By David Snowball
Dear friends,
Welcome to the midway point of … well, nothing in particular, really. Certainly six months have passed in 2014 and six remain, but why would you care? Unless you plan on being transported by aliens or cashing out your portfolio on December 31st, questions like “what’s working this year?” are interesting only to the poor saps whose livelihoods are dependent on inventing explanations for, and investment responses to, something that happened 12 minutes ago and will be forgotten 12 minutes from now.
So, what’s working for investors in 2014? If you guessed “investments in India and gold,” you’ve at least got numbers on your side. The top funds YTD:
|
|
|
YTD return, through 6/30, for Investor or “A” shares
|
|
Tocqueville Gold
|
TGLDX
|
– 48.3
|
|
Van Eck International Gold
|
INIVX
|
– 48.9
|
|
Matthews India
|
MINDX
|
– 5.9
|
|
Gabelli Gold
|
GLDAX
|
– 51.3
|
|
ProFunds Oil Equipment
|
OEPIX
|
+ 38.1
|
|
OCM Gold
|
OCMGX
|
– 47.6
|
|
Fidelity Select Gold
|
FSAGX
|
– 51.4
|
|
Dreyfus India *
|
DIIAX
|
– 31.5
|
|
ALPS | Kotak India Growth
|
INDAX
|
– 5.1
|
Oh wait! Sorry! My bad. That’s how this year’s brilliant ideas did last year. Here’s the glory I wanted to highlight for this year?
|
|
|
YTD return, through 6/30, for Investor or “A” shares
|
|
Tocqueville Gold
|
TGLDX
|
36.7
|
|
Van Eck International Gold
|
INIVX
|
36.0
|
|
Matthews India
|
MINDX
|
35.9
|
|
Gabelli Gold
|
GLDAX
|
35.5
|
|
ProFunds Oil Equipment
|
OEPIX
|
34.6
|
|
OCM Gold
|
OCMGX
|
31.7
|
|
Fidelity Select Gold
|
FSAGX
|
30.7
|
|
Dreyfus India *
|
DIIAX
|
30.6
|
|
ALPS | Kotak India Growth
|
INDAX
|
30.5
|
* Enjoy it while you can. Dreyfus India is slated for liquidation by summer’s end.
Now doesn’t that make you feel better?
The Two Morningstar conferences
We had the opportunity to attend June’s Morningstar Investor Conference where Bill Gross, the world’s most important investor, was scheduled to give an after lunch keynote address today. Apparently he actually gave two addresses: the one that Morningstar’s folks attended and the one I attended.
Morningstar heard a cogent, rational argument for why a real interest rate of 0-1% is “the new neutral.” At 2% real, the economy might collapse. In that fragile environment, PIMCO models bond returns in the 3-4% range and stocks in the 4-5% range. In an act of singular generosity, he also explained the three strategies that allows PIMCO Total Return to beat everyone else and grow to $280 billion. Oops, $230 billion now as ingrates and doubters fled the fund and weren’t around to reap this year’s fine returns: 3.07% YTD. He characterized that as something like “fine” or “top tier” returns, though the fund is actually modest trailing both its benchmark and peer group YTD.

Representatives of other news outlets also attended that speech and blandly reported Gross’s generous offer of “the keys to the PIMCO Mercedes” and his “new neutral” stance. One went so far as to declare the whole talk “charming.”
I missed out on that presentation and instead sat in on an incoherent, self-indulgent monologue that was so inappropriate to the occasion that it made me seriously wonder if Gross was off his meds. He walked on stage wearing sunglasses and spent some time looking at himself on camera; he explained that he always wanted to see himself in shades on the big screen. “I’m 70 years old and looking good!” he concluded. He tossed the shades aside and launched into a 20 minute reflection on the film The Manchurian Candidate, a Cold War classic about brainwashing and betrayal. I have no idea of why. He seemed to suggest that we’d been brainwashed or that he wasn’t able to brainwash us but wished he could or he needed to brainwash himself into not hating the media. 20 minutes. He then declared PIMCO to be “the happiest workplace in the world,” allowing that if there was any place happier, it was 15 miles up the road at Disneyland. That’s an apparent, if inept, response to the media reports of the last month that painted Gross as arrogant, ill-tempered, autocratic and nigh unto psychotic in the deference he demanded from employees. He then did an ad for the superiority of his investment process before attempting an explanation of “the new neutral” (taking pains to establish that the term was PIMCO’s, not Bloomberg’s). After 5-10 minutes of his beating around the bush, I couldn’t take it any more and left.
