By David Snowball
Dear friends,
As most of you know, my day job is as a professor at Augustana College in Rock Island, Illinois. We have a really lovely campus (one prospective student once joked that we’re the only college he’d visited that actually looked like its postcards) and, as the weather has warmed, I’ve returned to taking my daily walk over the lunch hour.
 We have three major construction projects underway, a lot for a school our size. We’re renovating Old Main, which was built in 1884, originally lit gas lanterns and warmed by stoves in the classrooms. After a century of fiddling with it, we finally resolved to strip out a bunch of “improvements” from days gone by, restore some of its original grandeur and make it capable of supporting 21st century classes.
We have three major construction projects underway, a lot for a school our size. We’re renovating Old Main, which was built in 1884, originally lit gas lanterns and warmed by stoves in the classrooms. After a century of fiddling with it, we finally resolved to strip out a bunch of “improvements” from days gone by, restore some of its original grandeur and make it capable of supporting 21st century classes.
We’re also building Charles D. Lindberg Stadium, where our football team will finally get to have a locker room and seating for 1800. It’s emblematic that our football stadium is actually named for a national debate champion; we’re kind of into the whole scholar-athlete ethos. (We have the sixth greatest number of Academic All-Americans of any school in the country, just behind Stanford and well ahead of Texas.)
And we’re creating a Center for Student Life, which is “fused” to the 4th floor of our library. The Center will combine dining, study, academic support and student activities. It’s stuff we do now but that’s scattered all over creation.
Two things occurred to me on my latest walk. One is that these buildings really are investments in our future. They represent acts of faith that, even in turbulent times, we need to plan and act prudently now to create the future we imagine. And the other is that they represent a remarkable balance: between curricular, co-curricular and extra-curricular, between mind, body and spirit, between strengthening what we’ve always had and building something new.
On one level, that’s just about one college and one set of hopes. But, at another, it strikes me as surprisingly useful guidance for a lot more than that: plan, balance, act, dare.
Oh! So that’s what a Stupid Pill looks like!
In a widely misinterpreted March 25th column, Chuck Jaffe raises the question of whether it’s time to buy a bear market fund. Most folks, he argues, are addicted to performance-chasing. What better time to buy stocks than after they’ve doubled in price? What better time to hedge your portfolio than after they’re been halved? That, of course, is the behavior of the foolish herd. We canny contrarians are working now to hedge our gains with select bets against the market, right?
Talk to money managers and the guys behind bear-market funds, however, and they will tell you their products are designed mostly to be a hedge, diversifying risks and protecting against declines. They say the proper use of their offerings involves a small-but-permanent allocation to the dark side, rather than something to jump into when everything else you own looks to be in the tank.
They also say — and the flows of money into and out of bear-market issues shows — that investors don’t act that way.
At base, he’s not arguing for the purchase of a bear-market fund or a gold fund. He’s using those as tools for getting folks to think about their own short time horizons and herding instincts.

He generously quotes me as making a more-modest observation: that managers, no matter the length or strength of their track records, are quickly dismissed (or ignored) if they lag their peers for more than a quarter. Our reaction tends to be clear: the manager has taken stupid pills and we’re leaving. Jeff Vinik at Magellan: Manager of the Year in 1993, Stupid Pill swallower in ’95, gone in ’96. (Started a hedge fund, making a mint.) Bill Nygren at Oakmark Select: intravenous stupid drip around 2007. (Top 1% since then on both his funds.) Bruce Berkowitz at Fairholme: Manager of the Decade, slipped off to Walgreen’s in 2011 for stupid pills, got trashed and saw withdrawals of a quarter billion dollars a week. (Top 1% in 2012, closed his funds to new investments, launching a hedge fund now).
By way of example, one of the most distinguished small cap managers around is Eric Cinnamond who has exercised the same rigorous absolute-return discipline at three small cap funds: Evergreen, Intrepid and now Aston/River Road. His discipline is really simple: don’t buy or hold anything unless it offers a compelling, absolute value. Over the period of years, that has proven to be a tremendously rewarding strategy for his investors.
When I spoke to Eric late in March, he offered a blunt judgment: “small caps overall appear wildly expensive as people extrapolate valuations from peak profits.” That is, current valuations make sense only if you believe that firms experiencing their highest profits won’t ever see them drop back to normal levels. And so he’s selling stuff as it becomes fully valued, nibbling at a few things (“hard asset companies – natural gas, precious metals – are getting treated as if they’re in a permanent depression but their fundamentals are strong and improving”), accumulating cash and trailing the market. By a mile. Over the twelve months ending March 29, 2013, ARIVX returned 7.5% – which trailed 99% of his small value peers.
The top SCV fund over that period? Scott Barbee’s microcap Aegis Value (AVALX) fund with a 32% return and absolutely no cash on the books. As I noted in a FundAlarm profile, it’s perennially a one- or two-star fund with more going for it than you’d imagine.
Mr. Cinnamond seemed acquainted with the sorts of comments made about his fund on our discussion board: “I bailed on ARIVX back in early September,” “I am probably going to bail soon,” and “in 2012 to the present the funds has ranked, in various time periods, in the 97%-100% rank of SCV… I’d look at other SCV Funds.” Eric nods: “there are investors better suited to other funds. If you lose assets, so be it but I’d rather lose assets than lose my shareholders’ capital.” John Deysher, long-time manager of Pinnacle Value (PVFIX), another SCV fund that insists on an absolute rather than relative value discipline, agrees, “it’s tough holding lots of cash in a sizzling market like we’ve seen . . . [cash] isn’t earning much, it’s dry powder available for future opportunities which of course aren’t ‘visible’ now.”
One telling benchmark is GMO Benchmark-Free Allocation IV (GBMBX). GMO’s chairman, Jeremy Grantham, has long argued that long-term returns are hampered by managers’ fear of trailing their benchmarks and losing business (as GMO so famously did before the 2000 crash). Cinnamond concurs, “a lot of managers ‘get it’ when you read their letters but then you see what they’re doing with their portfolios and wonder what’s happening to them.” In a bold move, GMO launched a benchmark-free allocation fund whose mandate was simple: follow the evidence, not the crowd. It’s designed to invest in whatever offers the best risk-adjusted rewards, benchmarks be damned. The fund has offered low risks and above-average returns since launch. What’s it holding now? European equities (35%), cash (28%) and Japanese stocks (17%). US stocks? Not so much: just under 5% net long.
For those interested in other managers who’ve followed Mr. Cinnamond’s prescription, I sorted through Morningstar’s database for a list of equity and hybrid managers who’ve chosen to hold substantial cash stakes now. There’s a remarkable collection of first-rate folks, both long-time mutual fund managers and former hedge fund guys, who seem to have concluded that cash is their best option.
This list focuses on no-load, retail equity and hybrid funds, excluding those that hold cash as a primary investment strategy (some futures funds, for example, or hard currency funds). These folks all hold over 25% cash as of their last portfolio report. I’ve starred the funds for which there are Observer profiles.
|
Name
|
Ticker
|
Type
|
Cash %
|
|
* ASTON/River Road Independent Value
|
ARIVX
|
Small Value
|
58.4
|
|
Beck Mack & Oliver Global
|
BMGEX
|
World Stock
|
31.8
|
|
Beck Mack & Oliver Partners
|
BMPEX
|
Large Blend
|
27.0
|
|
* Bretton Fund
|
BRTNX
|
Mid-Cap Blend
|
28.7
|
|
Buffalo Dividend Focus
|
BUFDX
|
Large Blend
|
25.6
|
|
Chadwick & D’Amato
|
CDFFX
|
Moderate Allocation
|
33.5
|
|
Clarity Fund
|
CLRTX
|
Small Value
|
67.8
|
|
First Pacific Low Volatility
|
LOVIX
|
Aggressive Allocation
|
27.3
|
|
* FMI International
|
FMIJX
|
Foreign Large Blend
|
60.0
|
|
Forester Discovery
|
INTLX
|
Foreign Large Blend
|
59.6
|
|
FPA Capital
|
FPPTX
|
Mid-Cap Value
|
31.0
|
|
FPA Crescent
|
FPACX
|
Moderate Allocation
|
33.7
|
|
* FPA International Value
|
FPIVX
|
Foreign Large Value
|
34.4
|
|
GaveKal Knowledge Leaders
|
GAVAX
|
Large Growth
|
26.1
|
|
Hennessy Balanced
|
HBFBX
|
Moderate Allocation
|
51.7
|
|
Hennessy Total Return Investor
|
HDOGX
|
Large Value
|
51.1
|
|
Hillman Focused Advantage
|
HCMAX
|
Large Value
|
27.8
|
|
Hussman Strategic Dividend Value
|
HSDVX
|
Large Value
|
53.3
|
|
Intrepid All Cap
|
ICMCX
|
Mid-Cap Value
|
27.5
|
|
Intrepid Small Cap
|
ICMAX
|
Small Value
|
49.3
|
|
NorthQuest Capital
|
NQCFX
|
Large Value
|
29.9
|
|
Oceanstone Fund
|
OSFDX
|
Mid-Cap Value
|
83.3
|
|
Payden Global Equity
|
PYGEX
|
World Stock
|
44.6
|
|
* Pinnacle Value
|
PVFIX
|
Small Value
|
36.8
|
|
PSG Tactical Growth
|
PSGTX
|
World Allocation
|
46.2
|
|
Teberg
|
TEBRX
|
Conservative Allocation
|
34.1
|
|
* The Cook & Bynum Fund
|
COBYX
|
Large Blend
|
32.6
|
|
* Tilson Dividend
|
TILDX
|
Mid-Cap Blend
|
28.0
|
|
Weitz Balanced
|
WBALX
|
Moderate Allocation
|
45.1
|
|
Weitz Hickory
|
WEHIX
|
Mid-Cap Blend
|
30.6
|
(We’re not endorsing all of those funds. While I tried to weed out the most obvious nit-wits, like the guy who was 96% cash and 4% penny stocks, the level of talent shown by these managers is highly variable.)
Mr. Deysher gets to the point this way: “As Buffett says, Rule 1 is ‘Don’t lose capital.’ Rule 2 is ‘Don’t forget Rule 1.’” Steve Romick, long-time manager of FPA Crescent (FPACX), offered both the logic behind FPA’s corporate caution and a really good closing line in a recent shareholder letter:
At FPA, we aspire to protect capital, before seeking a return on it. We change our mind, not casually, but when presented with convincing evidence. Despite our best efforts, we are sometimes wrong. We take our mea culpa and move on, hopefully learning from our mistakes. We question our conclusions constantly. We do this with the approximately $20 billion of client capital entrusted to us to manage, and we simply ask the same of our elected and appointed officials whom we have entrusted with trillions of dollars more.
Nobody has all the answers. Genius fails. Experts goof. Rather than blind faith, we need our leaders to admit failure, learn from it, recalibrate, and move forward with something better. Although we cannot impose our will on this Administration as to Mr. Bernanke’s continued role at the Fed, we would at least like to make our case for a Fed chairman more aware (at least publicly) of the unintended consequences of ultra-easy monetary policy, and one with less hubris. As the author Malcolm Gladwell so eloquently said, “Incompetence is the disease of idiots. Overconfidence is the mistake of experts…. Incompetence irritates me. Overconfidence terrifies me.”
It’s clear that over-confidence can infest pessimists as well as optimists, which was demonstrated in a March Business Insider piece entitled “The Idiot-Maker Rally: Check Out All Of The Gurus Made To Look Like Fools By This Market.” The article is really amusing and really misleading. On the one hand, it does prick the balloons of a number of pompous prognosticators. On the other, it completely fails to ask what happened to invalidate – for now, anyway – the worried conclusions of some serious, first-rate strategists?
