invest long and short across the global bond and currency markets to capitalize on opportunities in the broad areas of credit, currencies and yield curve strategies. We think focusing on the three Cs: Credit, Currency and Curve gives us an advantage in seeking to deliver positive returns over a complete market cycle.
The fund has five share classes. The minimum initial investment for the no-load Investor class is $2,500. Expenses are 1.27% on about $300 million in assets.
The fund’s website is functional but spare. You get the essential information, but there’s no particular wealth of insight or commentary on this strategy (and there is one odd picture of a bunch of sailboats barely able to get out of one another’s way).
Our earlier Elevator Talks were:
- February 2013: Tom Kerr, Rocky Peak Small Cap Value (RPCSX), whose manager has a 14 year track record in small cap investing and a passion for discovering “value” in the intersection of many measures: discounted cash flows, LBO models, M&A valuations and traditional relative valuation metrics.
- March 2013: Dale Harvey, Poplar Forest Partners (PFPFX and IPFPX), a concentrated, contrarian value stock fund that offers “a once-in-a-generation opportunity to invest with a successful American Funds manager who went out on his own.”
- April 2013: Bayard Closser, Vertical Capital Income Fund (VCAPX), “a closed-end interval fund, VCAPX invests in whole mortgage loans and first deeds of trust. We purchase the loans from lenders at a deep discount and service them ourselves.”
- May 2013: Jim Hillary, LS Opportunity Fund (LSOFX), a co-founder of Marsico Capital Management whose worry that “the quality of research on Wall Street continues to decline and investors are becoming increasingly concerned about short-term performance” led to his faith in “in-depth research and long-term orientation in our high conviction ideas.”
- July 2013: Casey Frazier, Versus Capital Multi-Manager Real Estate Income Fund (VCMRX), a second closed-end interval fund whose portfolio “includes real estate private equity and debt, public equity and debt, and broad exposure across asset types and geographies. We target a mix of 70% private real estate with 30% public real estate to enhance liquidity, and our objective is to produce total returns in the 7 – 9% range net of fees.”
- August 2013: Brian Frank, Frank Value Fund (FRNKX), a truly all-cap value fund with a simple, successful discipline: if one part of the market is overpriced, shop elsewhere.
- August 2013: Ian Mortimer and Matthew Page of Guinness Atkinson Inflation Managed Dividend (GAINX), a global equity fund that pursues firms with “sustainable and potentially rising dividends,” which also translates to firms with robust business models and consistently high return on capital.
- September 2013: Steven Vannelli of GaveKal Knowledge Leaders (GAVAX), which looks to invest in “the best among global companies that are tapping a deep reservoir of intangible capital to generate earnings growth,” where “R&D, design, brand and channel” are markers of robust intangible capital. From launch through the end of June, 2013, the fund modestly outperformed the MSCI World Index and did so with two-thirds less volatility
- October 2013: Bashar Qasem of Wise Capital (WISEX), which provides investors with an opportunity for global diversification in a fund category (short term bonds) mostly distinguished by bland uniformity.
Conference Call Highlights: Zac Wydra of Beck, Mack & Oliver Partners

We looked for a picture of Zac Wydra on the web but found Wydra the Otter instead. We decided that Zac is cute but Wydra is cuter, so… If we can find a t-shirt with Wydra’s picture on it, we might send it along to Zac with our best wishes.
In mid-October we spoke for about an hour with Zac Wydra of Beck, Mack & Oliver Partners Fund (BMPEX). There were about 30 other participants on the call. I’ve elsewhere analogized Beck, Mack to Dodge & Cox: an old money, white shoe firm whose core business is helping the rich stay rich. In general, you need a $3 million minimum investment to engage with them. Partners was created in 1991 as a limited partnership to accommodate the grandkids or staff of their clients, folks who might only have a few hundred thousand to commit. (Insert about here: “Snowball gulps”) The “limited” in limited partnership signals a maximum number of investors, 100. The partnership filled up and prospered. When the managing partner retired, Zac made a pitch to convert the partnership to a ’40 fund and make it more widely available. He argued that he thought there was a wider audience for a disciplined, concentrated fund.
He was made the fund’s inaugural manager. He’s 41 and anticipates running BMPEX for about the next quarter century, at which point he’ll be required – as all partners are – to move into retirement and undertake a phased five year divestment of his economic stake in the firm. His then-former ownership stake will be available to help attract and retain the best cadre of younger professionals that they can find. Between now and retirement he will (1) not run any other pooled investment vehicle, (2) not allow BMPEX to get noticeably bigger than $1.5 billion – he’ll return capital to investors first – and (3) will, over a period of years, train and oversee a potential successor.
