Dear friends,
We’ve always enjoyed and benefited from your reactions to the Observer. Your notes are read carefully, passed around and they often shape our work in the succeeding months. The most common reaction to our July issue was captured by one reader who shared this observation:
Dear David: I really love your writing. I just wish there weren’t so much of it. Perhaps you could consider paring back a bit?
Each month’s cover essay, in Word, ranges from 22 – 35 pages, single-spaced. June and July were both around 30 pages, a length perhaps more appropriate to the cool and heartier months of late autumn and winter. In response, we’ve decided to offer you the Seersucker Edition of Mutual Fund Observer. We, along with the U.S. Senate, are celebrating seersucker, the traditional fabric of summer suits in the South. Light, loose and casual, it is “a wonderful summer fabric that was designed for the hot summer months,” according to Mississippi senator Roger Wicker. In respect of the heat and the spirit of bipartisanship, this is the “light and slightly rumpled” edition of the Observer that “retains its fashionable good looks despite summer’s heat and humidity.”
For September we’ll be adding a table of contents to help you navigate more quickly around the essay. We’ll target “Tweedy”, and perhaps Tweedy Browne, in November!
“There’ll never be another Bill Gross.” Lament or marketing slogan?
Up until July 31, the market seemed to be oblivious to the fact that the wheels seemed to be coming off the global geopolitical system. We focused instead on the spectacle of major industry players acting like carnies (do a Google image search for the word, you’ll get the idea) at the Mississippi Valley Fair.
Exhibit One is PIMCO, a firm that we lauded as having the best record for new fund launches of any of the Big Five. In signs of what must be a frustrating internal struggle:
PIMCO icon Bill Gross felt compelled to announce, at Morningstar, that PIMCO was “the happiest place in the world” to work, allowing that only Disneyland might be happier. Two notes: 1) when a couple says “our marriage is doing great,” divorce is imminent, and 2) Disneyland is, reportedly, a horrible place to work.

(Reuters, Jim King)
Gross also trumpeted “a performance turnaround” which appears not to be occurring at Gross’s several funds, either an absolute return or risk-adjusted return basis.
After chasing co-CIO Mohammed el-Erian out and convincing fund manager Jeremie Banet (a French national whose accent Gross apparently liked to ridicule) that he’d be better off running a sandwich truck, Gross took to snapping at CEO Doug Hodge for his failure to stanch fund outflows.
PIMCO insiders have reportedly asked Mr. Gross to stop speaking in public, or at least stop venting to the media. Mr. Gross threatened to quit, then publicly announced that he’s never threatened to quit.
Despite PIMCO’s declaration that the Wall Street Journal article that detailed many of these promises was “full of untruths and mischaracterizations that are unworthy of a major news daily,” they’ve also nervously allowed that “Pimco isn’t only Bill Gross” and lamented (or promised) that there will never been another PIMCO “bond king” after Gross’s departure.
Others in the industry, frustrated that PIMCO was hogging the silly season limelight, quickly grabbed the red noses and cream pies and headed at each other.

The most colorful is the fight between Morningstar and DoubleLine. On July 16, Morningstar declared that “On account of a lack of information … [DoubleLine Total Return DBLNX] is Not Ratable.” That judgment means that DoubleLine isn’t eligible for a metallic (Gold, Silver, Bronze) Analyst Rating but it doesn’t affect that fund’s five-star rating or the mechanical judgment that the $34 billion fund has offered “high” returns and “below average” risk. Morningstar’s contention is that the fund’s strategies are so opaque that risks cannot be adequately assessed at arm’s length and the DoubleLine refuses to disclose sufficient information to allow Morningstar’s analysts to understand the process from the inside. DoubleLine’s rejoinder (which might be characterized as “oh, go suck an egg!”) is that Morningstar “has made false statement about DoubleLine” and “mischaracterized the fund,” in consequence of which they’ll have “no further communication with Morningstar.com” (“How Bad is the Blood Between DoubleLine and Morningstar?” 07/18/2014).
DoubleLine declined several requests for comment on the fight and, specifically, for a copy of the reported eight page letter of particulars they’d sent to Morningstar. Nadine Youssef, speaking for Morningstar, stressed that
It’s not about refusing to answer questions—it’s about having sufficient information to assign an Analyst Rating. There are a few other fund managers who don’t answer all of our questions, but we assign an Analyst Rating if we have enough information from filings and our due diligence process.
If a fund produced enough information in shareholder letters and portfolios, we could still rate it. For example, stock funds are much easier to assess for risk because our analysts can run good portfolio analytics on them. For exotic mortgages, we can’t properly assess the risk without additional information.
It’s a tough call. Many fund managers, in private, deride Morningstar as imperious, high-handed, sanctimonious and self-serving. Others aren’t that positive. But in the immediate case Morningstar seems to be acting with considerable integrity. The mere fact that a fund is huge and famous can’t be grounds, in and of itself, for an endorsement by Morningstar’s analysts (though, admittedly, Morningstar does not have a single Negative rating on even one of the 234 $10 billion-plus funds). To the extent that this kerfuffle shines a spotlight on the larger problem of investors placing their money in funds whose strategies that don’t actually understand and couldn’t explain, it might qualify as a valuable “teachable moment” for the community.
Somewhere in there, one of the founders of DoubleLine’s equity unit quit and his fund was promptly liquidated with an explanation that almost sounded like “we weren’t really interested in that fund anyway.”
Waddell & Reed, adviser to the Ivy Funds, lost star manager Bryan Krug to Artisan. He was replaced on Ivy High Income (IVHIX) by William Nelson, who had been running Waddell & Reed High Income (UNHIX) since 2008. On July 9th Nelson was fired “for cause” and for reasons “unrelated to his portfolio management responsibilities,” which raised questions about the management of nearly $14 billion in high-yield assets. They also named a new president, had their stock downgraded, lost a third high-profile manager, drew huge fund inflows and blew away earnings expectations.
