By David Snowball
Dear friends,
 Talk about sturm und drang. After 75 days with in which the stock market rose or fell by 1% or more, the Vanguard Total Stock Market Index managed to roar ahead to a gain … of 0.29%. Almost 3000 mutual funds hung within two percentage points, up or down, of zero. Ten managed the rare feat of returning precisely zero. Far from a Santa Claus rally, 2015 couldn’t even manage a Grinchy Claus one.
Talk about sturm und drang. After 75 days with in which the stock market rose or fell by 1% or more, the Vanguard Total Stock Market Index managed to roar ahead to a gain … of 0.29%. Almost 3000 mutual funds hung within two percentage points, up or down, of zero. Ten managed the rare feat of returning precisely zero. Far from a Santa Claus rally, 2015 couldn’t even manage a Grinchy Claus one.
And the Steelers lost to the Ravens. Again! Just rip my heart out, why doncha?
Annus horribilis or annus mediocris?
In all likelihood, the following three statements described your investment portfolio: your manager lost money, you suspect he’s lost touch with the market, and you’re confused.
Welcome to the club! 2015 saw incredibly widespread disappointment for investors. Investors saw losses in:
- 8 of 9 domestic equity categories, excluding large growth
- 17 of 17 asset allocation categories, from retirement income to tactical allocation
- 8 of 15 international stock categories
- 14 of 15 taxable bond categories and
- 6 of 6 alternative or hedged fund categories.
Anything that smacked of “real assets” (energy, MLPs, natural resources) or Latin America posted 20-30% declines. Foreign and domestic value strategies, regardless of market cap, trailed their growth-oriented peers by 400-700 basis points. The average hedge fund finished the year down about 4% and Warren Buffett’s Berkshire-Hathaway dropped 11.5%. The Masters of the Universe – William Ackman, David Einhorn, Joel Greenblatt, and Larry Robbins among them – are all spending their holidays penning letters that explain why 10-25% losses are no big deal. The folks at Bain, Fortress Investments and BlackRock spared themselves the bother by simply closing their hedge funds this year.
And among funds I actually care about (a/k/a “own”), T. Rowe Price Spectrum Income (RPSIX) lost money for just the third time in its 25 year history. As in 1994, it’s posting an annual loss of about 2%.
What to make of it? Opinions differ. Neil Irwin, writing in The New York Times half-celebrated:
Name a financial asset — any financial asset. How did it do in 2015?
The answer, in all likelihood: Meh.
It might have made a little money. It might have lost a little money. But, barring any drastic moves in the final trading days of 2015, the most widely held classes of assets, including stocks and bonds across the globe, were basically flat … While that may be disappointing news for people who hoped to see big returns from at least some portion of their portfolio, it is excellent news for anyone who wants to see a steady global economic expansion without new bubbles and all the volatility that can bring. (“Financial markets were flat in 2015. Thank goodness.” 12/30/2015)
Stephanie Yang, writing for CNBC, half-despaired:
It’s been a really, really tough year for returns.
According to data from Societe Generale, the best-performing asset class of 2015 has been stocks, whose meager 2 percent total return (that is, including dividends) still surpasses those of long-term bonds, short-term Treasury bills and commodities. These minimal gains make 2015 the worst year for finding returns since 1937, when the cash-like 3-month Treasury bill beat out other major asset classes with a return of 0.3 percent. (“2015 was the hardest year to make money in 78 years,” 12/31/2015).
Thirty-one liquid alts funds subsequently liquidated, the most ever (“The Year the Hedge-Fund Model Stalled on Main Street,” WSJ, 12/31/2015).
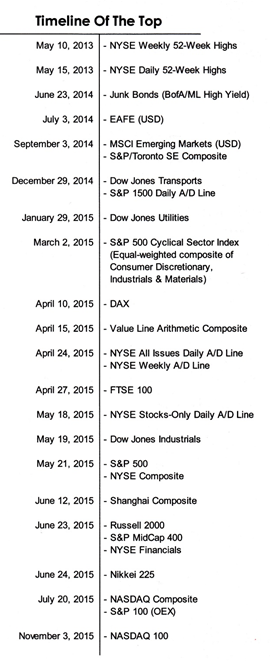
Courtesy of Leuthold Group
The most pressing question is whether 2015 is a single bad year or the prelude to something more painful than “more or less flat.” The folks at the Leuthold Group, advisers to the Leuthold funds as well as good institutional researchers, make the argument that the global equity markets have topped out. In support of that position, they break the market out into both component parts (MSCI Emerging Markets or FTSE 100) and internal measures (number of new 52-week highs in the NYSE or the ratio of advancing to declining stocks). With Leuthold’s permission, we’ve reproduced their timeline here.
Two things stand out. First, it appears that “the market’s” gains, if any, are being driven by fewer and fewer stocks. That’s suggested by the fact the number of 52-week highs peaked in 2013 and the number of advancing stocks peaked in spring 2015. The equal-weight version of the S&P 500 (represented by the Guggenheim S&P 500 Equal Weight ETF RSP) trailed the cap-weighted version by 370 basis points. The Value Line Arithmetic Index, which tracks the performance of “the average stock” by equally weighting 1675 issues, is down 11% from its April peak. Nearly 300 of the S&P 500 stocks will likely finish the year in the red. Second, many of the components followed the same pattern: peak in June, crash in August, partially rally in September then fade. The battle cry “there’s always a bull market somewhere!” seems not to be playing out just now.
The S&P 500 began 2015 at 2058. The consensus of market strategists in Barron’s was that it would finish 2015 just north of 2200. It actually ended at 2043. The new consensus is that it will finish 2016 just north of 2200.
The Leuthold Group calculates that, if we were to experience a typical bear market over the next year, the S&P 500 would drop to somewhere between 1500-1600.
By most measures, US stocks remain overpriced. There’s not much margin for safety in the bond market right now with US interest rates near zero and other major developing markets cutting theirs. Those interest rate cuts reflect concerns about weak growth and the potential for a China-led recession. The implosion of Third Avenue Focused Credit (TFCVX) serves as a reminder that liquidity challenges remain unresolved ahead of potentially disruptive regulations contemplated by the SEC.
 The path forward is not particularly clear to me because we’ve never managed such a long period of global economic weakness and zero to negative interest rates before. My plan is to remind myself that I need to care about 2026 more than about 2016, to rebalance soon, and to stick with my discipline which is, roughly put, “invest regularly and automatically in sensible funds that execute a reasonable plan, ignore the market and pay attention to the moments, hours and days that life presents me.” On whole, an hour goofing around with my son or the laughter of dinner guests really does make a much bigger difference in my life than anything my portfolio might do today.
The path forward is not particularly clear to me because we’ve never managed such a long period of global economic weakness and zero to negative interest rates before. My plan is to remind myself that I need to care about 2026 more than about 2016, to rebalance soon, and to stick with my discipline which is, roughly put, “invest regularly and automatically in sensible funds that execute a reasonable plan, ignore the market and pay attention to the moments, hours and days that life presents me.” On whole, an hour goofing around with my son or the laughter of dinner guests really does make a much bigger difference in my life than anything my portfolio might do today.
As Sergeant Phil Esterhaus used to remind the guys at Hill Street station as they were preparing to leave on patrol, “Hey, let’s be careful out there.”
For those seeking rather more direct guidance, our colleague Leigh Walzer of Trapezoid offers guidance, below, on the discipline of finding all-weather managers. Helpfully enough, he names a couple for you.
Good-Bye to All That
I cribbed the title from Robert Graves’ 1929 autobiography, one of a host of works detailing the horrors of fighting the Great War and the British military’s almost-criminal incompetence.
We bid farewell, sometimes with sadness, to a host of friends and funds.
Farewell to the Whitebox Funds
The Whitebox Advisors come from The Land of Giants. From the outside, I could never tell whether their expression was “swagger” or “sneer” but I found neither attractive. Back in 2012 readers urged us to look into the funds, and so we did. Our first take was this:
There are some funds, and some management teams, that I find immediately compelling. Others not.
So far, this is a “not.”
Here’s the argument in favor of Whitebox: they have a Multi-Strategy hedge fund which uses some of the same strategies and which, per a vaguely fawning article in Barron’s, returned 15% annually over the past decade while the S&P returned 5%. I’ll note that the hedge fund’s record does not get reported in the mutual fund’s, which the SEC allows when it believes that the mutual fund replicates the hedge.
Here’s the reservation: their writing makes them sound arrogant and obscure. They advertise “a proprietary, multi-factor quantitative model to identify dislocations within and between equity and credit markets.” At base, they’re looking for irrational price drops. They also use broad investment themes (they like US blue chips, large cap financials and natural gas producers), are short both the Russell 2000 (which is up 14.2% through 9/28) and individual small cap stocks, and declare that “the dominant theories about how markets behave and the sources of investment success are untrue.” They don’t believe in the efficient market hypothesis (join the club).
I’ll try to learn more in the month ahead, but I’ll first need to overcome a vague distaste.
I failed to overcome it. The fact that their own managers largely avoided the funds did not engender confidence.
In the face of poor performance and shrinking assets, they announced the closure of their three liquid alts funds in December. My colleague Charles offers a bit of further reflection on the closure, below.
Farewell to The House of Whitman
Marty Whitman become a fund manager at age 60 and earned enormous respect for his outspokenness and fiercely independent style. Returns at Third Avenue Value Fund (TAVFX) were sometimes great, sometimes awful but always Marty. Somewhere along the way, he elevated David Barse to handle all the business stuff that he had no earthly interest in, got bought by AMG, promised to assemble at least $25 billion in assets and built a set of funds that, save perhaps Third Avenue Real Estate Value (TAREX), never quite matched the original. It’s likely that his ability to judge people, or perhaps the attention he was willing to give to judging them, matched his securities analysis. The firm suffered and Mr. Whitman, in his 80s, either drifted or was pushed aside. Last February we wrote:
In sum, the firm’s five mutual funds are down by $11 billion from their peak asset levels and nearly 50% of the investment professionals on staff five years ago, including the managers of four funds, are gone. At the same time, only one of the five funds has had performance that meets the firm’s long-held standards of excellence.
Many outsiders noted not just the departure of long-tenured members of the Third Avenue community, but also the tendency to replace some those folks with outsiders … Industry professionals we talked with spoke of “a rolling coup,” the intentional marginalization of Mr. Whitman within the firm he created and the influx of outsiders. Understandably, the folks at Third Avenue reject that characterization.
Mr. Barse was, reportedly, furious about our story. An outstanding bit of reporting by Gregory Zuckerman and Matt Wirz from The Wall Street Journal in the wake of the collapse of Third Avenue Focused Credit revealed that “furious” was a more-or-less constant state for him.
Mr. Barse also harangued other fund managers who grew disgruntled. Mr. Whitman took no public steps to rein in the CEO, the people said, preferring to focus on investing.
The dispute boiled over in the fall of 2011, when about 50 employees gathered in the firm’s largest conference room after an annual meeting with investors. Mr. Barse screamed at Mr. Whitman, inches from his face, demanding better performance, according to people who were in the room.
Mr. Whitman “was pounding the table so hard with his fist it was shaking,” said another person at the meeting. Mr. Whitman eventually withdrew money from the Value Fund and quit running it to focus on investing for himself, while remaining chairman of the firm.
As most of Third Avenue’s funds underperformed relevant benchmarks … Mr. Barse seemed to become more irritated, the people said.
Staff stopped using the conference room adjoining Mr. Barse’s office because sometimes he could be heard shouting through the walls.
Most employees received part of their pay on a deferred basis. After 2008, Mr. Barse began personally determining compensation for most personnel, often without explaining his decision, one of the people said. (“How the Third Avenue Fund Melted Down,” 12/23/2015).
Yikes. The Focused Credit fund, Mr. Barse’s brainchild, came into the summer of 2015 with something like one third of its assets invested in illiquid securities, so-called “Level 3 securities.” There are two things you need to know about illiquid securities: you probably can’t sell them (at least not easily or quickly) and you probably can’t know what they’re actually worth (which is defined as “what someone is willing to buy it for”). A well-documented panic ensued when it looked like Focused Credit would need to hurriedly sell securities for which there were no buyers. Mr. Barse ordered the fund’s assets moved to a “liquidating trust,” which meant that shareholders (a) no longer knew what their accounts were worth and (b) no longer could get to the money. The plan, Third Avenue writes, is to liquidate the illiquid securities whenever they find someone willing to pay a decent price for them. Investors will receive dribs and drabs as that process unfolds.
We wrote Third Avenue to ask whether the firm would honor the last-published NAV for their fund and whether the firm had a commitment to “making whole” their investors. Like The Wall Street Journal reporters, we found that folks were unwilling to talk.
And so now investors wait. How long might they wait? Oh, could be eight or ten years. The closest analogue we have is the 2006 blowup of the Amaranth Advisors hedge fund. Amaranth announced that they’d freeze redemptions for two months. That’s now stretched to ten years with the freeze extended until at least December 2016. (“Ten Years After Blowup, Amaranth Investors Waiting to Get Money Back,” WSJ, 12/30/2015). In the interim, it’s hard to understand why investment advisors wouldn’t follow Mr. Whitman out the door.
Farewell to Mainstay Marketfield
Marketfield (MFLDX) was an excellent small no-load liquid alts fund that aspired to be more. It aspired to be a massive liquid alts fund, a goal achieved by selling themselves to New York Life and becoming Mainstay Marketfield. New York Life adopted a $1.7 billion overachiever in 2012 and managed to jam another $20 billion in assets into the fund in two years. The fund hasn’t been the same since. Over the past three years, it’s earned a one-star rating from Morningstar and lost almost 90% of its assets while trailing 90% of its peers.
On December 15, 2015, Mainstay announced an impending divorce:
At a meeting held on December 8-10, 2015, the Board of Trustees of MainStay Funds Trust approved an Agreement and Plan of Reorganization [which] provides for the reorganization of the Fund into the Marketfield Fund (the “New Fund”) …
Prior to the Reorganization, which is expected to occur on or about March 23, 2016, Marketfield Asset Management, LLC, the Fund’s current subadvisor, will continue to manage the Fund … The New Fund will have the same investment objective, principal investment strategies and investment process.
There are very few instances of a fund recovering from such a dramatic fall, but we wish Mr. Aronstein and his remaining investors the very best.
Farewell to Sequoia’s mystique
The fact that Sequoia (SEQUX) lost money in 2015 should bother no one. The fact that they lost their independence should bother anyone who cares about the industry. Sequoia staked its fate to the performance of Valeant Pharmaceuticals, a firm adored by hedge fund managers and Sequoia – which plowed over a third of its portfolio into the stock – for its singular strategy: buy small drug companies with successful niche medicines, then skyrocket the price of those drugs. One recent story reported:
The drugstore price of a tube of Targretin gel, a topical treatment for cutaneous T cell lymphoma, rose to about $30,320 this year from $1,687 in 2009. Most of that increase appears to have occurred after Valeant acquired the drug early in 2013. A patient might need two tubes a month for several months, Dr. Rosenberg said.
The retail price of a tube of Carac cream, used to treat precancerous skin lesions called actinic keratoses, rose to $2,865 this summer from $159 in 2009. Virtually all of the increase occurred after 2011, when Valeant acquired the product. (“Two Valeant drugs lead steep price increases,” 11/25/2015)
Remember that Valeant didn’t do anything to discover or create the drugs; they simply gain control of them and increase the price by 1800%.
Sequoia’s relationship to Valeant’s CEO struck me as deeply troubling: Valeant’s CEO Michael Pearson was consistently “Mike” when Sequoia talked about him, as in “my buddy Mike.”
We met with Mike a few weeks ago and he was telling us how with $300 million, you can get an awful lot done.
Mike can get a lot done with very little.
Mike is making a big bet.
The Sequoia press releases about Valeant sound like they were written by Valeant, two members of the board of trustees resigned in protest, a third was close to following them and James Stewart, writing for The New York Times, described “Sequoia’s infatuation with Valeant.” In a desperate gesture, Sequoia’s David Poppe tried to analogize Sequoia’s investment in Valeant with a long-ago bet on Berkshire Hathaway. Mr. Stewart drips acid on the argument.
Sequoia’s returns may well rebound. Their legendary reputation, built over decades of principled decision-making, will not. Our November story on Sequoia ended this way:
Sequoia’s recent shareholder letter concludes by advising Valeant to start managing with “an eye on the company’s long-term corporate reputation.” It’s advice that we’d urge upon Sequoia’s managers as well.
Farewell to Irving Kahn
Mr. Kahn died at his home in February 2015. At age 109, he was the nation’s oldest active professional investor. He began trading in the summer of 1929, made good money by shorting overvalued stock at the outset of the Crash, and continued working steadily for 85 more years. He apprenticed with Benjamin Graham and taught, at Graham’s behest, at the Columbia Business School. At 108, he still traveled to his office three days a week, weather permitted. His firm, Kahn Brothers Group, manages over a billion dollars.
Where Are the Jedi When You Need Them?
 “In present-day America it’s very difficult, when commenting on events of the day, to invent something so bizarre that it might not actually come to pass while your piece is still on the presses.”
“In present-day America it’s very difficult, when commenting on events of the day, to invent something so bizarre that it might not actually come to pass while your piece is still on the presses.”
Calvin Trillin, remarking on the problems in writing satire today.
So, the year has ended and again there is no joy in Mudville. The investors have no yachts or NetJet cards but on a trailing fee basis, fund managers still got rich. The S&P 500, which by the way has 30-35% of the earnings of its component companies coming from overseas so it is internationally diversified, trounced most active managers again. We continued to see the acceleration of the generational shift at investment management companies, not necessarily having anything to do with the older generation becoming unfit or incompetent. After all, Warren Buffett is in his 80’s, Charlie Munger is even older, and Roy Neuberger kept working, I believe, well into his 90’s. No, most such changes have to do with appearances and marketing. The buzzword of the day is “succession planning.” In the investment management business, old is generally defined as 55 (at least in Boston at the two largest fund management firms in that town). But at least it is not Hollywood.
One manager I know who cut his teeth as a media analyst allegedly tried to secure a place as a contestant on “The Bachelor” through his industry contacts. Alas, he was told that at age 40 he was too old. Probably the best advice I had in this regard was a discussion with a senior infantry commander, who explained to me that at 22, a man (or woman) was probably too old to be in the front lines in battle. They no longer believed they couldn’t be killed. The same applies to investment management, where the younger folks, especially when dealing with other people’s money, think that this time the “new, new thing” really is new and this time it really is different. That is a little bit of what we have seen in the energy and commodity sectors this year, as people kept doubling down and buying on the dips. This is not to say that I am without sin in this regard myself, but at a certain point, experience does cause one to stand back and reassess. Those looking for further insight, I would advise doing a search on the word “Passchendaele.” Continuing to double down on investments especially where the profit of the underlying business is tied to the price of a commodity has often proved to be a fool’s errand.
The period between Christmas and New Year’s Day is when I usually try to catch up on seeing movies. If you go to the first showing in the morning, you get both the discounted price and, a theater that is usually pretty empty. This year, we saw two movies. I highly recommend both of them. One of them was “The Big Short” based on the book by Michael Lewis. The other was “Spotlight” which was about The Boston Globe’s breaking of the scandal involving abusive priests in the Archdiocese of Boston.
Now, I suspect many of you will see “The Big Short” and think it is hyped-up entertainment. That of course, the real estate bubble with massive fraud taking place in the underwriting and placement of mortgages happened in 2006-2008 but ….. Yes, it happened. And a very small group of people, as you will see in the story, saw it, thought something did not make sense, asked questions, researched, and made a great deal of money going against the conventional wisdom. They did not just avoid the area (don’t invest in thrifts or banks, don’t invest in home building stocks, don’t invest in mortgage guaranty insurers) but found vehicles to invest in that would go up as the housing market bubble burst and the mortgages became worthless. I wish I could tell you I was likewise as smart to have made those contrary investments. I wasn’t. However, I did know something was wrong, based on my days at a bank and on its asset-liability committee. When mortgages stopped being retained on the books by the institutions that had made them and were packaged to be sold into the secondary market (and then securitized), it was clear that, without ongoing accountability, underwriting standards were being stretched. Why? With gain-on-sale accounting, profits and bonuses were increased and stock options went into the money. That was one of the reasons I refused to drink the thrift/bank Kool-Aid (not the only time I did not go along to get along, but we really don’t change after the age of 8). One food for thought question – are we seeing a replay event in China, tied as their boom was to residential construction and real estate?
One of the great scenes in “The Big Short” is when two individuals from New York fly down to Florida to check on the housing market and find unfinished construction, mortgages on homes being occupied by renters, people owning four or five homes trying to flip them, and totally bogus underwriting on mortgage lending. The point here is that they did the research – they went and looked. Often in fund management, a lot of people did not do that. After all, fill-in-the blank sell-side firm would not be recommending purchase of equities in home builders or mortgage lenders, without actually doing the real due diligence. Leaving aside the question of conflicts of interest, it was not that difficult to go look at the underlying properties and check valuations out against the deeds in the Recorder’s Office (there is a reason why there are tax stamps on deeds). So you might miss a few of your kid’s Little League games. But what resonates most with me is that no senior executive that I can remember from any of the big investment banks, the big thrifts, the big commercial banks was criminally charged and went to jail. Instead, what seems to have worked is what I will call the “good German defense.” And another aside, in China, there is still capital punishment and what are capital crimes is defined differently than here.