Triumph of the optimists: Financial “journalists” and you
It’s no secret that professional journalism seems to be circling a black hole: people want more information, but they want it now, free and simple. That’s not really a recipe for thoughtful, much less profitable, reporting. The universe of personal finance journals is down to two (the painfully thin Money and Kiplinger’s), CNBC’s core audience viewership is down 40% from 2008, the PBS show “Nightly Business Report” has been sold to CNBC in a bid to find viewers, and collectively newspapers have cut something like 40% of their total staff in a decade.
One response has been to look for cheap help: networks and websites look to publish content that’s provided for cheap or for free. Often that means dressing up individuals with a distinct vested interest as if they were journalists.
Case in point: Mellody Hobson, CBS Financial Analyst
I was astounded to see the amiable talking heads on the CBS Morning News turn to “CBS News Financial Analyst Mellody Hobson” for insight on how investors should be behaving (Bullish, not a bubble, 03/18/2013). Ms. Hobson, charismatic, energetic, confident and poised, received a steady stream of softball pitches (“Do you see that there’s a bubble in the stock market?” “I know people are saying we’re entering bubble territory. I don’t agree. We’re far from it. It’s a bull market!”) while offering objective, expert advice on how investors should behave: “The stock market is not overvalued. Valuations are really pretty good. This is the perfect environment for a strong stock market. I’m always a proponent of being in the market.” Nods all around.
The problem isn’t what CBS does tell you about Ms. Hobson; it’s what they don’t tell you. Hobson is the president of a mutual fund company, Ariel Investments, whose only product is stock mutual funds. Here’s a snippet from Ariel’s own website:
Should CBS mention this to you? The Code of Ethics for the Society of Professional Journalists kinda hints at it:
Journalists should be free of obligation to any interest other than the public’s right to know.
Journalists should:
- Avoid conflicts of interest, real or perceived.
- Remain free of associations and activities that may compromise integrity or damage credibility.
- Refuse gifts, favors, fees, free travel and special treatment, and shun secondary employment, political involvement, public office and service in community organizations if they compromise journalistic integrity.
- Disclose unavoidable conflicts.
CBS’s own 2012 Business Conduct Statement exults “our commitment to the highest standards of appropriate and ethical business behavior” and warns of circumstances where “there is a significant risk that the situation presented is likely to affect your business judgment.” My argument is neither that Ms. Hobson was wrong (that’s a separate matter) nor that she acted improperly; it’s that CBS should not be presenting representatives of an industry as disinterested experts on that industry. They need to disclose the conflict. They failed to do so on the air and don’t even offer a biography page for Hobson where an interested party might get a clue.
MarketWatch likewise puts parties with conflicts of interest center-stage in their Trading Deck feature which lives in the center column of their homepage, but at least they warn people that something might be amiss:

That disclaimer doesn’t appear on the homepage with the teasers, but it does appear on the first page of stories written by people who . . . well, probably shouldn’t be taken at face value.
The problem is complicated when a publisher such as MarketWatch mixes journalists and advocates in the same feature, as they do at The Trading Deck, and then headline writers condense a story into eight or ten catchy, misleading words.
The headline says “This popular mutual fund type is losing you money.” The story says global stock funds could boost their returns by up to 2% per year through portfolio optimization, which is a very different claim.
The author bio says “Roberto Rigobon is the Society of Sloan Fellows Professor of Applied Economics at MIT’s Sloan School of Management.” He is a first-class scholar. The bio doesn’t say “and a member of State Street Associates, which provides consulting on, among other things, portfolio optimization.”
The other response by those publications still struggling to hold on is adamant optimism.
In the April 2013 issue of Kiplinger’s Personal Finance, editor Knight Kiplinger (pictured laughing at his desk) takes on Helaine Olen’s Pound Foolish: Exposing the Dark Side of the Personal Finance Industry (2012). She’s a former LA Times personal finance columnist with a lot of data and a fair grasp of her industry. She argues “most of the financial advice published and dished out by the truckload is useless” – its sources are compromised, its diagnosis misses the point and its solutions are self-serving. To which Mr. Kiplinger responds, “I know quite a few longtime Kiplinger readers who might disagree with that.” That’s it. Other than for pointing to Obamacare as a solution, he just notes that . . . well, she’s just not right.
Skipping the stories on “How to Learn to Love (Stocks) Again” and “The 7 Best ETFs to Buy Now,” we come to Jane Bennett Clark’s piece entitled “The Sky Isn’t Falling.” The good news about retirement: a study by the Investment Company Institute says that investment companies are doing a great job and that the good ol’ days of pensions were an illusion. (No mention, yet again, of any conflict of interest that the ICI might have in selecting either the arguments or the data they present.) The title claim comes from a statement of Richard Johnson of the Employee Retirement Benefit Institute, whose argument appears to be that we need to work as long as we can. The oddest statement in the article just sort of glides by: “43% of boomers … and Gen Xers … are at risk of not having enough to cover basic retirement expenses and uninsured health costs.” Which, for 43% of the population, might look rather like their sky is falling.
April’s Money magazine offered the same sort of optimistic take: bond funds will be okay even if interest rates rise, Japan’s coming back, transportation stocks are signaling “full steam ahead for the market,” housing’s back and “fixed income never gets scary.”
Optimism sells. It doesn’t necessarily encourage clear thinking, but it does sell.
Folks interested in examples of really powerful journalism might turn to The Economist, which routinely runs long and well-documented pieces that are entirely worth your time, or the radio duo of American Public Media (APM) and National Public Radio (NPR). Both have really first rate financial coverage daily, serious and humorous. The most striking example of great long-form work is “Unfit for Work: The startling rise of disability in America,” the NPR piece on the rising tide of Americans who apply for and receive permanent disability status. 14 million Americans – adults and children – are now “disabled,” out of the workforce (hence out of the jobless statistics) and unlikely ever to hold a job again. That number has doubled in a generation. The argument is that disability is a last resort for older, less-educated workers who get laid off from a blue collar job and face the prospect of never being able to find a job again. The piece stirred up a storm of responses, some of which are arguable (telling the story of hard-hit Hale County makes people think all counties are like that) and others seem merely to reinforce the story’s claim (the Center for Budget and Policy Priorities says most disabled workers are uneducated and over 50 – which seems consistent with the story’s claim).
Who says mutual funds can’t make you rich?
Forbes magazine published their annual list of “The Richest People on the Planet” (03/04/2013), tracking down almost 1500 billionaires in the process. (None, oddly, teachers by profession.)
MFWire scoured the list for “The Richest Fundsters in the Game” (03/06/2013). They ended up naming nine while missing a handful of others. Here’s their list with my additions in blue:
- Charles Brandes, Brandes funds, #1342, $1.0 billion
- Thomas Bailey, Janus founder, #1342, $1.0 billion
- Mario Gabelli, Gamco #1175, $1.2 billion
- Michael Price, former Mutual Series mgr, #1107, $1.3 billion
- Fayez Sarofim, Dreyfus Appreciation mgr, #1031, $1.4 billion
- Ron Baron, Baron Funds #931, $1.6 billion
- Howard Marks, TCW then Oaktree Capital, #922, $1.65 billion
- Joe Mansueto, Morningstar #793, $1.9 billion
- Ken Fisher, investment guru and source of pop-up ads, #792, $1.9 billion
- Bill Gross, PIMCO, #641, $2.3 billion
- Charles Schwab (the person), Charles Schwab (the company) #299, $4.3 billion
- Paul Desmarais, whose Power Financial backs Putnam #276, $4.5 billion
- Rupert Johnson, Franklin Templeton #215, $5.6 billion
- Charles Johnson, Franklin Templeton #211, $5.7 billion
- Ned Johnson, Fidelity #166, worth $7 billion
- Abby Johnson, Fidelity #74, $12.7 billion
For the curious, here’s the list of billionaire U.S. investors, which mysteriously doesn’t include Bill Gross. He’s listed under “finance.”
The thing that strikes me is how much of these folks I’d entrust my money to, if only because so many became so rich on wealth transfer (in the form of fees paid by their shareholders) rather than wealth creation.
Two new and noteworthy resources: InvestingNerd and Fundfox
I had a chance to speak this week with the folks behind two new (one brand-new, one pretty durn new) sites that might be useful to some of you folks.
InvestingNerd (a little slice of NerdWallet)

NerdWallet launched in 2010 as a tool to find the best credit card offers. It claimed to be able to locate and sort five times as many offers as its major competitors. With time they added other services to help consumers save money. For example the TravelNerd app to help travelers compare costs related to their travel plans, like finding the cheapest transportation to the airport or comparing airport parking prices, the NerdScholar has a tool for assessing law schools based on their placement rates. NerdWallet makes its money from finder’s fees: if you like one of the credit card offers they find for you and sign up for that card, the site receives a bit of compensation. That’s a fairly common arrangement used, for example, by folks like BankRate.com.
On March 27, NerdWallet launched a new site for its investing vertical, InvestingNerd. It brings together advice (TurboTax vs H&R Block: Tax Prep Cost Comparison), analysis (Bank Stress Test Results: How Stressful Were They?) and screening tools.
I asked Neda Jafarzadeh, a public relations representative over at InvestingNerd, what she’d recommend as most distinctive about the site. She offered up three features that she thought would be most intriguing for investors in particular:
- InvestingNerd recently rolled out a new tool – the Mutual Fund Screener. This tool allows investors to find, search and compare over 15,000 funds. In addition, it allows investors to filter through funds based on variables like the fund’s size, minimum required investment, and the fund’s expense ratio. Also, investors can screen funds using key performance metrics such as the fund’s risk-adjusted return rate, annual volatility, market exposure and market outperformance.
- In addition, InvestingNerd has a Brokerage Comparison Tool which provides an unbiased comparison of 69 of the most popular online brokerage accounts. The tool can provide an exact monthly cost for the investor based on their individual trading behavior.
- InvestingNerd also has a blog where we cover news on financial markets and the economy, release studies and analyses related to investing, in addition to publishing helpful articles on various other investment and tax related topics.
Their fund screener is . . . interesting. It’s very simple and updates a results list immediately. Want an equity fund with a manager who’s been around more than 10 years? No problem. Make it a small cap? Sure. Click. You get a list and clickable profiles. There are a couple problems, though. First, they have incomplete or missing explanations of what their screening categories (“outperformance”) means. Second, their results list is inexplicably incomplete: the same search in Morningstar turns up noticeably more funds. Finally, they offer a fund rating (“five stars”) with no evidence of what went into it or what it might tell us about the fund’s future. When I ask with the folks there, it seemed that the rating was driven by risk-adjusted return (alpha adjusted for standard deviation) and InvestingNerd makes no claim that their ratings have predictive validity.
It’s worth looking at and playing with. Their screener, like any, is best thought of as a tool for generating a due diligence list: a way to identify some funds worth digging into. Their articles cover an interesting array of topics (considering a gray divorce? Shopping tips for folks who support gay rights?) and you might well use one of their tools to find the free checking account you’ve always dreamed of.
Fundfox

Fundfox is a site for those folks who wake in the morning and ask themselves, “I wonder who’s been suing the mutual fund industry this week?” or “I wonder what the most popular grounds for suing a fund company this year is?”
Which is to say fund company attorneys, compliance folks, guys at the SEC and me.
It was started by David Smith, who used to work for the largest liability insurance provider to the fund industry, as a simpler, cleaner, more specialized alternative to services such as WestLaw or Lexis. It covers lawsuits filed against mutual funds, period. That really reduces the clutter. The site does include a series of dashboards (what fund types are most frequently the object of suits?) and some commentary.