In the interim, the discipline is simple:
- never hold more than 30 securities – he can hold bonds but hasn’t found any that offer a better risk/return profile than the stocks he’s found.
- only invest in firms with great management teams, a criterion that’s met when the team demonstrates superior capital allocation decisions over a period of years
- invest only in firms whose cash flows are consistent and predictable. Some fine firms come with high variable flows and some are in industries whose drivers are particularly hard to decipher; he avoids those altogether.
- only buy when stocks sell at a sufficient discount to fair value that you’ve got a margin of safety, a patience that was illustrated by his decision to watch Bed, Bath & Beyond for over two and a half years before a short-term stumble triggered a panicky price drop and he could move in. In general, he is targeting stocks which have the prospect of gaining at least 50% over the next three years and which will not lose value over that time.
- ignore the question of whether it’s a “high turnover” or “low turnover” strategy. His argument is that the market determines the turnover rate. If his holdings become overpriced, he’ll sell them quickly. If the market collapses, he’ll look for stocks with even better risk/return profiles than those currently in the portfolio. In general, it would be common for him to turn over three to five names in the portfolio each year, though occasionally that’s just recycling: he’ll sell a good firm whose stock becomes overvalued then buy it back again once it becomes undervalued.
Two listener questions, in particular, stood out:
Kevin asked what Zac’s “edge” was. A focus on cash, rather than earnings, seemed to be the core of it. Businesses exist to generate cash, not earnings, and so BM&O’s valuations were driven by discounted cash flow models. Those models were meaningful only if it were possible to calculate the durability of cash flows over 5 years. In industries where cash flows have volatile, it’s hard to assign a meaningful multiple and so he avoids them.
Seth asked what mistakes have you made and what did you learn from them? Zac hearkened back to the days when the fund was still a private partnership. They’d invested in AIG which subsequently turned into a bloody mess. Ummm, “not an enjoyable experience” was his phrase. He learned from that that “independent” was not always the same as “contrary.” AIG was selling at what appeared to be a lunatic discount, so BM&O bought in a contrarian move. Out of the resulting debacle, Zac learned a bit more respect for the market’s occasionally unexplainable pricings of an asset. At base, if the market says a stock is worth twenty cents a share, you’d better than remarkably strong evidence in order to act on an internal valuation of twenty dollars a share.
Bottom Line: On whole, it strikes me as a remarkable strategy: simple, high return, low excitement, repeatable, sustained for near a quarter century and sustainable for another.
For folks interested but unable to join us, here’s the complete audio of the hour-long conversation.
As with all of these funds, we’ve created a new featured funds page for Beck, Mack & Oliver Partners Fund, pulling together all of the best resources we have for the fund, including a brand new audio profile in .mp3 format.
When you click on the link, the file will load in your browser and will begin playing after it’s partially loaded. If the file downloads, instead, you may have to double-click to play it.
As promised, my colleague Charles Boccadoro weighs in on your almost-magical ability to turn a temporary loss of principal into a …
Permanent Loss of Capital
The father of value investing, Benjamin Graham, employed the concept of “Margin of Safety” to minimize risk of permanent loss. His great student, Warren Buffett, puts it like this: “Rule No. 1: never lose money; rule No. 2: don’t forget rule No. 1.”
Zachary Wydra, portfolio manager of the 5-star Beck Mack & Oliver Partners (BMPEX) fund, actually cited Mr. Buffett’s quote during the recent MFO conference call.
But a look at Berkshire Hathaway, one of the great stocks of all time, shows it dropped 46% between December 2007 and February of 2009. And, further back, it dropped about the same between June 1998 and February 2002. So, is Mr. Buffett not following his own rule? Similarly, a look at BMPEX shows an even steeper decline in 2009 at -54%, slightly worse than the SP500.
The distinction, of course, is that drawdown does not necessarily mean loss, unless one sells at what is only a temporary loss in valuation – as opposed to an unrecoverable loss, like experienced by Enron shareholders. Since its 2009 drawdown, BMPEX is in fact up an enviable 161%, beating the SP500 by 9%.
Robert Arnott, founder of Research Associates, summarizes as follows: “Temporary losses of value are frequent; at times they can become so frightening that they become permanent—for those that sell.” Distinguishing between temporary drawdown and permanent loss of capital (aka “the ultimate risk”) is singularly the most important, if unnerving, aspect of successful value investing.
Mr. Wydra explains his strategy is to target stocks that have an upside potential over the next three years of at least 50% and will not lose value over that time. Translation: “loss,” as far as BMPEX is concerned, equates to no drawdown over a three year period. A very practical goal indeed, since any longer period would likely not be tolerated by risk averse investors.
And yet, it is very, very hard to do, perhaps even impossible for any fund that is primarily long equities.