This brings me to “Spotlight” where one of the great lines is, “We all knew something was going on and we didn’t do anything about it.” And the reason it resonates with me is that you see a similar conspiracy of silence in the financial services industry. Does the investor come first or the consultant? Is it most important that the assets grow so the parent company gets a bigger return on its investment, or is investment performance most important? John Bogle, when he has spoken about conflicts of interest, is right when he talks about the many conflicts that came about when investment firms were allowed to sell themselves and basically eliminate personal responsibility.
This year, we have seen the poster child for what is wrong with this business with the ongoing mess at The Third Avenue Funds. There is a lot that has been written so far. I expect more will be written (and maybe even some litigation to boot). I commend all of you to the extensive pieces that have appeared in the Wall Street Journal. But what they highlight that I don’t think has been paid enough attention to is the problem of a roll-up investment (one company buying up and owning multiple investment management firms) with absentee masters. In the case of Third Avenue, we have Affiliated Managers Group owning, as reported by the WSJ, 60% of Third Avenue, and those at Third Avenue keeping a 40% stake (to incentivize them). With other companies from Europe, such as Allianz, the percentages may change but the ownership is always majority. So, 60% of the revenues come off the top, and the locals are left to grow the business, reinvest in it by hiring and retaining talent, focus on investment performance, etc., with their percentage. Unfortunately, when the Emperor is several states, or an ocean away, one often does not know what is really going on. You get to see numbers, you get told what you want to hear (ISIS has been contained, Bill Gross is a distraction to the other people), and you accept it until something stops working.
So I leave you with my question for you all to ponder for 2016. Is the 1940 Act mutual fund industry, the next big short? Investors, compliments of Third Avenue, have now been reminded that daily liquidity and redemption is that until it is not. As I have mentioned before, this is an investment class with an unlimited duration and a mismatch of assets and liabilities. This is perhaps an unusual concern for a publication named “Mutual Fund Observer.” But I figure if nothing else, we can always start a separate publication called “Mutual Fund Managers Address Book” so you can go look at the mansions and townhouses in person.
– by Edward A. Studzinski
Quietly successful: PYGSX, RSAFX, SCLDX, ZEOIX
Amidst the turmoil, a handful of the funds we’re profiled did in 2015 exactly what they promised. They made a bit of money with little drama and, sadly, little attention. You might want to glance in their direction if you’ve found that your managers were getting a little too creative and stretching a little too far in their pursuit of “safe” income.
Payden Global Low Duration (PYGSX): the short-term global bond fund made a modest 0.29% in 2015 while its peers lost about 4.6%. In our 2013 profile we suggested that “flexibility and opportunism coupled with experienced, disciplined management teams will be invaluable” and that Payden offered that combo.
Riverpark Structural Alpha (RSAFX): this tiny fund used a mix of options which earned their investors 1.3% while its “market neutral” peers lost money. The fund, we suggested, was designed to answer the question, “where should investors who are horrified by the prospects of the bond market but are already sufficiently exposed to the stock market turn for stable, credible returns?” It’s structurally exposed to short-term losses but also structurally designed to rebound, automatically and quickly, from them. In the last five years, for example, it’s had four losing quarters but has never had back-to-back losing quarters.
Scout Low Duration Bond Fund (SCLDX): this flexible, tiny short-term bond tiny fund made a bit of money in 2015 (0.6%), but it’s more impressive that the underlying strategy also made money (1.4%) during the 2008 meltdown. Mr. Eagan, the lead manager, explained it this way: “Many short-term bond funds experienced negative returns in 2008 because they were willing to take on what we view as unacceptable risks in the quest for incremental yield or income …When the credit crisis occurred, the higher risks they were willing to accept produced significant losses, including permanent impairment. We believe that true risk in fixed income should be defined as a permanent loss of principle. Focusing on securities that are designed to avoid this type of risk has served us well through the years.”
Zeo Strategic Income (ZEOIX): this short-term, mostly high-yield fund made 2.0% in 2015 while its peers dropped 4.1%. It did a particularly nice job in the third quarter, making a marginal gain as the high-yield market tanked. Positioned as a home for your “strategic cash holdings,” we suggested that “Modestly affluent folks who are looking to both finish ahead of inflation and sleep at night should likely make the effort to reach out and learn more.”
RiverPark Short-Term High Yield (RPHYX) likewise posted a gain – 0.86% – for the year but remains closed to new investors. PIMCO Short Asset Investment (PAIUX) which provides the “cash” strategy for all the PIMCO funds, eked out a 0.25% gain, modestly ahead of its ultra-short peers.
These are very different strategies, but are unified by the presence of thoughtful, experienced managers who are exceedingly conscious of market risk.
Candidates for Rookie of the Year
We’ve often asked, by journalists and others, which are the young funds to keep an eye on. We decided to search our database for young funds that have been exceptionally risk-sensitive and have, at the same time, posted strong returns over their short lives. We used our premium screener to identify funds that had several characteristics:
They were between 12 and 24 months old; that is, they’d completed at least one full year of existence but were no more than two. I suspect a few funds in the 2-3 year range slipped through, but it should be pretty few.
They had a Martin Ratio greater than one; the Martin Ratio is a variation of the Sharpe ratio which is more sensitive to downward movements
They had a positive Sharpe ratio and had one of the five highest Sharpe ratios in their peer group.
Hence: young, exceptional downside sensitivity so far and solid upside. We limited our search to a dozen core equity categories, such as Moderate Balanced and Large Growth.
In all of these tables, “APR vs Peer” measures the difference in Annual Percentage Return between a fund’s lifetime performance and its average peers. A fund might have a 14 month record which the screener annualizes; that is, it says “at this rate, you’d expect to earn X in a year.” That’s important because a fund with a scant 12 month record is going to look a lot worse than one at 20 or 24 months since 2015, well, sucked.
Herewith, the 2016 Rookie of the Year nominees:
| Small cap rookies |
Sharpe Ratio |
Martin Ratio |
APR vs Peer |
|
| Acuitas US Microcap (AFMCX) |
0.83 |
3.10 |
9.6 |
Three sets of decent sub-advisors, tiny market cap but the fund is institutional only. |
| Hodges Small Intrinsic Value (HDSVX) |
0.79 |
2.37 |
9.3 |
Same team that manages the five-star Hodges Small Cap fund. |
| Perritt Low Priced Stock (PLOWX) |
0.74 |
2.05 |
8.8 |
The same manager runs Perritt UltraMicro and Microcap Opportunities, neither of which currently look swift when benchmarked against funds that invest in vastly larger stocks. |
| Hancock Horizon US Small Cap (HSCIX) |
0.70 |
2.61 |
8.6 |
Hmmm… the managers also run, with limited distinction, Hancock Horizon Growth, a large cap fund. |
| SunAmerica Small-Cap (SASAX) |
0.70 |
2.51 |
8.1 |
Some overlap with the management team for AMG Managers Cadence Emerging Companies, a really solid little institutional fund. |
| Mid cap rookies |
Sharpe Ratio |
Martin Ratio |
APR vs Peer |
|
| PowerShares S&P MidCap Low Volatility Portfolio (XMLV) |
0.99 |
4.11 |
10.4 |
Low vol. Good thought. |
| Diamond Hill Mid Cap (DHPAX) |
0.75 |
3.22 |
7.9 |
In various configurations, members of the team are responsible for six other Diamond Hill funds, some very fine. |
| Nuance Mid Cap Value (NMAVX) |
0.45 |
2.03 |
6.7 |
Two years old; kinda clubbed its competition in 2015. The lead manager handled $10 billion as an American Century manager. |
| Hodges Small-to-Midcap (HDSMX) |
0.43 |
1.32 |
5.5 |
Same team that manages the five-star Hodges Small Cap fund. |
| Barrow Value Opportunity (BALAX) |
0.41 |
1.58 |
5.3 |
David Bechtel talked through the fund’s strategy in a 2014 Elevator Talk. |
| Large cap rookies |
Sharpe Ratio |
Martin Ratio |
APR vs Peer |
|
| iShares MSCI USA Momentum Factor ETF (MTUM) |
0.64 |
2.68 |
3.6 |
Momentum tends to dominate at the ends of bull markets, so this isn’t particularly surprising. |
| iShares MSCI USA Quality Factor ETF (QUAL) |
0.53 |
2.61 |
2.5 |
|
| Arin Large Cap Theta (AVOLX) |
0.52 |
2.73 |
4.5 |
A covered call fund that both M* and Lipper track as if it were simple large cap equity. |
| SPDR MFS Systematic Core Equity ETF (SYE) |
0.48 |
1.99 |
6 |
An active ETF managed by MFS |
| SPDR MFS Systematic Value Equity ETF (SYV) |
0.46 |
1.8 |
8.0 |
And another. |
Hmmm … you might notice that the large cap list is dominated by ETFs, two active and two passive. There were a larger number of active funds on the original list but I deleted Fidelity funds (three of them) that were only available for use by other Fidelity managers.
| Multi-cap rookies |
Sharpe Ratio |
Martin Ratio |
APR vs Peer |
|
| SPDR MFS Systematic Growth Equity ETF (SYG) |
0.74 |
3.3 |
10.4 |
Another active ETF managed by MFS |
| Segall Bryant & Hamill All Cap (SBHAX) |
0.69 |
2.73 |
5.4 |
The lead manager used to run a Munder health care fund. M* treats this as a large growth fund, a category in which it does not excel. |
| Riverbridge Growth (RIVRX) |
0.66 |
2.43 |
4.6 |
The team has been subadvising a Dreyfus Select Managers small cap fund for about five years. |
| AT Mid Cap Equity (AWMIX) |
0.52 |
1.74 |
3.5 |
AT is Atlantic Trust, once known for the Atlantic Whitehall funds. It’s currently limiting itself to rich folks. Pity. |
| BRC Large Cap Focus Equity (BRCIX) |
0.37 |
1.31 |
5.3 |
Institutional only. Pity. |
This is another category where we had to dump a bunch of internal-only Fidelity funds. It’s interesting that no passive fund was even near the top of the list, perhaps because the ability to move between size ranges is active and useful?
| Global rookies |
Sharpe Ratio |
Martin Ratio |
APR vs Peer |
|
| William Blair Global Small Cap Growth (WGLIX) |
0.99 |
3.99 |
11.9 |
Sibling to an excellent but closed international small growth fund. They’re liquidating it anyway (Thanks for the reminder, JoJo). |
| Vanguard Global Minimum Volatility (VMVFX) |
0.96 |
3.96 |
9.4 |
A fund we profiled. |
| WCM Focused Global Growth (WFGGX) |
0.81 |
3.48 |
11.2 |
The team runs eight funds, mostly as sub-advisors, including the five star Focused International Growth fund. |
| QS Batterymarch Global Dividend (LGDAX) |
0.3 |
1.16 |
8.1 |
|
| Scharf Global Opportunity (WRLDX) |
0.3 |
1.14 |
4.1 |
0.50% e.r. The same manager runs four or five Scharf funds, several with exceptional track records. |
At the other end of the spectrum, it was durn tough to find strong performance among “rookie” international funds. In the emerging markets arena, for example, just one fund had a positive Martin Ratio: Brown Advisory Emerging Markets Small-Cap (BIANX). Everyone else was down a deep, deep hole.
While we’re not endorsing any of these funds just yet, they’ve distinguished themselves with creditable starts in tough markets. In the months ahead, we’ll be trying to learn more about them on your behalf.
For the convenience of MFO Premium members who are interesting in digging into rookie funds more deeply, Charles created a preset screen for high-achieving younger funds. He offers dozens of data points on each of those funds where we only have room, or need, for a handful here.
Premium Site Update
 New to MFO Premium this month are several additions to the MultiSearch Tool, which now can screen our monthly fund database with some 44 performance metrics and other parameters. (Here are links to current Input and Output MultiSearch Parameter Lists.) The new additions include SubType (a kind of super category), exchange-traded fund (ETF) flag, Profiled Funds flag, and some initial Pre-Set Screens.
New to MFO Premium this month are several additions to the MultiSearch Tool, which now can screen our monthly fund database with some 44 performance metrics and other parameters. (Here are links to current Input and Output MultiSearch Parameter Lists.) The new additions include SubType (a kind of super category), exchange-traded fund (ETF) flag, Profiled Funds flag, and some initial Pre-Set Screens.
SubType is a broad grouping of categories. Lipper currently defines 144 categories, excluding money market funds. MFO organizes them into 9 subtypes: U.S. Equity, Mixed Asset, Global Equity, International Equity, Sector Equity, Commodity, Alternative & Other, Bond, and Municipal Bond funds. The categories are organized further into broader types: Fixed Income, Asset Allocation, and Equity funds. The MultiSearch Tool enables screening of up to 9 categories, 3 subtypes, or 2 types along with other criteria.
The Profiled Funds flag enables screening of funds summarized monthly on our Dashboard (screenshot here). Each month, David (and occasionally another member of MFO’s staff), typically provides in-depth analysis of two to four funds, continuing a FundAlarm tradition. Through November 2015, 117 profiles are available on MFO legacy site Funds page. “David’s Take” precariously attempts to distill the profile into one word: Positive, Negative, or Mixed.
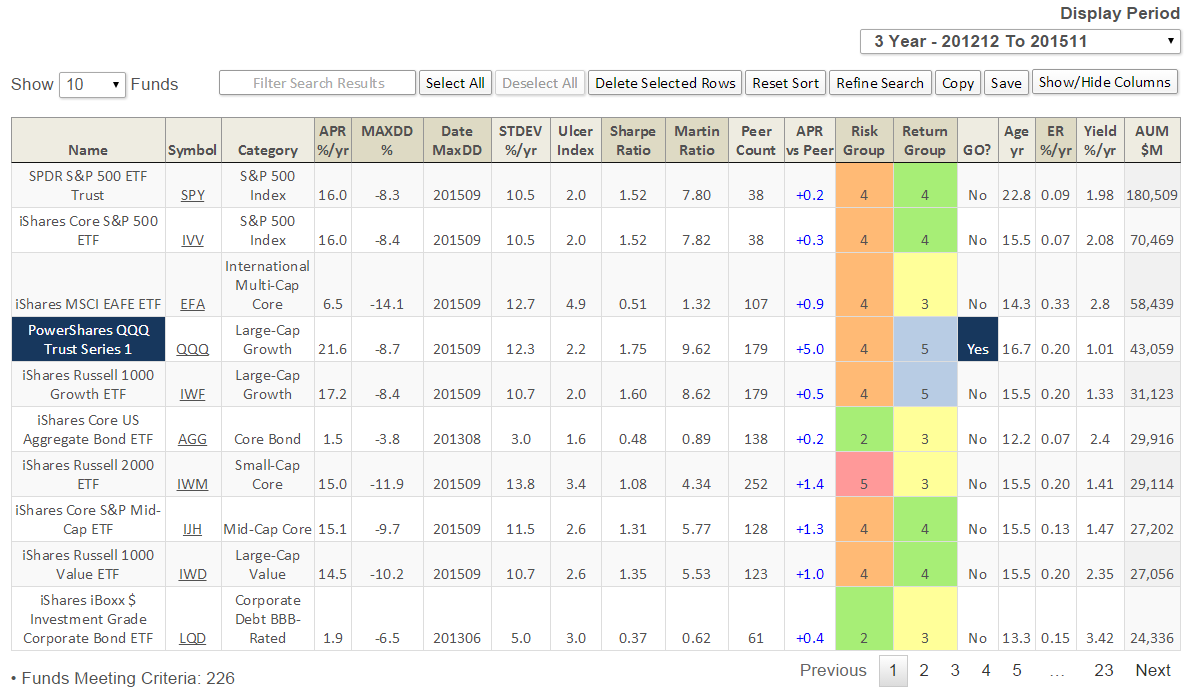
The ETF flag is self-explanatory, of course. How many ETFs are in our November database? A lot! 1,716 of the 9,034 unique (aka oldest share class) funds we cover are ETFs, or nearly 19%. The most populated ETF subtype is Sector Equity with 364, followed by International Equity with 343, US Equity with 279, and Bonds with 264. At nearly $2T in assets under management (AUM), ETFs represent 12% of the market. Our screener shows 226 ETFs with more than $1B in AUM. Here is a summary of 3-year performance for top ten ETFs by AUM (click on image to enlarge):
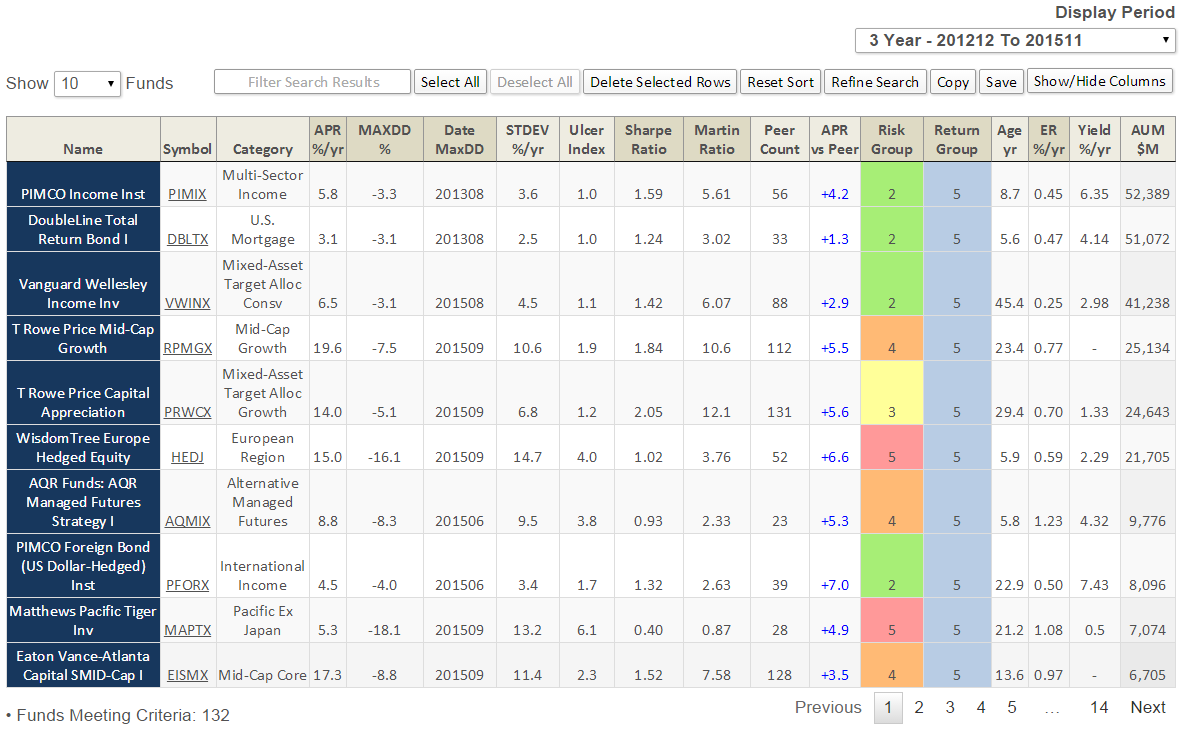
 The Pre-Set Screen option is simply a collection of screening criteria. The two initial screens are “Best Performing Rookie Funds” and “Both Great Owl and Honor Roll Funds.” The former generates a list of 160 funds that are between the age of 1 and 2 years old and have delivered top quintile risk adjusted return (based on Martin Ratio) since their inception. The latter generates a list of 132 funds that have received both our Great Owl distinction as well as Honor Roll designation. Here is a summary of 3-year performance for top ten such funds, again by AUM (click on image to enlarge) … it’s an impressive list:
The Pre-Set Screen option is simply a collection of screening criteria. The two initial screens are “Best Performing Rookie Funds” and “Both Great Owl and Honor Roll Funds.” The former generates a list of 160 funds that are between the age of 1 and 2 years old and have delivered top quintile risk adjusted return (based on Martin Ratio) since their inception. The latter generates a list of 132 funds that have received both our Great Owl distinction as well as Honor Roll designation. Here is a summary of 3-year performance for top ten such funds, again by AUM (click on image to enlarge) … it’s an impressive list:
 Other Pre-Screens David has recommended include “moderate allocation funds with the best Ulcer Index, small caps with the shortest recovery times, fixed-income funds with the smallest MAXDD …” Stay tuned.
Other Pre-Screens David has recommended include “moderate allocation funds with the best Ulcer Index, small caps with the shortest recovery times, fixed-income funds with the smallest MAXDD …” Stay tuned.
Along with the parameters above, new options were added to existing criteria in the MultiSearch Tool. These include 30, 40, and 50 year Age groups; a “Not Three Alarm” rating; and, a “0% Annual or More” Absolute Return setting.
Using the new “0% Annual or More” criterion, we can get a sense of how tough the past 12 months have been for mutual funds. Of the 8,450 funds across all categories at least 12 months old through November 2015, nearly 60% (4,835) returned less than 0% for the year. Only 36 of 147 moderate allocation funds delivered a positive return, which means nearly 75% lost money … believe it or not, this performance was worse than the long/short category.