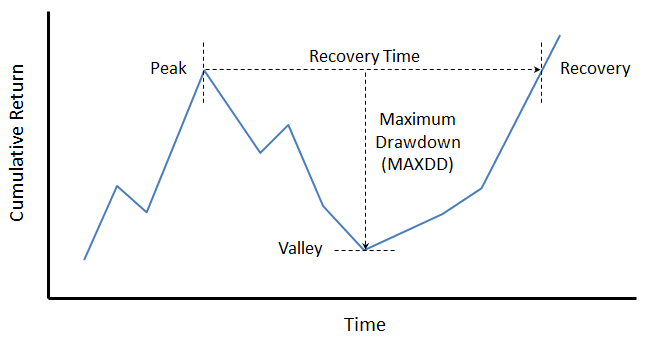
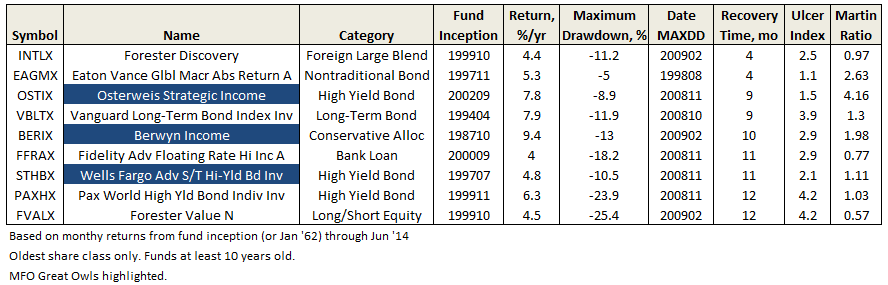
 Recovery Time
Recovery Time
In the book “Practical Risk-Adjusted Performance Measurement,” Carl Bacon defines recovery time or drawdown duration as the time taken to recover from an individual or maximum drawdown to the original level. In the case of maximum drawdown (MAXDD), the figure below depicts recovery time from peak. Typically, for equity funds at least, the descent from peak to valley happens more quickly than the ascent from valley to recovery level.
An individual’s risk tolerance and investment timeline certainly factor into expectations of maximum drawdown and recovery time. As evidenced in “Ten Market Cycles” from our April commentary, 20% drawdowns are quite common. Since 1956, the SP500 has fallen nearly 30% or more eight times. And, three times – a gut wrenching 50%. Morningstar advises that investors in equity funds need “investment horizons longer than 10 years.”
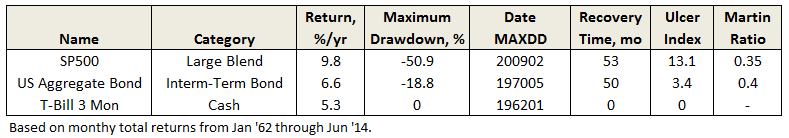
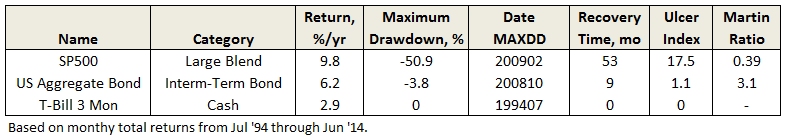
Since 1962, SP500’s worst recovery time is actually a modest 53 months. Perhaps more surprising is that aggregate bonds experienced a similar duration, before the long bull run. The difference, however, is in drawdown level.
During the past 20 years, bonds have recovered much more quickly, even after the financial crisis.
Long time MFO board contributor Bee posted recently:
MAXDD or Maximum Drawdown is to me only half of the story.
Markets move up and down. Typically the more aggressive the fund the more likely it is to have a higher MAXDD. I get that.
What I find “knocks me out of a fund” in a down market is the fund’s inability to bounce back.
Ulcer Index, as defined by Peter Martin and central to MFO’s ratings system, does capture both the MAXDD and recovery time, but like most indices, it is most easily interpreted when comparing funds over same time period. Shorter recovery times will have lower UIcer Index, even if they experience the same absolute MAXDD. Similarly, the attendant risk-adjusted-return measure Martin Ratio, which is excess return divided by Ulcer Index, will show higher levels.
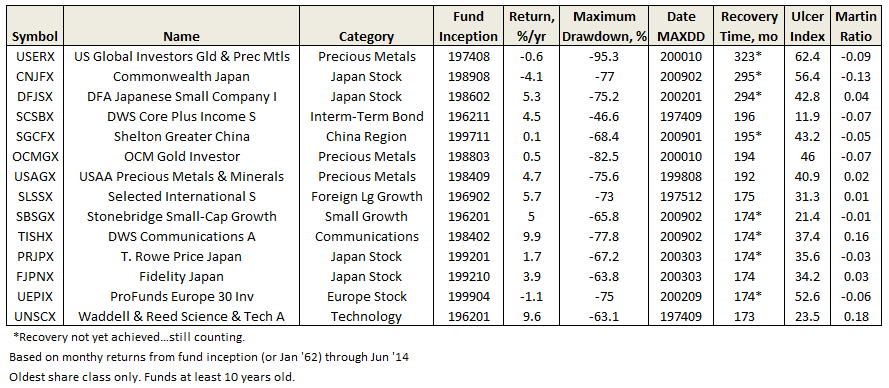
But nothing hits home quite like maximum drawdown and recovery time, whose absolute levels are easily understood. A review of lifetime MAXDD and recoveries reveals the following funds with some dreadful numbers, representing a cautionary tale at least:
In contrast, some notable funds, including three Great Owls, with recovery times at one year or less:
On Bee’s suggestion, we will be working to make fund recovery times available to MFO readers.
 Flash Geeks and Other Vagaries of Life …..
Flash Geeks and Other Vagaries of Life …..
By Edward Studzinski
“The genius of you Americans is that you never make clear-cut stupid moves, only complicated stupid moves which make us wonder at the possibility that there may be something to them which we are missing.”
Gamal Abdel Nasser
Some fifteen to twenty-odd years ago, before Paine Webber was acquired by UBS Financial Services, it had a superb annual conference. It was their quantitative investment conference usually held in Boston in early December. What was notable about it was that the attendees were the practitioners of what fundamental investors back then considered the black arts, namely the quants (quantitative investors) from shops like Acadian, Batterymarch, Fidelity, Numeric, and many of the other quant or quasi-quant shops. I made a point of attending, not because I thought of myself as a quant, but rather because I saw that an increasing amount of money was being managed in this fashion. WHAT I DID NOT KNOW COULD HURT BOTH ME AND MY INVESTORS.
One of the things you quickly learned about quantitative methods was that their factor-based models for screening stocks and industries, and then constructing portfolios, worked until they did not work. That is, inefficiencies that were discovered could be exploited until others noticed the same inefficiencies and adjusted their models accordingly. The beauty of this conference was that you had papers and presentations from the California Technology, MIT, and other computer geeks who had gone into the investment world. They would discuss what they had been working on and back-testing (seeing how things would have turned out). This usually gave you a pretty good snapshot of how they would be investing going forward. If nothing else, it helped you to know when you might want to step out of the way to keep from being run-over. It was certainly helpful to me in 1994.