Here is downside SP500 total return performance looking back about 52 years:
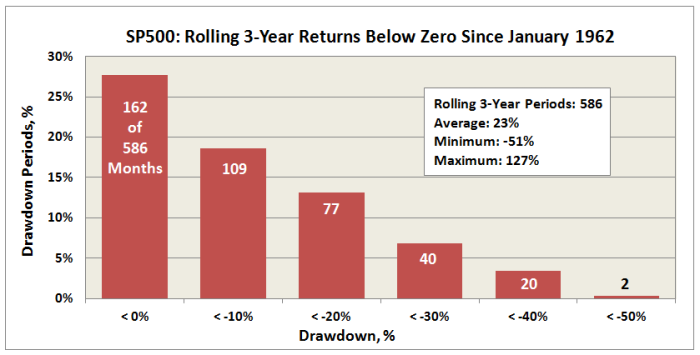
It says that 3-year returns fall below zero over nearly 30% of the time and the SP500 shows a loss of 20% or more in 15% of 3-year returns. If we compare returns against consumer price index (CPI), the result is even worse. But for simplicity (and Pete’s) sake, we will not. Fact is, over this time frame, one would need to have invested in the SP500 for nearly 12 years continuously to guarantee a positive return. 12 years!
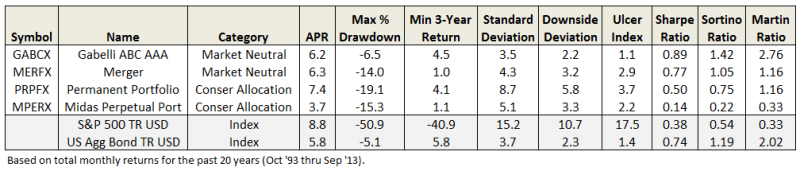
How many equity or asset allocation funds have not experienced a drawdown over any three year period? Very few. In the last 20 years, only four, or about 1-in-1000. Gabelli ABC (GABCX) and Merger (MERFX), both in the market neutral category and both focused on merger arbitrage strategies. Along with Permanent Portfolio (PRPFX) and Midas Perpetual Portfolio (MPREX), both in the conservative allocation category and both with large a percentage of their portfolios in gold. None of these four beat the SP500. (Although three beat bonds and GABCX did so with especially low volatility.)
So, while delivering equity-like returns without incurring a “loss” over a three year period may simply prove too high a goal to come true, it is what we wish was true.
29Oct2013/Charles
Conference Call Upcoming: John Park and Greg Jackson, Oakseed Opportunity, November 18, 7:00 – 8:00 Eastern
 On November 18, Observer readers will have the opportunity to hear from, and speak to John Park and Greg Jackson, co-managers of Oakseed Opportunity Fund (SEEDX and SEDEX). John managed Columbia Acorn Select for five and a half years and, at his 2004 departure, Morningstar announced “we are troubled by his departure: Park had run this fund since its inception and was a big driver behind its great long-term record. He was also the firm’s primary health-care analyst.” Greg co-managed Oakmark Global (OAKGX) for over four years and his departure in 2003 prompted an Eeyore-ish, “It’s never good news when a talented manager leaves.”
On November 18, Observer readers will have the opportunity to hear from, and speak to John Park and Greg Jackson, co-managers of Oakseed Opportunity Fund (SEEDX and SEDEX). John managed Columbia Acorn Select for five and a half years and, at his 2004 departure, Morningstar announced “we are troubled by his departure: Park had run this fund since its inception and was a big driver behind its great long-term record. He was also the firm’s primary health-care analyst.” Greg co-managed Oakmark Global (OAKGX) for over four years and his departure in 2003 prompted an Eeyore-ish, “It’s never good news when a talented manager leaves.”
The guys moved to Blum Capital, a venture capital firm. They did well, made money but had less fun than they’d like so they decided to return to managing a distinctly low-profile mutual fund.
Oakseed is designed to be an opportunistic equity fund. Its managers are expected to be able to look broadly and go boldly, wherever the greatest opportunities present themselves. It’s limited by neither geography, market cap nor stylebox. John Park laid out its mission succinctly: “we pursue the maximum returns in the safest way possible.”
I asked John where he thought they’d focus their opening comments. Here’s his reply:
We would like to talk about the structure of our firm and how it relates to the fund at the outset of the call. I think people should know we’re not the usual fund management company most people think of when investing in a fund. We discussed this in our first letter to shareholders, but I think it’s worthwhile for our prospective and current investors to know that Oakseed is the only client we have, primarily because we want complete alignment with our clients from not only a mutual investment perspective (“skin in the game”), but also that all of our time is spent on this one entity. In addition, being founders of our firm and this fund, with no intentions of ever starting and managing a new fund, there is much less risk to our investors that one or both of us would ever leave. I think having that assurance is important.