You can register for free and get a lot of information a la Morningstar or sign up for a premium membership and access serious quantities of filings and findings. There’s a two week trial for the premium service and I really respect David’s decision to offer a trial without requiring a credit card. Legal professionals might well find the combination of tight focus, easy navigation and frequent updates useful.
Introducing: The Elevator Talk
 The Elevator Talk is a new feature which began in February. Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
The Elevator Talk is a new feature which began in February. Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Elevator Talk #3: Bayard Closser, Vertical Capital Income Fund (VCAPX)
 Mr. Closser is president of the Vertical Capital Markets Group and one of the guys behind Vertical Capital Income Fund (VCAPX), which launched on December 30, 2011. VCAPX is structured as an interval fund, a class of funds rare enough that Morningstar doesn’t even track them. An interval fund allows you access to your investment only at specified intervals and only to the extent that the management can supply redemptions without disrupting the portfolio. The logic is that certain sorts of investments are impossible to pursue if management has to be able to accommodate the demands of investors to get their money now. Hedge funds, using lock-up periods, pursue the exact same logic. Given the managers’ experience in structuring hedge funds, that seems like a logical outcome. They do allow for the possibility that the fund might, with time, transition over to a conventional CEF structure:
Mr. Closser is president of the Vertical Capital Markets Group and one of the guys behind Vertical Capital Income Fund (VCAPX), which launched on December 30, 2011. VCAPX is structured as an interval fund, a class of funds rare enough that Morningstar doesn’t even track them. An interval fund allows you access to your investment only at specified intervals and only to the extent that the management can supply redemptions without disrupting the portfolio. The logic is that certain sorts of investments are impossible to pursue if management has to be able to accommodate the demands of investors to get their money now. Hedge funds, using lock-up periods, pursue the exact same logic. Given the managers’ experience in structuring hedge funds, that seems like a logical outcome. They do allow for the possibility that the fund might, with time, transition over to a conventional CEF structure:
Vertical chose an interval fund structure because we determined that it is the best delivery mechanism for alternative assets. It helps protect shareholders by giving them limited liquidity, but also provides the advantages of an open-end fund, including daily pricing and valuation. In addition, it is easy to convert an interval fund to a closed-end fund as the fund grows and we no longer want to acquire assets.
Here’s what Bayard has to say (in a Spartan 172 words) about VCAPX:
A closed-end interval fund, VCAPX invests in whole mortgage loans and first deeds of trust. We purchase the loans from lenders at a deep discount and service them ourselves through our sister company Vertical Recovery Management, which can even restructure loans for committed homeowners to help them keep current on monthly payments.
Increasingly, even small investors are seeking alternative investments to increase diversification. VCAPX can play that role, as its assets have no correlation or a slight negative correlation with the stock market.
While lenders are still divesting mortgages at a deep discount, the housing market is improving, creating a “Goldilocks” effect that may be “just right” for the fund.
VCAPX easily outperformed its benchmark in its first year of operation (Dec. 30, 2011 through Dec. 31, 2012), with a return of 12.95% at net asset value, compared with 2.59% for the Barclays U.S. Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) Index.
At the fund’s maximum 4.50% sales charge, the return was 7.91%. The fund also declared a 4.01% annualized dividend (3.54% after the sales charge).
The fund’s minimum initial investment is $5,000 for retail shares, reduced to $1,000 for IRAs. There’s a front sales load of 4.5% but the fund is available no-load at both Schwab and TDAmeritrade. They offer a fair amount of background, risk and performance information on the fund’s website. You might check under the “Resource Center” tab for copies of their quarterly newsletter.
The Cook and Bynum Fund, Conference Call Highlights
Recently published research laments the fact that actively-managed funds have become steadily less active and more index-like over time.
The changing imperatives of the fund industry have led many managers to become mediocre by design. Their response is driven by the anxious desire for so-called “sticky” assets. The strategy is simple: design a product to minimize the risk that it will ever spectacularly trail its peer group. If you make your fund very much like its benchmark, you will never be a singular disaster and so investors (retirement plan investors, particularly) will never be motivated to find something better. The fact that you never excel is irrelevant. The result is a legion of large, expensive, undistinguished funds who seek safety in the herd.
 The Cook and Bynum Fund (COBYX) strikes me as the antithesis of those. Carefully constructed, tightly focused, and intentionally distinct. On Tuesday, March 5, we spoke with Richard Cook and Dowe Bynum in the first of three conversations with distinguished managers who defy that trend through their commitment to a singular discipline: buy only the best. For Richard and Dowe, that translates to a portfolio with only seven holdings and a 34% cash stake. Since inception (through early March, 2013), they managed to capture 83% of the market’s gains with only 50% of its volatility; in the past twelve months, Morningstar estimates that they captured just 7% of the market’s downside.
The Cook and Bynum Fund (COBYX) strikes me as the antithesis of those. Carefully constructed, tightly focused, and intentionally distinct. On Tuesday, March 5, we spoke with Richard Cook and Dowe Bynum in the first of three conversations with distinguished managers who defy that trend through their commitment to a singular discipline: buy only the best. For Richard and Dowe, that translates to a portfolio with only seven holdings and a 34% cash stake. Since inception (through early March, 2013), they managed to capture 83% of the market’s gains with only 50% of its volatility; in the past twelve months, Morningstar estimates that they captured just 7% of the market’s downside.
Among the highlights of the call for me:
- The guys are willing to look stupid. There are times, as now, when they can’t find stocks that meet their quality and valuation standards. The rule for such situations is simply: “When compelling opportunities do not exist, it is our obligation not to put capital at risk.” They happily admit that other funds might well reap short-term gains by running with the pack, but you “have to be willing to look stupid.” Their current cash stake is about 34%, “the highest cash level ever in the fund.” That’s not driven by a market call; it’s a simple residue of their inability to find great opportunities.
- The guys are not willing to be stupid. Richard and Dowe grew up together and are comfortable challenging each other. Richard knows the limits of Dowe’s knowledge (and vice versa), “so we’re less likely to hold hands and go off the cliff together.” In order to avoid that outcome, they spend a lot of time figuring out how not to be stupid. They relegate some intriguing possibilities to the “too hard pile,” those businesses that might have a great story but whose business model or financials are simply too hard to forecast with sufficient confidence. They think about common errors (commitment bias, our ability to rationalize why we’re not going to stop doing something once we’ve started, chief among them) and have generated a set of really interesting tools to help contain them. They maintain, for example, a list all of the reasons why they don’t like their current holdings. In advance of any purchase, they list all of the conditions under which they’d quickly sell (“if their star CEO leaves, we do too”) and keep that on top of their pile of papers concerning the stock.
- They’re doing what they love. Before starting Cook & Bynum (the company), both of the guys had high-visibility, highly-compensated positions in financial centers. Richard worked for Tudor Investments in Stamford, CT, while Dowe was with Goldman Sachs in New York. The guys believe in a fundamental, value- and research-driven, stock-by-stock process. What they were being paid to do (with Tudor’s macro event-driven hedge fund strategies for Richard) was about as far from what they most wanted as they could get. And so they quit, moved back to Alabama and set up their own shop to manage their own money and the investments of high net-worth individuals. They created Cook & Bynum (the fund) in response to an investor’s request for a product accessible to family and friends. The $250 million invested with them (about $100 million in the fund) includes 100% of their own liquid net worth, with their investment split between the fund and the partnerships. Since both sets of vehicles use the same fees and structure, there’s no conflict between the two.
- They do prodigious research without succumbing to the “gotta buy something” impulse. While they spend the majority of their time in their offices, they’re also comfortable with spending two or three weeks at a time on the road. Their argument is that they’ve got to understand the entire ecosystem in which a firm operates – from the quality of its distribution network to the feelings of its customers – which they can only do first-hand. Nonetheless, they’ve been pretty good at resisting “deal momentum.” They spent, for example, some three weeks traveling around Estonia, Poland and Hungary. Found nothing compelling. Traveled Greece and Turkey and learned a lot, including how deeply dysfunctional the Greek economy is, but bought nothing.
- They’re willing to do what you won’t. Most of us profess a buy low / buy the unloved / break from the herd / embrace our inner contrarian ethos. And most of us are deluded. Cook and Bynum seem rather less so: they’re holding cash now while others buy stocks after the market has doubled and profits margins hit records but in the depth of the 2008 meltdown they were buyers. (They report having skipped Christmas presents in 2008 in order to have extra capital to invest.) As the market bottomed in March 2009, the fund was down to 2% cash.
Bottom Line: the guys seem to be looking for two elusive commodities. One is investments worth pursuing. The other is investing partners who share their passion for compelling investments and their willingness to let other investors charge off in a herd. Neither is as common as you might hope.
For folks interested but unable to join us, here’s the complete audio of the hour-long conversation.
The COBYX conference call
When you click on the link, the file will load in your browser and will begin playing after it’s partially loaded. If the file downloads, instead, you may have to double-click to play it.
We periodically invite our colleague, Charles Boccadoro, to share his perspectives on funds which were the focus of our conference calls. Charles’ ability to apprehend and assess tons of data is, we think, a nice complement to my strengths which might lie in the direction of answering the questions (1) does this strategy make any sense? And (2) what’s the prospect that they can pull it off? Without further ado, here’s Charles on Cook and Bynum
Inoculated By Value
To describe Richard P. Cook and J. Dowe Bynum (C&B) as value investors would be accurate, but certainly not adequate. Their website is rich with references to value investment principles championed by Benjamin Graham, John Burr Williams, Charlie Munger, and Warren Buffet. “The value investing inoculation took immediately,” C&B explain, after reading Mr. Buffett’s biography in high school. They have been investing together literally since childhood and at age 23 they actually tried to start their own mutual fund. That did not happen, but years later in 2001 they established Cook & Bynum Capital Management and in mid-2009 they launched their namesake The Cook & Bynum Fund COBYX, which turned out to be perfect timing.
Like many experienced investors on MFO, C&B do not view volatility as risk, but as opportunity. That said, the lack of volatility in 43 months of COBYX performance through February 2013 is very alluring and likely helped propel the fund’s popularity, now with $102M AUM. Its consistent growth rate resembles more a steady bond fund, say PONDX, than an equity fund. The fund received a 5-Star Morningstar Rating for the 3-year period ending mid-2012.
Other than strictly adhering to the three most important words of value investing (“Margin of Safety”) when assessing stock price against inherent value, C&B do not impose explicit drawdown control or practice dynamic allocation, like risk-parity AQRNX or long-short ARLSX. They try instead to buy wonderful businesses at discounted prices. To quote Mr. Buffett: “If you’re right about what, you don’t have to worry about when very much.”
Fortunately, history is on their side. The chart below depicts drawdowns for the last 50 years, comparing value versus growth large cap fund averages. Value funds indeed generally suffer smaller and shorter drawdowns. But not always. The term “value trap” became ubiquitous during the financial collapse of 2008, when many highly respected, long established, and top performing value funds (prime example DODGX) were simply hammered. And, when the forest is burning, all the trees go with it.