In late 2006, I was in New York at a financial markets presentation hosted by the Santa Fe Institute and Bill Miller of Legg Mason. It was my follow-on substitute for the Paine Webber conference. The speakers included people like Andrew Lo, who is both a brilliant scientist at MIT and the chief scientific officer of the Alpha Simplex Group. One of the other people I chanced to hear that day was Dan Mathisson of Credit Suisse, who was one of the early pioneers and fathers of algorithmic trading. In New York then on the stock exchanges people were seeing change not incrementally, but on a daily basis. The floor trading and market maker jobs which had been handed down in families from generation to generation (go to Fordham or NYU, get your degree, and come into the family business) were under siege, as things went electronic (anyone who has studied innovation in technology and the markets knows that the Canadians, as with air traffic control systems, beat us by many years in this regard). And then I returned to Illinois, where allegedly the Flat Earth Society was founded and still held sway. One of the more memorable quotes which I will take with me forever is this. “Trying to understand algorithmic trading is a waste of time as it will never amount to more than ten per cent of volume on the exchanges. One will get better execution by having” fill-in-the blank “execute your trade on the floor.” Exit, stage right.
Flash forward to 2014. Michael Lewis has written and published his book, Flash Boys. I have to confess that I purchased this book and then let it sit on my reading pile for a few months, thinking that I already understood what it was about. I got to it sitting in a hotel room in Switzerland in June, thinking it would put me to sleep in a different time zone. I learned very quickly that I did not know what it was about. Hours later, I was two-thirds finished with it and fascinated. And beyond the fascination, I had seen what Lewis talked about happen many times in the process of reviewing trade executions.
If you think that knowing something about algorithmic trading, black pools, and the elimination of floor traders by banks of servers and trading stations prepares you for what you learn in Lewis’ book, you are wrong. Think about your home internet service. Think about the difference in speeds that you see in going from copper to fiber optic cable (if you can actually get it run into your home). While much of the discussion in the book is about front-running of customer trades, more is about having access to the right equipment as well as the proximity of that equipment to a stock exchange’s computer servers. And it is also about how customer trades are often routed to exchanges that are not advantageous to the customer in terms of ultimate execution cost.
Now, a discussion of front running will probably cause most eyes to glaze over. Perhaps a better way to think about what is going on is to use the term “skimming” as it might apply for instance, to someone being able to program a bank’s computers to take a few fractions of a cent from every transaction of a particular nature. And this skimming goes on, day in and day out, so that over a year’s time, we are talking about those fractions of cents adding up to millions of dollars.
Let’s talk about a company, Bitzko Kielbasa Company, which is a company that trades on average 500,000 shares a day. You want to sell 20,000 shares of Bitzko. The trading screen shows that the current market is $99.50 bid for 20,000 shares. You tell the trader to hit the bid and execute the sale at $99.50. He types in the order on his machine, hits sell, and you sell 100 shares of Bitzko at $99.50. The bid now drops to $99.40 for 1,000 shares. When you ask what happened, the answer is, “the bid wasn’t real and it went away.” What you learn from Lewis’ book is that as the trade was being entered, before the send/execute button was pressed, other firms could read your transaction and thus manipulate the market in that security. You end up selling your Bitzko at an average price well under the original price at which you thought you could execute.
So, how is it that no one has been held accountable for this yet? I don’t know, although there seem to be a lot of investigations ongoing. You also learn that a lot here has to do with order flow, or to what exchange a sell-side firm gets to direct your order for execution. The tragi-comic aspect of this is that mutual fund trustees spend a lot of time looking at trading evaluations as to whether best execution took place. The reality is that they have absolutely no idea on whether they got best execution because the whole thing was based on a false premise from the get-go. And the consultant’s trading execution reports reflect none of that.
Who has the fiduciary obligation? Many different parties, all of whom seem to hope that if they say nothing, the finger will not get pointed at them. The other side of the question is, you are executing trades on behalf of your client, individual or institutional, and you know which firms are doing this. Do you still keep doing business with them? The answer appears to be yes, because it is more important to YOUR business than to act in the best interests of your clients. Is there not a fiduciary obligation here as well? Yes.
I would like to think that there will be a day of reckoning coming. That said, it is not an easy area to understand or explain. In most sell-side firms, the only ones who really understood what was going on were the computer geeks. All that management and the marketers understood was that they were making a lot of money, but could not explain how. All that the buy-side firms understood was that they and their customers were being disadvantaged, but by how much was another question.
As an investor, how do you keep from being exploited? The best indicators as usual are fees, expenses, and investment turnover. Some firms have trading strategies tied to executing trades only when a set buy or sell price is triggered. Batterymarch was one of the forerunners here. Dimensional Fund Advisors follows a similar strategy today. Given low turnover in most indexing strategies, that is another way to limit the degree of hurt. Failing that, you probably need to resign yourself to paying hidden tolls, especially as a purchaser or seller of individual securities. Given that, being a long-term investor makes a good bit of sense. I will close by saying that I strongly suggest Michael Lewis’ book as must-reading. It makes you wonder how an industry got to the point where it has become so hard for so many to not see the difference between right and wrong.
What does it take for Morningstar to notice that they’re not noticing you?
Based on the funds profiled in Russ Kinnel’s July 15th webcast, “7 Under the Radar Funds,” the answer is about $400 million and ten years with the portfolio.
|
|
Ten year record |
Lead manager tenure (years) |
AUM (millions) |
|
LKCM Equity LKEQX |
8.9% |
18.5 |
$331 |
|
Becker Value BVEFX |
9.2 |
10 |
325 |
|
FPA Perennial FPPFX |
9.2 |
15 |
317 |
|
Royce Special Equity Multi-Cap RSEMX |
n/a |
4 |
236 |
|
Bogle Small Cap Growth BOGLX |
9.9 |
14 |
228 |
|
Diamond Hill Small to Mid Cap DHMAX |
n/a |
9 |
486 |
|
Champlain Mid Cap CIPMX |
n/a |
6 |
705 |
|
|
|
10.9 |
$375 |
Let’s start with the obvious: these are pretty consistently solid funds and well worth your consideration. What most strikes me about the list is the implied judgment that unless you’re from a large fund complex, the threshold for Morningstar even to admit that they’ve been ignoring you is dauntingly high. While Don Phillips spoke at the 2013 Morningstar Investment Conference of an initiative to identify promising funds earlier in their existence, that promise wasn’t mentioned at the 2014 gathering and this list seems to substantiate the judgment that from Morningstar’s perspective, small funds are dead to them.
That’s a pity given the research that Mr. Kinnel acknowledges in his introduction…when it comes to funds, bigger is simply not better.
Investors might be beginning to suspect the same thing. Kevin McDevitt, a senior analyst on Morningstar’s manager research team (that’s what they’re calling the folks who cover mutual funds now), studied fund flows and noticed two things:
- Starting in early 2013, investors began pouring money into “risk on” funds. “Since the start of 2013, flows into the least-volatile group of funds have basically been flat. During that same six-quarter stretch, investors poured nearly $125 billion into the most-volatile category of funds.” That is, he muses, reminiscent of their behavior in the years (2004-07) immediately before the final crisis.