Our conference call will be Monday, November 18, from 7:00 – 8:00 Eastern. It’s free. It’s a phone call.
How can you join in?
If you’d like to join in, just click on register and you’ll be taken to the Chorus Call site. In exchange for your name and email, you’ll receive a toll-free number, a PIN and instructions on joining the call. If you register, I’ll send you a reminder email on the morning of the call.
Remember: registering for one call does not automatically register you for another. You need to click each separately. Likewise, registering for the conference call mailing list doesn’t register you for a call; it just lets you know when an opportunity comes up.
WOULD AN ADDITIONAL HEADS UP HELP?
Nearly two hundred readers have signed up for a conference call mailing list. About a week ahead of each call, I write to everyone on the list to remind them of what might make the call special and how to register. If you’d like to be added to the conference call list, just drop me a line.
Conference Call Queue: David Sherman, RiverPark Strategic Income, December 9, 7:00 – 8:00 Eastern
On Monday, December 9, from 7:00 – 8:00 Eastern, you’ll have a chance to meet David Sherman, manager of RiverPark Short Term High Yield (RPHYX) and the newly-launched RiverPark Strategic Income Fund (RSIVX). David positions RSIVX as the next step out on the risk-return ladder from RPHYX: capable of doubling its sibling’s returns with entirely manageable risk. If you’d like to get ahead of the curve, you can register for the call with David though I will highlight his call in next month’s issue.
Launch Alert: DoubleLine Shiller Enhanced CAPE
On October 29, DoubleLine Shiller Enhanced CAPE (DSEEX and DSENX) launched. The fund will use derivatives to try to outperform the Shiller Barclays CAPE US Sector Total Return Index. CAPE is an acronym for “cyclically-adjusted price/earnings.” The measure was propounded by Nobel Prize winning economist Robert Shiller as a way of taking some of the hocus-pocus out of the calculation of price/earnings ratios. At base, it divides today’s stock price by the average, inflation-adjusted earnings from the past decade. Shiller argues that current earnings are often deceptive since profit margins tend over time to regress to the mean and many firms earnings run on three to five year cycles. As a result, the market might look dirt cheap (high profit margins plus high cyclical earnings = low conventional P/E) when it’s actually poised for a fall. Looking at prices relative to longer-term earnings gives you a better chance of getting sucked into a value trap.
The fund will be managed by The Gundlach and Jeffrey Sherman. Messrs Gundlach and Sherman also work together on the distinctly disappointing Multi-Asset Growth fund (DMLAX), so the combination of these guys and an interesting idea doesn’t translate immediately into a desirable product. The fact that it, like many PIMCO funds, is complicated and derivatives-driven counsels for due caution in one’s due diligence. The “N” share class has a $2000 minimum initial investment and 0.91% expense ratio. The institutional shares are about one-third cheaper.
Those interested in a nice introduction to the CAPE research might look at Samuel Lee’s 2012 CAPE Crusader essay at Morningstar. There’s a fact sheet and a little other information on the fund’s homepage.
Funds in Registration (The New Year’s Edition)
New mutual funds must be registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission before they can be offered for sale to the public. The SEC has a 75-day window during which to call for revisions of a prospectus; fund companies sometimes use that same time to tweak a fund’s fee structure or operating details. Any fund that wanted to launch before the end of the year needed to be in registration by mid- to late October.
And there were a lot of funds targeting a year-end launch. Every day David Welsch, firefighter/EMT/fund researcher, scours new SEC filings to see what opportunities might be about to present themselves. This month he tracked down 24 no-load retail funds in registration, which represents our core interest. But if you expand that to include ETFs, institutional funds, reorganized funds and load-bearing funds, you find nearly 120 new vehicles scheduled for Christmas delivery.
Close readers might find the answers to four funds in reg quiz questions:
- Which manager of a newly-registered fund had the schmanciest high society wedding this year?
- Which fund in registration gave Snowball, by far, the biggest headache as he tried to translate their prose to English?
- Which hedge fund manager decided that the perfect time to launch a mutual fund was after getting bludgeoned on returns for two consecutive years?
- Which managers seem most attuned to young investors, skippering craft that might be described as Clifford the Big Red Mutual Fund and the Spongebob Fund?
Manager Changes
On a related note, we also tracked down 51 fund manager changes.
Updates
One of the characteristics of good managers is their ability to think clearly and one of the best clues to the existence of clear thinking is clear writing. Here’s a decent rule: if they can’t write a grocery list without babbling, you should avoid them. Contrarily, clear, graceful writing often reflects clear thinking.