A closer look at the long/short category shows 56 of 121 funds delivered positive absolute return. Of those, here are the top five based on risk adjusted return (Martin Ratio) … click on image to enlarge:
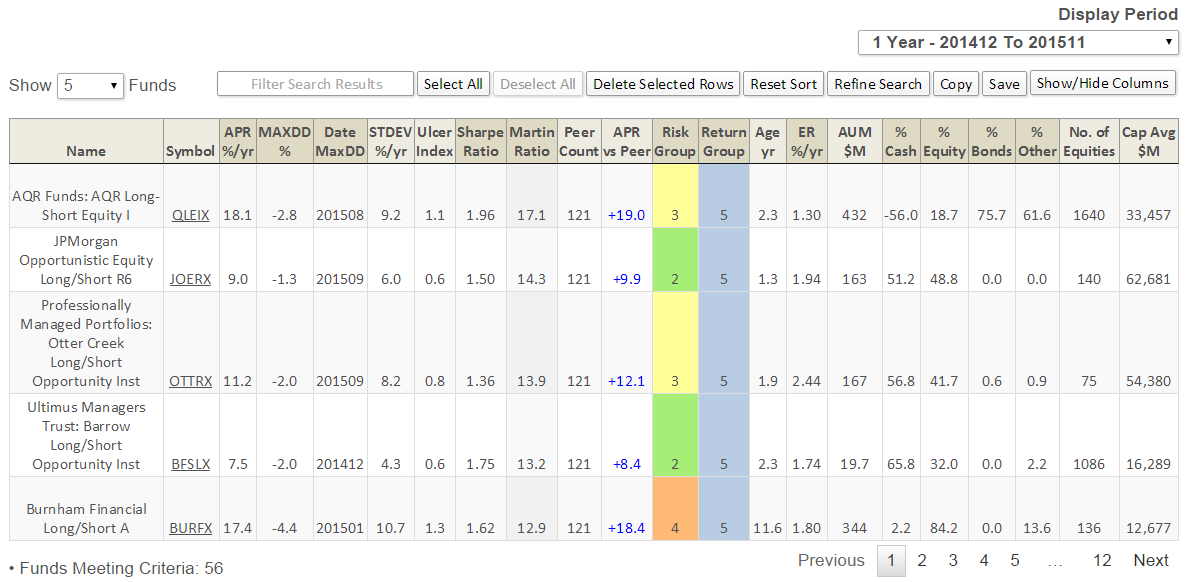
AQR Long/Short
AQR’s rookie Long/Short Equity I (QLEIX) has been eye-watering since inception, as can be seen in its Risk Profile (click on images to enlarge):
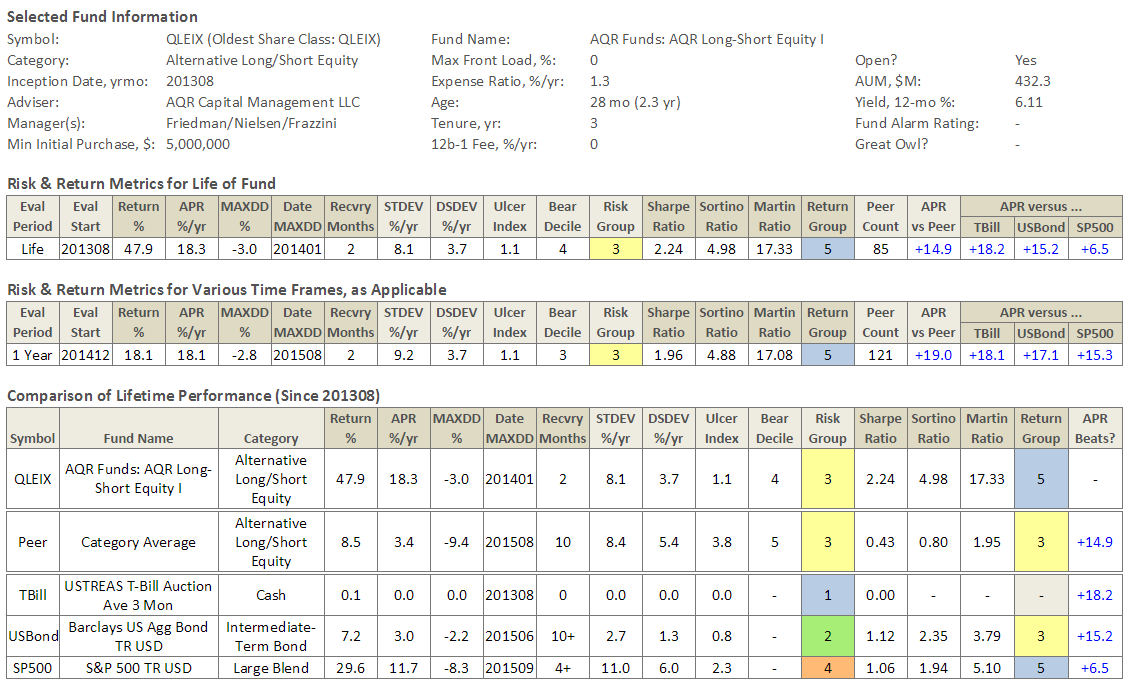
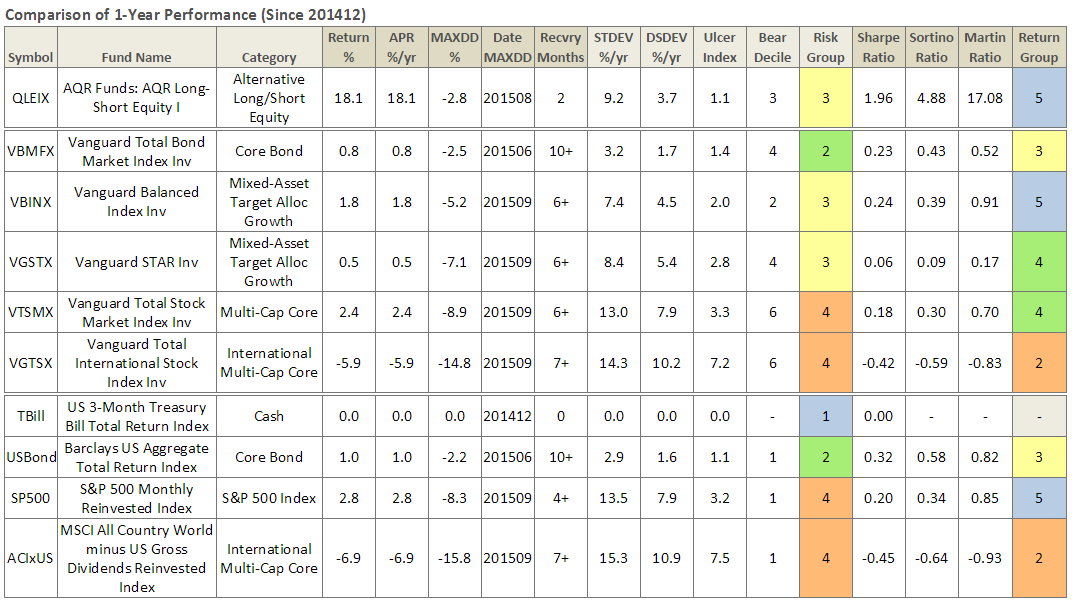
While I’ve always been a fan of Cliff Asness and the strategies at AQR, I’m not a fan of AQR Funds, since experiencing unfriendly shareholder practices, namely lack of disclosure when its funds underperform … but nothing speaks like performance.
Whitebox Funds
I have also always been a fan of Andrew Redleaf and Whitebox Funds, which we featured in the March 2015 Whitebox Tactical Opportunities 4Q14 Conference Call and October 2013 Whitebox Tactical Opportunities Conference Call. David has remained a bit more guarded, giving them a “Mixed” profile in April 2013 Whitebox Market Neutral Equity Fund, Investor Class (WBLSX), April 2013.
This past month the Minneapolis-based shop decided to close its three open-end funds, which were based on its hedge-fund strategies, less than four years after launch. A person familiar with the adviser offered: “They were one large redemption away from exposing remaining investors to too great a concentration risk … so, the board voted to close the funds.” AUM in WBMIX had grown to nearly $1B, before heading south. According to the same person, Whitebox hedge funds actually attracted $2B additional AUM the past two years and that was where they wanted to concentrate their efforts.
The fund enjoyed 28 months (about as long as QLEIX is old) of strong performance initially, before exiting the Mr. Market bus. Through November 2015, it’s incurred 19 consecutive months of drawdown and a decline from its peak of 24.2%. Depicting its rise and fall, here is a Morningstar growth performance plot of WBMIX versus Vanguard’s Balanced Fund Index (VBINX), as well as the MFO Risk Profile (click on images to enlarge):
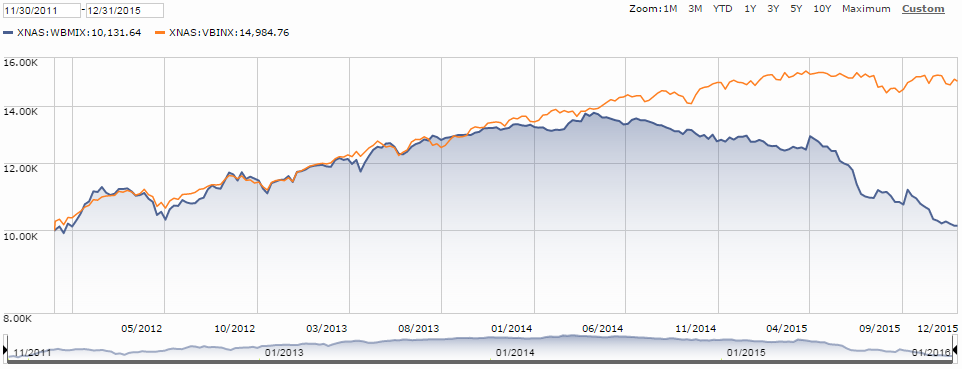
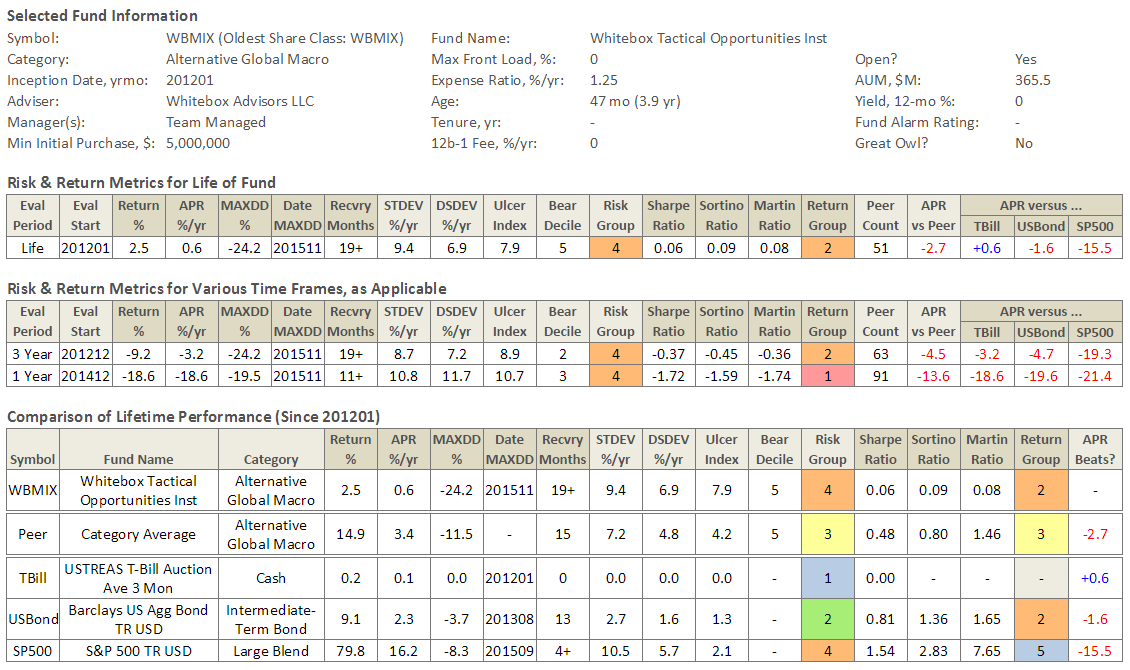
Ultimately, Mr. Redleaf and company failed to deliver returns across the rather short life span of WBMIX consistent with their goal of “the best endowments.” Ultimately, they also failed to deliver performance consistent with the risk tolerance and investment timeframe of its investors. Ultimately and unfortunately, there was no “path to victory” in the current market environment for the fund’s “intelligent value” strategy, as compelling as it sounded and well-intended as it may have been.
As always, a good discussion can be found on the MFO Board Whitebox Mutual Funds Liquidating Three Funds, along with news of the liquidations.
Year-end MFO ratings will be available on or about 4th business day, which would be January 7th on both our premium and legacy sites.
Snow Tires and All-Weather portfolios

Leigh Walzer, founder and principal of Trapezoid, LLC. Leigh’s had a distinguished career working in investment management, in part in the tricky field of distressed securities analysis. He plied that trade for seven years with Michael Price and the Mutual Series folks. He followed that with a long stint as a director at Angelo, Gordon & Co., a well-respected alternatives manager and a couple private partnerships. Through it all, Leigh has been insatiably curious about not just “what works?” but, more importantly, “why does it work?” That’s the work now of Trapezoid LLC.
By Leigh Walzer
Readers of a certain age will remember when winter meant putting on the snow tires. All-season tires were introduced in 1978 and today account for 96% of the US market. Not everyone is sure this is a good idea; Edmunds.com concludes “snow and summer tires provide clear benefits to those who can use them.”
As we begin 2016, most of the country is getting its first taste of winter weather. “Putting on the snow tires” is a useful metaphor for investors who are considering sacrificing performance for safety. Growth stocks have had a great run while the rest of the market sits stagnant. Fed-tightening, jittery credit markets, tight-fisted consumer, commodity recession, and sluggishness outside the US are good reasons for investor caution.
Some clients have been asking if now is a good time to dial back allocations to growth. In other words, should they put the snow tires on their portfolio.
The dichotomy between growth and value and the debate over which is better sometimes approaches theological overtones. Some asset allocators are convinced one or the other will outperform over the long haul. Others believe each has a time and season. There is money to be made switching between growth and value, if only we had 20/20 hindsight about when the business cycle turns.
When has growth worked better than value?
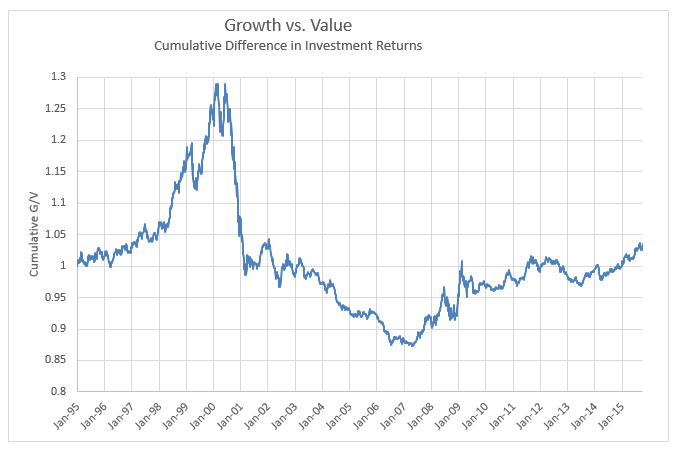
Historically, the race between growth and value has been nearly a dead heat. Exhibit 1 shows the difference in the Cumulative return of Growth and Value strategies over the past twenty years. G/V is a measure of the difference in return between growth and value in a given period Generally speaking, growth performed better in the 90s, a period of loose money up to the internet bust. Value did better from 2000-2007. Since 2007, growth has had the edge despite a number of inflections. Studies going back 50 years suggest value holds a slight advantage, particularly during the stagflation of the 1970s.
Exhibit I
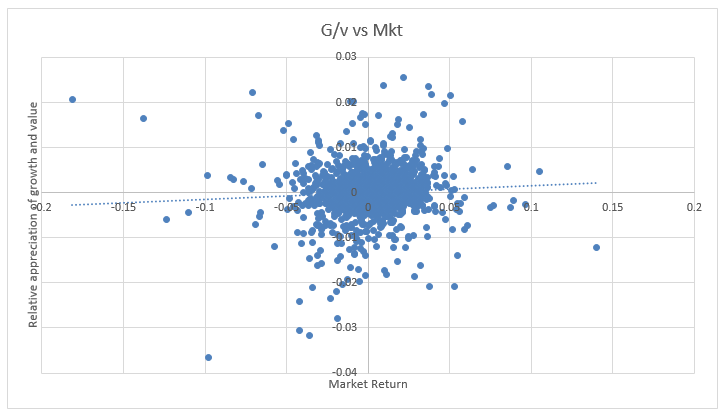
Growth tends to perform better in up-markets. This relationship is statistically valid but the magnitude is almost negligible. Over the past twenty years Trapezoid’s US Growth Index had a beta of 1.015 compared with 0.983 for Value.
Exhibit II
The conventional wisdom is that growth stocks should perform better early to mid-cycle while value stocks perform best late in the business cycle and during recession. That might loosely describe the 90s and early 2000s. However, in the run up the great recession, value took a bigger beating as financials melted down. And when the market rebounded in April 2009, value led the recovery for the first six months.
Value investors expect to sacrifice some upside capture in order to preserve capital during declining markets. Exhibit III, which uses data from Morningstar.com about their Large Growth (“LG”) and Large Value (“LV”) fund categories, shows the reality is less clear. In 2000-2005 LV lived up to its promise: it captured 96% of LG’s upside but only 63% of its downside. But since 2005 LV has actually participated more in the downside than LG.
Exhibit III
|
2001-2005 |
2006-2010 |
2011- 2015 |
| |
|
|
|
| LG Upside Capture |
105% |
104% |
98% |
| LG Downside Capture |
130% |
101% |
106% |
| |
|
|
|
| LV Upside Capture |
101% |
99% |
94% |
| LV Downside Capture |
82% |
101% |
111% |
| |
|
|
|
| LV UC / LG Up Capt |
96% |
95% |
97% |
| LV DC / LG Dn Capt |
63% |
100% |
104% |
Recent trend
In 2015 (with the year almost over as of this writing), value underperformed growth by about 5%. Value funds are overweight energy and underweight consumer discretionary which contributed to the shortfall.
Can growth/value switches be predicted accurately?
In the long haul, the two strategies perform nearly equally. If the weatherman can’t predict the snow, maybe it makes sense to leave the all-season tires on all year.
We can look through the historical Trapezoid database to see which managers had successfully navigated between growth and value. Recall that Trapezoid uses the Orthogonal Attribution Engine to attribute the performance of active equity managers over time to a variety of skills. Trapezoid calculates the contribution to portfolio return from overweighting growth or value in a given period. We call this sV.
Demonstrable skill shifting between growth and value is surprisingly scarce.
Bear in mind that Trapezoid LLC does not call market turns or rate sectors for timeliness. And Trapezoid doesn’t try to forecast whether growth or value will work better in a given period. But we do try to help investors make the most of the market. And we look at the historic and projected ability of money managers to outperform the market and their peer group based on a number of skills.
The Trapezoid data does identify managers who scored high in sV during particular periods. Unfortunately, high sV doesn’t seem to carry over from period to period. As Professor Snowball would say, sV lacks predictive validity; the weatherman who excelled last year missed the big storm this year. However, the data doesn’t rule out the possibility that some managers may have skill. As we have seen, growth or value can dominate for many years, and few managers have sufficient tenure to draw a strong conclusion.
We also checked whether market fundamentals might help investors allocate between growth and value. We are aware of one macroeconomic model (Duke/Fuqua 2002) which claims to successfully anticipate 2/3 of growth and value switches over the preceding 25 years.
One hypothesis is that value excels when valuations are stretched while growth excels when the market is not giving enough credit to earnings growth. In principle this sounds almost tautologically correct. However, implementing an investment strategy is not easy. We devised an index to see how much earnings growth the market is pricing in a given time (S&P500 E/P less 7-year AAA bond yield adjusted for one year of earning growth). When the index is high, it means either the equity market is attractive relative bonds or that the market isn’t pricing in much earnings growth. Conversely, when the index is low it means valuations of growth stocks are stretched and therefore investors should load up on value. We looked at data from 1995-2015 and compared the relative performance of growth and value strategies over the following 12 months. We expected that when the index is high growth would do better.
Exhibit IV
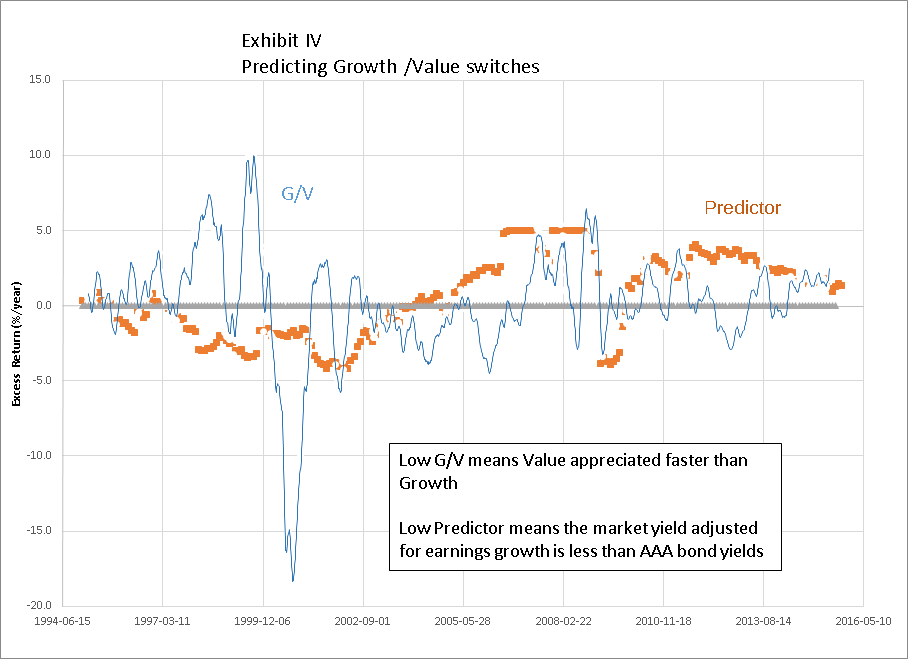
There are clearly times when investors who heeded this strategy would have correctly anticipated investing cycles. We found the index was directionally correct but not statistically significant. Exhibit IV shows the Predictor has been trending lower in 2015 which would suggest that the growth cycle is nearly over.