- Investors are pouring money into recently-launched funds. He writes: “What’s interesting about this recent stretch is that a sizable chunk of inflows has gone to funds without a three-year track record. If those happen to be higher-risk funds too, then people really have embraced risk once more. It’s pretty astonishing that these fledgling funds have collected more inflows over the past 12 months through June ($154 billion) than the other four quartiles (that is, funds with at least a three-year record) combined ($117 billion).”
I’ve got some serious concerns about that paragraph (you can’t just assume newer funds as “higher-risk funds too”) and I’ve sent Mr. McDevitt a request for clarification since I don’t have any ideas of what “the other four quartiles” (itself a mathematical impossibility) refers to. See “Investors Show Willingness to Buy Untested Funds,” 07/31/2014.
That said, it looks like investors and their advisors might be willing to listen. Happily, the Observer’s willing to speak with them about newer, smaller, independent funds. Our willingness to do so is based on the research, not simple altruism. Small, nimble, independent, investment-driven rather than asset-driven works.
And so, for the 3500 funds smaller than the smallest name on Morningstar’s list and the 4100 smaller than the average fund on this list, be of good cheer! For the 141 small funds that have a better 10-year record than any of these, be brave! To the 17 unsung funds that have a five-star rating for the past three years, five years, ten years and overall, your time will come!
Thanks to Akbar Poonawala for bringing the webcast to my attention!
What aren’t you reading this summer?
If you’re like me, you have at your elbow a stack of books that you promised yourself you were going to read during summer’s long bright evenings and languid afternoons. Mine includes Mark Miodownik’s Stuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials that Shape Our Manmade World (2013) and Sherry Turkle’s Alone Together: Why We Expect More from Technology and Less from Each Other (2012). Both remain in lamentably pristine condition.
How are yours?
Professor Jordan Ellenberg, a mathematician at Wisconsin-Madison, wrote an interesting but reasonably light-hearted essay attempting to document the point at which our ambition collapses and we surrender our pretensions of literacy. He did it by tracking the highlights that readers embed in the Kindle versions of various books. His thought is that the point at which readers stop highlighting text is probably a pretty good marker of where they stopped reading it. His results are presented in “The Summer’s Most Unread Book Is…” (7/5/14). Here are his “most unread” nominees:
Thinking Fast and Slow by Daniel Kahneman : 6.8%
Apparently the reading was more slow than fast. To be fair, Prof. Kahneman’s book, the summation of a life’s work at the forefront of cognitive psychology, is more than twice as long as “Lean In,” so his score probably represents just as much total reading as Ms. Sandberg’s does.
A Brief History of Time by Stephen Hawking: 6.6%
The original avatar backs up its reputation pretty well. But it’s outpaced by one more recent entrant—which brings us to our champion, the most unread book of this year (and perhaps any other). Ladies and gentlemen, I present:
Capital in the Twenty-First Century by Thomas Piketty: 2.4%
Yes, it came out just three months ago. But the contest isn’t even close. Mr. Piketty’s book is almost 700 pages long, and the last of the top five popular highlights appears on page 26. Stephen Hawking is off the hook; from now on, this measure should be known as the Piketty Index.
At the other end of the spectrum, one of the most read non-fiction works is a favorite of my colleague Ed Studzinski’s or of a number of our readers:
Flash Boys by Michael Lewis : 21.7%
Mr. Lewis’s latest trip through the sewers of financial innovation reads like a novel and gets highlighted like one, too. It takes the crown in my sampling of nonfiction books.
What aren’t you drinking this summer?
The answer, apparently, is Coca-Cola in its many manifestations. US consumption of fizzy drinks has been declining since 2005. In part that’s a matter of changing consumer tastes and in part a reaction to concerns about obesity; even Coca-Cola North America’s president limits himself to one 8-ounce bottle a day.
Some investors, though, suspect that the problem arises from – or at least is not being effectively addressed by – Coke’s management. They argue that management is badly misallocating capital (to, for example, buying Keurig rather than investing in their own factories) and compensating themselves richly for the effort.
Enter David Winters, manager of Wintergreen Fund (WGRNX). While some long-time Coke investors (that would be Warren Buffett) merely abstain rather than endorse management proposals, Mr. Winters loudly, persistently and thoughtfully objects. His most public effort is embodied in the website Fix Big Soda.
David’s aged more gracefully than have I. Rich, smart, influential and youthful. Nuts.
This is far from Winters’ first attempt to influence the direction of one of his holdings. He stressed two things in a long ago interview with us: (1) the normal fund manager’s impulse to simply sell and let a corporation implode struck him as understandable but defective, and (2) the vast majority of management teams welcomed thoughtful, carefully-researched advice from qualified outsiders. But some don’t, preferring to run a corporation for the benefit of insiders rather than shareholders or other stakeholders. When Mr. Winters perceives that a firm’s value might grow dramatically if only management stopped being such buttheads (though I’m not sure he uses the term), he’s willing to become the catalyst to unlock that value for the benefit of his own shareholders. A fairly high profile earlier example was his successful conflict with the management of Florida real estate firm Consolidated-Tomoka.
You surely wouldn’t want all of your managers pursuing such a strategy but having at least one of them gives you access to another source of market-independent gains in your portfolio. So-called “special situation” or “distressed” investments can gain value if the catalyst is successful, even if the broader market is declining.
Observer Fund Profiles:
Each month the Observer provides in-depth profiles of between two and four funds. Our “Most Intriguing New Funds” are funds launched within the past couple years that most frequently feature experienced managers leading innovative newer funds. “Stars in the Shadows” are older funds that have attracted far less attention than they deserve.
This month we profile two funds that offer different – and differently successful – takes on the same strategy. There’s a lot of academic research that show firms which are seriously and structurally devoted to innovation far outperform their rivals. These firms can exist in all sectors; it’s entirely possible to have a highly innovative firm in, say, the cement industry. Conversely, many firms systematically under-invest in innovation and the research suggests these firms are more-or-less doomed.
Why would firms be so boneheaded? Two reasons come to mind:
- Long-term investments are hard to justify in a market that demands short-term results.
- Spending on research and training are accounted as “overhead” and management is often rewarded for trimming unnecessary overhead.
Both of this month’s profiles target funds that are looking for ways to identify firms that are demonstrably and structurally (that is, permanently) committed to innovation or knowledge leadership. While their returns are very different, each is successful on its own terms.
GaveKal Knowledge Leaders (GAVAX) combines a search for high R&D firms with sophisticated market risks screens that force it to reduce its market exposure when markets begin teetering into “the red zone.” The result is an equity portfolio with hedge fund like characteristics which many advisors treat as a “liquid alts” option.
