By David Snowball
Dear friends,
I am not, in a monetary sense, rich. Teaching at a small college pays rather less, and raising a multi-talented 12-year-old costs rather more, than you’d imagine. I tend to invest cautiously in low-minimum, risk-conscious funds. I have good friends, drink good beer, laugh a lot and help coach Little League (an activity to which the beer and laughter both contribute).
 This comes up only because I was moved to sudden and profound pity over the cruel ways in which the poor, innocent rich folks are being ruthlessly exploited. Two new articles highlight their plight.
This comes up only because I was moved to sudden and profound pity over the cruel ways in which the poor, innocent rich folks are being ruthlessly exploited. Two new articles highlight their plight.
Mark Hulbert published a fairly relentless critique, “The Verdict Is In: Hedge Funds Aren’t Worth the Money”(WSJ, 06/01/2013), (While we can’t link directly to the article, you should be able to Google the title and get in) that looks at the performance –both risk and returns – of the average hedge fund since the last market top (October 2007) and from the last market bottom (March 2009). The short version of his findings:
- The average hedge fund has trailed virtually every conceivable benchmark (gold, the total bond market, the total stock market, a 60/40 index, and the average open-end mutual fund) whether measured from the top or the bottom
- The downside protection offered by hedge funds during the meltdown was not greater than what a simple balanced fund would offer.
- At best, one hedge fund manager in five outperforms their mutual fund counterparts, and those winners are essentially impossible to identify in advance.
Apparently Norway figured this out before you. While the Yale endowment, led by David Swensen, was making a mint investing in obscure and complex alternatives, Jason Zweig (“Norway: The New Yale,” WSJ, 03/07/2013) reported that Norway’s huge pension fund has outperformed the stock market and, recently, Yale, through the simple expedient of a globally diversified, long-only portfolio biased toward “small” and “value.” Both Swensen and the brilliantly cranky Bill Bernstein agree that the day of outsized profits from “alternative investments” has passed. Given that fact that the herd is now gorging on alternative investments:
 “it’s somewhere between highly probable and certain that you will underperform [a stock portfolio] if you are being sold commodities, hedge funds and private equity right now.”
“it’s somewhere between highly probable and certain that you will underperform [a stock portfolio] if you are being sold commodities, hedge funds and private equity right now.”
Think of it like this, he says: “The first person to the buffet table gets the lobster. The people who come a little later get the hamburger. And the ones who come at the end get whatever happens to be stuck to the tablecloth.”
That doesn’t deny the fact that there’s huge money to be made in hedge fund investing. Barry Ritholz published a remarkable essay, “A hedge fund for you and me? The best move is to take a pass” (Washington Post, 05/24/2013) that adds a lot of evidence about who actually profits from hedge funds. He reports on research by Simon Lack, author of The Hedge Fund Mirage,” who concludes that the usual 2 and 20 “fee arrangement is effectively a wealth transference mechanism, moving dollars from investors to managers.” Lack used to allocate money to hedge funds on behalf of JPMorgan Chase. Among Lack’s findings
- From 1998 to 2010, hedge fund managers earned $379 billion in fees. The investors of their funds earned only $70 billion in investing gains.
- Managers kept 84% of investment profits, while investors netted only 16%.
- As many as one-third of hedge funds are funded through feeder funds and/or fund of funds, which tack on yet another layer of fees. This brings the industry fee total to $440 billion — that’s 98 %of all the investing gains, leaving the people whose capital is at risk with only 2%, or $9 billion.
Oh, poor rich people. At the same time, the SEC is looking to relax restrictions on hedge fund marketing and advertising which means that even more of them might become subject to the cruel exploitation of … well, the richer people.
On whole, I think I’m happy to be living down here in 40-Act Land.
Introducing MFO Fund Ratings
One of the most frequent requests we receive is for the reconstruction of FundAlarm’s signature “most alarming funds” database. Up until now, we haven’t done anything like it. There are two reasons: (1) Snowball lacked both the time and the competence even to attempt it and (2) the ratings themselves lacked evidence of predictive validity. That is, we couldn’t prove that an “Honor Roll” fund was any likelier to do well in the future than one not on the honor roll.
We have now budged on the matter. In the spirit of those beloved fund ratings, MFO will maintain a new system to highlight funds that have delivered superior absolute returns while minimizing down side volatility. We’re making the change for two reasons. (1) Associate editor Charles Boccadoro, a recently-retired aerospace engineer, does have the time and competence. And, beyond that, a delight in making sense of data. And (2) there is some evidence that risk persists even if returns don’t. That is, managers who’ve taken silly, out-sized, improvident risks in the past will tend to do so in the future. We think of it as a variant of the old adage, “beauty is just skin-deep, but ugly goes all the way to the bone.”