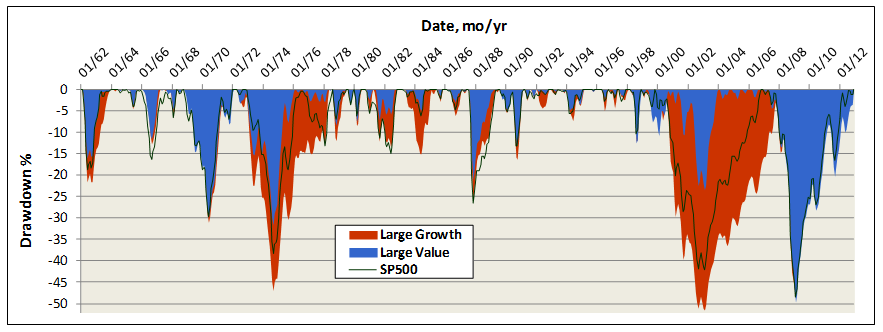
While Mr. Cook and Mr. Bynum must have managed their private accounts through such turbulent times, COBYX has enjoyed bull market conditions since its inception. (Perhaps a reluctant bull, but nonetheless…) Still, when the market dipped 7% in May 2012, COBYX did not drop at all. In September 2011, SP500 dropped 16%, COBYX dipped only 5%. Its biggest drawdown was June 2010 at 9% versus 13% for the market. The tame behavior is due partly to C&B’s propensity to hold cash. Not as a strategy, they explain, but as residual to value opportunities available. They unloaded Kraft, for example, shortly after the company split its international and domestic businesses. Here is an excerpt from COBYX’s 2012 annual report explaining their move:
Despite neither of the companies’ fundamental business prospects changing one iota, the market reacted to the news by trading both of the stocks higher. We used this opportunity to liquidate our stake in both companies. It is popular, even within our value discipline, for investors to advocate various financial engineering strategies in an attempt to drive near-term stock price appreciation rather than to focus on a company’s long-term cash flows – where real value resides.
C&B take pride in not being “closet indexers” to their benchmarks SP500 and MSCI All Country World Index (ACWI). So far they have tended to hold consumer defensive stocks, like Wal-Mart, Procter & Gamble, and Coca-Cola. Although more recently, they own Microsoft, which accounts for 16% of the portfolio. COBYX’s lifetime correlation to SP500 is 66% and its beta is only 0.47.
The strategy has delivered handsomely. Just how good is it? Below compares COBYX with several other Morningstar 5 star funds, including Charles Akre’s AKREX, Steven Romick’s FPA Crescent Fund, Donald Yacktman’s YAFFX, Sequoia Fund (perhaps the greatest fund ever), plus landmark Berkshire Hathaway.
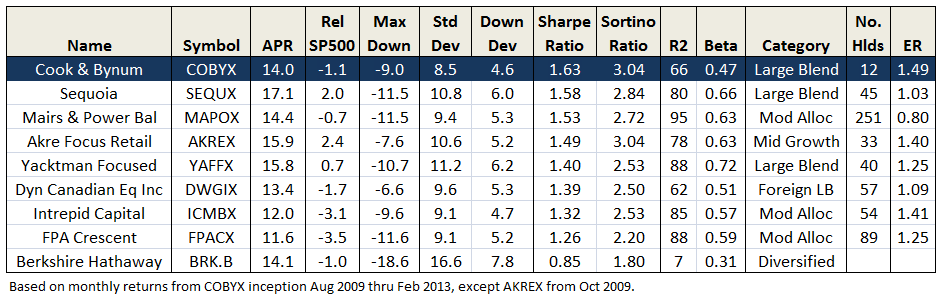
Since COBYX inception, it has produced the highest risk adjusted returns, based on both Sharpe and Sortino Ratios, with the lowest standard and downside volatilities. It has delivered more than 90% of SP500 total return with less than 60% of its volatility. Interestingly, all of these top-performing mutual funds have low beta against SP500, like COBYX, but again for the record, C&B reject metrics like beta: “Risk is not volatility.”
COBYX is also highly concentrated. As of December 2012, it held only seven equities. C&B’s strategy is to focus only on companies whose businesses they can understand – depth of insight is the edge they seek. They employ Kelly Criterion to size positions in their portfolio, which represents an implicit form of risk management. John Kelly developed it in 1950s at AT&T’s Bell Labs to optimize transmission rate through long distance phone lines. Edward Thorpe then famously employed the technique to “Beat the Dealer” and later to help optimize his hedge fund investments at Princeton/Newport Partners. In C&B’s implementation, Kelly is edge over odds, or expected returns over range of outcomes. What is currently their biggest position? Cash at 34%.
Bottom-line: Hard not to love this young fund, performance to date, and philosophy employed by its managers. High ER, recently dropped from 1.88 to 1.49, has been its one detractor. Hopefully, ER reduction continues with AUM growth, since world-stock fund median is already a hefty 1.20 drag.
(Thank you, sir! David)
Conference Call Upcoming: RiverPark Wedgewood Growth, April 17
Large-cap funds, and especially large large-cap funds, suffer from the same tendency toward timidity and bloat that I discussed above. On average, actively-managed large growth funds hold 70 stocks and turn over 100% per year. The ten largest such funds hold 311 stocks on average and turn over 38% per year.
The well-read folks at Wedgewood see the path to success differently. Manager David Rolfe endorses Charles Ellis’s classic essay, “The Losers Game” (Financial Analysts Journal, July 1975). Reasoning from war and sports to investing, Ellis argues that losers games are those where, as in amateur tennis:
The amateur duffer seldom beats his opponent, but he beats himself all the time. The victor in this game of tennis gets a higher score than the opponent, but he gets that higher score because his opponent is losing even more points.
Ellis argues that professional investors, in the main, play a losers game by becoming distracted, unfocused and undistinguished. Mr. Rolfe and his associates are determined not to play that game. They position themselves as “contrarian growth investors.” In practical terms, that means:
- They force themselves to own fewer stocks than they really want to. After filtering a universe of 500-600 large growth companies, Wedgewood holds only “the top 20 of the 40 stocks we really want to own.” Currently, 55% of the fund’s assets are in its top ten picks.
- They buy when other growth managers are selling. Most growth managers are momentum investors, they buy when a stock’s price is rising. Wedgewood would rather buy during panic than during euphoria.
- They hold far longer once they buy. The historical average for Wedgewood’s separate accounts which use this exact discipline is 15-20% turnover and the fund is around 25%.
- And then they spend a lot of time watching those stocks. “Thinking and acting like business owners reduces our interest to those few businesses which are superior,” Rolfe writes, and he maintains a thoughtful vigil over those businesses.
David is articulate, thoughtful and successful. His reflections on “out-thinking the index makers” strike me as rare and valuable, as does his ability to manage risk while remaining fully invested.
Our conference call will be Wednesday, April 17, from 7:00 – 8:00 Eastern.
How can you join in?
 If you’d like to join in, just click on register and you’ll be taken to the Chorus Call site. In exchange for your name and email, you’ll receive a toll-free number, a PIN and instructions on joining the call. If you register, I’ll send you a reminder email on the morning of the call.
If you’d like to join in, just click on register and you’ll be taken to the Chorus Call site. In exchange for your name and email, you’ll receive a toll-free number, a PIN and instructions on joining the call. If you register, I’ll send you a reminder email on the morning of the call.
Remember: registering for one call does not automatically register you for another. You need to click each separately. Likewise, registering for the conference call mailing list doesn’t register you for a call; it just lets you know when an opportunity comes up.
Observer Fund Profiles
Each month the Observer provides in-depth profiles of between two and four funds. Our “Most Intriguing New Funds” are funds launched within the past couple years that most frequently feature experienced managers leading innovative newer funds. “Stars in the Shadows” are older funds that have attracted far less attention than they deserve. This month’s lineup features:
The Cook and Bynum Fund (COBYX): an updated profile of this concentrated value fund.
Whitebox Long Short Equity (WBLSX): the former hedge fund has a reasonably distinctive, complicated strategy and I haven’t had much luck in communicating with fund representatives over the last month or so about the strategy. Given a continued high level of reader interest in the fund, it seemed prudent to offer, with this caveat, a preliminary take on what they do and how you might think about it.
Launch Alert: BBH Global Core Select (BBGRX)
There are two things particularly worth knowing about BBH (for Brown Brothers Harriman) Core Select (BBTRX): (1) it’s splendid and (2) it’s closed. It’s posted a very consistent pattern of high returns and low risk, which eventually drew $5 billion to the fund and triggered its soft close in November. At the moment that BBH closed Core Select, they announced the launch of Global Core Select. That fund went live on March 28, 2013.
Global Core Select will be co-managed by Regina Lombardi and Tim Hartch, two members of the BBH Core Select investment team. Hartch is one of Core Select’s two managers; Lombardi is one of 11 analysts. The Fund is the successor to the BBH private investment partnership, BBH Global Funds, LLC – Global Core Select, which launched on April 2, 2012. Because the hedge fund had less than a one year of operation, there’s no performance record for them reported. The minimum initial investment in the retail class is $5,000. The expense ratio is capped at 1.50% (which represents a generous one basis-point sacrifice on the adviser’s part).
The strategy snapshot is this: they’ll invest in 30-40 mid- to large-cap companies in both developed and developing markets. They’ll place at least 40% outside the US. The strategy seems identical to Core Select’s: established, cash generative businesses that are leading providers of essential products and services with strong management teams and loyal customers, and are priced at a discount to estimated intrinsic value. They profess a “buy and own” approach.
What are the differences: well, Global Core Select is open and Core Select isn’t. Global will double Core’s international stake. And Global will have a slightly-lower target range: its investable universe starts at $3 billion, Core’s starts at $5 billion.
I’ll suggest three reasons to hesitate before you rush in:
- There’s no public explanation of why closing Core and opening Global isn’t just a shell game. Core is not constrained in the amount of foreign stock it owns (currently under 20% of assets). If Core closed because the strategy couldn’t handle the additional cash, I’m not sure why opening a fund with a nearly-identical strategy is warranted.
- Expenses are likely to remain high – even with $5 billion in a largely domestic, low turnover portfolio, BBH charges 1.25%.
- Others are going to rush in. Core’s record and unavailability is going to make Global the object of a lot of hot money which will be rolling in just as the market reaches its seasonal (and possibly cyclical) peak.
That said, this strategy has worked elsewhere. The closed Oakmark Select (OAKLX) begat Oakmark Global Select (OAKWX) and closed Leuthold Core (LCORX) led to Leuthold Global (GLBLX). In both cases, the young fund handily outperformed its progenitor. Here’s the nearly empty BBH Global Core Select homepage.
Launch Alert: DoubleLine Equities Small Cap Growth Fund (DLESX)
DoubleLine continues to pillage TCW, the former home of its founder and seemingly of most of its employees. DoubleLine, which manages more than $53 billion in mostly fixed income assets, has created a DoubleLine Equity LP division. The unit’s first launch, DoubleLine Equities Small Cap Growth Fund, occurs April 1, 2013. Growth Fund (DLEGX) and Technology Fund (DLETX) are close behind in the pipeline.
Husam Nazer, who oversaw $4-5 billion in assets in TCW’s Small and Mid-Cap Growth Equities Group, will manage the new fund. DoubleLine hired Nazer’s former TCW investing partner, Brendt Stallings, four stock analysts and a stock trader. Four of the new hires previously worked for Nazer and Stallings at TCW.
The fund will invest mainly in stocks comparable in size to those in the Russell US Growth index (which tops out at around $4 billion). They’ll invest mostly in smaller U.S. companies and in foreign small caps which trade on American exchanges through ADRs. The manager professes a “bottom up” approach to identify investment. He’s looking for a set of reasonable and unremarkable characteristics: consistent and growing earnings, strong balance sheet, good competitive position, good management and so on. The minimum initial investment in the retail class is $2,000, reduced to $500 for IRAs. The expense ratio is capped at 1.40%.