Many managers update their commentaries and fund materials quarterly and we want to guide you to the most recent discussions and data possible for the funds we’ve written about. The indefatigable Mr. Welsch has checked (and updated) every link and linked document for every fund we’ve profiled in 2013 and for most of 2012. Here’s David’s summary table, which will allow you to click through to a variety of updated documents.
|
Advisory Research Strategic Income |
|
|
Artisan Global Equity Fund |
|
|
Artisan Global Value Fund |
|
|
Beck, Mack & Oliver Partners Fund |
|
|
Bretton Fund |
|
|
Bridgeway Managed Volatility |
|
|
FPA International Value |
|
|
FPA Paramount |
|
|
Frank Value |
|
|
FundX Upgrader Fund |
|
|
Grandeur Peak Global Opportunities |
|
|
Grandeur Peak Global Reach |
|
|
LS Opportunity Fund |
|
|
Matthews Asia Strategic Income |
|
|
Oakseed Opportunity Fund |
|
|
Oberweis International Opportunities |
|
|
Payden Global Low Duration Fund |
|
|
PIMCO Short Asset Investment Fund “D” shares |
|
|
RiverPark/Gargoyle Hedge Value |
|
|
Scout Low Duration Bond Fund |
|
|
Sextant Global High Income |
|
|
Smead Value Fund |
|
|
The Cook and Bynum Fund |
|
|
Tributary Balanced |
|
|
Whitebox Long Short Equity Investor Class |
Briefly Noted
A big ol’ “uhhh” to Advisory Research Emerging Markets All Cap Value Fund (the “Fund”) which has changed both manager (“Effective immediately, Brien M. O’Brien is no longer a portfolio manager of the Fund”) and name (it will be Advisory Research Emerging Markets Opportunities Fund), both before the fund even launched. A few days after that announcement, AR also decided that Matthew Dougherty would be removed as a manager of the still-unlaunched fund. On the bright side, it didn’t close to new investors before launch, so that’s good. Launch date is November 1, 2013.
In a singularly dark day, Mr. O’Brien was also removed as manager of Advisory Research Small Micro Cap Value Fund, which has also not launched and has changed its name: Advisory Research Small Company Opportunities Fund.”
 A Centaur arises! The Tilson funds used to be a two-fund family: the one that Mr. Tilson ran and the one that was really good. After years of returns that never quite matched the hype, Mr. Tilson liquidated his Tilson Focus (TILFX) fund in June 2013. That left behind the Tilson-less Tilson Dividend Fund (TILDX) which we described as “an awfully compelling little fund.”
A Centaur arises! The Tilson funds used to be a two-fund family: the one that Mr. Tilson ran and the one that was really good. After years of returns that never quite matched the hype, Mr. Tilson liquidated his Tilson Focus (TILFX) fund in June 2013. That left behind the Tilson-less Tilson Dividend Fund (TILDX) which we described as “an awfully compelling little fund.”
Effective November 1, Tilson Dividend became Centaur Total Return Fund (TILDX), named after its long-time sub-adviser, Centaur Capital Partners. Rick Schumacher, the operations guy at the Centaur funds, elaborates:
Since Tilson is no longer involved in the mutual fund whatsoever, and since the Dividend Fund has historically generated as much (if not more) income from covered call premiums rather than pure dividends, we felt that it was a good time to rebrand the fund. So, effective today, our fund is now named the Centaur Total Return Fund. We have kept the ticker (TILDX), as nothing’s really changed as far as the investment objective or strategy of the fund, and besides, we like our track record. But, we’re very excited about our new Centaur Mutual Funds brand, as it will provide us with potential opportunities to launch other strategies under this platform in the future.
They’ve just launched a clean and appropriate dignified website that both represents the new fund and archives the analytic materials relevant to its old designation. The fund sits at $65 million in assets with cash occupying about a quarter of its portfolio. All cap, four stars, low risk. It’s worth considering, which we’ll do again in our December issue.
Laudus Growth Investors U.S. Large Cap Growth Fund is having almost as much fun. On September 24, its Board booted UBS Global Asset Management as the managers of the fund in favor of BlackRock. They then changed the name (to Laudus U.S. Large Cap Growth Fund) and, generously, slashed the fund’s expense ratio by an entire basis point from 0.78% to 0.77%.
But no joy in Mudville: the shareholder meeting being held to vote on the merger of Lord Abbett Classic Stock Fund (LRLCX) into Lord Abbett Calibrated Dividend Growth Fund (LAMAX) has been adjourned until November 7, 2013 for lack of a quorum.