Gross’s apologists claimed that this was a rhetorical masterpiece whose real audience was finance ministers who might otherwise screw up monetary policy. A far larger number of folks – managers, marketers, advisors – came away horrified. “I’ve heard Gross six times in 20 years and he’s always given to obscure analogies but this was different. This was the least coherent I’ve ever heard him,” said one. “That was absolutely embarrassing,” opined someone with 40 years in the field. “An utter train wreck,” was a third’s. I’ve had friends dependent on psychoactive medications; this presentation sounded a lot like what happens when one of them failed to take his meds, a brilliant guy stumbling about with no sense of appropriateness.
Lisa Shidler at RIA Advisor was left to wonder how much damage was done by a speech that was at times “bizarre” and, most optimistically, “not quite a disaster.”
Bottom line: Gross allowed that “I could disappear today and it wouldn’t have a material effect on PIMCO for 3-5 years.” It might be time to consider it.
The Morningstar highlight: Michael Hasenstab on emerging markets
Michael Hasenstab, a CIO and manager of the four-star, $70 billion Templeton Global Bond Fund (TPINX), was the conference keynote. Over 40% of the fund is now invested in emerging markets, including 7% in Ukraine. He argued that investors misunderstand the fundamental strength of the emerging markets. Emerging markets were, in the past, susceptible to collapse when interest rates began to rise in the developed world. Given our common understanding that the Fed is likelier to raise rates in the coming year than to reduce them, the question is: are we on the cusp of another EM collapse.
He argues that we are not. Two reasons: the Bank of Japan is about to bury Asia in cash and emerging markets have shown a fiscal responsibility far in excess of anything seen in the developed world.
The Bank of Japan is, he claims, on the verge of printing a trillion dollars worth of stimulus. Prime Minister Abe has staked his career on his ability to stimulate the Japanese economy. He’s using three tools (“arrows,” in his terms) but only one of those three (central bank stimulus) is showing results. In consequence, Japan is likely to push this one tool as far as they’re able. Hasenstab thinks that the stimulus possible from the BOJ will completely, and for an extended period, overwhelm any moderation in the Fed’s stimulus. In particular, BOJ stimulus will most directly impact Asia, which is primarily emerging. The desire to print money is heightened by Japan’s need to cover a budget deficit that domestic sources can’t cover and foreign ones won’t.
Emerging markets are in exemplary fiscal shape, unlike their position during past interest rate tightening phases. In 1991, the emerging markets as a whole had negligible foreign currency reserves; when, for example, American investors wanted to pull $100 million out, the country’s banks did not hold 100 million in US dollars and crisis ensued. Since 1991, average foreign currency reserves have tripled. Asian central banks hold reserves equal to 40% of their nation’s GDPs and even Mexico has reserves equal to 20% of GDP. At base, all foreign direct investment could leave and the EMs would still maintain large currency reserves.
Hasenstab also noted that emerging markets have undergone massive deleveraging so that their debt:GDP ratios are far lower than those in developed markets and far lower than the historic levels in the emerging markets. Finally we’re already at the bottom of the EM growth cycle with growth rates over the next several years averaging 6-7%.
As an active manager, he likely felt obliged to point out that EM stocks have decoupled; nations with negative real interest rates and negative current account balances are vulnerable. Last year, for example, Hungary’s market returned 4000 bps more than Indonesia’s which reflects their fundamentally different situations. As a result, it’s not time to buy a broad-based EM index.
Bottom line: EM exposure should be part of a core portfolio but can’t be pursued indiscriminately. While the herd runs from manic to depressed on about a six month cycle, the underlying fundamentals are becoming more and more compelling. For folks interested in the argument, you should read the MFO discussion board thread on it. There’s a lot of nuance and additional data there for the taking.
 Feeding the Beast
Feeding the Beast
by Edward Studzinski
“Finance is the art of passing currency from hand to hand until it finally disappears.”
Robert Sarnoff
A friend of mine, a financial services reporter for many years, spoke to me one time about the problem of “feeding the beast.” With a weekly deadline requirement to come up with a story that would make the editors up the chain happy and provide something informative to the readers, it was on more than one occasion a struggle to keep from repeating one’s self and avoid going through the motions. Writing about mutual funds and the investment management business regularly presents the same problems for me. Truth often becomes stranger than fiction, and many readers, otherwise discerning rational people, refuse to accept that the reality is much different than their perception. The analogy I think of is the baseball homerun hitter, who through a combination of performance enhancing chemicals and performance enhancing bats, breaks records (but really doesn’t).
So let’s go back for a moment to the headline issue. One of my favorite “Shoe” cartoons had the big bird sitting in the easy chair, groggily waking up to hear the break-in news announcement “Russian tanks roll down Park Avenue – more at 11.” The equivalent in the fund world would be “Famous Fund Manager says nothing fits his investment parameters so he is sending the money back.” There is not a lot of likelihood that you will see that happening, even though I know it is a concern of both portfolio managers and analysts this year, for similar reasons but with different motivations. In the end however it all comes back to job security, about which both John Bogle and Charlie Ellis have written, rather than a fiduciary obligation to your investors.