I’ll suggest one decent reason to hesitate before you bet that DoubleLine’s success in bonds will be matched by its success in stocks:
Mr. Nazer’s last fund wasn’t really all that good. His longest and most-comparable charge is TCW Small Cap Growth (TGSNX). Morningstar rates it as a two-star fund. In his eight years at the fund, Mr. Nazer had a slow start (2005 was weak) followed by four very strong years (2006-2009) and three really bad ones (2010-2012). The fund’s three-year record trails 97% of its peers. It has offered consistently above-average to high volatility, paired with average to way below-average returns. Morningstar’s generally-optimistic reviews of the fund ended in July 2011. Lipper likewise rates it as a two-star fund over the past five years.
The fund might well perform brilliantly, assuming that Mr. Gundlach believed he had good reason to import this team. That said, the record is not unambiguously positive.
Funds in Registration
New mutual funds must be registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission before they can be offered for sale to the public. The SEC has a 75-day window during which to call for revisions of a prospectus; fund companies sometimes use that same time to tweak a fund’s fee structure or operating details. Every day we scour new SEC filings to see what opportunities might be about to present themselves. Many of the proposed funds offer nothing new, distinctive or interesting. Some are downright horrors of Dilbertesque babble (see “Synthetic Reverse Convertibles,” below).
Funds in registration this month won’t be available for sale until, typically, the beginning of June 2013. We found a handful of no-load, retail funds in the pipeline, notably:
Robeco Boston Partners Global Long/Short Fund will offer a global take on Boston Partner’s highly-successful long/short strategy. They expect at least 40% international exposure, compared to 10% in their flagship Long/Short Equity Fund (BPLEX) and 15% in the new Long/Short Research Fund (BPRRX). There are very few constraints in the prospectus on their investing universe. The fund will be managed by Jay Feeney, an original Boston Partner, co-CEO and CIO-Equities, and Christopher K. Hart, Equity Portfolio Manage. The minimum initial investment in the retail class is $2,500. The expense ratio will be 3.77% after waivers. Let me just say: “Yikes.” At the risk of repeating myself, “Yikes!” With a management fee of 1.75%, this is likely to remain a challenging case.
T. Rowe Price Global Allocation Fund will invest in stocks, bonds, cash and hedge funds. Yikes! T. Rowe is getting you into hedge funds. They’ll active manage their asset allocation. The baseline is 30% US stocks, 30% international stocks, 20% US bonds, 10% international bonds and 10% alternative investments. A series of macro judgments will allow them to tweak those allocations. The fund will be managed by Charles Shriver, lead manager for their Balanced, Personal Strategy and Spectrum funds. The minimum initial purchase is $2500, reduced to $1000 for IRAs. Expense ratio will be 1.05%.
Details on these funds and the list of all of the funds in registration are available at the Observer’s Funds in Registration page or by clicking “Funds” on the menu atop each page.
Manager Changes: Two giants begin to step back
On a related note, we also tracked down 71 fund manager changes. Those include decisions by two fund company founders to begin lightening their loads. Nicholas Kaiser, president of Saturna Investments which advises the Sextant and Amana funds, no longer co-manages Sextant Growth (SSGFX) and John Kornitzer, founder of Kornitzer Capital which advises the Buffalo funds, stepped back from Buffalo Dividend Focus (BUFDX) four months after launch.
Snowball on the transformative power of standing around, doing little
I’m occasionally asked to contribute 500 words to Amazon’s Money & Markets blog. Amazon circulates a question (in this case, “how should investors react to sequestration?”) and invites responses. I knew they won’t publish “oh, get real,” so I wrote something just slightly longer.
Don’t Just Do Something. Stand There.
When exactly did the old midshipman’s rule, “When in danger or in doubt, run in circles, scream and shout,” get enshrined as investing advice?
There are just three things we don’t know about sequestration: (1) what will happen, (2) how long it will last and (3) what will follow. Collectively, they tell you that the most useful thing a stock investor might do in reaction to the sequestration is, nothing. Whatever happens will certainly roil the markets but stock markets are forever being roiled. This one is no different than all of the others. Go check your portfolio and ask four things:
- Do I have an adequate reserve in a cash-management account to cover my basic expenses – that is, to maintain a normal standard of living – if I need six months to find a new job?
- Do I have very limited stock exposure (say, under 20%) in the portion of the portfolio that I might reasonably need to tap in the next three or five years?
- Do I have a globally diversified portfolio in the portion that I need to grow over a period of 10 years or more?
- Am I acting responsibly in adding regularly to each?
If yes, the sequestration is important, but not to your portfolio. If no, you’ve got problems to address that are far more significant than the waves caused by this latest episode of our collective inability to manage otherwise manageable problems. Address those, as promptly and thoughtfully as you can.
The temptation is clear: do something! And the research is equally clear: investors who reactively do something lose. Those who have constructed sensible portfolios and leave them be, win.
Be a winner: stand there.
Happily, the other respondents were at least as sensible. There’s the complete collection.
Briefly Noted ….
Vanguard is shifting
Perhaps you should, as well? Vanguard announced three shifts in the composition of income sleeve of their Target Retirement Funds.
- They are shifting their bond exposure from domestic to international. Twenty percent of each fund’s fixed income exposure will be reallocated to foreign bonds through investment in Vanguard Total International Bond Index Fund.
- Near term funds are maintaining their exposure to TIPS but are shifting all of their allocation to the Short-Term Inflation-Protected Securities Index Fund rather than Vanguard Inflation-Protected Securities Fund.
- The Retirement Income and Retirement 2010 funds are eliminating their exposure to cash. The proceeds will be used to buy foreign bonds.
PIMCO retargets
As of March 8, 2013 the PIMCO Global Multi-Asset Fund changed its objective from “The Fund seeks total return which exceeds that of a blend of 60% MSCI World Index/40% Barclays U.S. Aggregate Index” to “The Fund seeks maximum long-term absolute return, consistent with prudent management of portfolio volatility.” At the same time, the Fund’s secondary index is the 1 Month USD LIBOR Index +5% which should give you a good idea of what they expect the fund to be able to return over time.
PIMCO did not announce any change in investment policies but did explain that the new, more conservative index “is more closely aligned with the Fund’s investment philosophy and investment objective” than a simple global stock/bond blend would be.
Capital Group / American Funds is bleeding
Our recent series on new fund launches over the past decade pointed out that, of the five major fund groups, the American Funds had – by far – the worst record. They managed to combine almost no innovation with increasingly bloated funds whose managers were pleading for help. A new report in Pensions & Investments (Capital Group seeking to rebuild, 03/18/2013) suggests that the costs of a decade spent on cruise control were high: the firm’s assets under management have dropped by almost a half-trillion dollars in six years with the worst losses coming from the institutional investment side.
Matthews and the power of those three little words.
Several readers have noticed that Matthews recently issued a supplement to the Strategic Income Fund (MAINX) portfolio. The extent of the change is this: the advisor dropped the words “and debt-related” from a proviso that at least 50% of the fund’s portfolio would be invested in “debt and debt-related securities” which were rated as investment-grade.
In talking with folks affiliated with Matthews, it turns out that the phrase “and debt-related” put them in an untenable bind. “Debt-related securities” includes all manner of derivatives, including the currency futures contracts which allow them to hedge currency exposure. Such derivatives do not receive ratings from debt-rating firms such as Fitch meaning that it automatically appeared as if the manager was buying “junk” when no such thing was happening. That became more complicated by the challenge of assigning a value to a futures contract: if, hypothetically, you buy $1 million in insurance (which you might not need) for a $100 premium, do you report the value of $100 or $1 million?
In order to keep attention focused on the actual intent of the proviso – that at least 50% of the debt securities will be investment grade – they struck the complicating language.
Good news and bad for AllianzGI Opportunity Fund shareholders
Good news, guys: you’re getting a whole new fund! Bad news: it’s gonna cost ya.
AllianzGI Opportunity Fund (POPAX) is a pretty poor fund. During the first five years of its lead manager’s ten year tenure, it wasn’t awful: two years with well above average returns, two years below average and one year was a draw. The last five have been far weaker: four years way below average, with 2013 on course for another. Regardless of returns, the fund’s volatility has been consistently high.
The clean-up began March 8 2013 with the departure of co-manager Eric Sartorius. On April 8 2013, manager Mike Corelli departs and the fund’s investment strategy gets a substantial rewrite. The current strategy “focuses on bottom-up, fundamental analysis” of firms with market caps under $2 billion. Ironically, despite the “GI” designation in the name (code for Growth & Income, just as TR is Total Return and AR is Absolute Return), the prospectus assures us that “no consideration is given to income.” The new strategy will “utilize a quantitative process to focus on stocks of companies that exhibit positive change, sustainability, and timely market recognition” and the allowable market cap will rise to $5.3 billion.
Two bits of bad news. First, it’s likely to be a tax headache. Allianz warns that “the Fund will liquidate a substantial majority of its existing holdings” which will almost certainly trigger a substantial 2013 capital gains bill. Second, the new managers (Mark Roemer and Jeff Parker) aren’t very good. I’m sure they’re nice people and Mr. Parker is CIO for the firm’s U.S. equity strategies but none of the funds they’ve been associated with (Mr. Roemer is a “managed volatility” specialist, Mr. Parker focuses on growth) have been very good and several seem not to exist anymore.
Direxion splits
A bunch of Direxion leveraged index and reverse index products split either 2:1 or 3:1 at the close of business on March 28, 2013. They were
|
Fund Name
|
Split Ratio
|
|
Direxion Daily Financial Bull 3X Shares
|
3 for 1
|
|
Direxion Daily Retail Bull 3X Shares
|
3 for 1
|
|
Direxion Daily Emerging Markets Bull 3X Shares
|
3 for 1
|
|
Direxion Daily S&P 500 Bull 3X Shares
|
3 for 1
|
|
Direxion Daily Real Estate Bull 3X Shares
|
2 for 1
|
|
Direxion Daily Latin America Bull 3X Shares
|
2 for 1
|
|
Direxion Daily 7-10 Year Treasury Bull 3X Shares
|
2 for 1
|
|
Direxion Daily Small Cap Bull 3X Shares
|
2 for 1
|
Small Wins for Investors
Effective April 1, 2013, Advisory Research International Small Cap Value Fund’s (ADVIX) expense ratio is capped at 1.25%, down from its current 1.35%. Morningstar will likely not reflect this change for a while
Aftershock Strategies Fund (SHKNX) has lowered its expense cap, from 1.80 to 1.70%. Their aim is to “preserve capital in a challenging investment environment.” Apparently the absence of a challenging investment environment inspired them to lose capital: the fund is down 1.5% YTD, through March 29, 2013.
Good news: effective March 15, 2013, Clearwater Management increased its voluntary management fee waiver for three of its Clearwater Funds (Core, Small Companies, Tax-Exempt Bond). Bad news, I can’t confirm that the funds actually exist. There’s no website and none of the major the major tracking services now recognizes the funds’ ticker symbols. Nothing posts at the SEC suggests cessation, so I don’t know what’s up.
 Fidelity is offering to waive the sales loads on an ever-wider array of traditionally load-only funds through its supermarket. I learned of the move, as I learn of so many things, from the folks at MFO’s discussion board. The list of load-waived funds is detailed in msf’s thread, entitled Fidelity waives loads. A separate thread, started by Scott, with similar good news announces that T. Rowe Price funds are available without a transaction fee at Ameritrade.
Fidelity is offering to waive the sales loads on an ever-wider array of traditionally load-only funds through its supermarket. I learned of the move, as I learn of so many things, from the folks at MFO’s discussion board. The list of load-waived funds is detailed in msf’s thread, entitled Fidelity waives loads. A separate thread, started by Scott, with similar good news announces that T. Rowe Price funds are available without a transaction fee at Ameritrade.
Vanguard is dropping expenses on two more funds including the $69 billion Wellington (VWELX) fund. Wellington’s expenses have been reduced in three consecutive years.