There are two ways of explaining what we’re up to. We think of them as “the mom and pop explanation” and the “Dr. Mom and Ph.D. Pop explanation.” We’ll start with the M&P version, which should be enough for most of us.
Dear Mom and Pop,
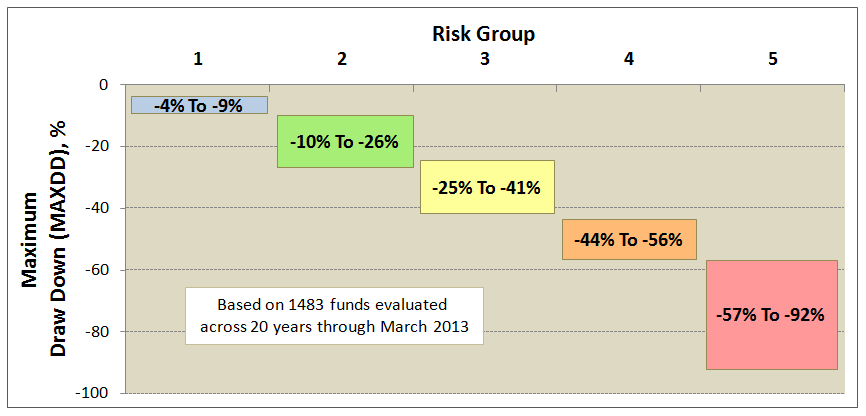
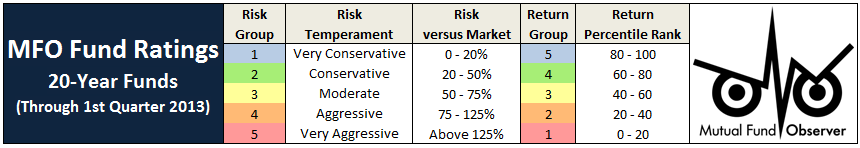
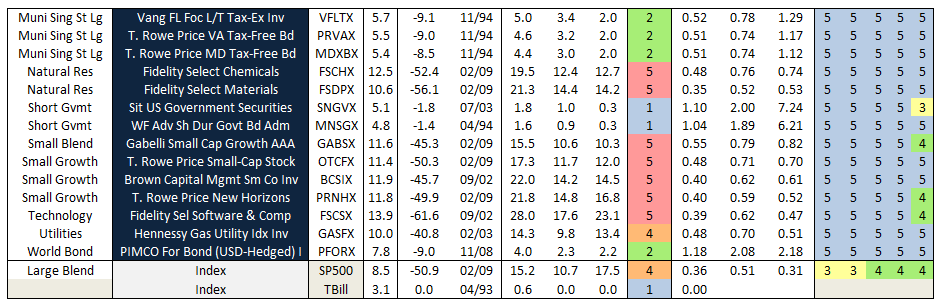
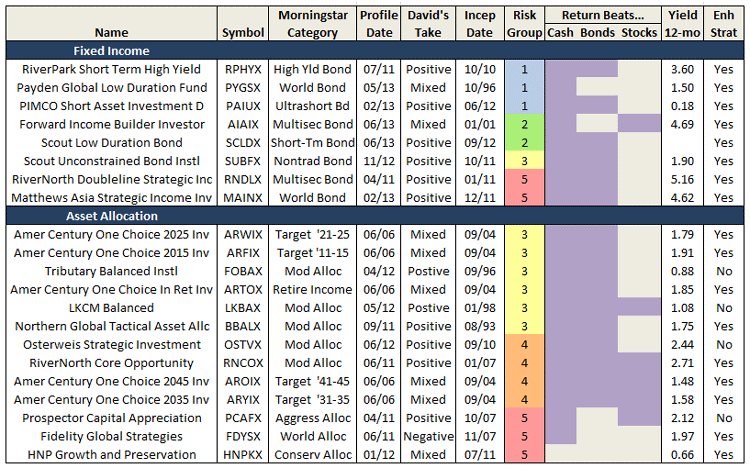
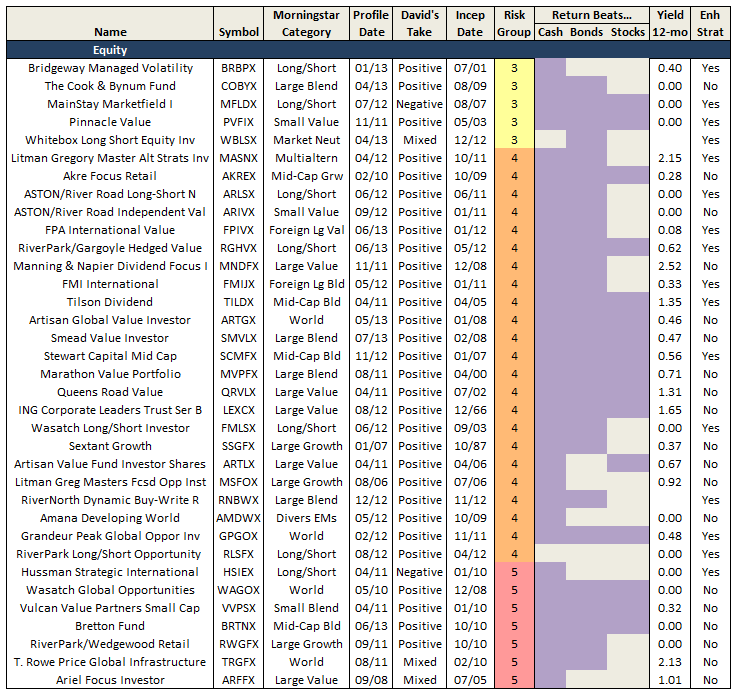
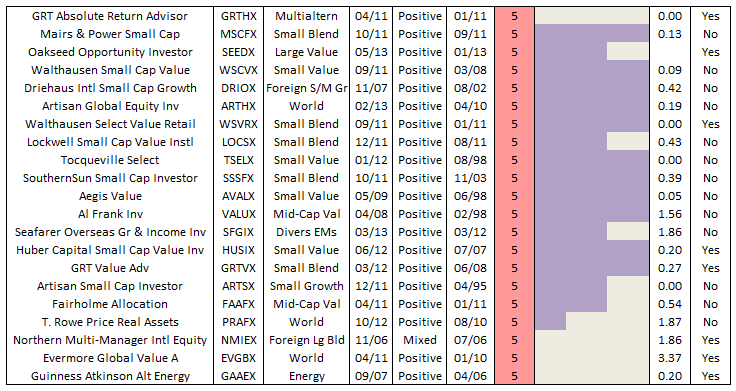
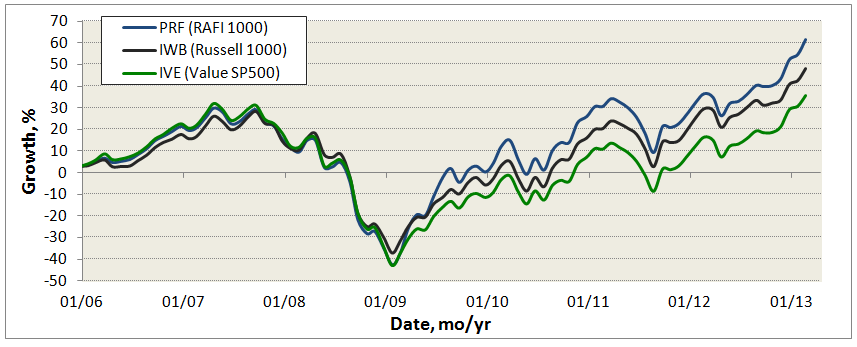
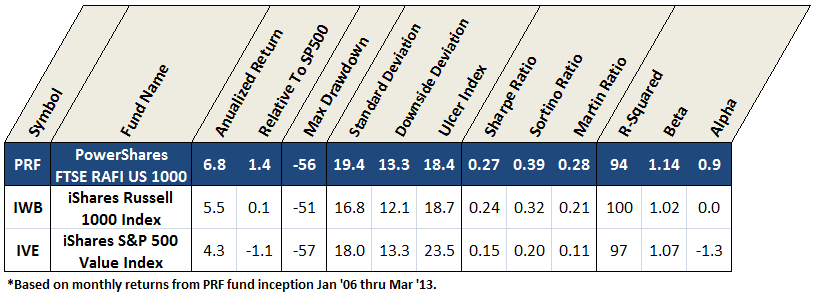
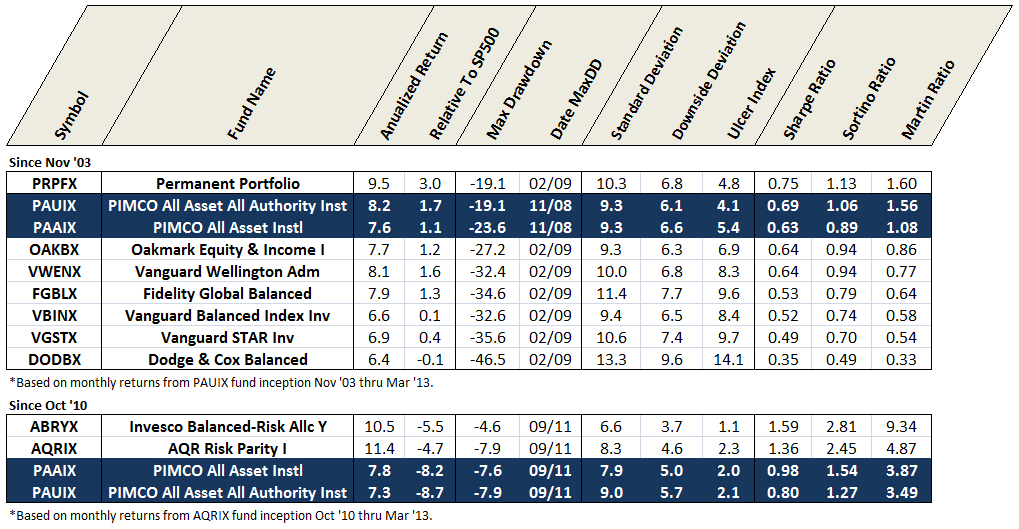
Many risk measures look at the volatility or bounciness of a portfolio, both on the upside and the downside. As it turns out, investors don’t mind having funds that outperform their peers in rising markets; that is, they don’t immediately reject upside volatility. What they (we!) dread are excessive drawdowns: that is, having their returns go down far and hard. What Charles has done is to analyze the performance of more than 7000 funds for periods ranging back 20 years. He’s calculated seven different measures of risk for each of those funds and has assigned every fund into one of five risk groups from “very conservative” funds which typically absorb no more than 20% of a stock market decline to “very aggressive” ones which absorb more than 125% of the fall. We’ve assembled those in a large spreadsheet which is on its way to becoming a large, easily searchable database.
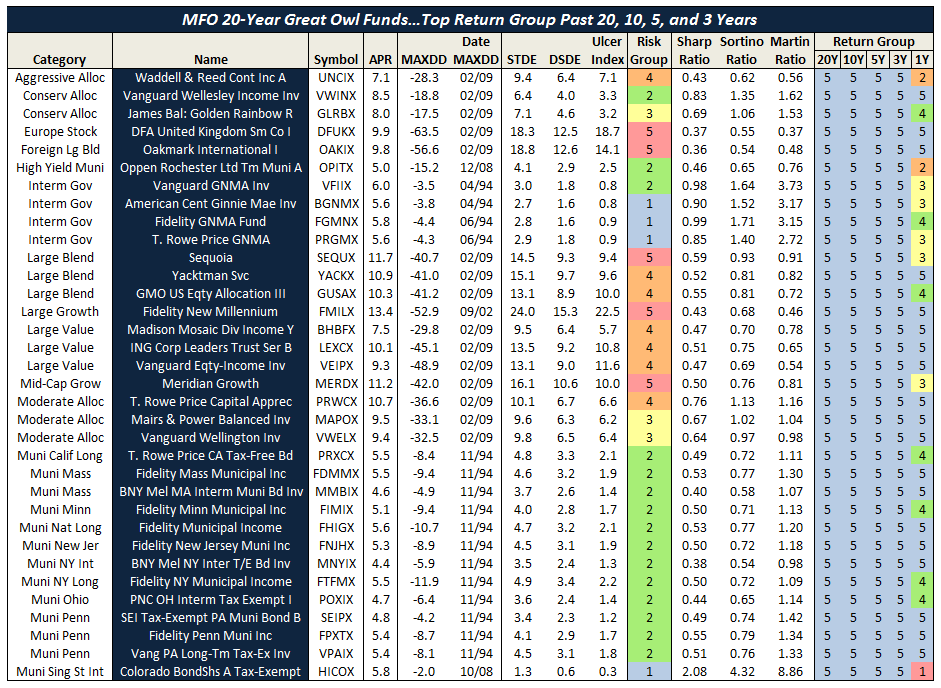
For now, we’ve got a preview. It focuses on the funds with the most consistently excellent 20-year returns (the happy blue boxes on the right hand side, under “return group”), lets you see how much risk you had to absorb to achieve those returns (the blue to angry red boxes under risk group) and the various statistical measures of riskiness. In general, you’d like to see low numbers in the columns to the left of the risk group and high numbers in the columns to the right.
I miss the dog. My roommate is crazy. The pizza has been good. I think the rash is mostly gone but it’s hard to see back there. I’m broke. Say “hi” to gramma. Send money soon.
Love, your son,
Dave
And now back to the data and the serious explanation from Charles:
The key rating metric in our system is Martin ratio, which measures excess return divided by the drawdown (a/k/a Ulcer) index. Excess return is how much a fund delivers above the 90-day Treasury bill rate. Ulcer index measures depth and duration of drawdowns from recent peaks – a very direct gauge of unpleasant performance. (More detailed descriptions can be found at Ulcer Index and A Look at Risk Adjusted Returns.)
The rating system hierarchy is first by evaluation period, then investment category, and then by relative return. The evaluation periods are 20, 10, 5, 3, and 1 years. The categories are by Morningstar investment style (e.g., large blend). Within each category, funds are ranked based on Martin ratio. Those in the top 20 percentile are placed in return group 5, while those in bottom 20 percentile are in return group 1. Fund ratings are tabulated along with attendant performance and risk metrics, by age group, then category, then return group, and finally by absolute return.
MFO “Great Owl” designations are assigned to consistent top performers within the 20 and 10 year groups, and “Aspiring Great Owl” designations are similarly assigned within the 5 and 3 year groups.
The following fund performance and risk metrics are tabulated over each evaluation period:
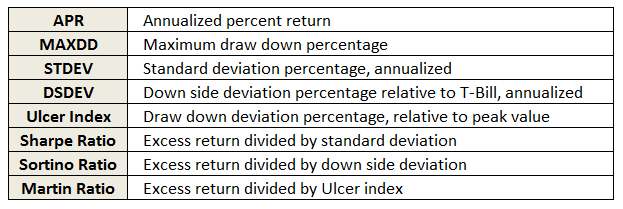
A risk group is also tabulated for each fund, based simply on its risk metrics relative to SP500. Funds less than 20% of market are placed in risk group 1, while those greater than 125% are placed in risk group 5. This table shows sample maximum drawdowns by risk group, depicting average to worst case levels.
Some qualifications:
- The system includes oldest share class only and excludes the following categories: money market, bear market, trading inverse and leveraged, volatility, and specialized commodities.
- The system does not account for category drift.
- Returns reflect maximum front load, if applicable.
- Funds are presented only once based on age group, but the return rankings reflect all funds existing. For example, if a 3 year fund scores a 5 return, it did so against all existing funds over the 3 year period, not just the 3 year olds.
- All calculations are made with Microsoft’s Excel using monthly total returns from the Morningstar database provided in Steele Mutual Fund Expert.
- The ratings are based strictly on historical returns.
- The ratings will be updated quarterly.
We will roll-out the new system over the next month or two. Here’s a short preview showing the MFO 20-year Great Owl funds – there are only 48, or just about 3% of all funds 20 years and older.