Guinness Atkinson Global Innovators (IWIRX) stays fully invested regardless of market conditions in the world’s 30 most innovative firms. What started in the 1990s as the Wired 40 Index Fund has been crushing its competition as an actively managed for fund over a decade. Lipper just ranked it as the best performing Global Large Cap Growth fund of the past year. And of the past three years. Also the #1 performer for the past five years and, while we’re at it, for the past 10 years as well.
Elevator Talk: Jim Cunnane, Advisory Research MLP & Energy Income Fund (INFRX/INFIX)
 Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
The Observer has presented the case for investing in Master Limited Partnerships (MLPs) before, both when we profiled SteelPath Alpha (now Oppenheimer SteelPath Alpha MLPAX) and in our Elevator Talk with Ted Gardiner of Salient MLP Alpha and Energy Infrastructure II (SMLPX). Here’s the $0.50 version of the tale:
MLPs are corporate entities which typically own energy infrastructure. They do not explore for oil and they do not refine it, but they likely own the pipelines that connect the E&P firm with the refiner. Likewise they don’t mine the coal nor produce the electricity, but might own and maintain the high tension transmission grid that distributes it.
MLPs typically make money by charging for the use of their facilities, the same way that toll road operators do. They’re protected from competition by the ridiculously high capital expenses needed to create infrastructure. The rates they charge as generally set by state rate commissions, so they’re very stable and tend to rise by slow, predictable amounts.
The prime threat to MLPs is falling energy demand (for example, during a severe recession) or falling energy production.
From an investor’s perspective, direct investment in an MLP can trigger complex and expensive tax requirements. Indeed, a fund that’s too heavily invested in MLPs alone might generate those same tax headaches.
That having been said, these are surprisingly profitable investments. The benchmark Alerian MLP Index has returned 17.2% annually over the past decade with a dividend yield of 5.2%. That’s more than twice the return of the stock market and twice the income of the bond market.
The questions you need to address are two-fold. First, do these investments make sense for your portfolio? If so, second, does an actively-managed fund make more sense than simply riding an index. Jim Cunnane thinks that two yes’s are in order.
 Mr. Cunnane manages Advisory Research MLP & Energy Infrastructure Fund which started life as a Fiduciary Asset Management Company (FAMCO) fund until the complex was acquired by Advisory Research. He’d been St. Louis-based FAMCO’s chief investment officer for 15 years. He’s the CIO for the MLP & Energy Infrastructure team and chair of AR’s Risk Management Committee. He also manages two closed-end funds which also target MLPs: the Fiduciary/Claymore MLP Opportunity Fund (FMO) and the Nuveen Energy MLP Total Return Fund (JMF). Here are his 200 words (and one picture) on why you might consider INFRX:
Mr. Cunnane manages Advisory Research MLP & Energy Infrastructure Fund which started life as a Fiduciary Asset Management Company (FAMCO) fund until the complex was acquired by Advisory Research. He’d been St. Louis-based FAMCO’s chief investment officer for 15 years. He’s the CIO for the MLP & Energy Infrastructure team and chair of AR’s Risk Management Committee. He also manages two closed-end funds which also target MLPs: the Fiduciary/Claymore MLP Opportunity Fund (FMO) and the Nuveen Energy MLP Total Return Fund (JMF). Here are his 200 words (and one picture) on why you might consider INFRX:
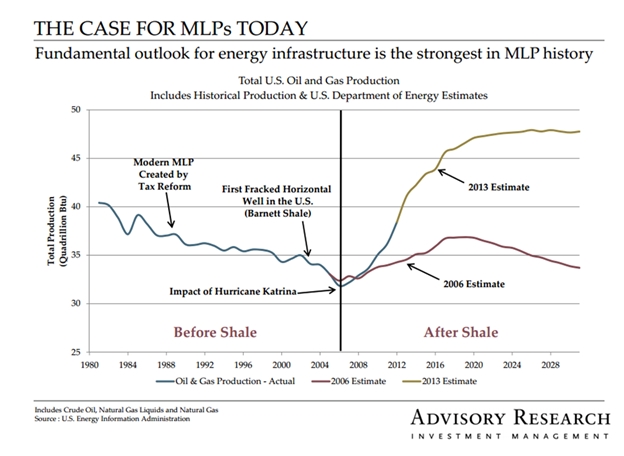
We’re always excited to talk about this fund because it’s a passion of ours. It’s a unique way to manage MLPs in an open-end fund. When you look at the landscape of US energy, it really is an exciting fundamental story. The tremendous increases in the production of oil and gas have to be accompanied by tremendous increases in energy infrastructure. Ten years ago the INGA estimated that the natural gas industry would need $3.6 billion/year in infrastructure investments. Today the estimate is $14.2 billion. We try to find great energy infrastructure and opportunistically buy it.
There are two ways you can attack investing in MLPs through a fund. One would be an MLP-dedicated portfolio but that’s subject to corporate taxation at the fund level. The other is to limit direct MLP holdings to 25% of the portfolio and place the rest in attractive energy infrastructure assets including the parent companies of the MLPs, companies that might launch MLPs and a new beast called a YieldCo which typically focus on solar or wind infrastructure. We have the freedom to move across the firms’ capital structure, investing in either debt or equity depending on what offers the most attractive return.
Our portfolio in comparison to our peers offers a lot of additional liquidity, a lower level of volatility and tax efficiency. Despite the fact that we’re not exclusively invested in MLPs we manage a 90% correlation with the MLP index.
While there are both plausible bull and bear cases to be made about MLPs, our conclusion is that risk and reward is fairly balanced and that MLP investors will earn a reasonable level of return over a 10-year horizon. To account for the recent strong performance of MLPs, we are adjusting our long term return expectation down to 5-9% per annum, from our previous estimate of 6-10%. We also expect a 10% plus MLP market correction at some point this year.
The “exciting story” that Mr. Cunnane mentioned above is illustrated in a chart that he shared:
The fund has both institutional and retail share classes. The retail class (INFRX) has a $2500 minimum initial investment and a 5.5% load. Expenses are 1.50% with about $725 million in assets. The institutional share class (INFIX) is $1,000,000 and 1.25%. Here’s the fund’s homepage.
Funds in Registration
The Securities and Exchange Commission requires that funds file a prospectus for the Commission’s review at least 75 days before they propose to offer it for sale to the public. The release of new funds is highly cyclical; it tends to peak in December and trough in the summer.
This month the Observer’s other David (research associate David Welsch) tracked down nine new no-load funds in registration, all of which target a September launch. It might be the time of year but all of this month’s offerings strike me as “meh.”
Manager Changes
Just as the number of fund launches and fund liquidations are at seasonal lows, so too are the number of fund manager changes. Chip tracked down a modest 46 manager changes, with two retirements and a flurry of activity at Fidelity accounting for much of the activity.