Closings
American Century Equity Income (TWEAX) closed to new investors on March 29, 2013. The fund recently passed $10 billion in assets, a hefty weight to haul. The fund, which has always been a bit streaky, has trailed its large-value peers in five of the past six quarters which might have contributed to the decision to close the door.
The billion-dollar BNY Mellon Municipal Opportunities Fund (MOTIX) closed to new investors on March 28, 2013.
Effective April 30, 2013 Cambiar Small Cap Fund (CAMSX) will close to new investors. It’s been a very strong performer and has drawn $1.4 billion in assets.
Prudential Jennison Mid Cap Growth (PEEAX) will close to new investors on April 8, 2013. The fund’s assets have grown substantially over the past three years from under $2 billion at the beginning of 2010 to over $8 billion as of February 2013. While some in the media describe this as “a shareholder-friendly decision,” there’s some question about whether Prudential friended its shareholders a bit too late. The fund’s 10 year performance is top 5%, 5-year declines to top 20%, 3 year to top 40% and one year to mediocre.
Effective April 12, 2013, Oppenheimer Developing Markets Fund (ODMAX) closed to both new and existing shareholders. In the business jargon, that’s a “hard close.”
Touchstone Sands Capital Select Growth (PTSGX) and Touchstone Sands Institutional Growth (CISGX), both endorsed by Morningstar’s analysts, will close to new investors effective April 8, 2013. Sands is good and also subadvises from for GuideStone and MassMutual.
Touchstone has also announced that Touchstone Merger Arbitrage (TMGAX), subadvised by Longfellow Investment Management, will close to new investors effective April 8. The two-year old fund has about a half billion in assets and management wants to close it to maintain performance.
Effective April 29, 2013, Westcore International Small-Cap Fund (WTIFX) will close to all purchase activity with the exception of dividend reinvestment. That will turn the current soft-close into a hard-close.
Old Wine in New Bottles
On or about May 31, 2013. Alger Large Cap Growth Fund (ALGAX) will become Alger International Growth Fund, but its investment objective to seek long-term capital appreciation will not change. The Fund will be managed by Pedro V. Marcal. At the same time, Alger China-U.S. Growth Fund (CHUSX) will become Alger Global Growth Fund, but its investment objective to seek long-term capital appreciation will not change. The Fund will continue to be managed by Dan Chung and Deborah Vélez Medenica, with the addition of Pedro V. Marcal. These are both fundamentally sorrowful funds. About the only leads I have on Mr. Marcal is that he’s either a former Olympic fencer for Portugal (1960) or the author of a study on market timing and technical analysis. I’m not sure which set of skills would contribute more here.
Effective April 19, BlackRock S&P 500 Index (MASRX) will merge into BlackRock S&P 500 Stock (WFSPX). Uhhh … they’re both S&P500 index funds. The reorganization will give shareholders a tiny break in expenses (a drop from 13 bps to 11) but will slightly goof with their tax bill.
Buffalo Micro Cap Fund (BUFOX) will become Buffalo Emerging Opportunities Fund, around June 3, 2013. That’s a slight delay in the scheduled renaming, which should have already taken place under the original plan. The renamed beast will invest in “domestic common stocks, preferred stocks, convertible securities, warrants and rights of companies that, at the time of purchase by the Fund, have market capitalizations of $1 billion or less.
Catalyst Large Cap Value Fund (LVXAX) will, on May 27 2013, become Catalyst Insider Buying Fund. The fund will no longer be constrained to invest in large cap value stocks.
Effective April 1, 2013, Intrepid All Cap Fund (ICMCX) changed its name to Intrepid Disciplined Value Fund. There was a corresponding change to the investment policies of the fund to allow it to invest in common stocks and “preferred stocks, convertible preferred stocks, warrants and foreign securities, which include American Depositary Receipts (ADRs).”
PIMCO Worldwide Fundamental Advantage TR Strategy (PWWIX) will change its name to PIMCO Worldwide Fundamental Advantage AR Strategy. Also, the fund will change from a “total return” strategy to an “absolute return” strategy, which has more flexibility with sector exposures, non-U.S. exposures, and credit quality.
Value Line changed the names of Value Line Emerging Opportunities Fund to the Value Line Small Cap Opportunities Fund (VLEOX) and the Value Line Aggressive Income Trust to the Value Line Core Bond Fund (VAGIX).
Off to the Dustbin of History
AllianzGI Focused Opportunity Fund (AFOAX) will be liquidated and dissolved on or about April 19, 2013.
Armstrong Associates (ARMSX) is merging into LKCM Equity Fund (LKEQX) effective on or about May 10, 2013. C.K. Lawson has been managing ARMSX for modestly longer – 45 years – than many of his peers have been alive.
Artio Emerging Markets Local Debt (AEFAX) will liquidate on April 19, 2013.
You thought you invested in what? The details of db X-trackers MSCI Canada Hedged Equity Fund will, effective May 31 2013, be tweaked just a bit. The essence of the tweak is that it will become db X-trackers MSCI Germany Hedged Equity Fund (DBGR).
The Forward Focus and Forward Strategic Alternatives funds will be liquidated pursuant to a Board-approved Plan of Liquidation on or around April 30, 2013.
The Guardian Fund (LGFAX) guards no more. It is, as of March 28, 2013, a former fund.
ING International Value Choice Fund (IVCAX) will merge with ING International Value Equity Fund (NIVAX, formerly ING Global Value Choice Fund), though the date is not yet set.
Janus Global Research Fund merged into Janus Worldwide Fund (JAWWX) effective on March 15, 2013.
In a minor indignity, Dreman has been ousted as the manager of MIST Dreman Small Cap Value Portfolio, an insurance product distributed by MET Investment Series Trust (hence “MIST”) and replaced by J.P. Morgan Investment Management. Effective April 29, 2013, the fund becomes JPMorgan Small Cap Value Portfolio. No-load investors can still access Mr. Dreman’s services through Dreman Contrarian Small Cap Value (DRSVX). Folks with the attention spans of gnats and a tendency to think that glancing at the stars is the same as due diligence, will pass quickly by. This small fund has a long record of outperformance, marred by 2010 (strong absolute returns, weak relative ones) and 2011 (weak relative and absolute returns). 2012 was so-so and 2013, through March, has been solid.
Munder Large-Cap Value Fund was liquidated on March 25, 2013.
JPMorgan is planning a leisurely merger JPMorgan Value Opportunities (JVOIX) into JPMorgan Large Cap Value (HLQVX), which won’t be effective until Oct. 31, 2014. The funds share the same manager and strategy and . . . . well, portfolio. Hmmm. Makes you wonder about the delay.
Lord Abbett Stock Appreciation Fund merged into Lord Abbett Growth Leaders Fund (LGLAX) on March 22, 2013.
Pioneer Independence Fund is merging into Pioneer Disciplined Growth Fund (SERSX) which is expected to occur on or about May 17, 2013. The Disciplined Growth management team, fees and record survives while Independence’s vanishes.
Effective March 31, 2013 Salient Alternative Strategies Fund, a hedge fund, merged into the Salient Alternative Strategies I Fund (SABSX) because, the board suddenly discovered, both funds “have the same investment objectives, policies and strategies.”
Sentinel Mid Cap II Fund (SYVAX) has merged into the Sentinel Mid Cap Fund (SNTNX).
Target Growth Allocation Fund would like to merge into Prudential Jennison Equity Income Fund (SPQAX). Shareholders consider the question on April 19, 2013 and approval is pretty routine but if they don’t agree to merge the fund away, the Board has at least resolved to firm Marsico as one of the fund’s excessive number of sub-advisers (10, currently).
600,000 visits later . . .
609,000, actually. 143,000 visitors since launch. About 10,000 readers a month nowadays. That’s up by 25% from the same period a year ago. Because of your support, either direct contributions (thanks Leah and Dan!) or use of our Amazon link (it’s over there, on the right), we remain financially stable. And a widening circle of folks are sharing tips and leads with us, which gives us a chance to serve you better. And so, thanks for all of that.
The Observer celebrates its second anniversary with this issue. We are delighted and honored by your continuing readership and interest. You make it all worthwhile. (And you make writing at 1:54 a.m. a lot more manageable.) We’re in the midst of sprucing the place up a bit for you. Will, my son, clicked through hundreds of links to identify deadsters which Chip then corrected. We’ve tweaked the navigation bar a bit by renaming “podcasts” as “featured” to better reflect the content there, and cleaned out some dead profiles. Chip is working to track down and address a technical problem that’s caused us to go offline for between two and 20 minutes once or twice a week. Anya is looking at freshening our appearance a bit, Junior is updating our Best of the Web profiles in advance of adding some new, and a good friend is looking at creating an actual logo for us.
Four quick closing notes for the months ahead:
- We are still not spam! Some folks continue to report not receiving our monthly reminders or conference call updates. Please check your spam folder. If you see us there, just click on the “not spam” icon and things will improve.
- Morningstar is coming. Not the zombie horde, the annual conference. The Morningstar Investor Conference is June 12-14, in Chicago. I’ll be attending the conference on behalf of the Observer. I had the opportunity to spend time with a dozen people there last year: fund managers, media relations folks, Observer readers and others. If you’re going to be there, perhaps we might find time to talk.
- We’re getting a bit backed-up on fund profiles, in several cases because we’ve had trouble getting fund reps to answer their mail. Our plan for the next few months will be to shorten the cover essay by a bit in order to spend more time posting new profiles. If you have folks who strike you as particularly meritorious but unnoticed, drop me a note!
- Please do use the Amazon link, if you don’t already. We’re deeply grateful for direct contributions but they tend to be a bit unpredictable (many months end up in the $50 range while one saw many hundreds) while the Amazon relationship tends to produce a pretty predictable stream (which makes planning a lot easier). It costs you nothing and takes no more effort than clicking and hitting the “bookmark this page” button in your browser. After that, it’s automatic and invisible.
Take great care!


 We have three major construction projects underway, a lot for a school our size. We’re renovating Old Main, which was built in 1884, originally lit gas lanterns and warmed by stoves in the classrooms. After a century of fiddling with it, we finally resolved to strip out a bunch of “improvements” from days gone by, restore some of its original grandeur and make it capable of supporting 21st century classes.
We have three major construction projects underway, a lot for a school our size. We’re renovating Old Main, which was built in 1884, originally lit gas lanterns and warmed by stoves in the classrooms. After a century of fiddling with it, we finally resolved to strip out a bunch of “improvements” from days gone by, restore some of its original grandeur and make it capable of supporting 21st century classes.





 The Elevator Talk is a new feature which began in February. Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
The Elevator Talk is a new feature which began in February. Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
 The Cook and Bynum Fund (COBYX) strikes me as the antithesis of those. Carefully constructed, tightly focused, and intentionally distinct. On Tuesday, March 5, we spoke with Richard Cook and Dowe Bynum in the first of three conversations with distinguished managers who defy that trend through their commitment to a singular discipline: buy only the best. For Richard and Dowe, that translates to a portfolio with only seven holdings and a 34% cash stake. Since inception (through early March, 2013), they managed to capture 83% of the market’s gains with only 50% of its volatility; in the past twelve months, Morningstar estimates that they captured just 7% of the market’s downside.
The Cook and Bynum Fund (COBYX) strikes me as the antithesis of those. Carefully constructed, tightly focused, and intentionally distinct. On Tuesday, March 5, we spoke with Richard Cook and Dowe Bynum in the first of three conversations with distinguished managers who defy that trend through their commitment to a singular discipline: buy only the best. For Richard and Dowe, that translates to a portfolio with only seven holdings and a 34% cash stake. Since inception (through early March, 2013), they managed to capture 83% of the market’s gains with only 50% of its volatility; in the past twelve months, Morningstar estimates that they captured just 7% of the market’s downside.