All-Weather Managers
Since it is hard to tell when value will start working, investors could opt for all-weather managers, i.e. managers with a proven ability to thrive during value and growth periods.
We combed our database for active equity managers who had an sV contribution of at least 1%/year in both the growth era since 1q07 and the value market which preceded it. Our filter excludes a large swath of managers who haven’t been around 9 years. Only six funds passed this screen – an indication that skill at navigating between growth and value is rare. We knocked out four other funds because, using Trapezoid’s standard methodology, projected skill is low or expenses are high. This left just two funds.
Century Shares Trust (CENSX), launched in 1928, is one of the oldest mutual funds in the US. The fund tracks itself against the Russell 1000 Growth Index but does not target a particular sector mix and apply criteria like EV/EBITDA more associated with value. Expenses run 109bps. CENSX’s performance has been strong over the past three years. Their long-term record selecting stocks and sectors is not sufficient for inclusion in the Trapezoid Honor Roll.
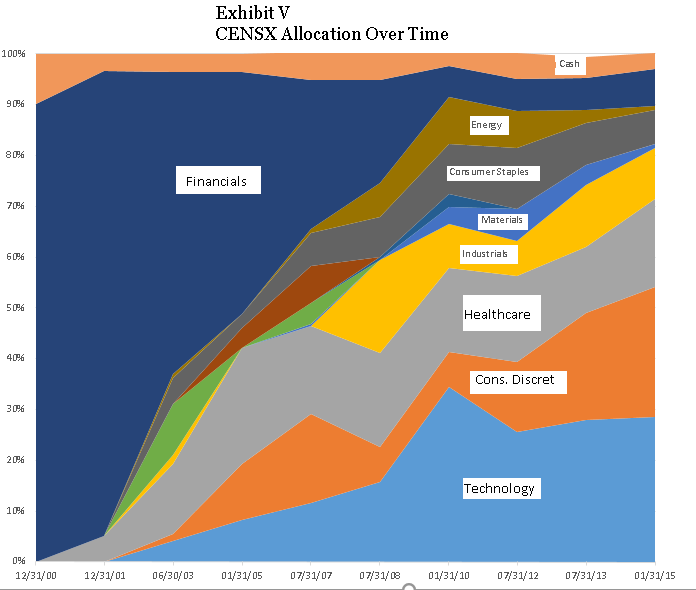 Does CENSX merit extra consideration because of the outstanding contribution from rotating between growth and value? Serendipity certainly plays a part. As Exhibit V illustrates, the current managers inherited in 1999 a fund which was restricted by its charter to financials, especially insurance. That weighting was very well-suited to the internet bust and recession which followed. They gradually repositioned the portfolio towards large growth. And he has made a number of astute switches. Notably, he emphasized consumer discretionary and exited energy which has worked extremely well over the past year. We spoke to portfolio manager Kevin Callahan. The fund is managed on a bottom-up fundamentals basis and does not have explicit sector targets. But he currently screens for stocks from the Russell 1000 Growth Index and seem reluctant to stray too far from its sector weightings, so we expect growth/value switching will be much more muted in the future.
Does CENSX merit extra consideration because of the outstanding contribution from rotating between growth and value? Serendipity certainly plays a part. As Exhibit V illustrates, the current managers inherited in 1999 a fund which was restricted by its charter to financials, especially insurance. That weighting was very well-suited to the internet bust and recession which followed. They gradually repositioned the portfolio towards large growth. And he has made a number of astute switches. Notably, he emphasized consumer discretionary and exited energy which has worked extremely well over the past year. We spoke to portfolio manager Kevin Callahan. The fund is managed on a bottom-up fundamentals basis and does not have explicit sector targets. But he currently screens for stocks from the Russell 1000 Growth Index and seem reluctant to stray too far from its sector weightings, so we expect growth/value switching will be much more muted in the future.
The other fund which showed up is Cohen & Steers Global Realty Fund (CSSPX). The entire real estate category had positive sV over the past 15-20 years; real estate (both domestic and global) clobbered the market during the value years, gave some back in the run-up to the financial crisis, and has been a market performer since then.
We are not sure how meaningful it is that CSSPX made this list over some other real estate funds with similar focus and longevity. Investors may be tempted to embrace real estate as an all-weather sector. But over the longer haul real estate has had a more consistent market correlation with beta averaging 0.6 which means it participated equally in up and down markets.
More complete information can be found at www.fundattribution.com. MFO readers can sign up for a free demo. Please click the link from the Model Dashboard (login required) to the All-Weather Portfolio.
The All-Season Portfolio
Since we are not sure that good historic sV predicts future success and managers with a good track record in this area are scarce, investors might take a portfolio approach to all-season investing.
- Find best of breed managers. Use Trapezoid’s OAE to find managers with high projected skill relative to cost. While the Trapezoid demo rates only Large Blend managers (link to the October issue of MFO), the OAE also identifies outstanding managers with a growth or value orientation.
- Strike the right balance. Many thoughtful investors believe “value is all you need” and some counsel 100% allocation to growth. Others apply age-based parameters. Based on the portfolio-optimization model I consulted and my dataset, the recommended weighting of growth and value is nearly 50/50. In other words: snow tires on the front, summer tires on the back. (Note this recommendation is for your portfolio, for auto advice please ask a mechanic.) I used 20 years of data; using a longer time frame, value might look better.
Bottom line:
It is hard to predict whether growth or value will outperform in a given year. Demonstrable skill shifting between growth and value is surprisingly scarce. Investors who are content to be passive can just stick to funds which index the entire market. A better strategy is to identify skillful growth and value managers and weight them evenly.
 What’s the Trapezoid story? Leigh Walzer has over 25 years of experience in the investment management industry as a portfolio manager and investment analyst. He’s worked with and for some frighteningly good folks. He holds an A.B. in Statistics from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from Harvard University. Leigh is the CEO and founder of Trapezoid, LLC, as well as the creator of the Orthogonal Attribution Engine. The Orthogonal Attribution Engine isolates the skill delivered by fund managers in excess of what is available through investable passive alternatives and other indices. The system aspires to, and already shows encouraging signs of, a fair degree of predictive validity.
What’s the Trapezoid story? Leigh Walzer has over 25 years of experience in the investment management industry as a portfolio manager and investment analyst. He’s worked with and for some frighteningly good folks. He holds an A.B. in Statistics from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from Harvard University. Leigh is the CEO and founder of Trapezoid, LLC, as well as the creator of the Orthogonal Attribution Engine. The Orthogonal Attribution Engine isolates the skill delivered by fund managers in excess of what is available through investable passive alternatives and other indices. The system aspires to, and already shows encouraging signs of, a fair degree of predictive validity.
The stuff Leigh shares here reflects the richness of the analytics available on his site and through Trapezoid’s services. If you’re an independent RIA or an individual investor who need serious data to make serious decisions, Leigh offers something no one else comes close to. More complete information can be found at www.fundattribution.com. MFO readers can sign up for a free demo.
The Alt Perspective: Commentary and news from DailyAlts.
 As they say out here in Los Angeles, that’s a wrap. 2015 has come to a close and we begin anew. But before we get too far into 2016, let’s do a quick recap of some of the activity in the liquid alternatives market that occurred over the past year, starting with a performance review.
As they say out here in Los Angeles, that’s a wrap. 2015 has come to a close and we begin anew. But before we get too far into 2016, let’s do a quick recap of some of the activity in the liquid alternatives market that occurred over the past year, starting with a performance review.
Performance Review
Let’s start with traditional asset classes for the full year of 2015, where the average mutual fund for all of the major asset classes (per Morningstar) delivered negative performance on the year:
- Large Blend U.S. Equity: -1.06%
- Foreign Equity Large Blend: -1.56%
- Diversified Emerging Markets: -13.83%
- Intermediate Term Bond: -0.35%
- World Bond: -4.09%
- Moderate Allocation: -1.96%
Now a look at the liquid alternative categories, per Morningstar’s classification. As with the traditional asset classes, none of the alternative categories escaped a negative return on the year:
- Long/Short Equity: -2.08%
- Non-Traditional Bonds: -1.84%
- Managed Futures: -1.06%
- Market Neutral: -0.39%
- Multi-Alternative: -2.48%
- Bear Market: -3.16%
And a few non-traditional asset classes, where real estate generated a positive return:
- Commodities: -24.16%
- Multi-Currency: -0.62%
- Real Estate: 2.39%
- Master Limited Partnerships: -35.12%
Overall, a less than impressive year across the board with energy leading the way to the bottom.
Asset Flows
Flows into alternative mutual funds and ETFs remained fairly constant over the year in terms of where the flows were directed, with a total of $20 billion of new assets being allocated to funds in Morningstar’s alternative categories. However, non-traditional bond funds, which are not included in Morningstar’s alternatives categories, saw nearly $10 billion of outflows through November.
While the flows appeared strong, only three categories had net positive flows over the past twelve months: Multi-alternative funds, managed futures funds and volatility based funds. The full picture is below (data source: Morningstar):
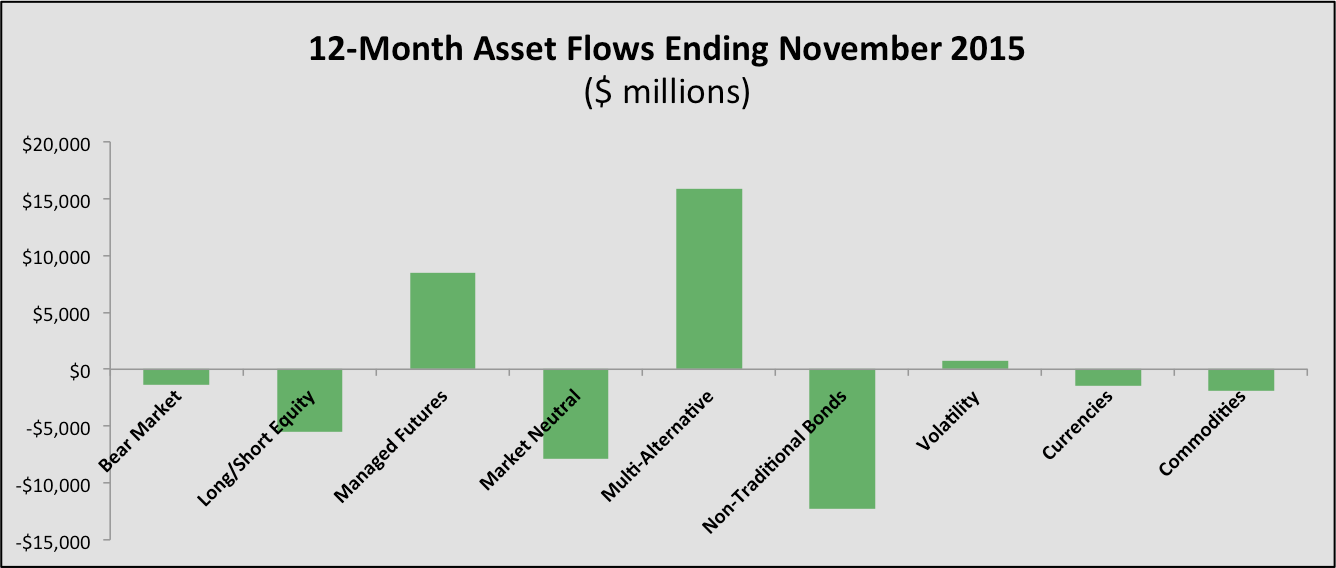
This concentration is not good for the industry, but just as we saw a shift from 2014 to 2015 (non-traditional bond funds were the largest asset gatherer in 2014), the flows will likely shift in 2016. I would expect managed futures to continue to see strong inflows, and both long/short equity and commodities could see a turn back to the positive.
Hot Topics
While there have been a slew of year-end fund launches (we will cover those next month), a dominant theme coming into the end of the year was fund closures. While the Third Avenue Focused Credit Fund announced an abrupt closure of its mutual fund due to significant outflows, the concentration of asset flows to alternative funds is causing a variety of managers to liquidate funds. Most recently, the hedge fund firm Whitebox Advisors decided to close three alternative mutual funds, the oldest of which was launched in 2011. This is a concerning trend, but reminds us that performance still rules.
On the research front, we published summaries of three important research papers in December, all three of which have been popular with readers:
If you would like to keep up with all the news from DailyAlts, feel free to sign up for our daily or weekly newsletter.
All the best for 2016! Have a happy, safe and prosperous year.
Elevator Talk: Randy Swan, Swan Defined Risk (SDRAX/SDRIX)
 Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we have decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we have decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
 Randy Swan manages SDRAX, which launched at the end of July 2012. He founded Swan Capital Management, which uses this strategy in their separately managed accounts in 1997. Before then, Mr. Swan was a CPA and senior manager for KPMG’s Financial Services Group, primarily working with insurance companies and risk managers. Mr. Swan manages about $27 million in other accounts, including the new Swan Defined Risk Emerging Markets (SDFAX).
Randy Swan manages SDRAX, which launched at the end of July 2012. He founded Swan Capital Management, which uses this strategy in their separately managed accounts in 1997. Before then, Mr. Swan was a CPA and senior manager for KPMG’s Financial Services Group, primarily working with insurance companies and risk managers. Mr. Swan manages about $27 million in other accounts, including the new Swan Defined Risk Emerging Markets (SDFAX).
“Stocks for the long term” is an attractive claim, give or take two small problems. First, investors live in the short term; their tolerance for pain is somewhere between three days and three years with most sitting toward the shorter end of that range. Second, sharp losses in the short term push the long-term further off; many of the funds that suffered 50% losses in the 2007-09 debacle remain underwater seven years later.
Bright investors know both of those things and try to hedge their portfolios against risk. The questions become (1) what risk do you try to hedge out? and (2) what tools do you choose? The answers include “everything conceivable and several inconceivable risks” and “balanced portfolios” to “expensive, glitch, inexplicably complicated black box schemes.”
Mr. Swan’s answers are (1) the risk of grinding bear markets but not short-term panics and (2) cheap, value-oriented equity exposure and long-dated options. The strategy is, he says, “always invested, always hedged.”
It’s nice to note that the strategy has outperformed both pure equity and balanced strategies, net of fees, since inception. $10,000 invested with Swan in 1997 has now grown to roughly $44,000 while a comparable investment in the S&P500 climbed to $30,300 and a balanced portfolio would have reached $25,000. I’m more struck, though, by the way that Swan generated those returns. The graphic below compares the variability in returns of the S&P and Swan’s strategy over the nearly 19 years he’s run the strategy. Each line represents the performance for one 10-year period (1998-2007, 1999-2008 and so on).
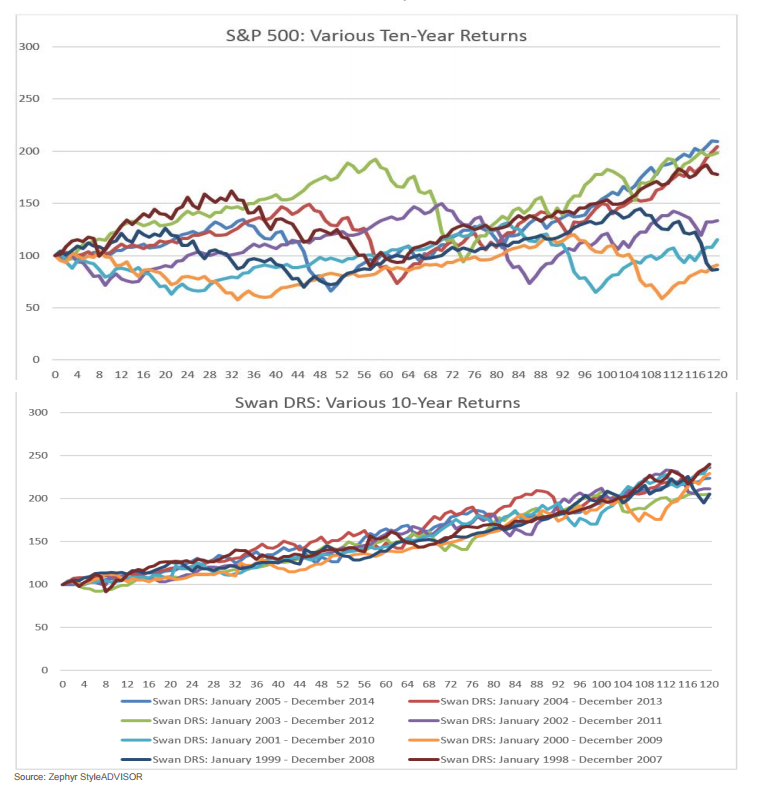
The consistency of Swan’s returns are striking: in his worst 10-year run, he averaged 7.5% annually while the best run generated 9%. The S&P returns are, in contrast, highly variable, unpredictable and lower.
Here are Mr. Swan’s 222 words on why you should add SDRAX to your due-diligence list:
We’ve managed this strategy since 1997 as a way of addressing the risks posed by bear markets. We combine tax-efficient, low-cost exposure to the U.S. stock market with long-dated options that protect against bears rather than corrections. We’re vulnerable to short-term declines like August’s correction but we’ve done a great job protecting against bears. That’s a worthwhile tradeoff since corrections recover in months (August’s losses are pretty much wiped out already) but bears take years.
Most investors try to manage risk with diversification but you can’t diversify market risk away. Instead, we choose to directly attack market risk by including assets that have an inverse correlation to the markets. At the same time, we maintain a stock portfolio that equally weights all nine sectors through the Select SPDR ETFs which we rebalance regularly. In the long-term, all of the research we’ve seen says an equal-weight strategy will outperform a cap-weighted one because it forces you to continually buy undervalued sectors. That strategy underperforms at the end of a bull market when index gains are driven by a handful of momentum-driven stocks, but over full market cycles it pays off.
Our maxim is KISS: keep it simple, stupid. Low-cost market exposure, reliable hedges against bear markets, no market timing, no attempts at individual security selection. It’s a strategy that has worked for us.
The fund lost about 4% in 2015. Over the past three years, the fund has returned 5.25% annually, well below the S&P 500’s 16%. With the fund’s structural commitment to keeping 10% in currently-loathed sectors such as energy, utilities and basic materials, that’s neither surprising nor avoidable.
Swan Defined-Risk has a $2500 minimum initial investment on its “A” shares, which bear a sales load, and $100,000 on its Institutional shares, which do not. Expenses on the “A” shares run a stiff 1.58% on assets of $1.4 billion, rather below average, while the institutional shares are 25 basis points less. Load-waived access to the “A” shares is available through Schwab, Fidelity, NFS, & TD Ameritrade. Pershing will be added soon.
Here’s the fund’s homepage. Morningstar also wrote a reasonably thoughtful article reflecting on the difference in August 2015 performance between Swan and a couple of apparently-comparable funds. A second version of the article features an annoying auto-launch video.
Funds in Registration
There are 14 new no-load funds in the pipeline. Most will be available by late February or early March. While the number is not extraordinarily high, their parentage is. This month saw filings on behalf of American Century (three funds), DoubleLine, T. Rowe Price (three) and Vanguard (two).
The most intriguing registrant, though, is a new fund from Seafarer. Seafarer Overseas Value Fund will invest in an all-cap EM stock portfolio. Beyond the bland announcement that they’ll use a “value” approach (“investing in companies that currently have low or depressed valuations, but which also have the prospect of achieving improved valuations in the future”), there’s little guidance as to what the fund’s will be doing.
The fund will be managed by Paul Espinosa. Mr. Espinosa had 15 years as an EM equity analyst with Legg Mason, Citigroup and J.P. Morgan before joining Seafarer in May, 2014. Seafarer’s interest in moving in the direction of a value fund was signaled in November, with their publication of Mr. Espinosa’s white paper entitled On Value in the Emerging Markets. It notes the oddity that while emerging markets ought to be rife with misvalued securities, only 3% of emerging markets funds appear to espouse any variety of a value investing discipline. That might reflect Andrew Foster’s long-ago observer that emerging markets were mostly value traps, where corporate, legal and regulatory structures didn’t allow value to be unlocked. More recently he’s mused that those circumstances might be changing.
In any case, after a detailed discussion of what value investing might mean in the emerging markets, the paper concludes:
This exploration discovered a large value opportunity set with an aggregate market capitalization of $1.4 trillion, characterized by financial metrics that strongly suggest the pervasive presence of discounts to intrinsic worth.
After examining most possible deterrents, this study found no compelling reason that investors would forgo value investing in the emerging markets. On the contrary, this paper documented a potential universe that was both large and compelling. The fact that such an opportunity set remains largely untapped should make it all the more attractive to disciplined value practitioners.
The initial expense ratio has not yet been set, though Seafarer is evangelical about providing their services at the lowest practicable cost to investors, and the minimum initial investment is $2,500.
Manager Changes
Fifty-six funds saw partial or complete turnover in their management teams in the past month. Most of the changes seemed pretty modest though, in one case, a firm’s president and cofounder either walked out, or was shown, the door. Curious.
Updates
Back in May, John Waggoner took a buyout offer from USA Today after 25 years as their mutual funds guru. Good news: he’s returning to join InvestmentNews as a senior contributor and mutual funds specialist. Welcome back, big guy!
Briefly Noted . . .