Scout Funds are sporting a redesigned website. Despite the fact that our profiles of Scout Unconstrained Bond and Scout Low Duration don’t qualify as “news” for the purposes of their media list (sniffles), I agree with reader Dennis Green’s celebration of the fact the new site is “thoughtful, with a classy layout, and—are you sitting down?— their data are no longer stale and are readily accessible!” Thanks to Dennis for the heads-up.
Snowball’s portfolio: in September, I noted that two funds were on the watchlist for my own, non-retirement portfolio. They were Aston River Road Long Short (ARLSX) and RiverPark Strategic Income (RSIVX). I’ve now opened a small exploratory position in Aston (I pay much more attention to a fund when I have actual money at risk) as I continue to explore the possibility of transferring my Northern Global Tactical Asset Allocation (BBALX) investment there. The Strategic Income position is small but permanent and linked to a monthly automatic investment plan.
For those interested, John Waggoner of USA Today talked with me for a long while about the industry and interesting new funds. Part of that conversation contributed to his October 17 article, “New Funds Worth Mentioning.”
SMALL WINS FOR INVESTORS
Eaton Vance Asian Small Companies Fund (EVASX) will eliminate its danged annoying “B” share class on November 4, 2013. It’s still trying to catch up from having lost 70% in the 2007-09 meltdown.
Green Owl Intrinsic Value Fund (GOWLX) substantially reduced its expense cap from 1.40% to 1.10%. It’s been a very solid little large cap fund since its launch in early 2012.
Invesco Balanced-Risk Commodity Strategy Fund (BRCAX) will reopen to new investors on November 8, 2013. The fund has three quarters of a billion in assets despite trailing its peers and losing money in two of its first three years of existence.
As of December, Vanguard Dividend Appreciation Index (VDAIX) will have new Admiral shares with a 0.10% expense ratio and a $10,000 minimum investment. That’s a welcome savings on a fund currently charging 0.20% for the Investor share class.
At eight funds, Vanguard will rename Signal shares as Admiral shares and will lower the minimum investment to $10,000 from $100,000.
Zeo Strategic Income Fund (ZEOIX) dropped its “institutional” minimum to $5,000. I will say this for Zeo: it’s very steady.
CLOSINGS (and related inconveniences)
The Brown Capital Management Small Company Fund (BCSIX) closed to new investors on October 18, 2013.
Buffalo Emerging Opportunities Fund (BUFOX) formally announced its intention to close to new investors when the fund’s assets under management reach $475 million. At last check, they’re at $420 million. Five star fund with consistently top 1% returns. If you’re curious, check quick!
GW&K Small Cap Equity Fund (GWETX) is slated to close to new investors on November 1, 2013.
Matthews Pacific Tiger Fund (MAPTX) closed to new investors on October 25, 2013.
Oakmark International (OAKIX) closed to most new investors as of the close of business on October 4, 2013
Templeton Foreign Smaller Companies (FINEX) will close to new investors on December 10th. I have no idea of why: it’s a small fund with an undistinguished but not awful record. Liquidation seems unlikely but I can’t imagine that much hot money has been burning a hole in the managers’ pockets.
Touchstone Merger Arbitrage Fund (TMGAX), already mostly closed, will limit access a bit more on November 11, 2013. That means closing the fund to new financial advisors.
OLD WINE, NEW BOTTLES
Advisory Research Emerging Markets All Cap Value Fund has renamed itself, before launch, as Advisory Research Emerging Markets Opportunities Fund.
Aegis Value Fund (AVALX) has been reorganized as … Aegis Value Fund (AVALX), except with a sales load (see story above).
DundeeWealth US, LP (the “Adviser”) has also changed its name to “Scotia Institutional Investments US, LP” effective November 1, 2013.
The Hatteras suite of alternative strategy funds (Hatteras Alpha Hedged Strategies, Hedged Strategies Fund, Long/Short Debt Fund, Long/Short Equity Fund and Managed Futures Strategies Fund) have been sold to RCS Capital Corporation and Scotland Acquisition, LLC. We know this because the SEC filing avers the “Purchaser will purchase from the Sellers and the Sellers will sell to the Purchaser, substantially all the assets related to the business and operations of the Sellers and … the “Hatteras Funds Group.” Morningstar has a “negative” analyst rating on the group but I cannot find a discussion of that judgment.
Ladenburg Thalmann Alternative Strategies Fund (LTAFX) have been boldly renamed (wait for it) Alternative Strategies Fund. It appears to be another in the expanding array of “interval” funds, whose shares are illiquid and partially redeemable just once a quarter. Its performance since October 2010 launch has been substantially better than its open-ended peers.
Effective October 7, 2013, the WisdomTree Global ex-US Growth Fund (DNL) became WisdomTree Global ex-US Dividend Growth Fund.