 Fidelity is offering to waive the sales loads on an ever-wider array of traditionally load-only funds through its supermarket. I learned of the move, as I learn of so many things, from the folks at MFO’s discussion board. The list of load-waived funds is detailed in msf’s thread, entitled
Fidelity is offering to waive the sales loads on an ever-wider array of traditionally load-only funds through its supermarket. I learned of the move, as I learn of so many things, from the folks at MFO’s discussion board. The list of load-waived funds is detailed in msf’s thread, entitled 
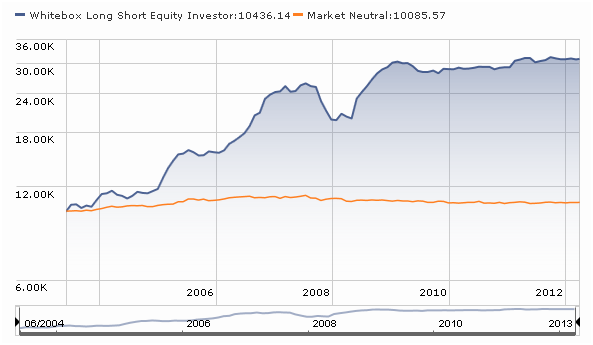
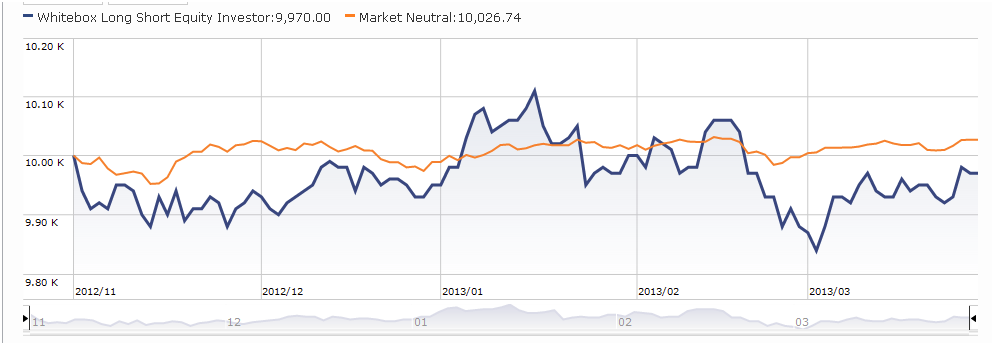

 At around the same time, I received a cheerful note from Tom Pinto, a long-time correspondent of ours and vice president at Mount & Nadler. Mount & Nadler (presided over, these last 33 years, by the redoubtable Hedda Nadler) does public relations for mutual funds and other money management folks. They’ve arranged some really productive conversations (with, for example, David Winters and Bruce Berkowitz) over the years and I tend to take their notes seriously. This one celebrated an entirely remarkable achievement for Tweedy Browne Global Value (TBGVX):
At around the same time, I received a cheerful note from Tom Pinto, a long-time correspondent of ours and vice president at Mount & Nadler. Mount & Nadler (presided over, these last 33 years, by the redoubtable Hedda Nadler) does public relations for mutual funds and other money management folks. They’ve arranged some really productive conversations (with, for example, David Winters and Bruce Berkowitz) over the years and I tend to take their notes seriously. This one celebrated an entirely remarkable achievement for Tweedy Browne Global Value (TBGVX): Why Hedda? I’ve never had the pleasure of meeting Hedda in person, but our long phone conversations over the years make it clear that she’s smart, funny, and generous and has an incredible institutional memory. When I think of Hedda, the picture that pops into mind is Edna Mode from The Incredibles, darling.
Why Hedda? I’ve never had the pleasure of meeting Hedda in person, but our long phone conversations over the years make it clear that she’s smart, funny, and generous and has an incredible institutional memory. When I think of Hedda, the picture that pops into mind is Edna Mode from The Incredibles, darling. 

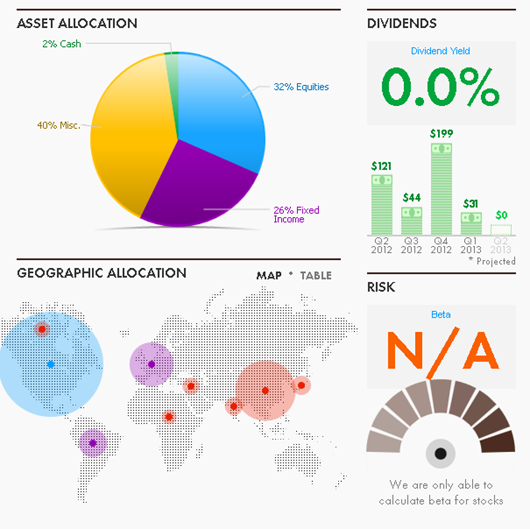
 The Elevator Talk is a new feature which began in February. Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
The Elevator Talk is a new feature which began in February. Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
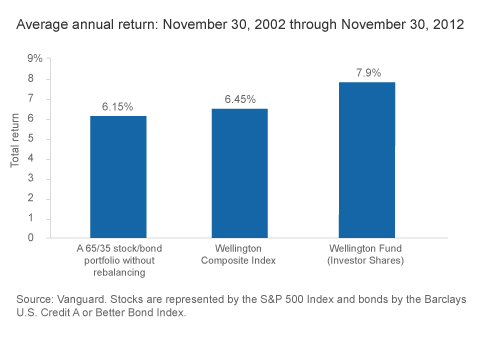
 Here’s an unexpectedly important announcement: we are not spam! You can tell because spam is pink, glisteny goodness. We are not. I mention that because there’s a good chance that if you signed up to be notified about our monthly update or our conference calls, and haven’t been receiving our mail, it’s because we’ve been trapped by your spam filter. Please check your spam folder. If you see us there, just click on the “not spam” icon and things will improve.
Here’s an unexpectedly important announcement: we are not spam! You can tell because spam is pink, glisteny goodness. We are not. I mention that because there’s a good chance that if you signed up to be notified about our monthly update or our conference calls, and haven’t been receiving our mail, it’s because we’ve been trapped by your spam filter. Please check your spam folder. If you see us there, just click on the “not spam” icon and things will improve. We’ve saved the most curious, and most disappointing, for last. American Funds has always been a sort of benevolent behemoth. They’re old (1931) and massive. They manage more than $900 billion in investments and over 50 million shareholder accounts, with $300 billion in non-U.S. assets.
We’ve saved the most curious, and most disappointing, for last. American Funds has always been a sort of benevolent behemoth. They’re old (1931) and massive. They manage more than $900 billion in investments and over 50 million shareholder accounts, with $300 billion in non-U.S. assets. 
 Mr. Kerr manages the Rocky Peak Small Cap Value Fund (RPCSX), which launched on April 2, 2012. He co-managed RCB’s Small Cap Value strategy and the CNI Charter RCB Small Cap Value Fund (formerly RCBAX, now CSCSX) fund. Tom offers these 200 words on why folks should check in:
Mr. Kerr manages the Rocky Peak Small Cap Value Fund (RPCSX), which launched on April 2, 2012. He co-managed RCB’s Small Cap Value strategy and the CNI Charter RCB Small Cap Value Fund (formerly RCBAX, now CSCSX) fund. Tom offers these 200 words on why folks should check in: There are, in addition, 123 beached whales: funds with more than a billion in assets that have trailed their peer groups for the past three, five and ten years. Of those, 29 earn ratings in the Bronze to Gold range, 31 are Neutral and just six warrant Negative ratings. So, being large and consistently bad makes you five times more likely to earn a positive rating than a negative one.
There are, in addition, 123 beached whales: funds with more than a billion in assets that have trailed their peer groups for the past three, five and ten years. Of those, 29 earn ratings in the Bronze to Gold range, 31 are Neutral and just six warrant Negative ratings. So, being large and consistently bad makes you five times more likely to earn a positive rating than a negative one.  We spent an hour on Tuesday, January 22, talking with Teresa Kong of Matthews Asia Strategic Income. The fund is about 14 months old, has about $40 million in assets, returned 13.6% in 2012 and 11.95% since launch (through Dec. 31, 2012).