At a Board meeting held on December 11, 2015, RiskX Investments, LLC (formerly American Independence Financial Services, LLC), the adviser to the RX Dynamic Stock Fund (IFCSX formerly, the American Independence Stock Fund), recommended to the Trustees of the Board that the Fund change its investment strategy from value to growth. On whole, that seems like a big honkin’ shift if you were serious about value in the first place but they weren’t: the fund’s portfolio – which typically has a turnover over 200% a year – shifted from core to value to core to value to growth over five consecutive years. That’s dynamic!
SMALL WINS FOR INVESTORS
“The closure of the 361 Managed Futures Strategy Fund (AMFQX) to investment by new investors that was disclosed by the Fund in Supplements dated September 9, 2015, and September 30, 2015, has been cancelled.” Well, okay then!
On December 31st, Champlain Emerging Markets Fund (CIPDX) announced that it was lowering its expense ratio from 1.85% to 1.60%. With middle-of-the-road performance and just $2 million in assets, it’s worth trying.
It appears that AMG Frontier Small Cap Growth Fund (MSSGX) and AMG TimesSquare Mid Cap Growth Fund (TMDIX) reopened to new investors on January 1. Their filings didn’t say that they reopening; they said, instead, that “With respect to the sub-section ‘Buying and Selling Fund Shares’ in the section ‘Summary of the Funds’ for the Fund, the first paragraph is hereby deleted in its entirety.” The first paragraph explained that the funds were soft-closed.
Effective January 1, ASTON/Cornerstone Large Cap Value Fund (RVALX) will reduce its expense ratio from 1.30% to 1.14% on its retail shares. Institutional shares will see a comparable drop.
Effective as of February 1, 2016, the Columbia Acorn Emerging Markets Fund (CAGAX) and Columbia Small Cap Growth Fund (CGOAX) will be opened to new investors and new accounts.
Effective January 1, 2016, Diamond Hill reduced its management fee for the four-star Diamond Hill Large Cap Fund (DHLAX) from an annual rate of 0.55% to 0.50%.
Effective immediately, the minimum initial investment requirements for the Class I Shares of Falcon Focus SCV Fund (FALCX) are being lowered to $5,000 for direct regular accounts and $2,500 for direct retirement accounts, automatic investment plans and gift accounts for minors.
Here’s why we claim to report nothing grander than “small wins” for investors: the board of Gotham Absolute 500 Fund (GFIVX) has graciously agreed to reduce the management fee from 2.0% to 1.5% and the expense cap from 2.25% to 1.75%. All of this on an institutional long/short fund with high volatility and a $250,000 minimum. The advisor calculates that it actually costs them 5.42% to run the fund. The managers both have over $1 million in each of their four funds.
Grandeur Peak has reduced fees on two of its funds. Grandeur Peak Emerging Markets Opportunities Fund (GPEOX) to 1.95% and 1.70% and Grandeur Peak Global Reach Fund (GPGRX) to 1.60% and 1.35%.
Effective January 4, 2016, Royce Premier Fund (RYPRX) and Royce Special Equity Fund (RYSEX) will reopen to new shareholders. Why, you ask? Each fund’s assets have tumbled by 50% since 2013 as Premier trailed 98% of its peers and Special trailed 92%. Morningstar describes Special as “a compelling small-cap option” and gives it a Gold rating.
Teton Westwood Mid-Cap Equity Fund (WMCRX) has reduced the expense cap for Class I shares of the Fund to 0.80%.
CLOSINGS (and related inconveniences)
Effective as of the close of business on December 31, 2015, Emerald Growth Fund (HSPGX) closed to new investors
The Class A shares of Hatteras Managed Futures Strategies Fund were liquidated in mid-December. The institutional class (HMFIX) remains in operation for now. Given that there’s a $1 million minimum initial investment and far less than $1 million in assets in the fund, I suspect we’ll continue thinning out of liquid-alts category soon.
Effective as of the close of business on January 28, 2016, Vontobel International Equity Institutional (VTIIX) and Vontobel Global Equity Institutional Fund (VTEIX) will soft close. Given that the funds have only $30 million between them, I suspect that they’re not long for this world.
OLD WINE, NEW BOTTLES
At the end of February, Aberdeen Small Cap Fund (GSXAX) becomes Aberdeen U.S. Small Cap Equity Fund. Two bits of good news: (1) it’s already a very solid performer and (2) it already invests 93% of its money in U.S. small cap equities, so it’s not likely that that’s going to change. At the same time, Aberdeen Global Small Cap Fund (WVCCX) will become Aberdeen International Small Cap Fund. The news here is mixed: (1) the fund kinda sucks and (2) it already invests more than 80% of its money in international small cap equities, so it’s not likely that that’s going to change either.
Sometime in the first quarter of 2016, Arden Alternative Strategies Fund (ARDNX) becomes Aberdeen Multi-Manager Alternative Strategies Fund, following Aberdeen’s purchase of Arden Asset Management.
Effective on February 1, 2016: AC Alternatives Equity Fund, which hasn’t even launched yet, will change its name to AC Alternatives Long Short Fund. After the change, the fund will no longer be required to invest at least 80% of its portfolio in equities.
As of February 27, 2016, Balter Long/Short Equity Fund (BEQRX) becomes Balter L/S Small Cap Equity Fund.
At an as-yet unspecified date, Capital Innovations Global Agri, Timber, Infrastructure Fund (INNAX) will become RidgeWorth Capital Innovations Global Resources and Infrastructure Fund. Interesting little fund, the subject of an Elevator Talk several months ago.
Gator Opportunities Fund (GTOAX) is on its way to becoming BPV Small Cap Fund, likely by the beginning of summer, 2016. The fund will shed its mid-cap holdings in the process.
At the end of January 2016, Marsico Growth FDP Fund (MDDDX) will become FDP BlackRock Janus Growth Fund. Which is to say, yes, Marsico lost another sub-advisory contract.
Effective December 31, 2015, the Meeder Strategic Growth Fund (FLFGX) changed its name to Global Opportunities Fund.
On February 24, 2016, the T. Rowe Price Diversified Small-Cap Growth Fund (PRDSX) will change its name to the T. Rowe Price QM U.S. Small-Cap Growth Equity Fund. The addition of “QM” in the fund’s name reflects the concept that the fund employs a “quantitative management” strategy.
On March 1, Transamerica Asset Management will make a few tweaks to Transamerica Growth Opportunities (ITSAX). The managers will change (from Morgan Stanley to Alta Capital); likewise the “fund’s investment objective, principal investment strategies, principal risks, benchmark index, portfolio managers [and] name, will change. The fund will also have a lower advisory fee schedule.” The reborn fund will be named Transamerica Multi-Cap Growth.
Effective January 31, 2016, the principal investment strategy of Turner Emerging Growth Fund (TMCGX) shifts from focusing on “small and very small” cap stocks to “small and mid-cap” ones. The fund will also change its name to the Turner SMID Cap Growth Opportunities Fund.
OFF TO THE DUSTBIN OF HISTORY
All Terrain Opportunity Fund (TERAX) liquidated on December 4, 2015. Why? It was only a year old, had $30 million in assets and respectable performance.
Big 4 OneFund (FOURX) didn’t make it to the New Years. The fund survived for all of 13 months before the managers despaired for the “inability to market the Fund.” It was a fund of DFA funds (good idea) which lost 12% in 12 months and trailed 94% of its peers. One wonders if the adviser should have ‘fessed up the “the inability to manage a fund that was worth buying”?
BPV Income Opportunities Fund liquidated on December 22, 2015, on about a week’s notice.
The Board of Trustees of Natixis Funds determined that it would be in the best interests of CGM Advisor Targeted Equity Fund (NEFGX) that it be liquidated, which will occur on February 17, 2016. Really, they said that: “it’s in the fund’s best interests to die.” The rest of the story is that CGM is buying itself back from Natixis; since Natixis won’t accept outside managers, the fund needed either to merge or liquidate. Natixis saw no logical place for it to merge, so it’s gone.
C Tactical Dynamic Fund (TGIFX) liquidated on December 31, 2015.
Clinton Long Short Equity Fund (WKCAX) liquidates on January 8, 2016.
Columbia has proposed merging away a half dozen of its funds, likely by mid-2016 though the date hasn’t yet been settled.
| Acquired Fund |
Acquiring Fund |
| Columbia International Opportunities |
Columbia Select International Equity |
| Columbia International Value |
Columbia Overseas Value |
| Columbia Large Cap Growth II, III, IV and V |
Columbia Large Cap Growth |
| Columbia Multi-Advisor Small Cap Value |
Columbia Select Smaller-Cap Value |
| Columbia Value and Restructuring |
Columbia Contrarian Core |
On or about March 31, 2016, the ESG Managers Growth Portfolio (PAGAX) will be consolidated into the ESG Managers Growth and Income Portfolio (PGPAX), which will then be renamed Pax Sustainable Managers Capital Appreciation Fund. At the same time, ESG Managers Balanced Portfolio (PMPAX) will be consolidated into the ESG Managers Income Portfolio (PWMAX) which will then be known as Pax Sustainable Managers Total Return Fund. The funds are all sub-advised by Morningstar staff.
Fortunatus Protactical New Opportunity Fund (FPOAX) liquidated on December 31, 2015. Why? The fund launched 12 months ago, had respectable performance and had drawn $40 million in assets. Perhaps combining the name of a 15th century adventurer (and jerk) with an ugly neologism (protactical? really?) was too much to bear.
Foundry Small Cap Value Fund liquidated on December 31, 2015.
Frost Cinque Large Cap Buy-Write Equity Fund (FCBWX) will cease operations and liquidate on or about February 29, 2016.
The tiny, one-star Franklin All Cap Value Fund (FRAVX), a fund that’s about 60% small caps, is slated to merge with huge, two-star Franklin Small Cap Value Fund (FRVLX), pending shareholder approval. That will likely occur at the beginning of April.
Back in 2008, if you wanted to pick a new fund that was certain to succeed, you’d have picked GRT Value. It combined reasonable expenses, a straightforward discipline and the services of two superstar managers (Greg Frasier, who’d been brilliant at Fidelity Diversified International and Rudy Kluiber who beat everyone as manager of State Street Research Aurora). Now we learn that GRT Value Fund (GRTVX) and GRT Absolute Return Fund (GRTHX) will liquidate on or about January 25, 2016. What happened? Don’t know. The fund rocketed out of the gate then, after two years, began to wobble, then spiral down. Both Value and its younger sibling ended up as tiny, failed shells. Perhaps the managers’ attention was riveted on their six hedge funds or large private accounts? Presumably the funds’ fate was sealed by GRT’s declining business fortunes. According to SEC filing, the firm started 2015 with $950 million in AUM, which dropped by $785 million by June and $500 million by September. The declining size of their asset base was accompanied by a slight increase in the number of accounts they were managing, which suggests the departure of a few major clients and a scramble to replace them with new, smaller accounts.
The folks behind the Jacobs/Broel Value Fund (JBVLX) have decided to liquidate the fund based on “its inability to market the Fund and the Adviser’s indication that it does not desire to continue to support the Fund.” Nearly all of the assets in the fund are the managers’ own money, perhaps because others wondered about paying 1.4% for:
The fund will liquidate on January 15, 2016.
On or around January 28, 2016, JOHCM Emerging Markets Small Mid Cap Equity Fund Service Class shares (JOMIX) will liquidate.
The Board of Directors of the Manning & Napier Fund, Inc. has voted to completely liquidate the Focused Opportunities Series (MNFSX) on or about January 25, 2016.
HSBC Growth Fund (HOTAX) will cease its investment operations and liquidate on or about February 12, 2016. Apparently the combination of consistently strong results with a $78 million asset base was not compelling.
McKinley Diversified Income Fund (MCDRX) is merging with Innovator McKinley Income Fund (IMIFX), pending shareholder approval. The reorganization will occur January 29, 2016.
Leader Global Bond Fund (LGBMX) will close, cease operations, redeem all outstanding shares and liquidate, all on January 29, 2016.
Madison Large Cap Growth Fund (MCAAX) merges with and into the Madison Investors Fund (MNVAX) on February 29, 2016. The Board mentions the identical objectives, strategies, risk profile and management as reason for why the merger is logical.
The Newmark Risk-Managed Opportunistic Fund (NEWRX) liquidated on December 31, 2015. The Board attributed the decision to the fund’s small size, rather than to the underlying problem: consistently bad short- and long-term performance.
Nile Frontier and Emerging Fund (NFRNX) liquidated, on about three weeks’ notice, on December 31, 2015.
QES Dynamic Fund (QXHYX) liquidated on December 17, 2015, after a week’s notice.
On January 29, 2016, Redmont Resolute Fund I (RMREX) becomes Redmont Dissolute Fund as it, well, dissolves.
Royce has now put the proposals to merge Royce European Small-Cap Fund (RESNX) and Global Value (RIVFX) into Royce International Premier Fund (RYIPX) to their shareholders. The proposal comes disturbingly close to making the argument that, really, there isn’t much difference among the Royce funds. Here is Royce’s list of similarities:
- the same objective;
- the same managers;
- the same investment approach;
- the same investment universe, small-cap equities;
- the same sort of focused portfolio;
- all provide substantial exposure to foreign securities;
- the same policy on hedging;
- the same advisory fee rates;
- the same restrictions on investments in developing country securities; and
- almost identical portfolio turnover rates.
Skeptics have long suggested that that’s true of the Royce funds in general; they have pretty much one or two funds that have been marketed in the guise of 20 distinct funds.
Third Avenue Focused Credit Fund (TFCVX) nominally liquidated on December 9, 2015. As a practical matter, cash-on-hand was returned to shareholders and the remainder of the fund’s assets were placed in a trust. Over the next year or so, the adviser will attempt to find buyers for its various illiquid holdings. The former fund’s shareholders will receive dribs and drabs as individual holdings are sold “at reasonable prices.”
Valspresso Green Zone Select Tactical Fund liquidated on December 30, 2015.
On December 2, 2015, Virtus Disciplined Equity Style, Virtus Disciplined Select Bond and Virtus Disciplined Select Country funds were liquidated.
Whitebox is getting out of the mutual fund business. They’ve announced plans to liquidate their Tactical Opportunities (WBMAX), Market Neutral Equity (WBLSX) and Tactical Advantage (WBIVX) funds on or about January 19, 2016.
In Closing . . .
In case you sometimes wonder, “Did I learn anything in the past year?” Josh Brown offered a great year-end compendium of observations from his friends and acquaintances, fittingly entitled “In 2015, I learned that …” Extra points if you can track down the source of “Everything’s amazing and nobody’s happy.”
And as for me, thanks and thanks and thanks! Thanks to the 140 or so folks who’ve joined MFO Premium as a way of supporting everything we’re doing. Thanks to the folks who’ve shared books, both classic (Irrational Exuberance, 3e) and striking (Spain: The Centre of the World, 1519-1682) and chocolates. I’m so looking forward to a quiet winter’s evening to begin them. Thanks to the folks who’ve read us and written to us, both the frustrated and the effusive. Thanks to my colleagues, Charles, Ed and Chip, who do more than I could possibly deserve. Thanks to the folks on the discussion board, who keep it lively and civil and funny and human. Thanks to the folks who’ve volunteered to help me learn to be halfway a businessperson, Sisyphus had it easier.
And thanks, especially, to all of you who’ll be here again next month.
We’ll look for you.



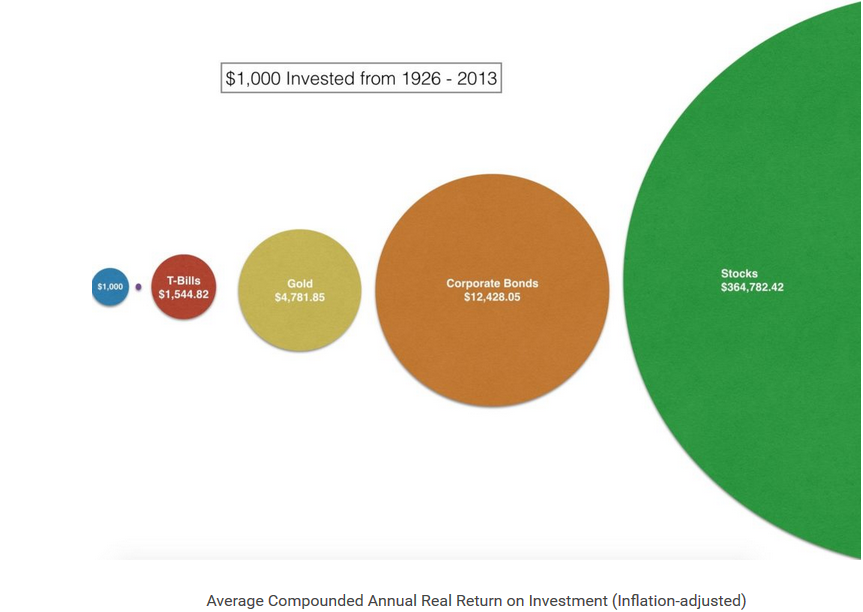
 This is another misconception about not being fully invested. If you have large discounts you can still generate attractive returns without being invested in what I call “fillers.” Just like with processed food, investment fillers are often there just to fill up the portfolio, but often provide little value and in some cases can be hazardous to your health! Open the hood of most fully invested small cap funds and you’ll find plenty of fillers these days, especially in sectors like consumer and health care. The stocks are clearly overvalued but managers think because they’re in lower risk sectors they won’t get destroyed. Good example WD-40 (WDFC) at 30x earnings! Great company but you could lose half your capital if it ever reverted to a more justifiable 7% free cash flow yield.
This is another misconception about not being fully invested. If you have large discounts you can still generate attractive returns without being invested in what I call “fillers.” Just like with processed food, investment fillers are often there just to fill up the portfolio, but often provide little value and in some cases can be hazardous to your health! Open the hood of most fully invested small cap funds and you’ll find plenty of fillers these days, especially in sectors like consumer and health care. The stocks are clearly overvalued but managers think because they’re in lower risk sectors they won’t get destroyed. Good example WD-40 (WDFC) at 30x earnings! Great company but you could lose half your capital if it ever reverted to a more justifiable 7% free cash flow yield. 


 We were delighted to announce last month that Bob Cochran joined MFO’s Board of Directors. Bob is the lead portfolio manager, Chief Compliance Officer, and a principal of PDS Planning in Columbus, Ohio, and a long-time contributor to the FundAlarm and MFO discussion boards.