Top Developments in Fund Industry Litigation – July 2014
![]() Fundfox is the only intelligence service to focus exclusively on litigation involving U.S.-registered investment companies, their directors and advisers. Publisher David Smith has agreed to share highlights with us. For a complete list of developments last month, and for information and court documents in any case, log in at www.fundfox.com and navigate to Fundfox Insider.
Fundfox is the only intelligence service to focus exclusively on litigation involving U.S.-registered investment companies, their directors and advisers. Publisher David Smith has agreed to share highlights with us. For a complete list of developments last month, and for information and court documents in any case, log in at www.fundfox.com and navigate to Fundfox Insider.
New Lawsuit
- In a copyright infringement lawsuit, the publisher of Oil Daily alleges that KA Fund Advisors (you might recognize them as Kayne Anderson) and its parent company have “for years” internally copied and distributed the publication “on a consistent and systematic basis,” and “concealed these activities” from the publisher. (Energy Intelligence Group, Inc. v. Kayne Anderson Capital Advisors, LP.)
Order
- The court granted American Century‘s motion for summary judgment in a lawsuit that challenged investments in an illegal Internet gambling business by the Ultra Fund. (Seidl v. Am. Century Cos.)
Briefs
- Plaintiffs filed their opposition to BlackRock‘s motion to dismiss excessive-fee litigation regarding its Global Allocation and Dividend Equity Funds. (In re BlackRock Mut. Funds Advisory Fee Litig.)
- First Eagle filed a motion to dismiss an excessive-fee lawsuit regarding its Global and Overseas Funds. (Lynn M. Kennis Trust v. First Eagle Inv. Mgmt., LLC.)
- J.P. Morgan filed a motion to dismiss an excessive- fee lawsuit regarding its Core Bond, High Yield, and Short Duration Bond Funds. (Goodman v. J.P. Morgan Inv. Mgmt., Inc.)
Answer
- Opting against a motion to dismiss, ING filed an answer in the fee lawsuit regarding its Global Real Estate Fund. (Cox v. ING Invs. LLC.)
– – –
A potentially fascinating case arose just a bit after David shared his list with us. A former Vanguard employee is suing Vanguard, alleging that they illegally dodged billions in taxes. While Vanguard itself warns that “The issues presented in the complaint are far too complex to get a full and proper hearing in the news media” (the wimps), it appears that the plaintiff has two allegations:
- That Vanguard charges too little for their services; they charge below-market rates while the tax code requires that, for tax purposes, transactions be assessed at market rates. A simple illustration: if your parents rented an apartment to you for $300/month when anyone else would expect to pay $1000/month for the same property, the $700 difference would be taxable to you since they’re sort of giving you a $700 gift each month.
- That Vanguard should have to pay taxes on the $1.5 billion “contingency reserve” they’ve built.
Joseph DiStephano of the Philadelphia Inquirer, Vanguard’s hometown newspaper, laid out many of the issues in “Vanguard’s singular model is under scrutiny,” 07/30/2014. If you’d like to be able to drop legalese casually at your next pool party, you can read the plaintiff’s filing in State of New York ex rel David Danon v. Vanguard Group Inc.
Updates
Aston/River Road Long-Short (ARLSX) passed its three year anniversary in May and received its first Morningstar rating recently. They rated it as a four-star fund which has captured a bit more of the upside and a bit less of the downside than has its average peer. The fund had a bad January (down more than 4%) but has otherwise been a pretty consistently above average, risk-conscious performer.
Zac Wydra, manager of Beck, Mack and Oliver Partners Fund (BMPEX), was featured in story in the Capitalism and Crisis newsletter. I suspect the title, “Investing Wisdom from Zac Wydra,” likely made Zac a bit queasy since it rather implies that he’s joined the ranks of the Old Dead White Guys (ODWGs) also with Graham and Dodd.
 Here’s a major vote of confidence: Effective August 1, 2014, John Neff and Thomas Saberhagen were named as co-portfolio managers for the Akre Focus Fund. They both joined Mr. Akre’s firm in 2009 after careers at William Blair and Aegis Financial, respectively. The elevation is striking. Readers might recall that Mr. Akre was squeezed out after running FBR Focus (now Hennessy Focus HFCSX) for 13 years. FBR decided to cut Mr. Akre’s contract by about 50% (without reducing shareholder expenses), which caused him to launch Akre Focus using the same discipline. FBR promptly poached Mr. Akre’s analysts (while he was out of town) to run their fund in his place. At that point, Mr. Akre swore never to repeat the mistake and to limit analysts to analyzing rather than teaching them portfolio construction. Time and experience with the team seems to have mellowed the great man. Given the success that the rapscallions have had at HFCSX, there’s a good chance that Mr. Akre, now in his 70s, has trained Neff and Saberhagen well which might help address investor concerns about an eventual succession plan.
Here’s a major vote of confidence: Effective August 1, 2014, John Neff and Thomas Saberhagen were named as co-portfolio managers for the Akre Focus Fund. They both joined Mr. Akre’s firm in 2009 after careers at William Blair and Aegis Financial, respectively. The elevation is striking. Readers might recall that Mr. Akre was squeezed out after running FBR Focus (now Hennessy Focus HFCSX) for 13 years. FBR decided to cut Mr. Akre’s contract by about 50% (without reducing shareholder expenses), which caused him to launch Akre Focus using the same discipline. FBR promptly poached Mr. Akre’s analysts (while he was out of town) to run their fund in his place. At that point, Mr. Akre swore never to repeat the mistake and to limit analysts to analyzing rather than teaching them portfolio construction. Time and experience with the team seems to have mellowed the great man. Given the success that the rapscallions have had at HFCSX, there’s a good chance that Mr. Akre, now in his 70s, has trained Neff and Saberhagen well which might help address investor concerns about an eventual succession plan.
Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX) passed the $100 million AUM threshold in July and is in the process of hiring a business development director. Manager Andrew Foster reports that they received a slug of really impressive applications. Our bottom line was, and is, “There are few more-attractive emerging markets options available.” We’re pleased that folks are beginning to have faith in that conclusion.
Stewart Capital Mid Cap Fund (SCMFX) has been named to the Charles Schwab’s Mutual Fund OneSource Select List for the third quarter of 2014. It’s one of six independent mid-caps to make the list. The recognition is appropriate and overdue. Our Star in the Shadow’s profile of the fund concluded that it was “arguably one of the top two midcap funds on the market, based on its ability to perform in volatile rising and falling markets. Their strategy seems disciplined, sensible and repeatable.” That judgment hasn’t changed but their website has; the firm made a major and welcome upgrade to it last year.
Briefly Noted . . .