We spent an hour on Tuesday, January 22, talking with Teresa Kong of Matthews Asia Strategic Income. The fund is about 14 months old, has about $40 million in assets, returned 13.6% in 2012 and 11.95% since launch (through Dec. 31, 2012).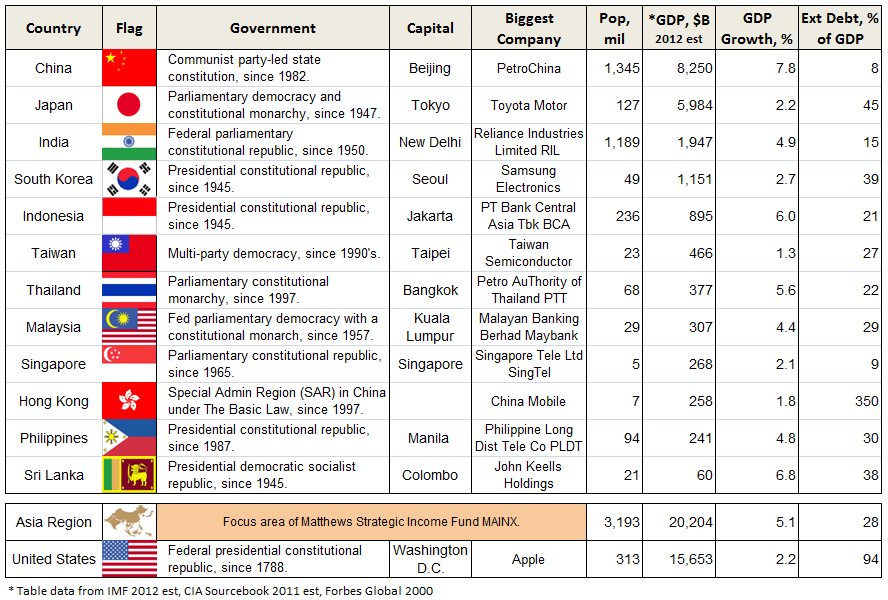
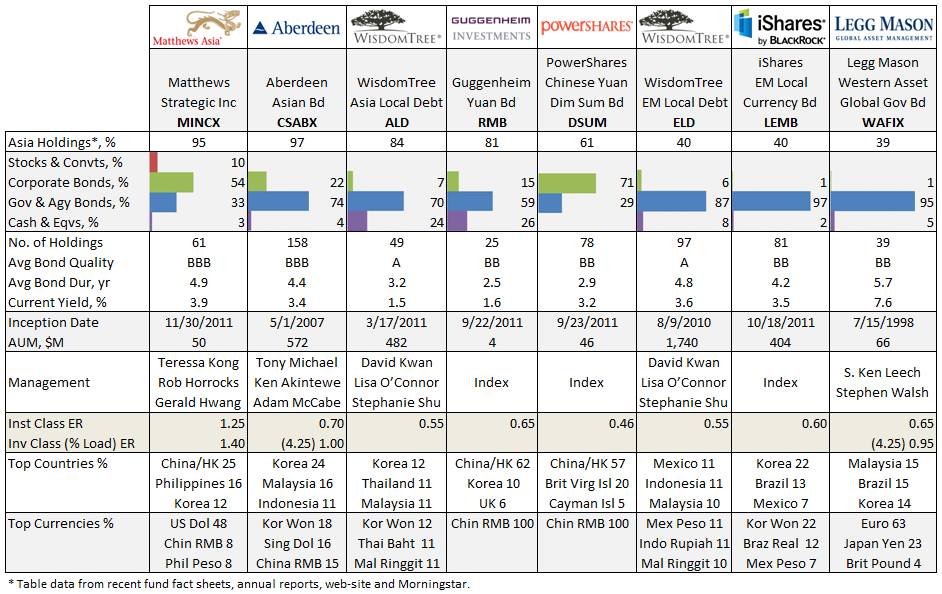
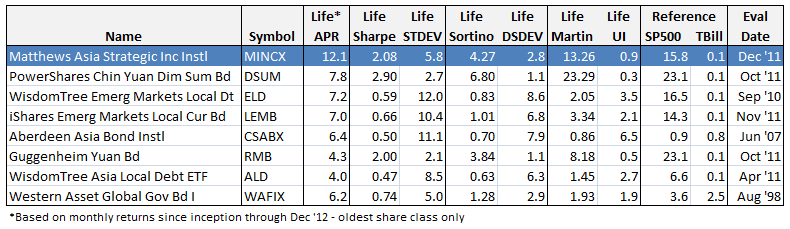
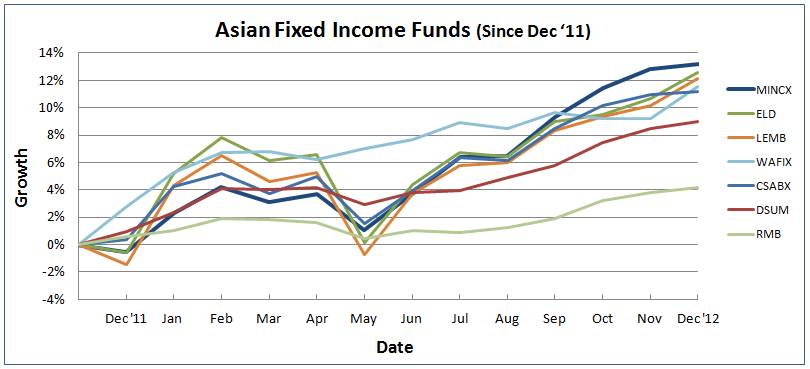
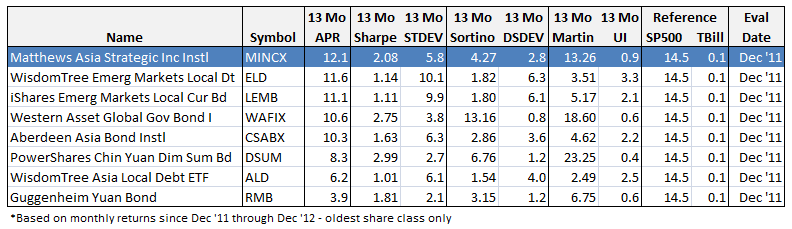
 As promised, we’re continuing our moderated conference calls through the winter. You should consider joining in. Here’s the story:
As promised, we’re continuing our moderated conference calls through the winter. You should consider joining in. Here’s the story: A couple months ago we profiled
A couple months ago we profiled  Our March conference call will occur unusually early in the month, so I wanted to give you advance word of it now. On
Our March conference call will occur unusually early in the month, so I wanted to give you advance word of it now. On 
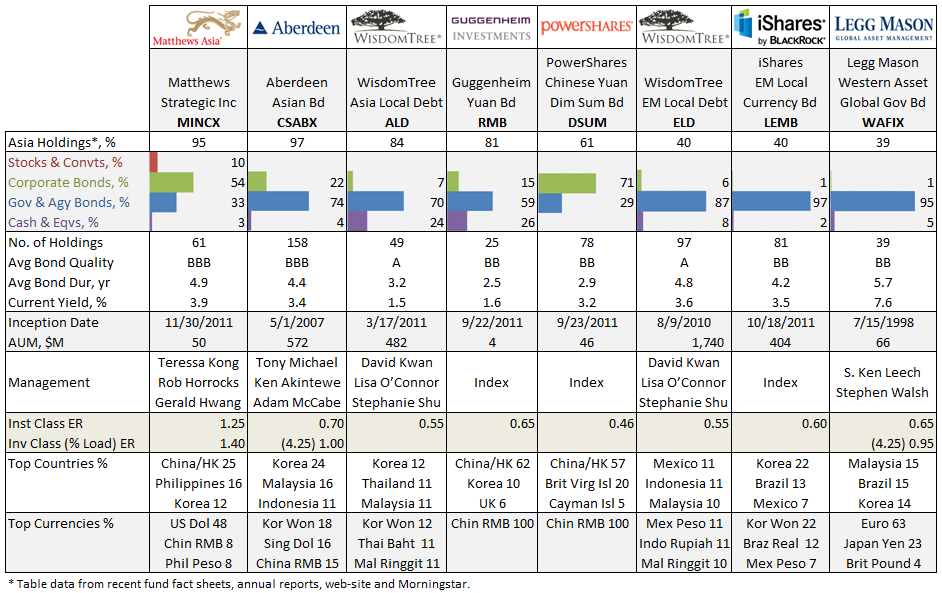

 In October we launched “The Last Ten,” a monthly series, running between now and February, looking at the strategies and funds launched by the Big Five fund companies (Fido, Vanguard, T Rowe, American and PIMCO) in the last decade.
In October we launched “The Last Ten,” a monthly series, running between now and February, looking at the strategies and funds launched by the Big Five fund companies (Fido, Vanguard, T Rowe, American and PIMCO) in the last decade. FundReveal’s strategy is to track daily return and volatility data, rather than the more common monthly or quarterly measures. They believe that allows them to look at many more examples of the managers’ judgment at work (they generate 250 data points a year rather than four or twelve) and to arrive at better predictions about a fund’s prospects. One of FundReveal’s key measures is Persistence, the likelihood that a particular pattern of risk and return repeats itself, day after day. In general, you can count on funds with higher persistence. Here are their highlights:
FundReveal’s strategy is to track daily return and volatility data, rather than the more common monthly or quarterly measures. They believe that allows them to look at many more examples of the managers’ judgment at work (they generate 250 data points a year rather than four or twelve) and to arrive at better predictions about a fund’s prospects. One of FundReveal’s key measures is Persistence, the likelihood that a particular pattern of risk and return repeats itself, day after day. In general, you can count on funds with higher persistence. Here are their highlights: I’m not sure that Chuck Jaffe is the hardest-working man in the fund biz, but he does have periods of prodigious output. December is one of those periods. Chuck ran four features this month worth special note.
I’m not sure that Chuck Jaffe is the hardest-working man in the fund biz, but he does have periods of prodigious output. December is one of those periods. Chuck ran four features this month worth special note. Our next conference call features Teresa Kong, manager of
Our next conference call features Teresa Kong, manager of 
 RiverNorth/Oaktree High Income Fund launched on December 28. This is a collaboration between RiverNorth, whose specialty has been tactical asset allocation and investing in closed-end funds (CEFs), and Oaktree. Oaktree is a major institutional bond investor with about $80 billion under management. Oaktree’s clientele includes “75 of the 100 largest U.S. pension plans, 300 endowments and foundations, 10 sovereign wealth funds and 40 of the 50 primary state retirement plans in the United States.” Their specialties include high yield and distressed debt and convertible securities. Until now, the only way for retail investors to access them was through Vanguard Convertible Securities (VCVSX), a four-star Gold rated fund.
RiverNorth/Oaktree High Income Fund launched on December 28. This is a collaboration between RiverNorth, whose specialty has been tactical asset allocation and investing in closed-end funds (CEFs), and Oaktree. Oaktree is a major institutional bond investor with about $80 billion under management. Oaktree’s clientele includes “75 of the 100 largest U.S. pension plans, 300 endowments and foundations, 10 sovereign wealth funds and 40 of the 50 primary state retirement plans in the United States.” Their specialties include high yield and distressed debt and convertible securities. Until now, the only way for retail investors to access them was through Vanguard Convertible Securities (VCVSX), a four-star Gold rated fund.

 Volatility is tremendously exciting for many investment managers. You’d be amazed by the number who get up every morning, hoping for a market panic. For the rest of us, it’s simply terrifying.
Volatility is tremendously exciting for many investment managers. You’d be amazed by the number who get up every morning, hoping for a market panic. For the rest of us, it’s simply terrifying. Our next conference call features Matt Moran and Dan Johnson, co-managers of
Our next conference call features Matt Moran and Dan Johnson, co-managers of  We’re hoping to start 2013 with a conversation with Andrew Foster of
We’re hoping to start 2013 with a conversation with Andrew Foster of 
 On November 1, Whitebox Advisors converted their Whitebox Long Short Equity Partners hedge fund into the Whitebox Long Short Equity Fund which has three share classes. As a hedge fund, Whitebox pretty much kicked butt. From 2004 – 2012, it returned 15.8% annually while the S&P500 earned 5.2%. At last report, the fund was just slightly net-long with a major short against the Russell 2000.
On November 1, Whitebox Advisors converted their Whitebox Long Short Equity Partners hedge fund into the Whitebox Long Short Equity Fund which has three share classes. As a hedge fund, Whitebox pretty much kicked butt. From 2004 – 2012, it returned 15.8% annually while the S&P500 earned 5.2%. At last report, the fund was just slightly net-long with a major short against the Russell 2000.
 The Observer is trying to help two distinct but complementary groups of folks. One group are investors who are trying to get past all the noise and hype. (CNBC’s ratings are dropping like a rock, which should help.) We’re hoping, in particular, to help folks examine evidence or possibilities that they wouldn’t normally see. The other group are the managers and other folks associated with small funds and fund boutiques. We believe in you. We believe that, as the industry evolves, too much emphasis falls on asset-gathering and on funds launched just for the sake of dangling something new and shiny (uhh … the All Cap Insider Sentiment ETF). We believe that small, independent funds run by smart, passionate investors deserve a lot more consideration than they receive. And so we profile them, write about them and talk with other folks in the media about them.
The Observer is trying to help two distinct but complementary groups of folks. One group are investors who are trying to get past all the noise and hype. (CNBC’s ratings are dropping like a rock, which should help.) We’re hoping, in particular, to help folks examine evidence or possibilities that they wouldn’t normally see. The other group are the managers and other folks associated with small funds and fund boutiques. We believe in you. We believe that, as the industry evolves, too much emphasis falls on asset-gathering and on funds launched just for the sake of dangling something new and shiny (uhh … the All Cap Insider Sentiment ETF). We believe that small, independent funds run by smart, passionate investors deserve a lot more consideration than they receive. And so we profile them, write about them and talk with other folks in the media about them.
 The best book there is on the subject of practical persuasion is Robert Cialdini’s
The best book there is on the subject of practical persuasion is Robert Cialdini’s 

 Three out of 30 funds managed by Royce outperformed their benchmarks for the 1-year period; 4 out of 24 for the 3-year period; 12 out of 19 for the 5-year period; and all 11 outperformed for the 10-year period.
Three out of 30 funds managed by Royce outperformed their benchmarks for the 1-year period; 4 out of 24 for the 3-year period; 12 out of 19 for the 5-year period; and all 11 outperformed for the 10-year period.
 Based on the success of our September conference call with David Sherman of Cohanzick Asset Management and RiverPark’s president, Morty Schaja, we have decided to try to provide our readers with one new opportunity each month to speak with an “A” tier fund manager.
Based on the success of our September conference call with David Sherman of Cohanzick Asset Management and RiverPark’s president, Morty Schaja, we have decided to try to provide our readers with one new opportunity each month to speak with an “A” tier fund manager.