We were delighted to announce last month that Bob Cochran joined MFO’s Board of Directors. Bob is the lead portfolio manager, Chief Compliance Officer, and a principal of PDS Planning in Columbus, Ohio, and a long-time contributor to the FundAlarm and MFO discussion boards. A family friend recently asked me to look at his mutual fund investments. He contributes to these investments periodically through his colleague, a
A family friend recently asked me to look at his mutual fund investments. He contributes to these investments periodically through his colleague, a 
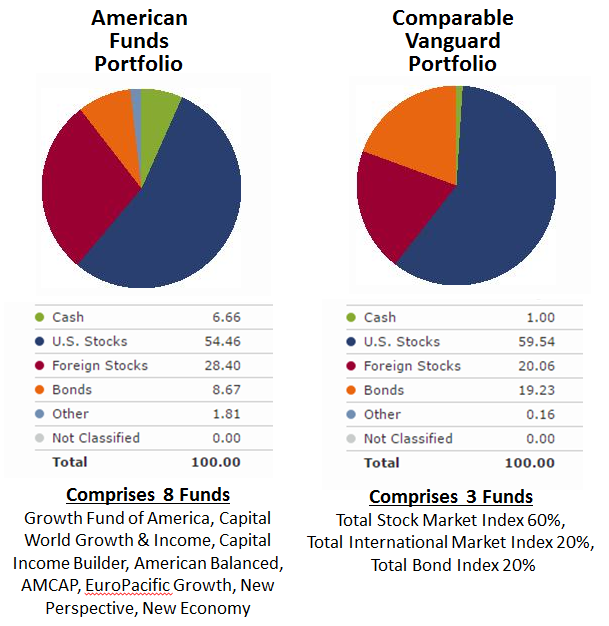
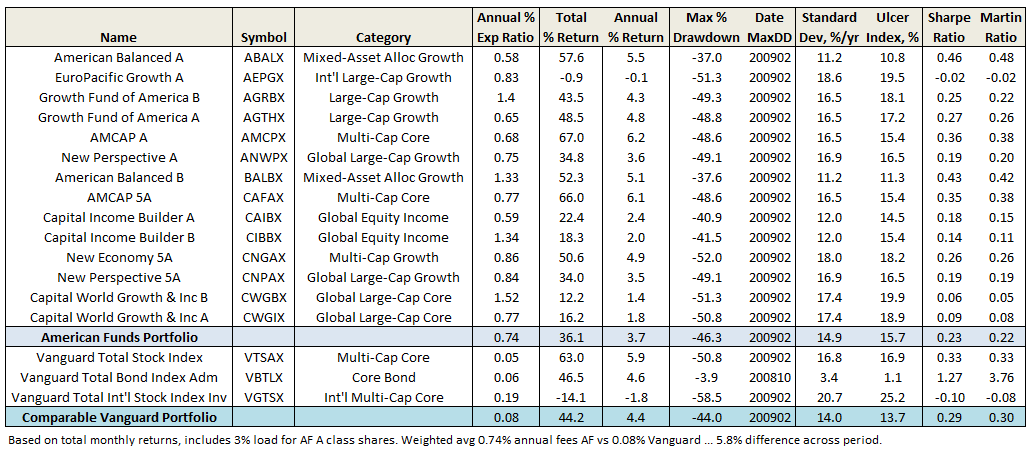
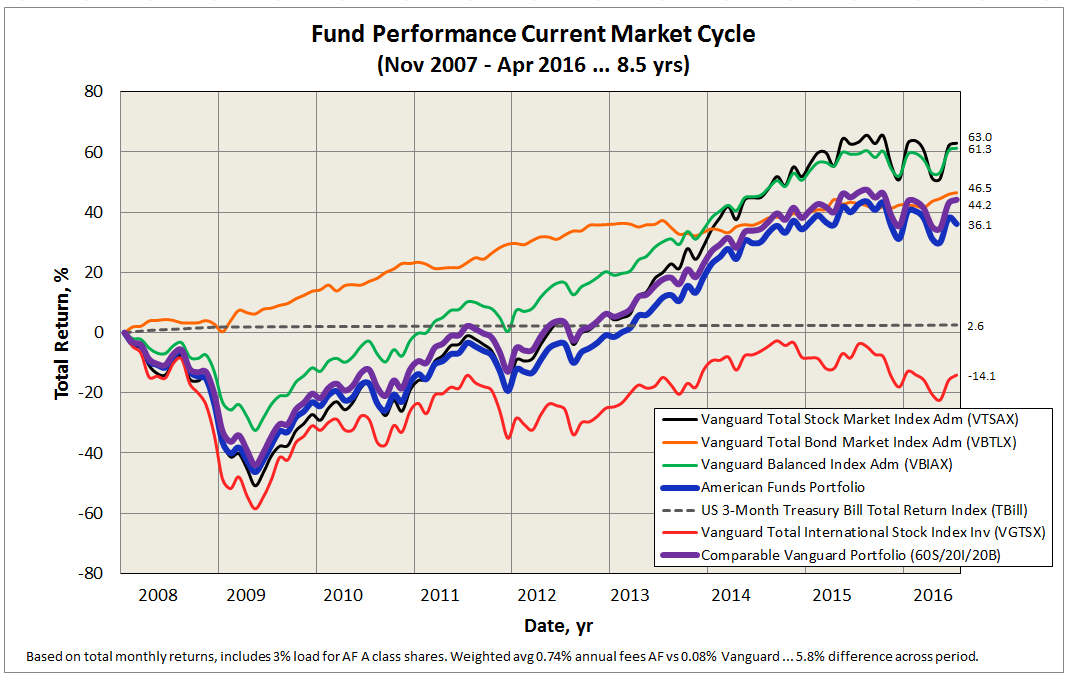
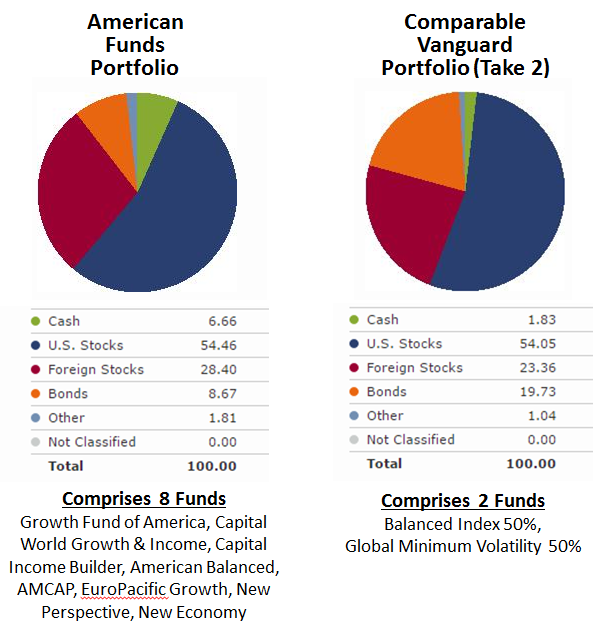
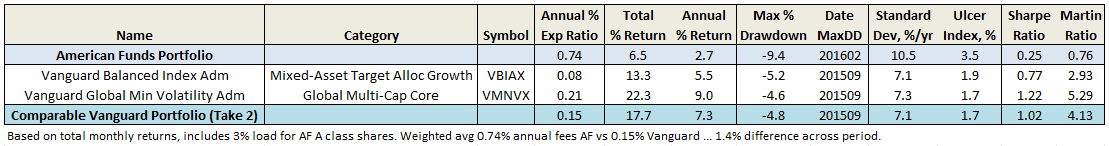
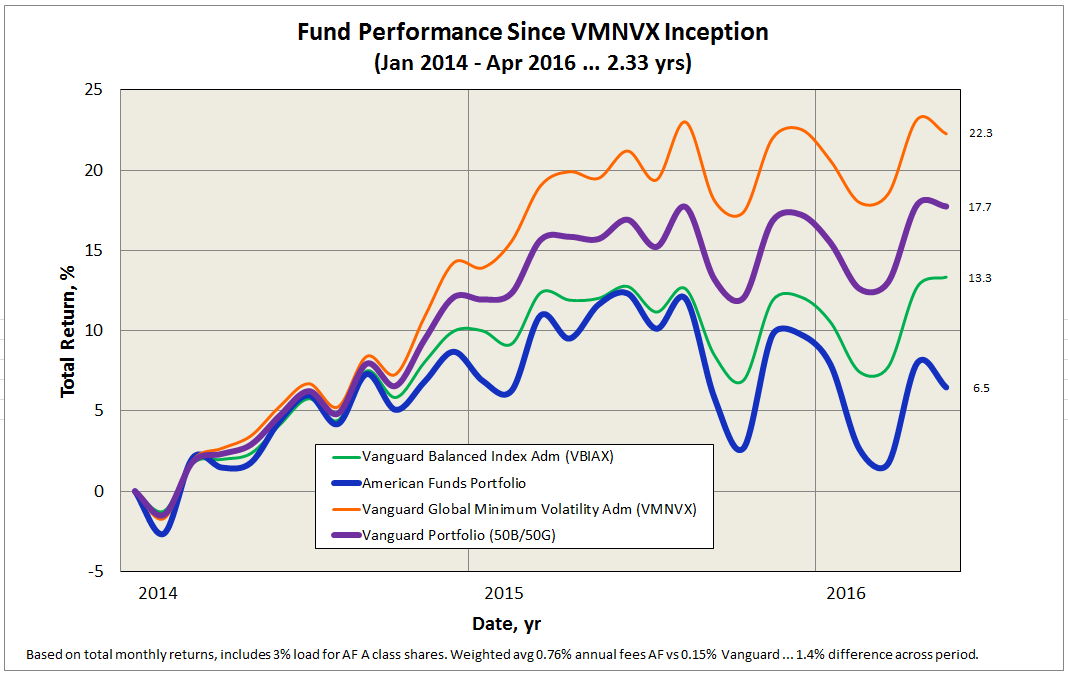
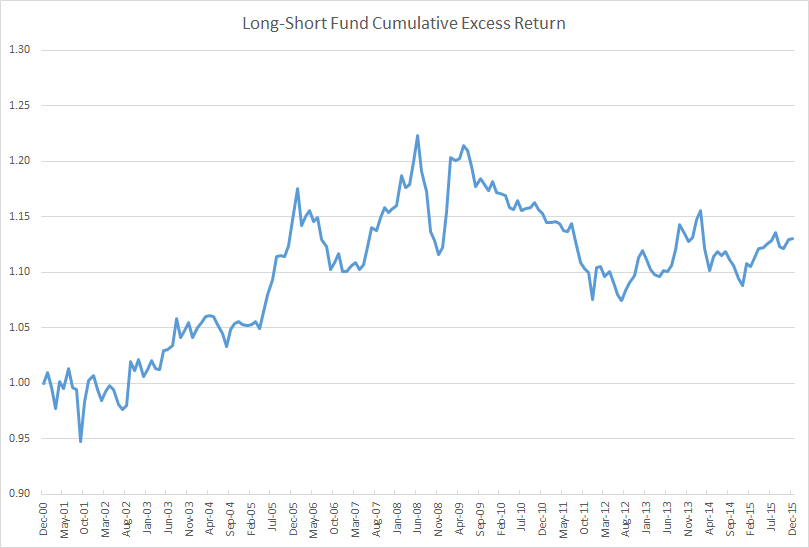
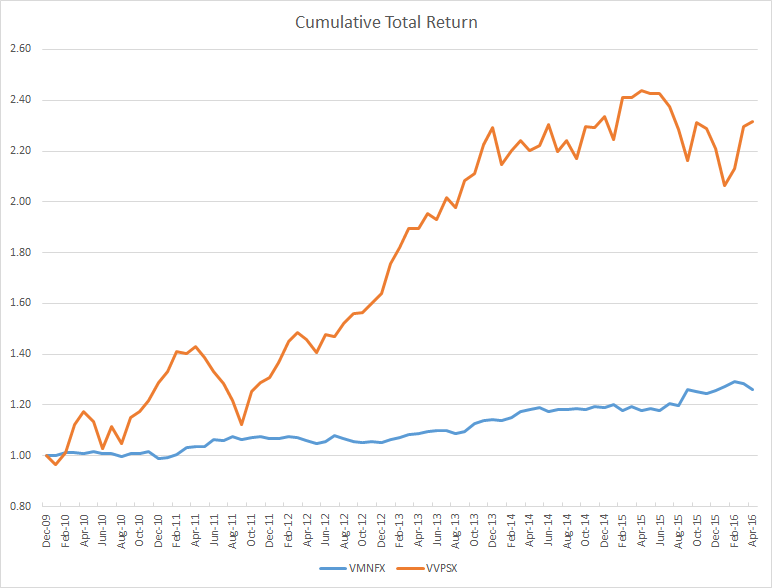
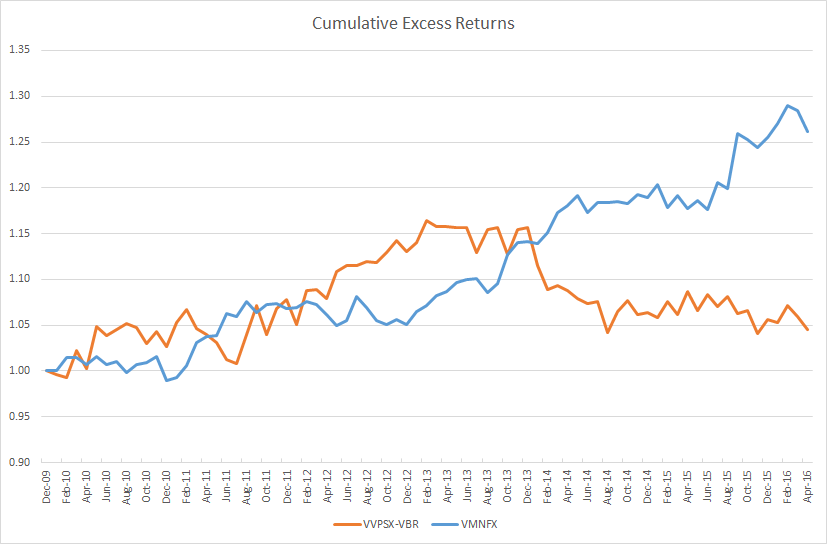
 Sam Lee and
Sam Lee and 
 What’s the Trapezoid story? Leigh Walzer has over 25 years of experience in the investment management industry as a portfolio manager and investment analyst. He’s worked with and for some frighteningly good folks. He holds an A.B. in Statistics from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from Harvard University. Leigh is the CEO and founder of Trapezoid, LLC, as well as the creator of the Orthogonal Attribution Engine. The Orthogonal Attribution Engine isolates the skill delivered by fund managers in excess of what is available through investable passive alternatives and other indices. The system aspires to, and already shows encouraging signs of, a fair degree of predictive validity.
What’s the Trapezoid story? Leigh Walzer has over 25 years of experience in the investment management industry as a portfolio manager and investment analyst. He’s worked with and for some frighteningly good folks. He holds an A.B. in Statistics from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from Harvard University. Leigh is the CEO and founder of Trapezoid, LLC, as well as the creator of the Orthogonal Attribution Engine. The Orthogonal Attribution Engine isolates the skill delivered by fund managers in excess of what is available through investable passive alternatives and other indices. The system aspires to, and already shows encouraging signs of, a fair degree of predictive validity. Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more. Mr. Thibodeaux founded Goodwood in 2012 after a nine year stint with Maple Leaf LP, a hedge fund that received a “seed” investment from Julian Robertson’s famous Tiger Management, leading to the informal designation of Maple Leaf as a “Tiger Seed.” Maple Leaf, like Goodwood, was a fundamental, value-biased long/short fund. Mr. Pesses joined Goodwood about a year later. Like Mr. Thibodeaux he was at Maple Leaf, served as a Partner and Senior Equity Research Analyst from 2007 to 2012. Their first products at Goodwood were long/short separate accounts which have done remarkably well. From January 1, 2008 – March 31, 2016, their long/short composite returned 8.6% annually after fees. The average Morningstar peer made 0.7%. That seems like a hopeful sign since those same strategies should help buoy GAMAX.
Mr. Thibodeaux founded Goodwood in 2012 after a nine year stint with Maple Leaf LP, a hedge fund that received a “seed” investment from Julian Robertson’s famous Tiger Management, leading to the informal designation of Maple Leaf as a “Tiger Seed.” Maple Leaf, like Goodwood, was a fundamental, value-biased long/short fund. Mr. Pesses joined Goodwood about a year later. Like Mr. Thibodeaux he was at Maple Leaf, served as a Partner and Senior Equity Research Analyst from 2007 to 2012. Their first products at Goodwood were long/short separate accounts which have done remarkably well. From January 1, 2008 – March 31, 2016, their long/short composite returned 8.6% annually after fees. The average Morningstar peer made 0.7%. That seems like a hopeful sign since those same strategies should help buoy GAMAX.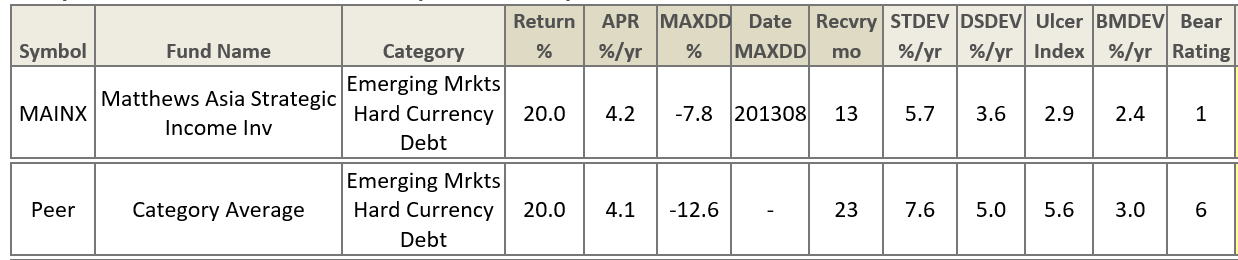
 In the instance above, it would take nearly four times as long to recharge my phone using the cable on the left. Every cable I tested produced a different charge rate, from a low of 300 mA to a high of 1200 mA.
In the instance above, it would take nearly four times as long to recharge my phone using the cable on the left. Every cable I tested produced a different charge rate, from a low of 300 mA to a high of 1200 mA.


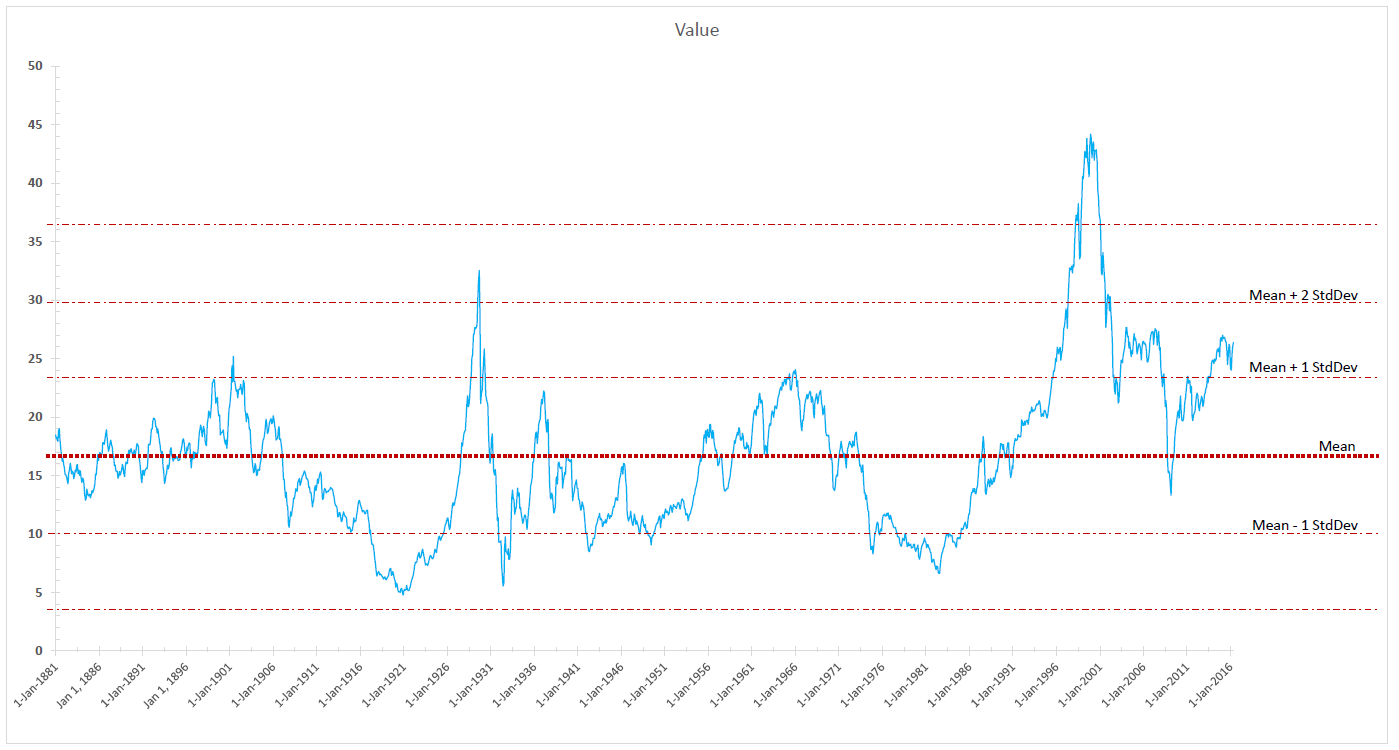
 I think of this as “the icicle chart.” Ben Carlson, one of the Ritholtz managers, wrote a really thoughtful essay, rich in visuals, in April. He posted it on his Wealth of Commonsense blog under the name “
I think of this as “the icicle chart.” Ben Carlson, one of the Ritholtz managers, wrote a really thoughtful essay, rich in visuals, in April. He posted it on his Wealth of Commonsense blog under the name “


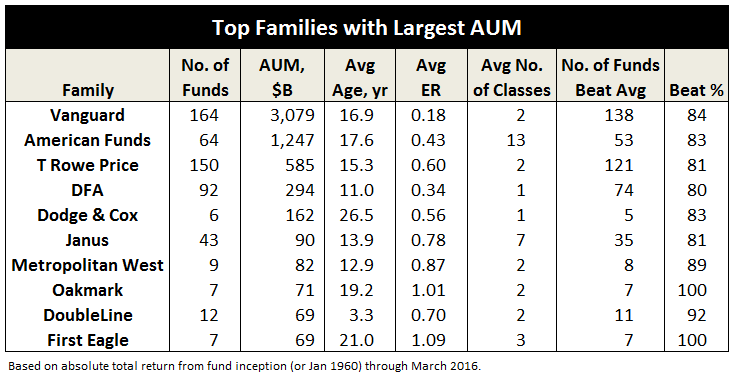
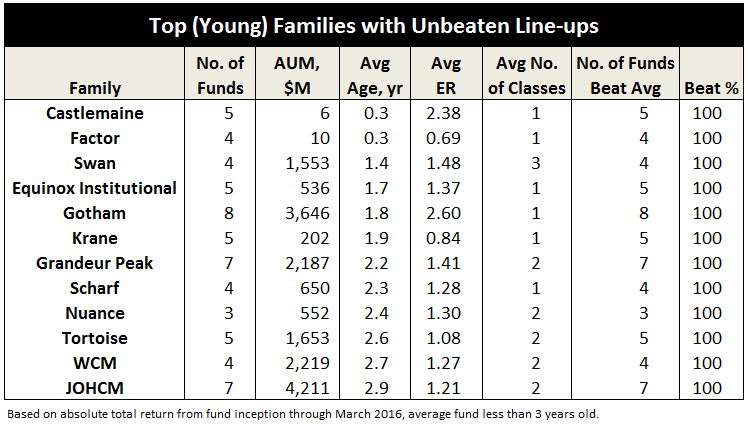
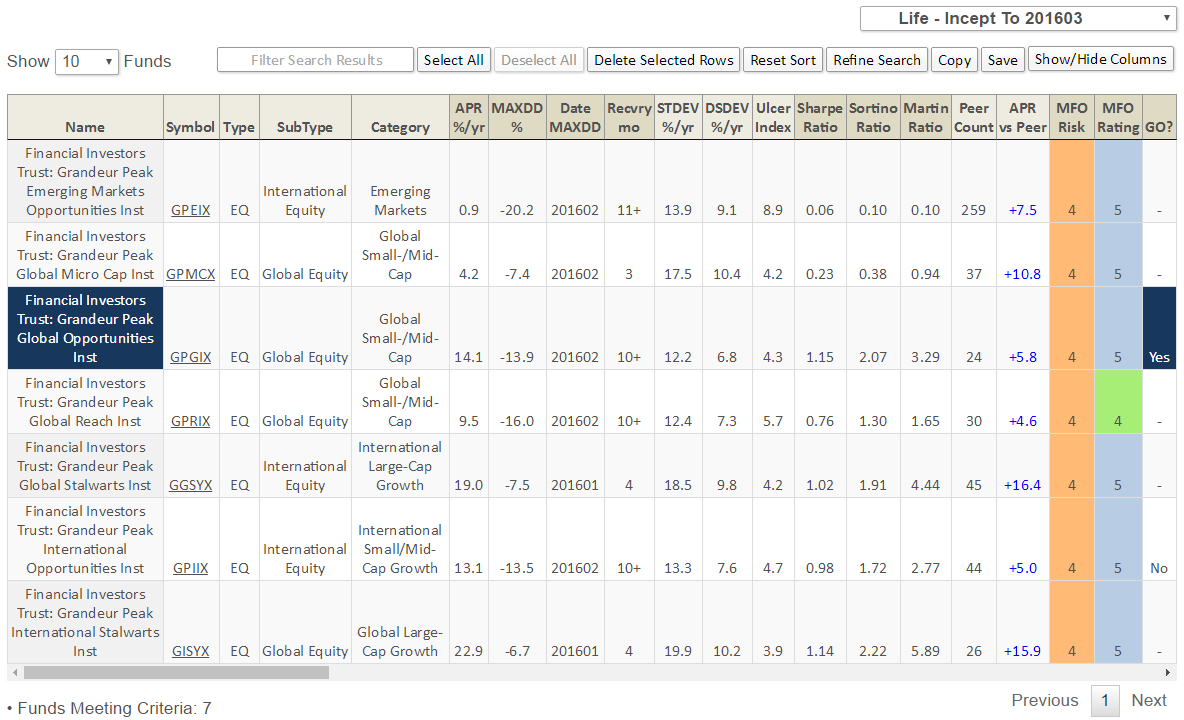
 One should forgive one’s enemies, but not before they are hanged.