Yikes. I mean, really yikes. On July 28, Aberdeen Asset Management Plc (ADN) reported that an unidentified but “very long standing” client had just withdrawn 4 billion pounds of assets from the firm’s global and Asia-Pacific region equity funds. The rough translation is $6.8 billion. Overall the firm saw over 8 billion pounds of outflow in the second quarter, an amount large enough that even Bill Gross would feel it.
We all have things that set us off. For some folks the very idea of “flavored” coffee (poor defenseless beans drenched in amaretto-kiwi goo) will do it. For others it’s the designated hitter rule or plans to descrecate renovate Wrigley Field. For me, it’s fund managers who refuse to invest in their own funds, followed closely behind by fund trustees who refuse to invest in the funds whose shareholders they represent.
Sarah Max at Barron’s published a good short column (07/12/14) on the surprising fact that over half of all managers have zero (not a farthing, not a penny, not a thing) invested in their own funds. The research is pretty clear (the more the insiders’ interests are aligned with yours, the better a fund’s risk-adjusted performance) and the atmospherics are even clearer (what on earth would convince you that a fund is worth an outsider’s money if it’s not worth an insider’s?). That’s one of the reasons that the Observer routinely reports on the manager and director investments and corporate policies for all of the funds we cover. In contrast to the average fund, small and independent funds tend to have persistently, structurally high levels of insider commitment.
SMALL WINS FOR INVESTORS
On June 30, both the advisory fee and the expense cap on The Brown Capital Management International Equity Fund (BCIIX) were reduced. The capped e.r. dropped from 2.00% to 1.25%.
Forward Tactical Enhanced Fund (FTEAX) is dropping its Investor Share class expense ratio from 1.99% to 1.74%. Woo hoo! I’d be curious to see if they drop their portfolio turnover rate from its current 11,621%. (No, I’m not making that up.)
Perritt Ultra MicroCap Fund (PREOX) reopened to new investors on July 8. It had been closed for three whole months. The fund has middling performance at best and a tiny asset base, so there was no evident reason to close it and no reason for either the opening or closing was offered by the advisor.
CLOSINGS (and related inconveniences)
Effective at the close of business on August 15, 2014, Grandeur Peak Emerging Opportunities Fund (GPEOX/GPEIX) the Fund will close to all purchases. There are two exceptions, (1) individuals who invested directly through Grandeur Peak and who have either a tax-advantaged account or have an automatic investing plan and (2) institutions with an existing 401(k) arrangement with the firm. The fund reports about $370M in assets and YTD returns of 11.6% through late July, which places it in the top 10% of all E.M. funds. There are a couple more G.P. funds in the pipeline and the guys have hinted at another launch sooner rather than later, but the next gen funds are likely more domestic than international.
Effective as of the close of business on October 31, 2014, the Henderson European Focus Fund (HFEAX) will be closed to new purchases. The fund sports both top tier returns and top tier volatility. If you like charging toward closing doors, it’s available no-load and NTF at Schwab and elsewhere.
Parametric Market Neutral Fund (EPRAX) closed to new investors on July 11, 2014. The fund is small and slightly under water since inception. Under those circumstances, such closures are sometimes a signal of bigger changes – new management, new strategy, liquidation – on the horizon.
 Citing “the lack of investment opportunities” and “high current cash levels” occasioned by the five year run-up in global stock prices, Tweedy Browne announced the impending soft close of Tweedy, Browne Global Value II (TBCUX). TBCUX is an offshoot of Tweedy, Browne Global Value (TBGVX) with the same portfolio and managers but Global Value often hedges its currency exposure while Global Value II does not. The decision to close TBCUX makes sense as a way to avoid “diluting our existing shareholders’ returns in this difficult environment” since the new assets were going mostly to cash. Will Browne planned “to reopen the Fund when new idea flow improves and larger amounts of cash can be put to work in cheap stocks.”
Citing “the lack of investment opportunities” and “high current cash levels” occasioned by the five year run-up in global stock prices, Tweedy Browne announced the impending soft close of Tweedy, Browne Global Value II (TBCUX). TBCUX is an offshoot of Tweedy, Browne Global Value (TBGVX) with the same portfolio and managers but Global Value often hedges its currency exposure while Global Value II does not. The decision to close TBCUX makes sense as a way to avoid “diluting our existing shareholders’ returns in this difficult environment” since the new assets were going mostly to cash. Will Browne planned “to reopen the Fund when new idea flow improves and larger amounts of cash can be put to work in cheap stocks.”
Here’s the question: why not close Global Value as well?
The good folks at Mount & Nadler arranged for me to talk with Tom Shrager, Tweedy’s president. Short version: they have proportionately less inflows into Global Value but significant net inflows, as a percentage of assets, into Global Value II. As a result, the cash level at GV II is 26% while GV sits at 20% cash. While they’ve “invested recently in a couple of stocks,” GV II’s net cash level climbed from 21% at the end of Q1 to 26% at the end of Q2. They tried adding a “governor” to the fund (you’re not allowed to buy $4 million or more a day without prior clearance) which didn’t work.
Mr. Shrager describes the sudden popularity of GV II as “a mystery to us” since its prime attraction over GV would be as a currency play and Tweedy doesn’t see any evidence of a particular opportunity there. Indeed, GV II has trailed GV over the past quarter and YTD while matching it over the past 12 months.
At the same time, Tweedy reports no particular interest in either Value (TWEBX, top 20% YTD) or High Dividend Yield Value (TBHDX, top 50% YTD), both at 11% cash.
The closing will not affect current shareholders or advisors who have been using the fund for their clients.
OLD WINE, NEW BOTTLES
Alpine Foundation Fund (ADABX) has been renamed Alpine Equity Income Fund. The rechristened version can invest no more than 20% in fixed income securities. The latest, prechange portfolio was 20.27% fixed income. Over the longer term, the fund trails its “aggressive allocation” peers by 160 – 260 basis points annually and has earned a one-star rating for the past three, five and ten year periods. At that point, I’m not immediately convinced that a slight boost in the equity stake will be a game-changer for anyone.
On October 1, the billion dollar Alpine Ultra Short Tax Optimized Income Fund (ATOAX) becomes Alpine Ultra Short Municipal Income Fund and promises to invest, mostly, in munis.
Effective October 1, SunAmerica High Yield Bond (SHNAX)becomes SunAmerica Flexible Credit. The change will free the fund of the obligation of investing primarily in non-investment grade debt which is good since it wasn’t particularly adept at investing in such bonds (one-star with low returns and above average risk during its current manager’s five-year tenure).
OFF TO THE DUSTBIN OF HISTORY
 Thanks, as always, go to The Shadow – an incredibly vigilant soul and long tenured member of the Observer’s discussion community for his contributions to this section. Really, very little gets past him and that gives me a lot more confidence in saying that we’ve caught of all of major changes hidden in the ocean of SEC filings.