31 May 2013/Charles
(p.s., the term “Great Owl” funds is negotiable. We’re looking for something snazzy and – for the bad funds – snarky. “Owl Chow funds”? If you’re a words person and have suggestions, we’d love to hear them. Heck, we’d love to have an excuse to trick Barb into designing an MFO t-shirt and sending it to you. David)
The Implosion of Professional Journalism will make you Poorer
You’ve surely noticed the headlines. Those of us who teach News Literacy do. The Chicago Sun-Times laid off all of its photo-journalists (28 staff members) on the morning of May 30, 2013, in hopes that folks with iPhone cameras would fill in. Shortly before the New York Daily News laid off 20, the Village Voice fired a quarter of its remaining staff, Newsweek closed its print edition and has announced that it’s looking for another owner. Heck, ESPN just fired 400 and even the revered Columbia Journalism Review cut five senior staff. The New York Times, meanwhile, has agreed to “native advertising” (ads presented as content on mobile devices) and is investigating “sponsored content;” that is, news stories identified and funded by their advertisers. All of that has occurred in under a month.
Since the rest of us remain intensely interested in receiving (if not paying for) news, two things happen simultaneously: (1) more news originates from non-professional sources and (2) fewer news organizations have the resources to check material before they publish it.
Here’s how that dynamic played out in a recent series of stories on the worst mutual funds.
Step One: NerdWallet sends out a news release heralding “the 12 most expensive and worst-performing mutual funds.”
Well, no. What they sent was a list of fund names, ticker symbols (mostly) for specific share classes of the fund and (frequently) inaccurate expense ratio reports. They report the worst of the worst as
- Oppenheimer Commodity Strat. Total Return (QRACX): 2.2% e.r.
Actually QRACX is the “C” class for the Oppenheimer fund. Morningstar reports the e.r. at 2.09%. The “A” shares have a 1.26% e.r. And where did the mysterious 2.20% number come from? One of the folks at NerdWallet wrote, “it seems it was an error on the part of our data provider.” NerdWallet promised to clear up the fund versus share class distinction and to get the numbers right.
But that’s not the way things work, because NerdWallet sent their press release to other folks, too.
Step Two: Investment News mindlessly reproduces the flawed information.
Within hours, they have grafted on some random photographs and turned the press release into a slide show, now entitled “Expensive – and underperforming – funds.” NerdWallet receives credit on just one of the slides. Apparently no one at Investment News stopped to double-check any of the details before going public. But they did find pretty pictures.
Step Three: Mutual Fund Wire trumpets Investment News’s study.
MFWire’s story touting of the article, “Investment News Unveils Mutual Fund Losers List,” might be better-titled “Investment News Reproduces another Press Release”. You’ll note, by the way, that the actual source of the story has disappeared.
Step Four: CNBC makes things worse by playing with the data.
On Friday, May 17, CNBC’s Jeff Cox posts ‘Dirty Dozen’: 12 Worst Mutual Funds. And they promptly make everything worse by changing the reported results.
Here’s the original: 1. Oppenheimer Commodity Strat. Total Return (QRACX): 2.2% e.r.
Here’s the CNBC version: 1. Oppenheimer Commodity Strategy Total Return (NASDAQ:QRAAX-O), -14.61 percent, 2.12 percent.
Notice anything different? CNBC changed the fund’s ticker symbol, so that it now pointed to Oppenheimer’s “A” share class. And those numbers are desperately wrong with regard to “A” shares, which charge barely half of the claimed rate (which is, remember, wrong even from the high cost “C” shares). They also alter the ticker symbol of Federated Prudent Bear, which started as the high cost “C” shares (PBRCX) but for which CNBC substitutes the low-cost “A” shares (BEARX). For the remaining 10 funds, CNBC simply disregards the tickers despite the fact that these are all high-cost “B” and “C” share classes.
Step Five: And then a bunch of people read and forward the danged thing.
Leading MFWire to celebrate it as one of the week’s “most read” stories. Great.
Step Six: NerdWallet themselves then draw an invalid conclusion from the data.
In a blog post, NerdWallet’s Susan Lyon opines:
As you can see, all of the funds listed above are actively managed, besides the Rydex Inverse S&P 500 Strategy Fund. Do the returns generated by actively managed mutual funds usually outweigh their costs? No, a recent NerdWallet Investing study found that though actively managed funds earned 0.12% higher annual returns than index funds on average, because they charged higher fees, investors were left with 0.80% lower returns.
No. The problem here isn’t that these funds are actively managed. It’s that NerdWallet tracked down the effects of the predatory pricing model behind “C” share classes. And investors have pretty much figured out the “expense = bad” thing, which explains why the Oppenheimer “C” shares that NerdWallet indicts have $68M in assets while the lower-cost “A” shares have $228M.
Step Seven: Word spreads like cockroaches.
The story, in one of its several variants, now appears on a bunch of little independent finance sites and rarely with NerdWallet’s own discussion of their research protocol, much less a thoughtful dissection of the data.
NerdWallet (at least their “investing silo”) is a new operation, so you can understand their goof as a matter of a young staff, start-up stumbles and all that. It’s less clear how you explain Investment News‘s mindless reproduction of the results (what? verify stuff before we publish it? Edit for accuracy? Who do you think we are, journalists?) or MFWire’s touting of the article as if it represented Investment News’s own work.
Before the Observer publishes a fund profile, we give the advisor a chance to review the text for factual accuracy. My standard joke is “I’m used to making errors of judgment, but I loathe making errors of fact and so would you please let us know if there are any factual misstatements or other material misrepresentations?” I entirely agree with NerdWallet’s original judgment: these are pricey under-performers. I just wish that folks all around were a bit more attentive to and concerned about accuracy and detail.
Then Morningstar makes it All Worse
When I began working on the story above, I checked the expense reports at Morningstar. Here’s what I found for QRACX:
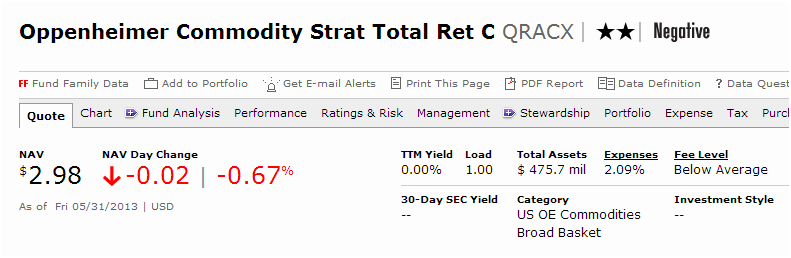
Ooookay. 2.09% is “Below Average.” But below average for what? Mob ransom demands? Apparently, below average for US Open-End Commodities Broad Basket Funds, right?
Well, no, not so much. Here’s Morningstar’s detailed expense report for the fund:
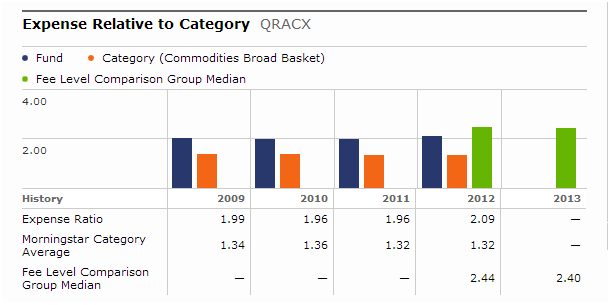
The average commodities fund – that is, the average fund in QRACX’s category – has a 1.32% expense ratio. So how on earth could QRACX at 2.09% be below average? Because it’s below the “fee level comparison group median.”
There are 131 funds in the “broad commodity basket” group. Exactly one has an expense ratio about 2.40%. If there’s one commodity fund above 2.40% and 130 below 2.40%, how could 2.40% be the group median?
Answer: Morningstar has, for the purpose of making expense comparisons, assigned QRACX to a group that has effectively nothing to do with commodity funds.
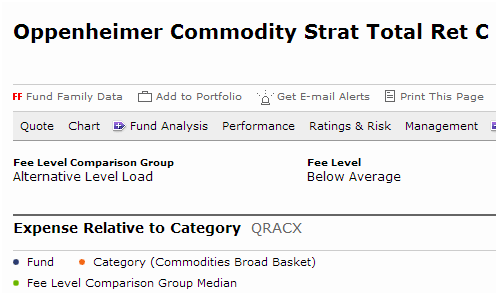
Mr. Rekenthaler, in response to an emailed query, explains, “‘Below average’ means that QRACX has below average expenses for a C share that is an Alternative fund.”
Morningstar is not comparing QRACX to other commodity funds when they make their expense judgment. No, no. They’re comparing it only to other “C” share classes of other types of “alternative investment” funds. Here are some of the funds that Morningstar is actually judging QRACX against:
|
|
Category
|
Expenses
|
|
Quantitative Managed Futures Strat C (QMFCX)
|
Mgd futures
|
9.10%
|
|
Princeton Futures Strategy C (PFFTX)
|
Mgd futures
|
5.65
|
|
Altegris Macro Strategy C (MCRCX)
|
Mgd futures
|
5.29
|
|
Prudential Jennison Market Neutral C (PJNCX)
|
Market neutral
|
4.80
|
|
Hatteras Alpha Hedged Strategies C (APHCX)
|
Multialternative
|
4.74
|
|
Virtus Dynamic AlphaSector C (EMNCX)
|
L/S equity
|
3.51
|
|
Dunham Monthly Distribution C (DCMDX)
|
Multialternative
|
3.75
|
|
MutualHedge Frontier Legends C (MHFCX)
|
Multi-alternative
|
3.13
|
|
Burnham Financial Industries C (BURCX)
|
L/S equity
|
2.86
|
|
Touchstone Merger Arbitrage C (TMGCX)
|
Market neutral
|
2.74
|
And so if you were choosing between the “C” class shares of this commodity fund and the “C” shares of a leveraged-inverse equity fund and a multicurrency fund, you’d know that you were probably getting a bargain for your money.
Why on earth you’d possibly benefit from the comparison of such of group of wildly incomparable funds remains unknown.
This affects every fund and every expense judgment in Morningstar’s database. It’s not just a problem for the miserable backwater that QRACX occupies.
Want to compare Artisan International (ARTIX) to the fund that Morningstar says is “most similar” to it, American Funds EuroPacific Growth, “A” shares (AEPGX)? Both are large, four-star funds in the Foreign Large Blend group. But for the purposes of an expense judgment, they have different “fee level comparison groups.” Artisan is judged as “foreign large cap no load,” which median is 1.14% while American is judged against “foreign large cap front load,” where the median is 1.44%. If Artisan charged 1.24% and American charged 1.34%, Artisan would be labeled “above average” and American “below average.” Meanwhile American’s “C” shares carry a 1.62% expense ratio and a celebratory “low” price label.