One should forgive one’s enemies, but not before they are hanged. The best performing asset class in this quarter has been – gold. Actually the best performing asset class has been the gold miners, with silver not too far behind. We have had gold with a mid-teen’s total return. And depending on which previous metals vehicle you have invested in, you may have seen as much as a 60%+ total return (looking at the germane Vanguard fund). Probably the second best area generically has been energy, but again, you had to choose your spots, and also distinguish between levered and unlevered investments, as well as proven reserves versus hopes and prayers.
The best performing asset class in this quarter has been – gold. Actually the best performing asset class has been the gold miners, with silver not too far behind. We have had gold with a mid-teen’s total return. And depending on which previous metals vehicle you have invested in, you may have seen as much as a 60%+ total return (looking at the germane Vanguard fund). Probably the second best area generically has been energy, but again, you had to choose your spots, and also distinguish between levered and unlevered investments, as well as proven reserves versus hopes and prayers.
 April has come to a close and another Fed meeting has passed without a rate rise. At the same time, markets have continued to rally with the equity market, as measured by the S&P 500 Index, gaining another 0.39% in April, bringing the 3-month total return to 7.05%. Bonds also rallied as the Barclays U.S. Aggregated Bond Index gained 0.38% in April, and 2.02% over the past 3-months. Not bad for traditional asset classes.
April has come to a close and another Fed meeting has passed without a rate rise. At the same time, markets have continued to rally with the equity market, as measured by the S&P 500 Index, gaining another 0.39% in April, bringing the 3-month total return to 7.05%. Bonds also rallied as the Barclays U.S. Aggregated Bond Index gained 0.38% in April, and 2.02% over the past 3-months. Not bad for traditional asset classes.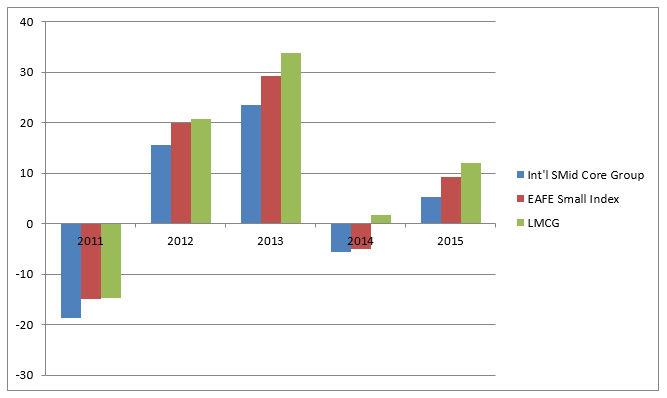
 The
The  We’ve been following Bob’s posts for the past 10 or 15 years where, as BobC, he’s been one of the most respected, thoughtful and generous contributors to our discussion board and the FundAlarm’s before that. The Observer aspires to serve two communities: the small, independent managers who are willing to stray from the herd and who are passionate about what they do (rather than about how much they can make) and the individual investors who deserve better than the timid, marketing-driven pap they’re so often fed. As we begin our sixth year, we thought that finding someone who is both active in the industry and broad in mind and spirit would allow us to serve folks better.
We’ve been following Bob’s posts for the past 10 or 15 years where, as BobC, he’s been one of the most respected, thoughtful and generous contributors to our discussion board and the FundAlarm’s before that. The Observer aspires to serve two communities: the small, independent managers who are willing to stray from the herd and who are passionate about what they do (rather than about how much they can make) and the individual investors who deserve better than the timid, marketing-driven pap they’re so often fed. As we begin our sixth year, we thought that finding someone who is both active in the industry and broad in mind and spirit would allow us to serve folks better.
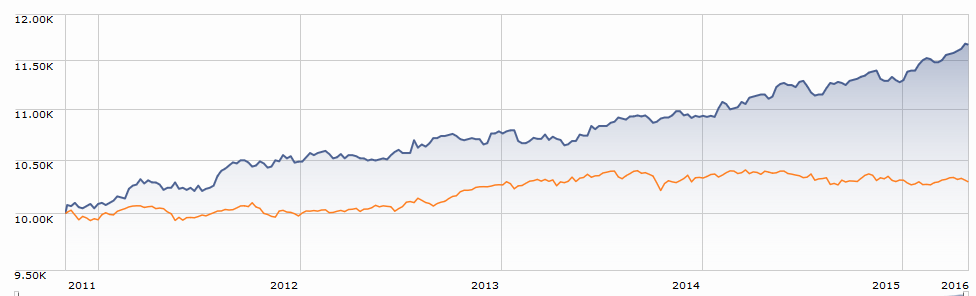
 A queer and wonderful ride. Bernie Klawans – an aerospace engineer – ran it for decades, from 1971-2011, likely out of his garage. One-page website, no 800-number, no reports or newsletters or commentaries. Also an incredibly blurry logo that might well have been run through a mimeograph machine once or twice. Mr. Klawans brought on a successor when he was in his late 80s, worked with him for a couple years, retired in April and passed away within about six months. Then his chosen successor, Craig Arnholt, died unexpectedly within a year. The Board of Trustees actually managed the fund for six months (quite successful – they beat both their LV peers and the S&P) before finding a manager who’d run the fund for a pittance. The new guy was doing fine then … kapow! He lost 22% in September and October of 2014, when the rest of the market was essentially flat. That was a combination of a big stake in Fannie and Freddie – adverse court ruling cut their market value by half in a month – and energy exposure. He’s been staggering toward the cliff ever since.
A queer and wonderful ride. Bernie Klawans – an aerospace engineer – ran it for decades, from 1971-2011, likely out of his garage. One-page website, no 800-number, no reports or newsletters or commentaries. Also an incredibly blurry logo that might well have been run through a mimeograph machine once or twice. Mr. Klawans brought on a successor when he was in his late 80s, worked with him for a couple years, retired in April and passed away within about six months. Then his chosen successor, Craig Arnholt, died unexpectedly within a year. The Board of Trustees actually managed the fund for six months (quite successful – they beat both their LV peers and the S&P) before finding a manager who’d run the fund for a pittance. The new guy was doing fine then … kapow! He lost 22% in September and October of 2014, when the rest of the market was essentially flat. That was a combination of a big stake in Fannie and Freddie – adverse court ruling cut their market value by half in a month – and energy exposure. He’s been staggering toward the cliff ever since.


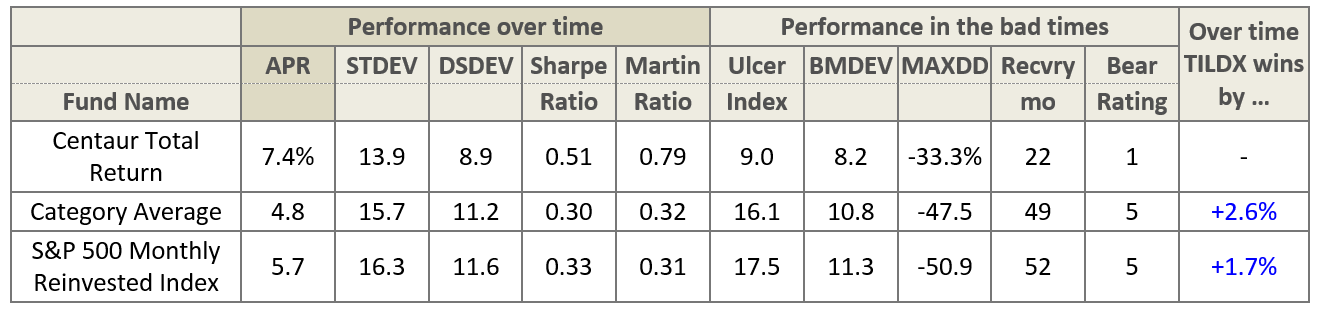

 Here’s the brief version of recent events:
Here’s the brief version of recent events:
 “Advertising is the modern substitute for argument; its function is to make the worse appear the better.”
“Advertising is the modern substitute for argument; its function is to make the worse appear the better.”
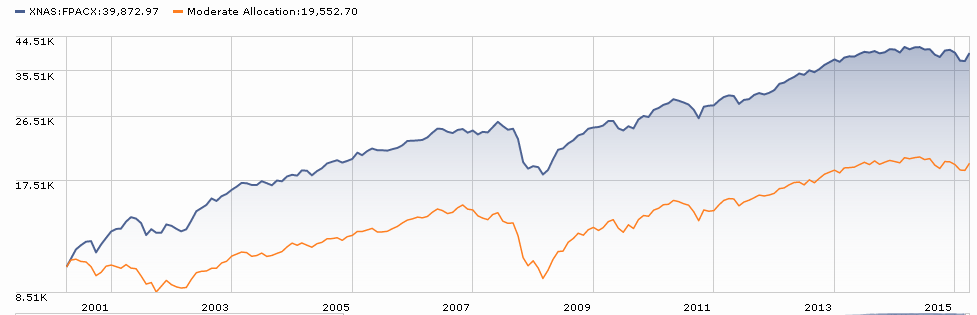
 Last month, David
Last month, David 
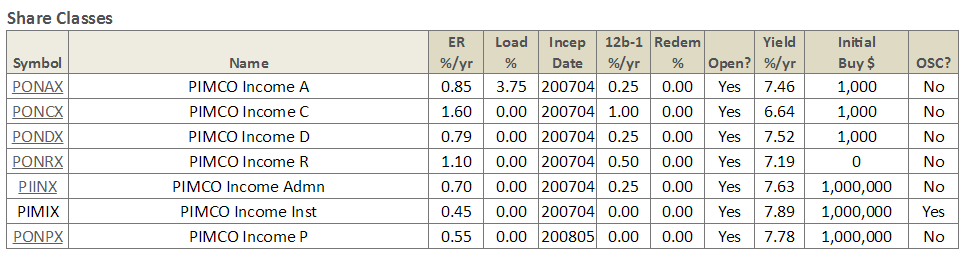
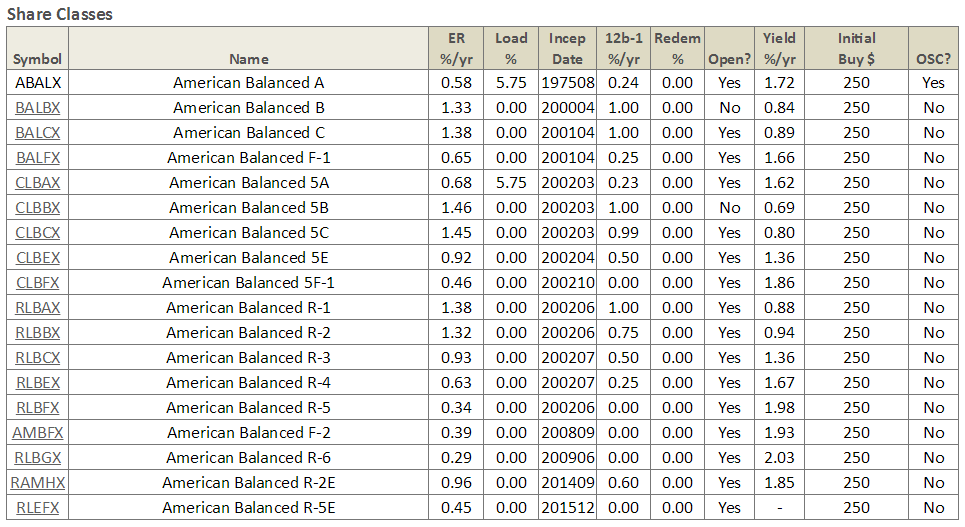
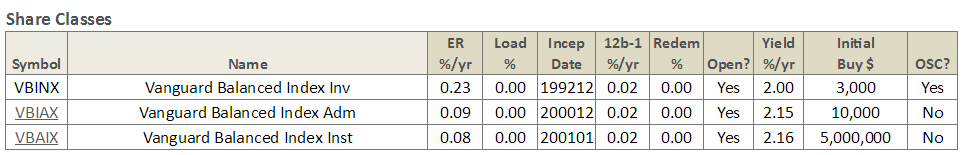
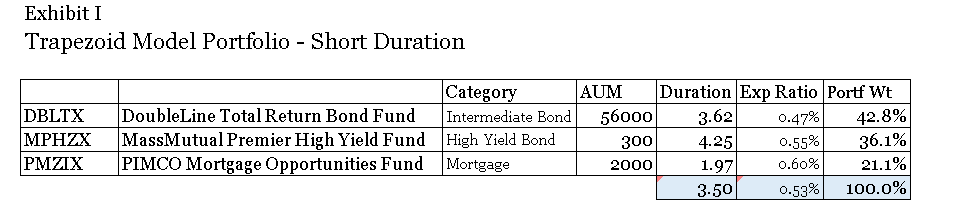
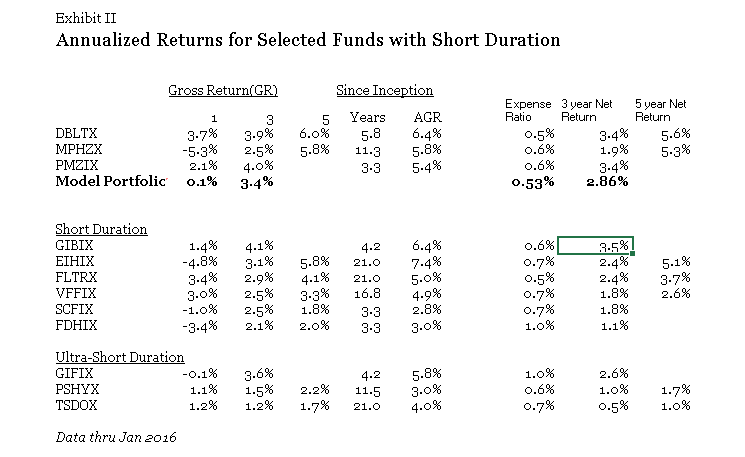

 Artisan has announced the liquidation of Artisan Small Cap Value (ARTVX), my oldest holding. My first fund, purchased when I was young and dumb, was AIM Constellation, then a very good mid-cap growth fund that carried a 5.5% load. After a bit, I learned that paying sales loads without any compensating benefit was stupid, so I stopped. I sold my shares and, shortly before it closed, invested the proceeds in Artisan Small Cap (ARTSX). Shortly after Artisan launched Small Cap Value in 1997, I moved my investment over from Small Cap. The $367 million fund, down from a peak of $3 billion in 2011, will be merged into Artisan Mid Cap Value (ARTQX) in May, 2016.
Artisan has announced the liquidation of Artisan Small Cap Value (ARTVX), my oldest holding. My first fund, purchased when I was young and dumb, was AIM Constellation, then a very good mid-cap growth fund that carried a 5.5% load. After a bit, I learned that paying sales loads without any compensating benefit was stupid, so I stopped. I sold my shares and, shortly before it closed, invested the proceeds in Artisan Small Cap (ARTSX). Shortly after Artisan launched Small Cap Value in 1997, I moved my investment over from Small Cap. The $367 million fund, down from a peak of $3 billion in 2011, will be merged into Artisan Mid Cap Value (ARTQX) in May, 2016. My single largest non-retirement holding is FPA Crescent (FPACX), which has always struck me as the quintessence of active management. While other managers were constrained to invest in a single asset class or in a single country, or to remain fully invested or unhedged, manager Steve Romick declared himself to be “the free-range chicken” of the investing world. He’d look for firms that offered compelling advantages, would analyze their capital structure and then invest in whatever instrument – common stock, warrants, senior debt – offered the most compelling opportunities. If nothing was compelling, he sat on cash.
My single largest non-retirement holding is FPA Crescent (FPACX), which has always struck me as the quintessence of active management. While other managers were constrained to invest in a single asset class or in a single country, or to remain fully invested or unhedged, manager Steve Romick declared himself to be “the free-range chicken” of the investing world. He’d look for firms that offered compelling advantages, would analyze their capital structure and then invest in whatever instrument – common stock, warrants, senior debt – offered the most compelling opportunities. If nothing was compelling, he sat on cash.
 “When we unleash the dogs of war, we must go where they take us.”
“When we unleash the dogs of war, we must go where they take us.”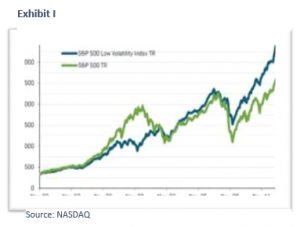 As Exhibit I illustrates low-volatility has been a successful investment strategy in recent years. A good argument can be made that historically, low-volatility stocks were mispriced. Players like Berkshire Hathaway and private equity capitalized on this by levering up these firms to deliver strong risk-adjusted returns. There is a heavy overlap between the low-volatility universe and the high-dividend universe. Many high-dividend stocks have dropped assets into REITs in recent years which have fueled better returns for this sector. Low volatility has outperformed the broad market meaningfully for the past two quarters, partly due its lower beta.
As Exhibit I illustrates low-volatility has been a successful investment strategy in recent years. A good argument can be made that historically, low-volatility stocks were mispriced. Players like Berkshire Hathaway and private equity capitalized on this by levering up these firms to deliver strong risk-adjusted returns. There is a heavy overlap between the low-volatility universe and the high-dividend universe. Many high-dividend stocks have dropped assets into REITs in recent years which have fueled better returns for this sector. Low volatility has outperformed the broad market meaningfully for the past two quarters, partly due its lower beta.
 Pruning Season
Pruning Season Jim Robinson formed Robinson Capital Management, located in Detroit’s ritzy Grosse Pointe suburb, in December, 2012. The firm manages about a quarter billion in assets for a handful of high net worth clients and advises two (soon to be three) mutual funds.
Jim Robinson formed Robinson Capital Management, located in Detroit’s ritzy Grosse Pointe suburb, in December, 2012. The firm manages about a quarter billion in assets for a handful of high net worth clients and advises two (soon to be three) mutual funds.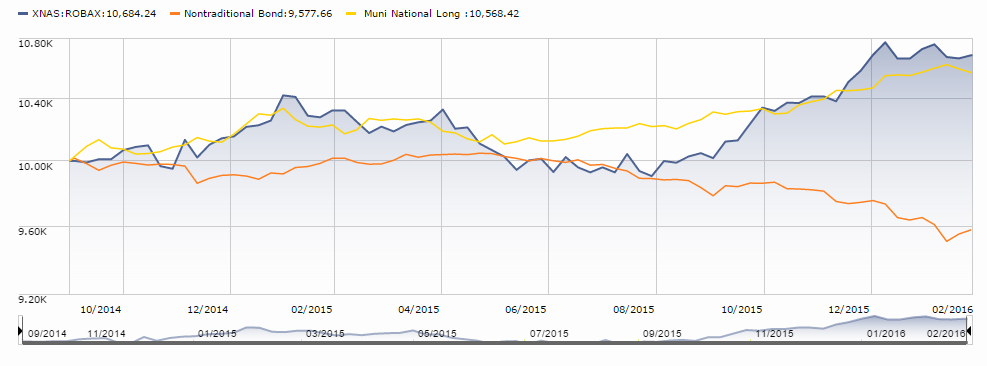
 Effective May 1, 2016, Donald A. Yacktman will transition to an advisory role and will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for AMG Yacktman (YACKX) and AMG Yacktman Focused (YAFFX) funds. The roughly corresponds with his 75th birthday. Mr. Yacktman has been managing mutual funds since 1968, starting with Stein, Roe and the Selected American Shares before founding Yacktman Asset Management in 1992. $10,000 invested in YACKX that year would have grown to $95,000 today, which compares well to the returns on an investment in the S&P500 ($76,000) or the average large-value fund ($56,000). He was named Morningstar’s Manager of the Year in 1991 and was joined on the management team by his son, Stephen, in 2002. Stephen Yacktman and Jason Subotky will manage the funds after the transition.