U.S. Global Investors MegaTrends Fund (MEGAX) will, on December 20, become Holmes Growth Fund
OFF TO THE DUSTBIN OF HISTORY
 On-going thanks to The Shadow for help in tracking the consequences of “the perennial gale of creative destruction” blowing through the industry. Shadow, a member of the Observer’s discussion community, has an uncanny talent for identifying and posting fund liquidations (and occasionally) launches to our discussion board about, oh, 30 seconds after the SEC first learns of the change. Rather more than three dozen of the changes noted here and elsewhere in Briefly Noted were flagged by The Shadow. While my daily reading of SEC 497 filings identified most of the them, his work really does contribute a lot.
On-going thanks to The Shadow for help in tracking the consequences of “the perennial gale of creative destruction” blowing through the industry. Shadow, a member of the Observer’s discussion community, has an uncanny talent for identifying and posting fund liquidations (and occasionally) launches to our discussion board about, oh, 30 seconds after the SEC first learns of the change. Rather more than three dozen of the changes noted here and elsewhere in Briefly Noted were flagged by The Shadow. While my daily reading of SEC 497 filings identified most of the them, his work really does contribute a lot.
And so, thanks, big guy!
On October 16, 2013, the Board of Trustees of the Trust approved a Plan of Liquidation, which authorizes the termination, liquidation and dissolution of the 361 Absolute Alpha Fund. In order to effect such liquidation, the Fund is closed to all new investment. Shareholders may redeem their shares until the date of liquidation. The Fund will be liquidated on or about October 30, 2013.
City National Rochdale Diversified Equity Fund (the “Diversified Fund”) has merged into City National Rochdale U.S. Core Equity Fund while City National Rochdale Full Maturity Fixed Income Fund was absorbed by City National Rochdale Intermediate Fixed Income Fund
Great-West Ariel Small Cap Value Fund (MXSCX) will merge into Great-West Ariel Mid Cap Value Fund (MXMCX) around Christmas, 2013. That’s probably a win for shareholders, since SCV has been mired in the muck while MCV has posted top 1% returns over the past five years.
As we suspected, Fidelity Europe Capital Appreciation Fund (FECAX) is merging into Fidelity Europe Fund (FIEUX). FECAX was supposed to be the aggressive growth version of FIEUX but the funds have operated as virtually clones for the past five years. And neither has particularly justified its existence: average risk, average return, high r-squared despite the advantages of low expenses and a large analyst pool.
The Board of the Hansberger funds seems concerned that you don’t quite understand the implications of having a fund liquidated. And so, in the announcement of the October 18 liquidation of Hansberger International Fund they helpfully explain: “The Fund no longer exists, and as a result, shares of the Fund are no longer available for purchase.”
Highland Alpha Trend Strategies Fund (HATAX), formerly Pyxis Alpha Trend Strategies Fund, will close on November 20, 2013. With assets not much greater than my retirement account (and performance vastly below it), I’m not sure that even the manager will notice the disappearance.
Huntington Income Equity (HUINX) will merge into Huntington Dividend Capture Fund (HDCAX) at the end of the first week of December. It’s never a good sign when the winning fund – the more attractive of the two – trails 80% of its peers.
The JPMorgan Global Opportunities Fund was liquidated and dissolved on or about October 25, 2013. Given that they’re speaking in the past tense, don’t you think that they’d know whether it was “on” or “about”?
Update on the JPMorgan Value Opportunities Fund: an attempt to merge the fund out of existence in September failed because the Board couldn’t get enough shareholders to vote one way or the other. On October 10, though, they reached a critical mass and folded the fund into JPMorgan Large Cap Value Fund (OLVAX) on October 18th.
 So long to LONGX! Longview Tactical Allocation Fund (LONGX) has closed and will liquidate on November 15, 2013. 700% turnover which might well have led to a joke about their ability to take the long view except for the fact that they’ve joined the zombie legion of walking dead funds.
So long to LONGX! Longview Tactical Allocation Fund (LONGX) has closed and will liquidate on November 15, 2013. 700% turnover which might well have led to a joke about their ability to take the long view except for the fact that they’ve joined the zombie legion of walking dead funds.
In a determinedly “WTF?” move, the Mitchell Capital’s Board of Trustees has determined to liquidate the Mitchell Capital All-Cap Growth Fund (MCAEX) “due to the adviser’s business decision that it no longer is economically viable to continue managing the Fund because of the Fund’s small size, the increasing costs associated with managing the Fund, and the difficulty encountered in distributing the Fund’s shares.” Huh? “No longer economically viable”? They only launched this sucker on March 1, 2013. Seven months, guys? You hung on seven months and that’s it? What sort of analytic abilities are on display here, do you suppose?