For investors who assume that Morningstar is comparing apples to apples (or foreign large blend to foreign large blend), this has the potential for being seriously misleading. I am very sympathetic to the complexity of Morningstar’s task, but they really need to be much clearer that these expense labels are not linked to the category labels immediately adjacent to them.
We Made the Cover!
Okay, so it wasn’t the cover of Rolling Stone. It was the cover of the BottomLine Personal newsletter (05/15/2013). And there wasn’t a picture (they reserved those for their two “Great Sex, Naturally” articles). And it was just 75 words long.
But at least they misrepresented my argument, so that’s something! The “Heard by our editors” column led off with “Consider ‘bear market funds’” and us. The bulk of the story is contained in the following two sentence fragments: “Consider ‘bear market funds’ as a kind of stock market disaster insurance . . . [they] should make up no more than 5% of your stock portfolio.”
Uhhh … what I said to the editors was “these funds are a disaster for almost everybody who holds them. By their nature, they’re going to lose money for you year after year … probably the best will cost you 7% a year in the long run. The only way they’ve work is if they represented a small fraction of your portfolio – say 5% – and you were absolutely disciplined about rebalancing so that you kept pouring money down this particular rat hole in order to maintain it as 5% of your portfolio. If you did that, you would indeed have a psychologically useful tool – a fund that might well soar in the face of our sharp downturn and that would help you stay disciplined and stay invested, rather than cutting and running. That said, we’re not wired that way and almost no one has that discipline. That why I think you’d be far better off recommending an equity fund with an absolute-returns discipline, such as Aston/River Road Independent Value, Cook and Bynum or FPA Crescent, or a reasonably priced long-short fund, like Aston/River Road Long-Short or RiverPark Long/Short Opportunity.”
They nodded, and wondered which specific bear market funds I’d recommend. They were trying hard to address their readers’ expressed interests, had 75 words to work with and so you got my recommendation of Federated Prudent Bear (BEARX, available at NAV) and PIMCO StocksPLUS AR Short Strategy (PSSDX).
Observer Fund Profiles
Each month the Observer provides in-depth profiles of between two and four funds. Our “Most Intriguing New Funds” are funds launched within the past couple years that most frequently feature experienced managers leading innovative newer funds. “Stars in the Shadows” are older funds that have attracted far less attention than they deserve.
Bretton Fund (BRTNX): if you were a fund manager looking to manage just your own family’s finances for the next generation, this is probably what you’d be doing.
RiverPark/Gargoyle Hedged Value (RGHVX): RiverPark has a well-earned reputation for bringing brilliant managers from the high net worth world to us. Gargoyle, whose discipline consistently and successfully marries stock selection and a substantial stake in call options, seems to be the latest addition to a fine stable of funds.
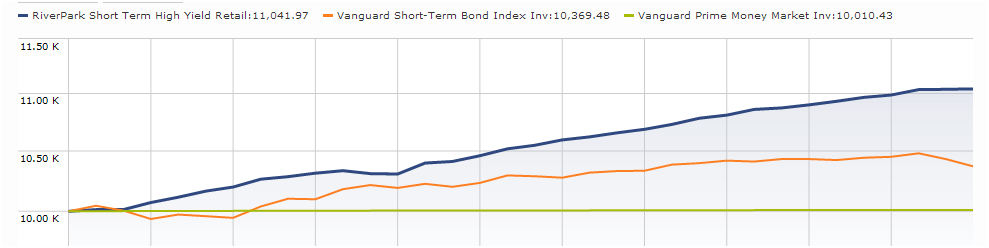
Scout Low Duration (SCLDX): there are very few fixed-income management teams that have earned the right to be trusted with a largely unconstrained mandate. Scout is managed by one of them on behalf of folks who need a conservative fund but can’t afford the foolishness of 0.01% interest.
Conference Call Highlights: Stephen Dodson and Bretton Fund
 Does it make sense to you that you could profit from following the real-life choices of the professionals in your life? What hospital does your doctor use when her family needs one? Where does the area’s best chef eat when he wants to go out for a weeknight dinner? Which tablet computer gets Chip and her IT guys all shiny-eyed?
Does it make sense to you that you could profit from following the real-life choices of the professionals in your life? What hospital does your doctor use when her family needs one? Where does the area’s best chef eat when he wants to go out for a weeknight dinner? Which tablet computer gets Chip and her IT guys all shiny-eyed?
If that strategy makes sense to you, so will the Bretton Fund (BRTNX).
Bretton Fund (BRTNX) is managed by Stephen Dodson. For a relatively young man, he’s had a fascinating array of experiences. After graduating from Berkeley, he booked 80-100 hour weeks with Morgan Stanley, taking telecom firms public. He worked in venture capital, with software and communications firms, before joining his father’s firm, Parnassus Investments. At Parnassus he did everything from answering phones and doing equity research, to co-managing a fixed-income fund and presiding over the company. He came to realize that “managing a family relationship and what I wanted in my career were incompatible at the time,” and so left to start his own firm.
In imagining that firm and its discipline, he was struck by a paradox: almost all investment professionals worshipped Warren Buffett, but almost none attempted to invest like him. Stephen’s estimate is that there are “a ton” of concentrated long-term value hedge funds, but fewer than 20 mutual funds (most visibly The Cook and Bynum Fund COBYX) that follow Buffett’s discipline: he invests in “a small number of good business he believes that he understands and that are trading at a significant discount to what they believe they’re worth.” He seemed particularly struck by his interviews of managers who run successful, conventional equity funds: 50-100 stocks and a portfolio sensitive to the sector-weightings in some index.
I asked each of them, “How would you invest if it was only your money and you never had to report to outside shareholders but you needed to sort of protect and grow this capital at an attractive rate for the rest of your life, how would you invest. Would you invest in the same approach, 50-100 stocks across all sectors.” And they said, “absolutely not. I’d only invest in my 10-20 best ideas.”
And that’s what Bretton does. It holds 15-20 stocks in industries that the manager feels he understands really well. “Understands really well” translates to “do I think I understand who’ll be making money five years from now and what the sources of those earnings will be?” In some industries (biotech, media, oil), his answer was “no.” “Some really smart guys say oil will be $50/bbl in a couple years. Other equally smart analysts say $150. I have no hope of knowing which is right, so I don’t invest in oil.” He does invest in industries such as retail, financial services and transportation, where he’s fairly comfortable with his ability to make sense of their dynamics.
When I say “he does invest,” I mean “him, personally.” Mr. Dodson reports that “I’ve invested all my investible net-worth, all my family members are invested in the fund. My mother is invested in the fund. My mother-in-law is invested in the fund (and that definitely sharpens the mind).” Because of that, he can imagine Bretton Fund functioning almost as a family office. He’s gathering assets at a steady pace – the fund has doubled in size since last spring and will be able to cover all of its ‘hard’ expenses once it hits $7 million in assets – but even if he didn’t get a single additional outside dollar he’d continue running Bretton as a mechanism for his family’s wealth management. He’s looking to the prospect of some day having $20-40 million, and he suspects the strategy could accommodate $500 million or more.
Bottom Line: The fund is doing well – it has handily outperformed its peers since inception, outperformed them in 11 of 11 down months and 18 of 32 months overall. It’s posted solid double-digit returns in 2012 and 2013, through May, with a considerable cash buffer. It will celebrate its three-year anniversary this fall, which is the minimum threshold for most advisors to consider the fund. While he’s doing no marketing now, he’s open to talking with folks and imagines some marketing effort once he’s got a three year record to talk about. Frankly, I think he has a lot to talk about already.
For folks interested but unable to join us, here’s the complete audio of the hour-long conversation.
|
|
| When you click on the link, the file will load in your browser and will begin playing after it’s partially loaded. If the file downloads, instead, you may have to double-click to play it. |
Launch Alert: T. Rowe and Vanguard
T. Rowe Price Global Allocation (RPGAX) launched on May 28, 2013. Color me intrigued. Price has always been good at asset allocation research and many of their funds allow for tactical tweaks to their allocations. This is Price’s most ambitious offering to date. The fund targets 60% stocks, 30% bonds and 10% hedge funds and other alternative investments and promises “an active asset allocation strategy” in pursuit of long-term capital appreciation and income. The fund will be managed by Charles M. Shriver, who has been with Price since 1991. Mr. Shriver also manages Price Balanced (RPBAX) fund and its Spectrum and Personal Strategy line of funds. The funds expenses are capped at 1.05% through 2016. There’s a $2500 initial investment minimum, reduced to $1000 for IRAs.
Vanguard Emerging Markets Government Bond Index Fund (VGOVX) and its ETF clone (VWOB) will launch in early June. The funds were open for subscription in May – investors could send Vanguard money but Vanguard wouldn’t invest it until the end of the subscription period. There are nearly 100 e.m. bond funds or ETFs already, though Vanguard’s will be the first index and the cheapest option (at 30-50 basis points). Apparently the launch was delayed by more than a year because Vanguard didn’t like the indexes available for e.m. bonds, so they commissioned a new one: Barclays USD Emerging Markets Government RIC Capped Index. The fund will invest only in bonds denominated in U.S. dollars. Investor shares start at $3000 and 0.50% e.r.
Pre-launch Alerts: Artisan and Grandeur Peak, Globe-trotting Again
Artisan Global Small Cap Fund launches June 19. It will be run by Mark Yockey and team. It’s been in registration for a while and its launch was delayed at least once.
Grandeur Peak Global Reach Fund (GPROX/GPRIX) will launch June 19, 2013 and will target owning 300-500 stocks, “with a strong bias” toward small and micro-caps in the American, developed, emerging and frontier markets. There’s an intriguing tension here, since the opening of Global Reach follows just six weeks after the firm closed Global Opportunities to new investors. At the time founder Robert Gardiner argued:
To be good small and micro cap investors it’s critical to limit your assets. Through my career I have seen time and again small cap managers who became a victim of their own success by taking in too many assets and seeing their performance languish.
Their claim is that they have six or seven potential funds in mind and they closed their first two funds early “in part to leave room for future funds that we intend to launch, like the Global Reach Fund.”
Funds in Registration
New mutual funds must be registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission before they can be offered for sale to the public. The SEC has a 75-day window during which to call for revisions of a prospectus; fund companies sometimes use that same time to tweak a fund’s fee structure or operating details. Every day we scour new SEC filings to see what opportunities might be about to present themselves. Many of the proposed funds offer nothing new, distinctive or interesting. Some are downright horrors of Dilbertesque babble (see “Synthetic Reverse Convertibles,” below).