David Snowball and I interviewed a number of money managers a few months ago. All of them were doing start-ups. They had generally left established organizations, consistently it seemed because they wanted to do things their own way. This often meant putting the clients first rather than the financial interests of a parent company or the senior partners. The thing that resonated the most with me was a comment from David Marcus at Evermore Global, who said that if you were going to set up a mutual fund, set up one that was different than what was available in the market place. Don’t just set up another large cap value fund or another global value fund. Great advice but advice that is rarely followed it seems.
If you want to have some fun, take a look at:
- an S&P 500 Index Fund’s top ten holdings vs.
- the top ten holdings at a quantitative run large cap value fund (probably one hundred stocks rather than five hundred, and thirty to sixty basis points in fees as opposed to five at the index fund) vs.
- the top ten holdings at a diversified actively managed large cap value fund (probably sixty stocks and eighty basis points in fees) vs.
- a non-diversified concentrated value fund (less than twenty holdings, probably one hundred basis points in fees).
Look at the holdings, look at the long-term performance (five years and up), and look at the fees, and draw your own conclusions. My suspicion is that you will find a lot of portfolio overlap, with the exception of the non-diversified concentrated fund. My other suspicion is that the non-diversified concentrated fund will show outlier returns (either much better or much worse). The fees should be much higher, but in this instance, the question you should be paying attention to is whether they are worth it. I realize this will shock many, but this is one of the few instances where I think they are justified if there is sustained outperformance.
Now I realize that some of you think that the question of fees has become an obsession with me, my version of Cato the Elder saying at every meeting of the Roman Senate, “Carthage must be destroyed.” But the question of fees is one that is consistently under appreciated by mutual fund investors, if for no other reason that they do not see the fees. In fact, if you were to take a poll of many otherwise sophisticated investors, they would tell you that they are not being charged fees on their mutual fund investment. And yet, high fees without a differentiated portfolio does more to degrade performance over time than almost anything else.
John Templeton once said that if your portfolio looks like everyone else’s, your returns also will look the same. The great (and I truly mean great) value investor Howard Marks of Oaktree Capital puts it somewhat differently but equally succinctly. Here I am paraphrasing but, if you want to make outsized returns than you have to construct a portfolio that is different than that held by most other investors. Sounds easy right?
But think about it. In large investment organizations, unconventional behavior is generally not rewarded. If anything, the distinction between the investors and the consultant intermediaries increasingly becomes blurred in terms of who really is the client to whom the fiduciary obligation is owed. Unconventional thinking loses out to job security. It may be sugar coated in terms of the wording you hear, with all the wonderful catch phrases about increased diversification, focus on generating a higher alpha with less beta, avoiding dispersion of investment results across accounts, etc., etc. But the reality is that if 90% of the client assets were invested in an idea that went to zero or the equivalent of zero and 10% of them did not because the idea was avoided by some portfolio managers, the ongoing discussion in that organization will not be about lessons learned relative to the investment mistake. Rather it will be about the management and organizational problems caused by the 10% managers not being “team players.”
The motto of the Special Air Service in Great Britain is, “Who dares, wins.” And once you spend some time around those people, you understand that the organization did not mold that behavior into them, but rather they were born with it and found the right place where they could use those talents (and the organization gave them a home). Superior long-term investment performance requires similar willingness to assess and take risks, and to be different than the consensus. It requires a willingness to be different, and a willingness to be uncomfortable with your investments. That requires both a certain type of portfolio manager, as well as a certain type of investor.
I have written before about some of the post-2008 changes we have seen in portfolio management behavior, such as limiting position sizes to a certain number of days trading volume, and increasing the number of securities held in a portfolio (sixty really is not concentrated, no matter what the propaganda from marketing says). But by the same token, many investors will not be comfortable with a very different portfolio. They will also not be comfortable investing when the market is declining. And they will definitely not be comfortable with short-term underperformance by a manager, even when the long-term record trashes the indices.
From that perspective, I again say that if you as an investor can’t sleep at night with funds off the beaten path or if you don’t want to do the work to monitor funds off the beaten path, then focus your attention on asset-allocation, risk and time horizon, and construct a portfolio of low-cost index funds.
At least you will sleep at night knowing that over time you will earn market returns. But if you know yourself, and can tolerate being different – than look for the managers where the portfolio is truly different, with the potential returns that are different.