Thanks, as always, go to The Shadow – an incredibly vigilant soul and long tenured member of the Observer’s discussion community for his contributions to this section. Really, very little gets past him and that gives me a lot more confidence in saying that we’ve caught of all of major changes hidden in the ocean of SEC filings.
Grazie!
CM Advisors Defensive Fund (CMDFX) “has terminated the public offering of its shares and will discontinue its operations effective on or about August 1, 2014.” Uhhh … what would be eight weeks after launch?
Direxion U.S. Government Money Market Fund (DXMXX) will liquidate on August 20, 2014. I’m less struck by the liquidation of a tiny, unprofitable fund than by the note that “the Fund’s assets will be converted to cash.” It almost feels like a money market’s assets should be describable as “cash.”
Geneva Advisors Mid Cap Growth Fund (the “Fund”) will be closed and liquidated on August 28. 2014. That decision comes nine months after the fund’s launch. While the fund’s performance was weak and it gathered just $4 million in assets, such hasty abandonment strikes me as undisciplined and unprofessional especially when the advisor reminds its investors of “the importance of … a long-term perspective when it comes to the equity portion of their portfolio.” The fund representatives had no further explanation of the decision.
GL Macro Performance Fund (GLMPX) liquidated on July 30, 2014. At least the advisor gave this fund 20 months of life so that it had time to misfire with style:
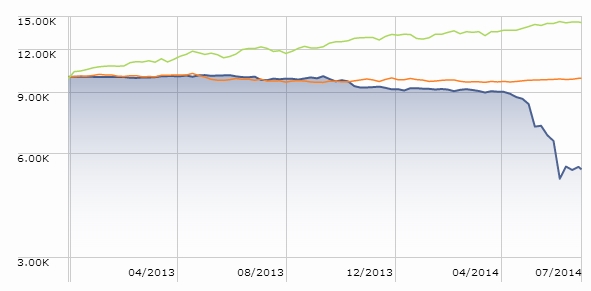
The Board of Trustees of Makefield Managed Futures Strategy Fund (MMFAX) has concluded that “it is in the best interests of the Fund and its shareholders that the Fund cease operations.” Having lost 17% for its few investors since launch, the Board probably reached the right conclusion. Liquidation is slated for August 15, 2014.
Following the sudden death of its enigmatic manager James Wang, the Board of the Oceanstone Fund (OSFDX) voted to liquidate the portfolio at the end of August. The fund had unparalleled success from 2007-2012 which generated a series of fawning (“awesome,” “the greatest investor you’ve never heard of,” “the most intriguing questions in the mutual fund world today”) stories in the financial media. Mr. Wang would neither speak to be media nor permit his board to do so (“he will be upset with me,” fretted one independent trustee) and his shareholder communications were nearly nonexistent. His trustees rightly eulogize him as “very sincere, hard working, humble, efficient and caring.” Our sympathies go out to his family and to those for whom he worked so diligently.
Pending shareholder approval, Sentinel Capital Growth Fund (BRGRX) and Sentinel Growth Leaders Fund (BRFOX) will be merged into Sentinel Common Stock Fund (SENCX) sometime this fall. Here’s the best face I can put on the merger: SENCX isn’t awful.
Effective October 16, SunAmerica GNMA (GNMAX) gets merged into SunAmerica U.S. Government Securities (SGTAX). Both funds fall just short of mediocre (okay, they both trail 65 – 95% of their peers over the past three, five and ten year periods so maybe it’s “way short” or “well short”) and both added two new managers in July 2014. We wish Tim and Kara well with their new charges.
With shareholder approval, the $16 million Turner All Cap Growth Fund (TBTBX) will soon merge into the Turner Midcap Growth Fund (TMGFX). Midcap has, marginally, the better record but All Cap has, massively, the greater assets so …
In Closing . . .
I’m busily finishing up the outline for my presentation to the Cohen Client Conference, which takes place in Milwaukee on August 20 and 21. The working title of my talk is “Seven things that matter, two that don’t … and one that might.” My hope is to tie some of the academic research on funds and investing into digestible snackage (it is at lunchtime, after all) that attempts to sneak a serious argument in under the cover of amiable banter. I’ll let you know how it goes.
I know that David Hobbs, Cook and Bynum’s president, will be there and I’m looking forward to a chance to chat with him. He’s offered some advice about the thrust of my talk that was disturbingly consistent with my own inclinations, which should worry at least one of us. I’ll be curious to get his reaction.
We’re also hoping to cover the Morningstar ETF Conference en masse; that is, Charles, Chip, Ed and I would like to meet there both to cover the presentations (Meb Faber, one of Charles’s favorite guys, and Eugene Fama are speaking) and to debate about ways to strengthen the Observer and better serve you folks. A lot depends on my ability to trick my colleagues into covering two of my classes that week. Perhaps we’ll see you there?
 My son Will, still hobbled after dropping his iPad on a toe, has taken to wincing every time we approach the mall. It’s festooned with “back to school sale! Sale! sale!” banners which seem, somehow, to unsettle him.
My son Will, still hobbled after dropping his iPad on a toe, has taken to wincing every time we approach the mall. It’s festooned with “back to school sale! Sale! sale!” banners which seem, somehow, to unsettle him.
Here’s a quick plug for using the Observer’s link to Amazon.com. If you’d like to spare your children, grandchildren, and yourself the agony of the mall parking lot and sound of wailing and keening, you might consider picking some of this stuff up online. The Observer receives a rebate equal to about 6% on whatever is purchased through our link. It’s largely invisible to you – if costs nothing extra and doesn’t involve any extra steps on your part – but it generates the majority of the funds that keep the lights on here.
Here are some ways to make support easy:
- Click on our Amazon link and bookmark it for easy referral.
- Look to your right, the dang thing is continually floating over there ->
- In Chrome, set us as one of your start pages. On the upper right of your screen, click on the three horizontal bars then click “settings.” You’ll see this option:
Click on “Set pages” then simply paste the Observer link in along with wherever else you like to start. Each time you open Chrome, it’ll launch several tabs including your regular homepage and our Amazon page.
- If, like many, you’re not comfortable with Amazon’s plan to take over everything …
 feel free to resort to PayPal or the USPS. It all helps and it’s all detailed on our Support Us page.
feel free to resort to PayPal or the USPS. It all helps and it’s all detailed on our Support Us page.
Finally, we offer cheerful greetings to our curiously large and diligent readership in Cebu City, Philippines; Cebu Citizens spend about a half hour on site per visit, about five times the global average. Greetings, too, to the good folks in A Coruña in the north of Spain. You’ve been one of our most persistent international audiences. The Madrileños are fewer in number, but diligent in their reading. To our sole Ukrainian visit, Godspeed and great care.
As ever,