Funds in registration this month won’t be available for sale until, typically, the beginning of August 2013. We found 10 – 20 no-load, retail funds in the pipeline, notably:
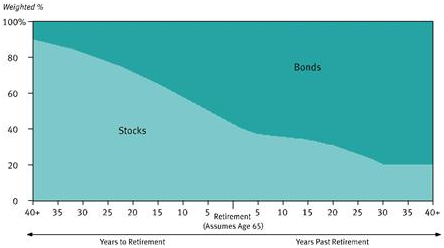
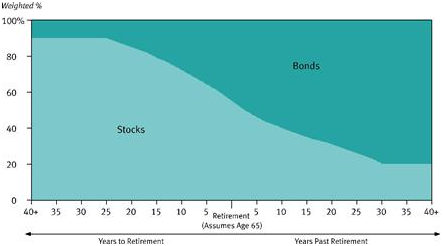
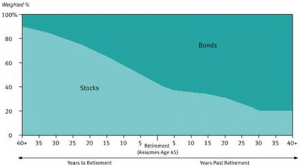
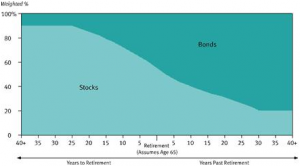
The 11 new T. Rowe Price Target Retirement 2005 – 2055 Funds will pursue that usual goal of offering a one-stop retirement investing solution. Each fund invests in a mix of other T. Rowe Price funds. Each mix becomes progressively more conservative as investors approach and move through retirement. T. Rowe Price already has an outstanding collection of retirement-date funds, called “Retirement [date]” where these will be “Target Retirement [date].” The key is that the new funds will have a more conservative asset allocation than their siblings, assuming “bonds” remain “conservative.” At the target date, the new funds will have 42.5% in equities while the old funds have 55% in equities. For visual learners, here are the two glidepaths:
 |
 |
|
The new funds’ glidepath
|
The old fund’s glidepath
|
The relative weights within the asset classes (international vs domestic, for example) are essentially the same. Each fund is managed by Jerome Clark and Wyatt Lee. The opening expense ratios vary from 0.60% – 0.77%, with the longer-dated funds incrementally more expensive than the shorter-dated ones (that is, 2055 is more expensive than 2005). These expenses are within a basis point or two of the older funds’. The minimum initial investment is $2500, reduced to $1000 for various tax-advantaged accounts.
This is a very odd time to be rolling out a bond-heavy line-up. On May 15th, The Great Gross tweeteth:
Gross: The secular 30-yr bull market in bonds likely ended 4/29/2013. PIMCO can help you navigate a likely lower return 2 – 3% future.
At least he doesn’t ramble when he’s limited to 140 characters.
The inclusion of hedge funds is fascinating, given the emerging sense (see this month’s intro) that they’re not worth a pitcher of warm bodily fluid (had I mentioned that the famous insult attributed to John Gardner, that the vice presidency “isn’t worth a bucket of warm spit” actually focused on a different bodily fluid but the newspaper editors of the day were reticent to use the word Gardner used?). The decision to shift heavily toward bonds at this moment, perplexing.
Details and the list of all of the funds in registration are available at the Observer’s Funds in Registration page or by clicking “Funds” on the menu atop each page.
MANAGER CHANGES
On a related note, we also tracked down 37 fund manager changes.
Updates …
 Oakseed Opportunity (SEEDX) released their first portfolio report (on a lovely form N-Q on file with the SEC). The fund has about $48 million in its portfolio. Highlights include:
Oakseed Opportunity (SEEDX) released their first portfolio report (on a lovely form N-Q on file with the SEC). The fund has about $48 million in its portfolio. Highlights include:
32 well-known stocks, one ETF, two individual shorts and a tiny call option
The largest five stock holdings are Teva Pharmaceuticals, Leucadia National, AbbVie (a 2013 spin-off of Abbott’s pharmaceutical division), Ross Stores, and Loews Corp.
15.8% of the fund is in cash
2.8% is in three short positions, mostly short ETF
The three largest sectors are pharmaceuticals (15.4%, four stocks), insurance (7%, two stocks) and retail (6.6%, two stocks).
(Thanks to Denny Baran of lovely Great Falls, MT, for the heads up on Oakseed’s filing.)
 Three more honors for RiverPark/Wedgewood (RWGFX). In May, Wedgewood became one of the Morningstar 500, “the top 500 funds that should be on your radar.” That same month, Wedgewood’s David Rolfe was recognized as SMA Manager of the Year at the Envestnet’s 2013 Advisor Summit. SMA’s are “separately managed accounts,” a tool for providing personalized portfolios for high net-worth investors. Wedgewood runs a bunch using the strategy behind the RiverPark/Wedgewood fund and they were selected from among 1600 management teams. Finally, Wedgewood received one of overall Large Cap awards from Envestnet, a repeat of a win in 2011, for its Large-Cap Focused Growth strategy. Those who haven’t listened to David talk about investing, should. Happily, we have a recorded hour-long conversation with David.
Three more honors for RiverPark/Wedgewood (RWGFX). In May, Wedgewood became one of the Morningstar 500, “the top 500 funds that should be on your radar.” That same month, Wedgewood’s David Rolfe was recognized as SMA Manager of the Year at the Envestnet’s 2013 Advisor Summit. SMA’s are “separately managed accounts,” a tool for providing personalized portfolios for high net-worth investors. Wedgewood runs a bunch using the strategy behind the RiverPark/Wedgewood fund and they were selected from among 1600 management teams. Finally, Wedgewood received one of overall Large Cap awards from Envestnet, a repeat of a win in 2011, for its Large-Cap Focused Growth strategy. Those who haven’t listened to David talk about investing, should. Happily, we have a recorded hour-long conversation with David.
 Valley Forge Fund (VAFGX) closes the gap, a bit. We reported in May that Valley Forge’s manager died on November 3, but that the Board of Directors didn’t seem to have, well, hired a new one. We stand corrected. First, according to an April proxy statement, the Board had terminated the manager three days before his actual, well, you know, termination.
Valley Forge Fund (VAFGX) closes the gap, a bit. We reported in May that Valley Forge’s manager died on November 3, but that the Board of Directors didn’t seem to have, well, hired a new one. We stand corrected. First, according to an April proxy statement, the Board had terminated the manager three days before his actual, well, you know, termination.
The Board determined to terminate the Prior Advisory Agreement because of, among other things, (i) the Prior Advisor’s demonstrated lack of understanding of the requirements set forth in the Fund’s prospectus, policies and procedures, (ii) the Prior Advisor’s demonstrated lack of knowledge of the terms of the Prior Advisory Agreement, (iii) the Prior Advisor’s failure to adhere to directives from the Board of Directors with respect to the Fund’s portfolio holdings; and (iv) the Fund’s poor performance.
That pretty much covers it. According to the newest prospectus (May 01, 2013), they did have a manager. Up until December 31st.
Investment Adviser Portfolio Managers: Boyle Capital Management, LLC (BCM) from November 01, 2012 to December 31, 2012.
And, for the months of April and May, the Board of Trustees ran the fund. Here’s the “principal risks” statement from the Prospectus:
Management Risk: for the months of April and May of 2013, the Board of Directors has taken over all trading pending the Shareholders’ Approval to be obtained in May 2013.
Still a bit unclear on January, February and March. Good news: under the Board’s leadership, the fund crushed the market in April and May based on a jump in NAV during the first week of May. Also a bit unclear about what happens now that it’s June: most of the Valley Forge website now leads to blank pages. Stay tuned!
Security Alert: A Word from our IT Folks
We know that many of you – fund managers, financial planners, restaurateurs and all – maintain your own websites. If, like the Mutual Fund Observer and 72.4 million others, your site runs on the WordPress software, you’re under attack. WordPress sites have been targeted for a relentless effort to gain access to your admin controls and, through them, to the resources of your web-host’s servers.
You’ve doubtless heard of “zombie computers,” individual PCs that have been compromised and which fall under the control of The Forces of Evil. In some cases zombie PCs serve spammers and phishers. In other cases, they’re used as part of coordinated distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks directed against high-profile targets including MasterCard, the Federal Reserve Bank, Google, and others.
There are three very, very bad aspects of these attacks:
- They’re aiming to seize control of enormously powerful network servers, using your website as a tool for achieving that. If you can imagine a zombie PCs potential output as equivalent to a garden hose set on full, then you could imagine a server as a fire hose set on full.
- They’re designed to keep you from knowing that you’ve been compromised; it’s not like a virus that goofs with your ability to use your machine or your site, these hacks are designed to be invisible to you.
- Once compromised, the hackers install secret backdoors into your system; that means that installing security patches or protocols after the fact does not work, you can close the main door but they’ve already built a separate entrance for themselves.
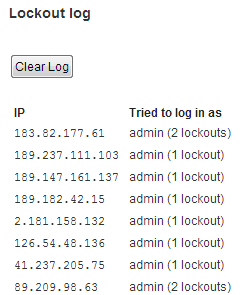 MFO has periodically been the object of as many at 400 break-in attempts an hour. Either manually or through our security software we’ve “blacklisted” nearly a thousand IP addresses, including a vast number from China.
MFO has periodically been the object of as many at 400 break-in attempts an hour. Either manually or through our security software we’ve “blacklisted” nearly a thousand IP addresses, including a vast number from China.
Here are three quick recommendations for anyone responsible for a small business or family website using WordPress (these tips might work for other platforms, too):
- Do not use the default administrator account! Rename it or create a new account with administrative rights. About 99% of the break-in attempts have been using some version of “admin” or “administrator” as the username.
- Use strong passwords. Yes, I know you hate them. They’re a pain in the butt. Use them anyway. This recent attack uses a brute force method, attempting to log in with the most commonly used passwords first. You can find some basic tips and passwords to avoid at “The 25 most common passwords of 2012.”
- Use security plug-ins. In WordPress, two to consider are Limit Login Attempts and Better WP Security. Both will temporarily lock out an IP address from which repeated login attempts occur. Better WP Security will allow you to easily make the temporary ban permanent, which is . . . strangely satisfying. (If you decide to try one of these, follow the directions carefully. It’s all too easy to lock yourself out!)