Effective May 1, 2016, Donald A. Yacktman will transition to an advisory role and will no longer serve as a portfolio manager for AMG Yacktman (YACKX) and AMG Yacktman Focused (YAFFX) funds. The roughly corresponds with his 75th birthday. Mr. Yacktman has been managing mutual funds since 1968, starting with Stein, Roe and the Selected American Shares before founding Yacktman Asset Management in 1992. $10,000 invested in YACKX that year would have grown to $95,000 today, which compares well to the returns on an investment in the S&P500 ($76,000) or the average large-value fund ($56,000). He was named Morningstar’s Manager of the Year in 1991 and was joined on the management team by his son, Stephen, in 2002. Stephen Yacktman and Jason Subotky will manage the funds after the transition.

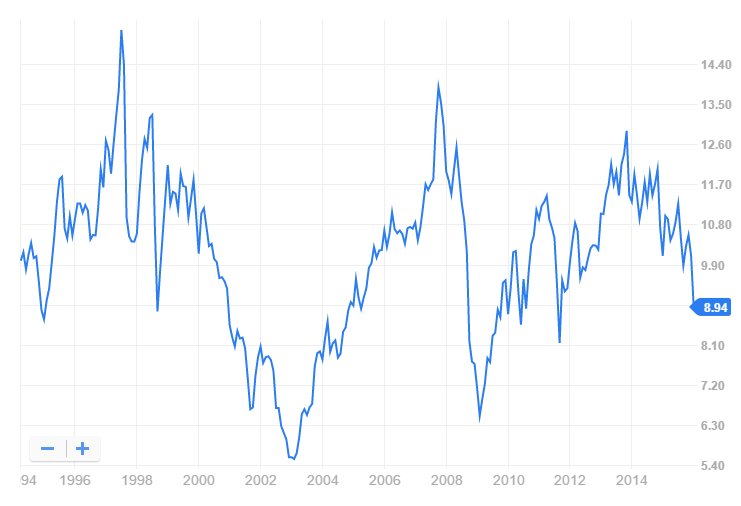
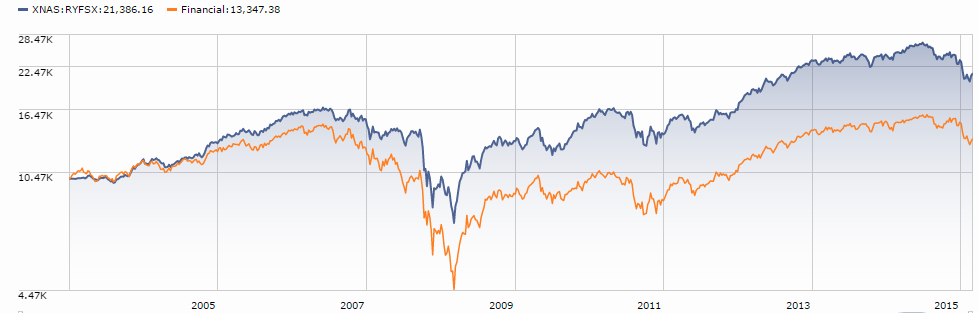
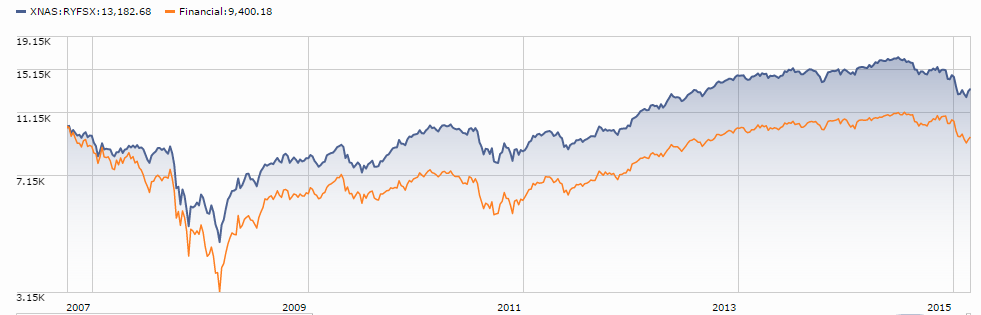
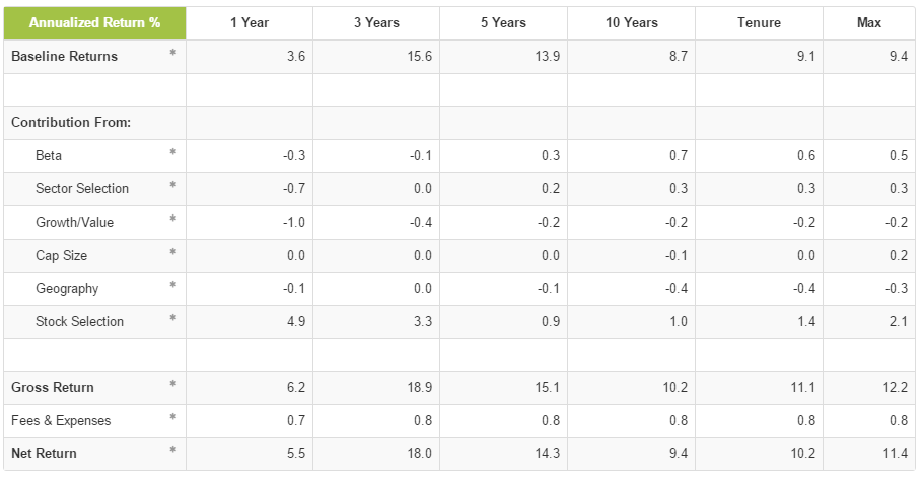
 For those of you who watched the World Series a few months ago, the NY Mets had a number of very young pitchers with fastballs close to 100 miles per hour. They also had some veteran pitchers like John Niese and the 42-year-old ageless wonder Bartolo Colon who couldn’t muster the same heat but had established their skill and consistency over a long period of time. We don’t know whether Bartolo Colon drank from the fountain of youth; he served a lengthy suspension a few years ago for using a banned substance. But his statistics in his 40s are on par with his prime ten year ago.
For those of you who watched the World Series a few months ago, the NY Mets had a number of very young pitchers with fastballs close to 100 miles per hour. They also had some veteran pitchers like John Niese and the 42-year-old ageless wonder Bartolo Colon who couldn’t muster the same heat but had established their skill and consistency over a long period of time. We don’t know whether Bartolo Colon drank from the fountain of youth; he served a lengthy suspension a few years ago for using a banned substance. But his statistics in his 40s are on par with his prime ten year ago. 

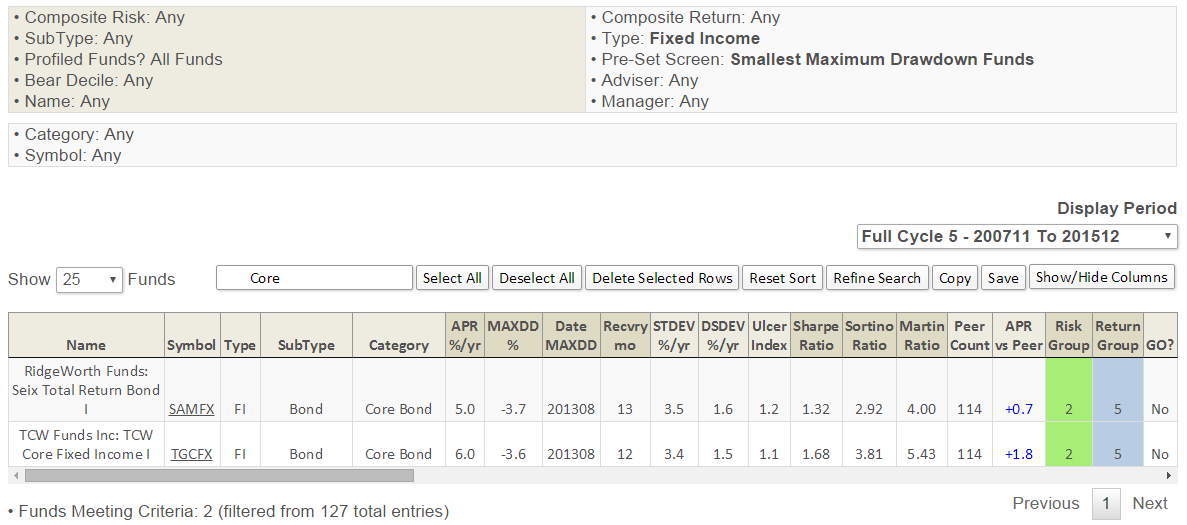
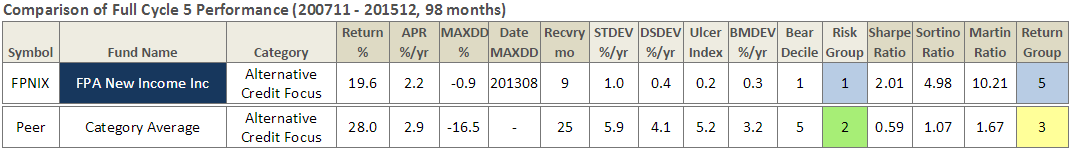
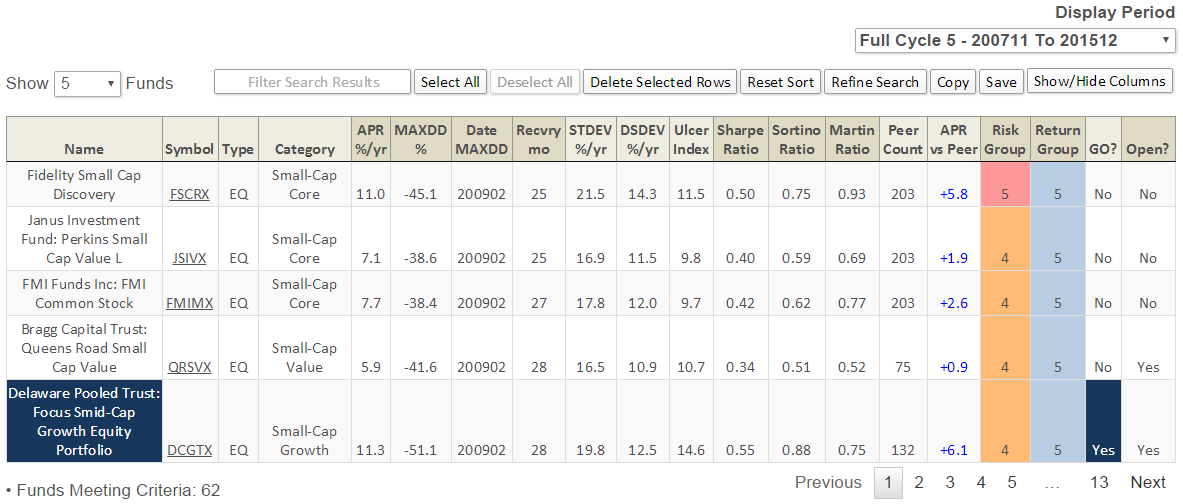
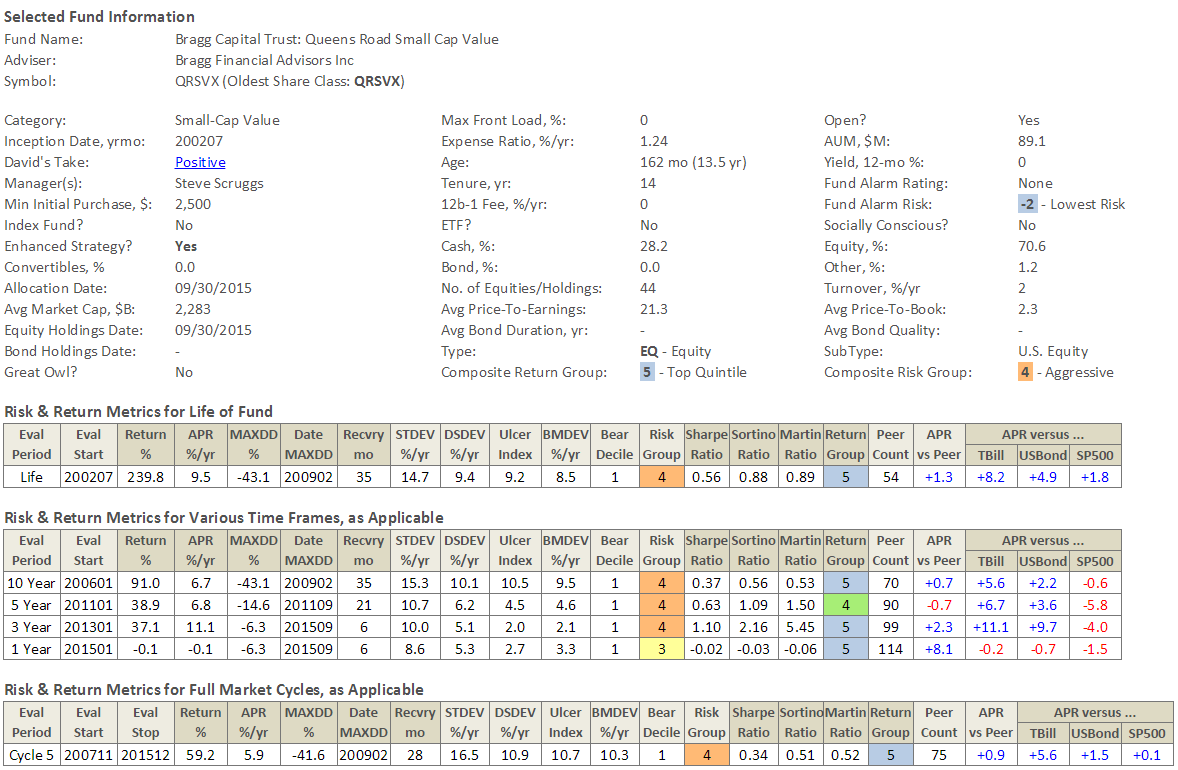
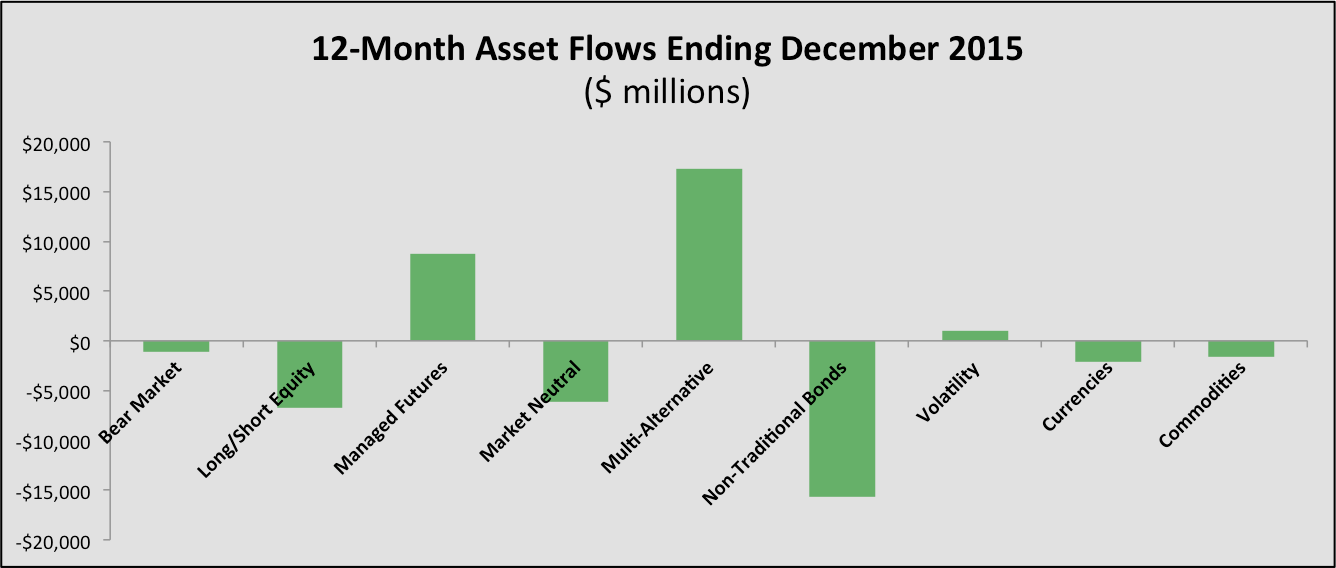
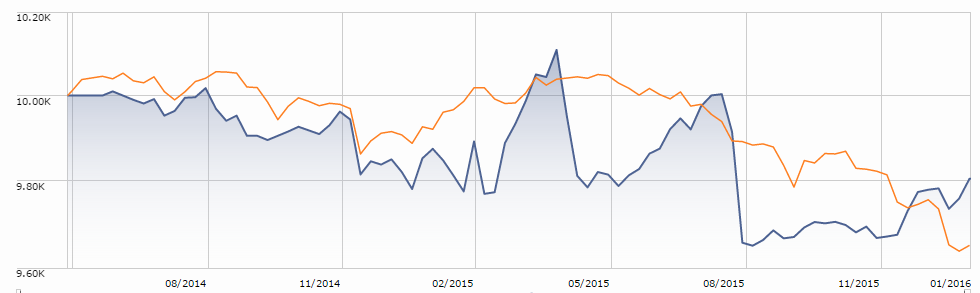
 There was
There was 
 Talk about sturm und drang. After 75 days with in which the stock market rose or fell by 1% or more, the Vanguard Total Stock Market Index managed to roar ahead to a gain … of 0.29%. Almost 3000 mutual funds hung within two percentage points, up or down, of zero. Ten managed the rare feat of returning precisely zero. Far from a Santa Claus rally, 2015 couldn’t even manage a Grinchy Claus one.
Talk about sturm und drang. After 75 days with in which the stock market rose or fell by 1% or more, the Vanguard Total Stock Market Index managed to roar ahead to a gain … of 0.29%. Almost 3000 mutual funds hung within two percentage points, up or down, of zero. Ten managed the rare feat of returning precisely zero. Far from a Santa Claus rally, 2015 couldn’t even manage a Grinchy Claus one.
 The path forward is not particularly clear to me because we’ve never managed such a long period of global economic weakness and zero to negative interest rates before. My plan is to remind myself that I need to care about 2026 more than about 2016, to rebalance soon, and to stick with my discipline which is, roughly put, “invest regularly and automatically in sensible funds that execute a reasonable plan, ignore the market and pay attention to the moments, hours and days that life presents me.” On whole, an hour goofing around with my son or the laughter of dinner guests really does make a much bigger difference in my life than anything my portfolio might do today.
The path forward is not particularly clear to me because we’ve never managed such a long period of global economic weakness and zero to negative interest rates before. My plan is to remind myself that I need to care about 2026 more than about 2016, to rebalance soon, and to stick with my discipline which is, roughly put, “invest regularly and automatically in sensible funds that execute a reasonable plan, ignore the market and pay attention to the moments, hours and days that life presents me.” On whole, an hour goofing around with my son or the laughter of dinner guests really does make a much bigger difference in my life than anything my portfolio might do today.











 Does CENSX merit extra consideration because of the outstanding contribution from rotating between growth and value? Serendipity certainly plays a part. As Exhibit V illustrates, the current managers inherited in 1999 a fund which was restricted by its charter to financials, especially insurance. That weighting was very well-suited to the internet bust and recession which followed. They gradually repositioned the portfolio towards large growth. And he has made a number of astute switches. Notably, he emphasized consumer discretionary and exited energy which has worked extremely well over the past year. We spoke to portfolio manager Kevin Callahan. The fund is managed on a bottom-up fundamentals basis and does not have explicit sector targets. But he currently screens for stocks from the Russell 1000 Growth Index and seem reluctant to stray too far from its sector weightings, so we expect growth/value switching will be much more muted in the future.
Does CENSX merit extra consideration because of the outstanding contribution from rotating between growth and value? Serendipity certainly plays a part. As Exhibit V illustrates, the current managers inherited in 1999 a fund which was restricted by its charter to financials, especially insurance. That weighting was very well-suited to the internet bust and recession which followed. They gradually repositioned the portfolio towards large growth. And he has made a number of astute switches. Notably, he emphasized consumer discretionary and exited energy which has worked extremely well over the past year. We spoke to portfolio manager Kevin Callahan. The fund is managed on a bottom-up fundamentals basis and does not have explicit sector targets. But he currently screens for stocks from the Russell 1000 Growth Index and seem reluctant to stray too far from its sector weightings, so we expect growth/value switching will be much more muted in the future.

 Randy Swan manages SDRAX, which launched at the end of July 2012. He founded Swan Capital Management, which uses this strategy in their separately managed accounts in 1997. Before then, Mr. Swan was a CPA and senior manager for KPMG’s Financial Services Group, primarily working with insurance companies and risk managers. Mr. Swan manages about $27 million in other accounts, including the new Swan Defined Risk Emerging Markets (SDFAX).
Randy Swan manages SDRAX, which launched at the end of July 2012. He founded Swan Capital Management, which uses this strategy in their separately managed accounts in 1997. Before then, Mr. Swan was a CPA and senior manager for KPMG’s Financial Services Group, primarily working with insurance companies and risk managers. Mr. Swan manages about $27 million in other accounts, including the new Swan Defined Risk Emerging Markets (SDFAX).