On October 15, Nomura Partners Funds closed all of its remaining five mutual funds to purchases and exchanges. They are The Japan Fund (NPJAX), Nomura Partners High Yield (NPHAX), Nomura Partners Asia Pacific Ex Japan (NPAAX), Nomura Partners Global Equity Income (NPWAX), and Nomura Partners Global Emerging Markets (NPEAX). Here’s a sentence you should take seriously: “The Board will consider the best interests of the investors in each of the Funds and may decide to liquidate, merge, assign the advisory contract or to take another course of action for one or more of the Funds.” The NPJAX board has acted boldly in the past. In 2002, it fired the fund’s long-standing adviser, Scudder,Stevens, and turned the fund over to Fidelity to manage. Then, in 2008, they moved it again from Fidelity to Nomura. No telling what they might do next.
The firm also announced that it, like DundeeWealth, is planning to get out of the US retail fund business.
The liquidations of Nuveen Tradewinds Global Resources Fund and Nuveen Tradewinds Small-Cap Opportunities Fund are complete. It’s an ill wind that blows …
Oppenheimer SteelPath MLP and Infrastructure Debt Fund went the way of the wild goose on October 4.
Transamerica is bumping off two sub-advised funds in mid-December: Transamerica International Bond (TABAX), subadvised by J.P. Morgan, and Transamerica International Value Opportunities Fund, subadvised by Thornburg but only available to other Transamerica fund managers.
UBS Global Frontier Fund became UBS Asset Growth Fund (BGFAX) on October 28. Uhhh … doesn’t “Asset Growth” strike you as pretty much “Asset Gathering”? Under the assumption that “incredibly complicated” is the magic strategy, the fund will adopt a managed volatility objective that tries to capture all of the upside of the MSCI World Free Index with a standard deviation of no more than 15. On the portfolio’s horizon: indirect real estate securities, index funds, options and derivatives with leverage of up to 75%. They lose a couple managers and gain a couple in the process.
U.S. Global Investors Global Emerging Markets Fund closed on October 1 and liquidated on Halloween. If you were an investor in the fund, I’m hopeful that you’d already noticed. And considered Seafarer as an alternative.
Vanguard plans to merge two of its tax-managed funds into very similar index funds. Vanguard Tax-Managed International (VTMNX) is merging into Vanguard Developed Markets Index (VDMIX) and Vanguard Tax-Managed Growth & Income (VTMIX) will merge into Vanguard 500 Index (VFINX). Since these were closet index funds to begin with – they have R-squared values of 98.5 and 100(!) – the merger mostly serves to raise the expenses borne by VTMNX investors from 10 basis points to 20 for the index fund.
Vanguard Growth Equity (VGEQX) is being absorbed by Vanguard US Growth (VWUSX). Baillie Gifford, managers of Growth Equity, will be added as another team for US Growth.
Vanguard Managed Payout Distribution Focus (VPDFX) and Vanguard Managed Payout Growth Focus (VPGFX) are slated to merge to create a new fund, Vanguard Managed Payout Fund. At that time, the payout in question will decrease to 4% from 5%.
WHV Emerging Markets Equity Fund (WHEAX) is suffering “final liquidation” on or about December 20, 2013. Okay returns, $5 million in assets.
In Closing . . .
As Chip reviewed how folks use our email notification (do they open it? Do they click through to MFO?), she discovered 33 clicks from folks in Toyko (youkoso!), 21 in the U.K. (uhhh … pip pip?), 13 in the United Arab Emirates (keep cool, guys!) and 10 scattered about India (Namaste!). Welcome to all.
Thanks to the kind folks who contributed to the Observer this month. I never second guess folks’ decision to contribute, directly or through PayPal, but I am sometimes humbled by their generosity and years of support. And so thanks, especially, to the Right Reverend Rick – a friend of many years – and to Andrew, Bradford, Matt, James (uhh… Jimmy?) and you all. You make it all possible.
Thanks to all of the folks who bookmarked or clicked on our Amazon link. Here’s the reminder of the easiest way to support the Observer: just use our Amazon link whenever you’d normally be doing your shopping, holiday or other, on Amazon anyway. They contribute an amount equal to about 7% of the value of all stuff purchased through the link. It costs you nothing (the cost is already built into their marketing budget) and is invisible. If you’re interested in the details, feel free to look at the Amazon section under “Support.”
Remember to join us, if you can, for our upcoming conversations with John, Greg and David. Regardless, enjoy the quiet descent of fall and its seasonal reminder to slow down a bit and remember all the things you have to be grateful for rather than fretting about the ones you don’t have (and, really, likely don’t need and wouldn’t enjoy).
Cheers!