Good luck! Chip and the MFO IT crowd
Meanwhile, in Footloose Famous Guys Land …
On May 3, hedge fund (and former Fidelity Magellan fund) manager Jeffrey Vinik announced plans to shut down his hedge fund and return all assets to his fund’s investors. Again. He did the same thing at the end of 2000, when he announced a desire to focus on his own investments. Now, he wants to focus on his sports investments (he owns the NHL’s Tampa Bay Lightning), his foundation, and his family. Given that he recently moved his family to Tampa to be closer to his hockey team, the priorities above might be rank-ordered.
The speculation is that three of Vinik’s managers (Doug Gordon, Jon Hilsabeck and Don Jabro) will band together to launch a long/short hedge fund based in Boston.
The fourth, David Iben, plans to start his own investment management firm. Up until Vinik recruited him in March 2012, Iben was CIO for Nuveen Investments’ Tradewinds affiliate. His departure, followed by the swift migration of three of Iben’s managers to Vinik (Isabel Satra, Alberto Jimenez Crespo and Gregory Padilla) cost Tradewinds billions in assets with a few days.
Vinik left Magellan in 1995 after getting grief for an ill-timed macro bet: be bailed on tech stocks and bought bonds about four years too early. The same boldness (dumping US stocks and investing in gold) cost his hedge fund dearly this year.
Former Janus Triton and Venture managers Chad Meade and Brian Schaub have joined Arrowpoint Partners, which has $2.3 billion in assets and a lot Janus refugees on staff. Their six portfolio managers (founders David Corkins and Karen Reidy, Tony Yao, Minyoung Sohn, Meade and Schaub) and two senior executives (COO Rick Grove and Managing Director Christopher Dunne) were Janus employees. Too, they own 100,000 shares of Janus stock. Arrowpoint runs Fundamental Opportunity, Income Opportunity, Structured Opportunity and Life Science funds.
For those who missed the earlier announcement, former T. Rowe Price Health Sciences Fund manager Kris Jenner will launch the Rock Springs Capital hedge fund by later this year. He’s raised more than $100 million for the health and bio-tech hedge fund and has two former T. Rowe analysts, Mark Bussard and Graham McPhail, on-board with him.
Briefly Noted . . .
 Alan Abelson (October 12, 1925 – May 9, 2013), Barron’s columnist and former editor, passed away at age 87. He joined Barron’s the year I was born, began his “Up & Down Wall Street” column during the Johnson Administration and continued it for 47 years. His crankiness made him, for a long while, one of the folks I actively sought out each week. In recent years he seemed to have become a sort of parody of his former self, cranky on principle rather than for any particular cause. I’ll remember him fondly and with respect. Randall Forsyth will continue the column.
Alan Abelson (October 12, 1925 – May 9, 2013), Barron’s columnist and former editor, passed away at age 87. He joined Barron’s the year I was born, began his “Up & Down Wall Street” column during the Johnson Administration and continued it for 47 years. His crankiness made him, for a long while, one of the folks I actively sought out each week. In recent years he seemed to have become a sort of parody of his former self, cranky on principle rather than for any particular cause. I’ll remember him fondly and with respect. Randall Forsyth will continue the column.
 Speaking of cranks, John Rekenthaler has resumed his Rekenthaler Report with a vengeance. During the lunatic optimism and opportunism of the 1990s (who now remembers Alberto Vilar, the NetNet and Nothing-but-Net funds, or mutual funds that clocked 200-300% annual returns?), Mr. R and FundAlarm founder Roy Weitz spent a lot of time kicking over piles of trash – often piles that had attracted hundreds of millions of dollars from worshipful innocents. John had better statistical analyses, Roy had better snarky graphics. At the end of 2000, John shifted his attention from columnizing to Directing Research. Beginning May 22, he returned to writing a daily column at Morningstar which he bills as an attempt to leverage his quarter century in the industry to “put today’s investment stories into perspective.” It might take him a while to return to his full stride, but column titles like “Die, Horse, Die!” do give you something to look forward to.
Speaking of cranks, John Rekenthaler has resumed his Rekenthaler Report with a vengeance. During the lunatic optimism and opportunism of the 1990s (who now remembers Alberto Vilar, the NetNet and Nothing-but-Net funds, or mutual funds that clocked 200-300% annual returns?), Mr. R and FundAlarm founder Roy Weitz spent a lot of time kicking over piles of trash – often piles that had attracted hundreds of millions of dollars from worshipful innocents. John had better statistical analyses, Roy had better snarky graphics. At the end of 2000, John shifted his attention from columnizing to Directing Research. Beginning May 22, he returned to writing a daily column at Morningstar which he bills as an attempt to leverage his quarter century in the industry to “put today’s investment stories into perspective.” It might take him a while to return to his full stride, but column titles like “Die, Horse, Die!” do give you something to look forward to.
Shareholders of Kinetics Alternative Income Fund (formerly, the Kinetics Water Infrastructure Fund) participated in a 10:1 reverse split on May 30, 2013. Insert: “Snowball rolls eyes” about here. Neither the radical mission change nor the silly repricing strike me as signs of a distinguished operation.
SMALL WINS FOR INVESTORS
The Berwyn Cornerstone Fund’s (BERCX) minimum initial investment requirement for taxable accounts has been dropped from $3,000 to $1,000. It’s a tiny large cap value fund of no particular distinction.
Vanguard continues to press down its expense ratios. Vanguard Dividend Appreciation Index (VDAIX), Dividend Appreciation ETF (VIG), Dividend Growth (VDIGX), Energy (VGENX), and Precious Metals and Mining (VGPMX) dropped their expenses by two to five basis points.
CLOSINGS (and related inconveniences)
Effective May 31, 2013, Invesco closed a bunch of funds to new investors. The funds involved are
Invesco Constellation Fund (CSTGX)
Invesco Dynamics Fund (IDYAX)
Invesco High Yield Securities Fund (ACTHX)
Invesco Leaders Fund (VLFAX)
Invesco Leisure Fund (ILSAX)
Invesco Municipal Bond Fund (AMBDX)
The four equity funds, three of which were once legitimate first-tier growth options, are all large underperformers that received new management teams in 2010 and 2011. The High Yield fund is very large and very good, while Muni is fine but not spectacular. No word on why any of the closures were made.
Effective July 1, 2013, Frontegra MFG Global Equity Fund (FMGEX) is bumping its Minimum Initial Investment Amount from $100k to $1 million.
Effective at market close on June 14, 2013, the Matthews Asia Dividend Fund (MAPIX) will be closed to most new investors.
Oppenheimer Discovery (OPOCX) will close to new investors on June 28, 2013. Top-tier returns over the past three years led to a doubling of the fund’s size and its closure.
Templeton Frontier Markets Fund (TFMAX) will close to new investors effective June 28, 2013. This is another “trendy niche, hot money” story: the fund has done really well and has attracted over a billion in assets in a fairly thinly-traded market niche.
Wasatch’s management continues trying to manage Wasatch Emerging Markets Small Cap (WAEMX) popularity. The fund continues to see strong inflows, which led Wasatch to implement a soft close in February 2012. They’ve now extended their purchase restrictions. As of June 7, 2013, investors who own shares through third-party distributions, such as Schwab and Scottrade, will not be able to add to their accounts. In addition, some financial advisors are also being locked out.
OLD WINE, NEW BOTTLES
American Century continues to distance itself from Lance Armstrong and his LiveStrong Foundation. All of the LiveStrong target date funds (e.g., LIVESTRONG® 2015 Portfolio) are now One Choice target date funds. No other changes were announced.
The Artio Global Funds (née Julius Baer) have finally passed away. The equity managers have been replaced, some of the funds (Emerging Markets Local Debt, for example) have been liquidated and the remaining funds rechristened:
|
Former Fund Name
|
New Fund Name
|
|
Artio International Equity Fund
|
Aberdeen Select International Equity Fund
|
|
Artio International Equity Fund II
|
Aberdeen Select International Equity Fund II
|
|
Artio Total Return Bond Fund
|
Aberdeen Total Return Bond Fund
|
|
Artio Global High Income Fund
|
Aberdeen Global High Income Fund
|
|
Artio Select Opportunities Fund
|
Aberdeen Global Select Opportunities Fund
|
The International Equity Fund, International Equity Fund II and the Select Opportunities Fund, Inc. will be managed by Aberdeen’s Global Equity team, a dedicated team of 16 professionals based in Edinburgh, Scotland. The Total Return Bond Fund and the Global High Income Fund will continue to be managed by their current portfolio managers, Donald Quigley and Greg Hopper, respectively, along with their teams.
BlackRock Long Duration Bond Portfolio is changing its name on July 29, 2013, to BlackRock Investment Grade Bond Portfolio. They’ll also shift the fund’s primary investment strategies to allow for a wider array of bonds.
Having failed as a multisector long/short bond fund, the Board of Trustees of the Direxion Funds thought it would be a good idea to give HCM Freedom Fund (HCMFX) something more challenging. Effective July 29, 2013, HCMFX goes from long/short global fixed income to long/short global fixed income and equities. There’s no immediate evidence that the Board added any competence to the management team to allow them to succeed.
Fidelity U.S. Treasury Money Market Fund has been renamed Fidelity Treasury Only Money Market Fund because otherwise you might think . . . well, actually, I have no idea of why this makes any sense on earth.
GAMCO Mathers (MATRX) is a dour little fund whose mission is “to achieve capital appreciation over the long term in various market conditions without excessive risk of capital loss.” Here’s a picture of what that looks like:
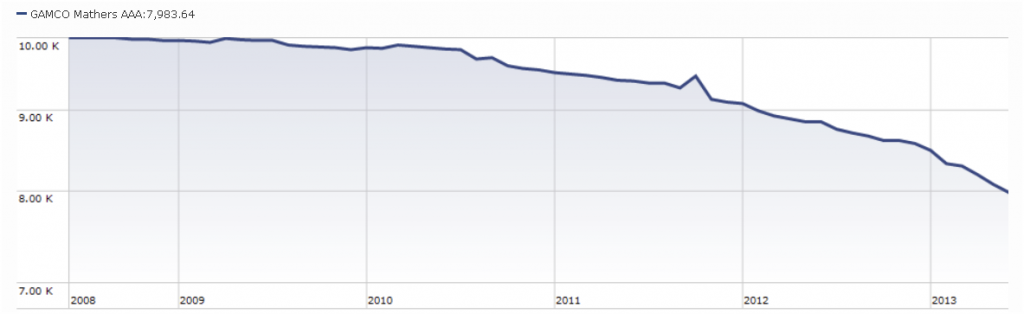
Apparently operating under the assumption that Mathers didn’t have sufficient flexibility to be as negative as they’d like, the advisor has modified their primary investment strategies to allow the fund to place 75% of the portfolio in short positions on stocks. That’s up from an allowance of 50% short.
Effective June 28, 2013, Lazard US Municipal Portfolio (UMNOX) becomes Lazard US Short Duration Fixed Income Portfolio. In addition to shortening its target duration, the revamped fund gets to choose among “US government securities, corporate securities, mortgage-related and asset-backed securities, convertible securities, municipal securities, structured products, preferred stocks and inflation-indexed-securities.” I’m always baffled by the decision to take a fund that’s overwhelmed by one task (buying munis) and adding a dozen more options for it to fumble.
On August 1, 2013 Oppenheimer U.S. Government Trust (OUSGX) will change its name to Oppenheimer Limited-Term Bond Fund. Apparently Trust in Government is wavering. The rechristened fund will be able to add corporate bonds to its portfolio. Despite being not very good, the fund has drawn nearly a billion in assets
Pinnacle Capital Management Balanced Fund (PINBX) is about to become Pinnacle Growth and Income Fund. The word “Balanced” in the name imposed a requirement “to have a specified minimum mix of equity and fixed income securities in its portfolio at all times.” By becoming un-Balanced, the managers gain the freedom to make more dramatic asset allocation shifts. It’s a tiny, expensive 30-month old fund whose manager seems to be trailing most reasonable benchmarks. I’m always dubious of giving more tools to folks who haven’t yet succeeded with the ones they have.
Pioneer Absolute Credit Return Fund (RCRAX) will, effective June 17, 2013, be renamed Pioneer Dynamic Credit Fund. Two years old, great record, over $300 million in assets … don’t get the need for the change.
Vanguard MSCI EAFE ETF has changed its name to Vanguard FTSE Developed Markets ETF.
OFF TO THE DUSTBIN OF HISTORY
AllianceBernstein U.S. Strategic Research Portfolio and AllianceBernstein International Focus 40 Portfolio will both be liquidated by June 27, 2013.
The CAMCO Investors Fund (CAMCX) has closed and will liquidate on June 27, 2013. After nine years of operation, it had earned a one-star rating and had gathered just $7 million in assets.
Litman Gregory will merge Litman Gregory Masters Value (MSVFX) into Litman Gregory Masters Equity (MSEFX) in June. Litman Gregory’s claim is that they’re expert at picking and monitoring the best outside management teams for its funds. In practice, none of their remaining funds has earned more than three stars from Morningstar (as of May, 2013). Value, in particular, substantially lagged its benchmark and saw a lot of shareholder redemptions. Litman Gregory Masters Alternative Strategies (MASNX), which we’ve profiled, has gathered a half billion in assets and continues to perform solidly.
Having neither performed nor preserved, the PC&J Performance Fund and PC&J Preservation Fund have been closed and will be liquidated on or about June 24, 2013.
ProShares Ultra High Yield and ProShares Ultra Investment Grade Corporate have been disappeared by their Board. The cold text reads: “Effective May 23, 2013, all information pertaining to the Funds is hereby removed from the Prospectus.”
I’m saddened to report that Scout International Discovery Fund (UMBDX) is being liquidated for failure to attract assets. It will be gone by June 28, 2013. This was a sort of smaller-cap version of Scout International (UMBWX) which has long distinguished itself for its careful risk management and competitive returns. Discovery followed the same discipline, excelled at risk management but gave up more in returns than it earned in risk-control. This is Scout’s second recent closure of an equity fund, following the elimination of Scout Stock.
Tatro Tactical Appreciation Fund (TCTNX ) has concluded that it can best serve its shareholders by ceasing operation, which will occur on June 21, 2013.
Tilson Focus Fund (TILFX) has closed and will be liquidated by June 21, 2013. The fund had been managed by Whitney Tilson and Glenn Tongue, founders of T2 Partners Management. Mr. Tilson removed himself from management of the fund a year ago. We’ve also found the fund perplexing and unattractive. It had two great years (2006 and 2009) in its seven full years of operation, but also four utterly horrible ones (2007, 2008, 2011, 2012), which meant that it was able to be bad in all sorts of market conditions. Mr. Tilson is very good at promotion but curiously limited at management it seems. Tilson Dividend Fund (TILDX), which we’ve profiled and which has a different manager, continues to thrive.
In Closing . . .

I will be at the Morningstar Investment Conference on your behalf, 12 – 14 June 2013. Friends have helped arrange interviews with several high-visibility professionals and there are a bunch of media breakfasts, media lunches and media dinners (some starting at hours that Iowans more associate with bedtimes than with meals). I also have one dinner and one warm beverage scheduled with incredibly cool people. I’m very excited. If you have leads you’d like me to pursue or if you’re going to be there and have a burning desire to graze the afternoon snack table with me, just drop me a note.
We’ll look for you.
As part of our visual upgrade, Barb (she of the Owl) has designed new business cards (which I’ll have for Morningstar) and new thank-you cards. I mention that latter because I need to extend formal thanks for three readers who’ve sent checks. Sorry about the ungracious delay, but I was sort of hoping to send grateful words along via the cards that haven’t yet arrived.
But will, soon! Keep an eye out in the mail.
In addition to our continuing work on visuals, the MFO folks will spend much of June putting together some wide-ranging improvements. Junior has been busily reviewing all of our “Best of the Web” features, and we’ll be incorporating new text throughout the month. Chip and Charles are working to create a friendly, easy-to-use screener for our new fund risk ratings database. Barb and Anya are conspiring to let the Owl perch in our top banner. And I’ll be learning as much as I can at the conference. We hope you like what we’ll be able to share in July.
Until then, take care and celebrate your friends and family!


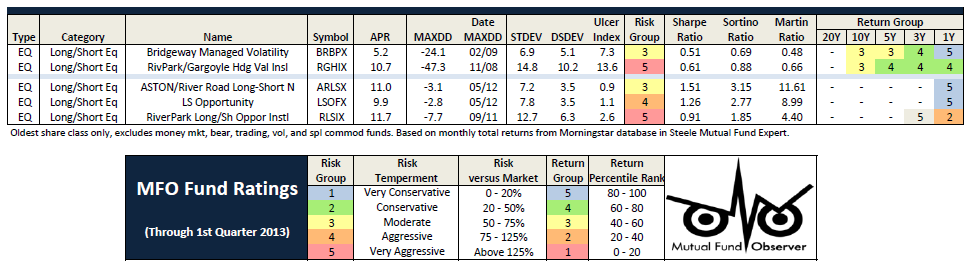
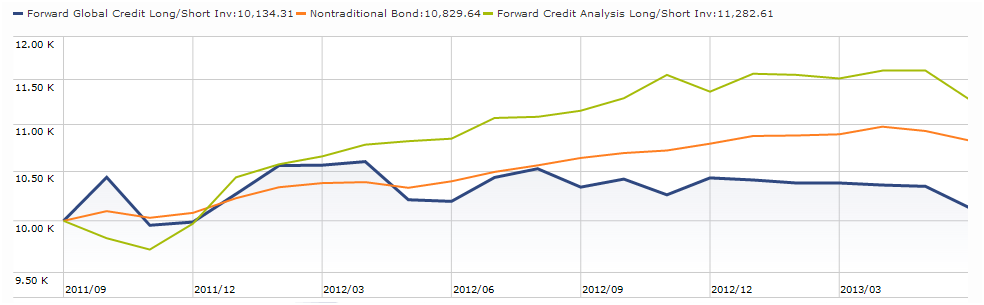
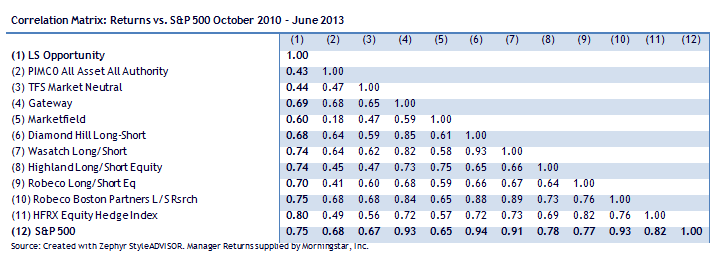 This does not automatically justify inclusion of a second or third long-short fund in your portfolio, but it does demonstrate two things. First, that long-short funds really are vastly different from one another, which is why their correlations are so low. Second, a single long-short fund offers considerable diversification in a long-only portfolio and a carefully selected second fund might add a further layer of independence.
This does not automatically justify inclusion of a second or third long-short fund in your portfolio, but it does demonstrate two things. First, that long-short funds really are vastly different from one another, which is why their correlations are so low. Second, a single long-short fund offers considerable diversification in a long-only portfolio and a carefully selected second fund might add a further layer of independence.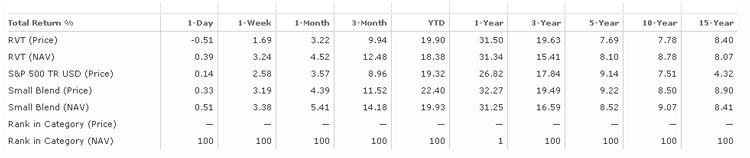


 Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.



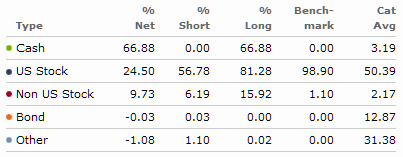
 Everybody’s talking about long/short funds. Google chronicles 273,000 pages that use the phrase. Bloomberg promises “a comprehensive list of long/short funds worldwide.” Morningstar, Lipper and U.S. News plunk nearly a hundred funds into a box with that label. (Not the same hundred funds, by the way. Not nearly.) Seeking Alpha offers up the “best and less long/short funds 2013.”
Everybody’s talking about long/short funds. Google chronicles 273,000 pages that use the phrase. Bloomberg promises “a comprehensive list of long/short funds worldwide.” Morningstar, Lipper and U.S. News plunk nearly a hundred funds into a box with that label. (Not the same hundred funds, by the way. Not nearly.) Seeking Alpha offers up the “best and less long/short funds 2013.”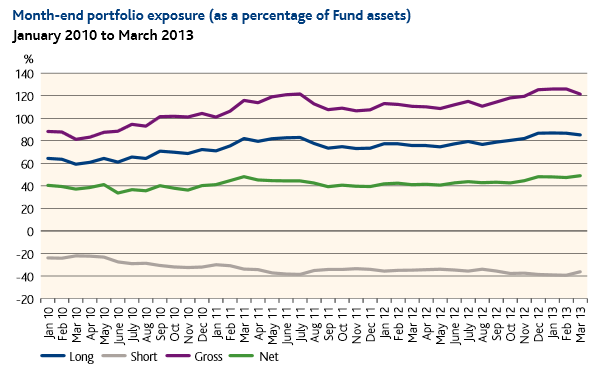

 The Healthy Debate
The Healthy Debate Versus Capital Multi-Manager Real Estate Income Fund is a closed-end interval fund. That means that you can buy Versus shares any day that the market is open, but you only have the opportunity to sell those shares once each quarter. The advisor has the option of meeting some, all or none of a particular quarter’s redemption requests, based on cash available and the start of the market.
Versus Capital Multi-Manager Real Estate Income Fund is a closed-end interval fund. That means that you can buy Versus shares any day that the market is open, but you only have the opportunity to sell those shares once each quarter. The advisor has the option of meeting some, all or none of a particular quarter’s redemption requests, based on cash available and the start of the market. 

 This comes up only because I was moved to sudden and profound pity over the cruel ways in which the poor, innocent rich folks are being ruthlessly exploited. Two new articles highlight their plight.
This comes up only because I was moved to sudden and profound pity over the cruel ways in which the poor, innocent rich folks are being ruthlessly exploited. Two new articles highlight their plight. “it’s somewhere between highly probable and certain that you will underperform [a stock portfolio] if you are being sold commodities, hedge funds and private equity right now.”
“it’s somewhere between highly probable and certain that you will underperform [a stock portfolio] if you are being sold commodities, hedge funds and private equity right now.”





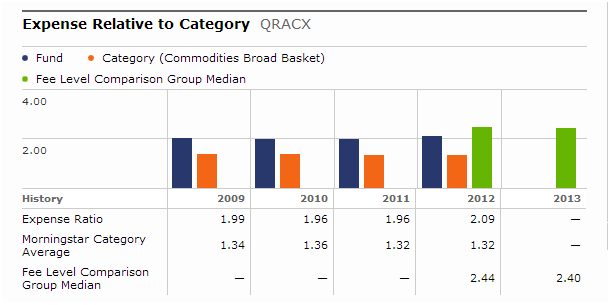

 Does it make sense to you that you could profit from following the real-life choices of the professionals in your life? What hospital does your doctor use when her family needs one? Where does the area’s best chef eat when he wants to go out for a weeknight dinner? Which tablet computer gets Chip and her IT guys all shiny-eyed?
Does it make sense to you that you could profit from following the real-life choices of the professionals in your life? What hospital does your doctor use when her family needs one? Where does the area’s best chef eat when he wants to go out for a weeknight dinner? Which tablet computer gets Chip and her IT guys all shiny-eyed?


 Valley Forge Fund (VAFGX) closes the gap, a bit. We reported in May that Valley Forge’s manager died on November 3, but that the Board of Directors didn’t seem to have, well, hired a new one. We stand corrected. First, according to an April proxy statement, the Board had terminated the manager three days before his actual, well, you know, termination.
Valley Forge Fund (VAFGX) closes the gap, a bit. We reported in May that Valley Forge’s manager died on November 3, but that the Board of Directors didn’t seem to have, well, hired a new one. We stand corrected. First, according to an April proxy statement, the Board had terminated the manager three days before his actual, well, you know, termination. MFO has periodically been the object of as many at 400 break-in attempts an hour. Either manually or through our security software we’ve “blacklisted” nearly a thousand IP addresses, including a vast number from China.
MFO has periodically been the object of as many at 400 break-in attempts an hour. Either manually or through our security software we’ve “blacklisted” nearly a thousand IP addresses, including a vast number from China. Alan Abelson (October 12, 1925 – May 9, 2013), Barron’s columnist and former editor, passed away at age 87. He joined Barron’s the year I was born, began his “Up & Down Wall Street” column during the Johnson Administration and continued it for 47 years. His crankiness made him, for a long while, one of the folks I actively sought out each week. In recent years he seemed to have become a sort of parody of his former self, cranky on principle rather than for any particular cause. I’ll remember him fondly and with respect. Randall Forsyth will continue the column.
Alan Abelson (October 12, 1925 – May 9, 2013), Barron’s columnist and former editor, passed away at age 87. He joined Barron’s the year I was born, began his “Up & Down Wall Street” column during the Johnson Administration and continued it for 47 years. His crankiness made him, for a long while, one of the folks I actively sought out each week. In recent years he seemed to have become a sort of parody of his former self, cranky on principle rather than for any particular cause. I’ll remember him fondly and with respect. Randall Forsyth will continue the column. Speaking of cranks, John Rekenthaler has resumed his
Speaking of cranks, John Rekenthaler has resumed his 


 We started by thinking about the Observer’s mission and ethos, and how best to capture that visually. The apparent dignity, quiet watchfulness and unexpected ferocity of the Great Horned Owl – they’re sometimes called “tigers with wings” and are quite willing to strike prey three times their own size – was immediately appealing. Barb’s genius is in identifying the essence of an image, and stripping away everything else. She admits, “I don’t know what to say about the wise old owl, except he lends himself soooo well to minimalist geometric treatment just naturally, doesn’t he? I wanted to trim off everything not essential, and he still looks like an owl.”
We started by thinking about the Observer’s mission and ethos, and how best to capture that visually. The apparent dignity, quiet watchfulness and unexpected ferocity of the Great Horned Owl – they’re sometimes called “tigers with wings” and are quite willing to strike prey three times their own size – was immediately appealing. Barb’s genius is in identifying the essence of an image, and stripping away everything else. She admits, “I don’t know what to say about the wise old owl, except he lends himself soooo well to minimalist geometric treatment just naturally, doesn’t he? I wanted to trim off everything not essential, and he still looks like an owl.”
 r. Hillary manages Independence Capital Asset Partners (ICAP), a long/short equity hedge fund he launched on November 1, 2004 that serves as the sub-advisor to the LS Opportunity Fund (LSOFX), which in turn launched on September 29, 2010. Prior to embarking on a hedge fund career, Mr. Hillary was a co-founder and director of research for Marsico Capital Management where he managed the Marsico 21st Century Fund (MXXIX) until February 2003 and co-managed all large cap products with Tom Marsico. In addition to his US hedge fund and LSOFX in the mutual fund space, ICAP runs a UCITS for European investors. Jim offers these 200 words on why his mutual fund could be right for you:
r. Hillary manages Independence Capital Asset Partners (ICAP), a long/short equity hedge fund he launched on November 1, 2004 that serves as the sub-advisor to the LS Opportunity Fund (LSOFX), which in turn launched on September 29, 2010. Prior to embarking on a hedge fund career, Mr. Hillary was a co-founder and director of research for Marsico Capital Management where he managed the Marsico 21st Century Fund (MXXIX) until February 2003 and co-managed all large cap products with Tom Marsico. In addition to his US hedge fund and LSOFX in the mutual fund space, ICAP runs a UCITS for European investors. Jim offers these 200 words on why his mutual fund could be right for you: I had a chance to speak with David Rolfe of Wedgewood Partners and Morty Schaja, president of RiverPark Funds. A couple dozen listeners joined us, though most remained shy and quiet. Morty opened the call by noting the distinctiveness of RWGFX’s performance profile: even given a couple quarters of low relative returns, it substantially leads its peers since inception. Most folks would expect a very concentrated fund to lead in up markets. It does, beating peers by about 10%. Few would expect it to lead in down markets, but it does: it’s about 15% better in down markets than are its peers. Mr. Schaja is invested in the fund and planned on adding to his holdings in the week following the call.
I had a chance to speak with David Rolfe of Wedgewood Partners and Morty Schaja, president of RiverPark Funds. A couple dozen listeners joined us, though most remained shy and quiet. Morty opened the call by noting the distinctiveness of RWGFX’s performance profile: even given a couple quarters of low relative returns, it substantially leads its peers since inception. Most folks would expect a very concentrated fund to lead in up markets. It does, beating peers by about 10%. Few would expect it to lead in down markets, but it does: it’s about 15% better in down markets than are its peers. Mr. Schaja is invested in the fund and planned on adding to his holdings in the week following the call. Manager Steve Dodson, former president of the Parnassus Funds, is an experienced investment professional, pursuing a simple discipline. He wants to buy deeply discounted stocks, but not a lot of them. Where some funds tout a “best ideas” focus and then own dozens of the same large cap stocks, Mr. Dodson seems to mean it when he says “just my best.”
Manager Steve Dodson, former president of the Parnassus Funds, is an experienced investment professional, pursuing a simple discipline. He wants to buy deeply discounted stocks, but not a lot of them. Where some funds tout a “best ideas” focus and then own dozens of the same large cap stocks, Mr. Dodson seems to mean it when he says “just my best.” This is Aston’s latest attempt to give the public – or at least “the mass affluent” – access to managers who normally employ distinctive strategies on behalf of high net worth individuals and institutions. LMCG is the Lee Munder Capital Group (no, not the Munder of Munder NetNet and Munder Nothing-but-Net fame – that’s Munder Capital Management, a different group). Over the five years ended December 30, 2012, the composite performance of LMCG’s emerging markets separate accounts was 2.8% while their average peer lost 0.9%. In 2012, a good year for emerging markets overall, LMCG made 24% – about 50% better than their average peer. The fund’s three managers, Gordon Johnson, Shannon Ericson and Vikram Srimurthy, all joined LMCG in 2006 after a stint at Evergreen Asset Management. The minimum initial investment in the retail share class is $2500, reduced to $500 for IRAs. The opening expense ratio will be 1.65% (with Aston absorbing an additional 4.7% of expenses).
This is Aston’s latest attempt to give the public – or at least “the mass affluent” – access to managers who normally employ distinctive strategies on behalf of high net worth individuals and institutions. LMCG is the Lee Munder Capital Group (no, not the Munder of Munder NetNet and Munder Nothing-but-Net fame – that’s Munder Capital Management, a different group). Over the five years ended December 30, 2012, the composite performance of LMCG’s emerging markets separate accounts was 2.8% while their average peer lost 0.9%. In 2012, a good year for emerging markets overall, LMCG made 24% – about 50% better than their average peer. The fund’s three managers, Gordon Johnson, Shannon Ericson and Vikram Srimurthy, all joined LMCG in 2006 after a stint at Evergreen Asset Management. The minimum initial investment in the retail share class is $2500, reduced to $500 for IRAs. The opening expense ratio will be 1.65% (with Aston absorbing an additional 4.7% of expenses).