But don’t think that any of this is easy. To quote Charlie Munger, “It’s not supposed to be easy. Anyone who finds it easy is stupid.” You have to be prepared to make mistakes, in both making investments and assessing managers. You also have to be willing to look different than the consensus. One other thing you have to be willing to do, especially in mutual fund investing, is look away from the larger fund organizations for your investment choices (with the exception of index funds, where size will drive down costs) for by their very nature, they will not attract and retain the kind of talent that will give you outlier returns (and as we are seeing with one large European-owned organization, the parent may not be astute enough to know when decay has set in). Finally, you have to be in a position to be patient when you are wrong, and not be forced to sell, either by reason of not having a long-term view or long-term resources, or in the case of a manager, not having the ability to weather redemptions while maintaining organizational and institutional support for the philosophy.
Next month: Flash geeks and other diversions from the mean.
Navigating Scylla and Charybdis: reading advice from the media saturated
Last month’s lead essay, “All the noise, noise, noise noise!” made the simple argument that you need to start paying less attention to what’s going on in the market, not more. Our bottom line:
It’s survival. I really want to embrace my life, not wander distractedly through it. For investors, that means making fewer, more thoughtful decisions and learning to trust that you’ve gotten it right rather than second-guessing yourself throughout the day and night.
The argument is neither new nor original to us. The argument is old. In 1821 the poet Percy Bysshe Shelley complained “We have more moral, political, and historical wisdom than we know how to reduce into practice.” By the end of the century, the trade journal Printer’s Ink (1890) complained that “the average [newspaper] reader skims lightly over the thousand facts massed in serried columns. To win his attention he must be aroused, excited, terrified.” (Certain broadcast outlets apparently took note.)
And the argument is made more eloquently by others than by us. We drew on the concerns raised by a handful of thoughtful investors who also happen to be graceful writers: Joshua Brown, Tadas Viskanta, and Barry Ritholtz.
We should have included Jason Zweig in the roster. Jason wrote a really interesting essay, Stock Picking for the Long, Long, Long Haul, on the need for us to learn to be long-term investors:
Fund managers helped cause the last financial crisis—and they will contribute to the next one unless they and their clients stop obsessing over short-term performance.
Jason studied the remarkable long-term performance of the British investment firm Baillie Gifford and find that their success is driven by firms whose management is extraordinarily far-sighted:
What all these companies have in common, Mr. Anderson [James, BG’s head of global equities] says, is that they aren’t “beholden to the habits of quarterly capitalism.” Instead of trying to maximize their short-term growth in earnings per share, these firms focus almost entirely on growing into the distant future.
“Very often, the best way to be successful in the long run is not to aim at being successful in the short run,” he says. “The history of capitalism has been lurched forward by people who weren’t looking primarily for the rewards of narrow, immediate gain.”
In short, he doesn’t just want to find the great companies of today—but those that will be even greater companies tomorrow and for decades to come.
The key for those corporate leaders is to find investors, fund managers and others, who “have a horizon of decades.” “It’s amazing how some of the largest and greatest companies hunger to have shareholders who are genuinely long-term,” Mr. Anderson says.
In June I asked those same writers to shift their attention from problem to solution. If the problem is that we become addled to paying attention – increasingly fragmented slivers of attention, anyway – to all the wrong stuff, where should we be looking? How should we be training our minds? Their answers were wide-ranging, eloquent, consistent and generous. We’ll start by sharing the themes and strategies that the guys offered, then we’ll reproduce their answers in full for you on their own pages.
“What to read if you want to avoid being addled and stupid.” It’s the Scylla and Charybdis thing: you can’t quite ignore it all but you don’t want to pay attention to most of it, so how do you steer between? I was hopeful of asking the folks I’d quoted for their best answer to the question: what are a couple things, other than your own esteemed publication, that it would benefit folks to read or listen to regularly?
Three themes seem to run across our answers.
-
Don’t expose yourself to any more noise than your job demands.
As folks in the midst of the financial industry, the guys are all immersed in the daily stream but try to avoid being swept away by it. Josh reports that “at no time do I ever visit the home page of a blog or media company’s site.” He scans headlines and feeds, looking for the few appearances (whether Howard Marks or “a strategist I care about”) worth focusing on. Jason reads folks like Josh and Tadas “who will have short, sharp takes on whatever turns out to matter.” For the rest of us, Tadas notes, “A monthly publication is for the vast majority of investors as frequent as they need to be checking in on the world of investing.”
-
Take scientific research seriously.
Jason is “looking for new findings about old truths – evidence that’s timely about aspects of human nature that are timeless.” He recommends that the average reader “closely follow the science coverage in a good newspaper like The Wall Street Journal or The New York Times.” Tadas concurs and, like me, also regularly listens to the Science Friday podcast which offers “an accessible way of keeping up.”
-
Read at length and in depth.
All of us share a commitment to reading books. They are, Tadas notes, “an important antidote to the daily din of the financial media,” though he wryly warns that “many of them are magazine articles padded out to fill out the publisher’s idea of how long a book should be.”
Of necessity, the guys read (and write) books about finance, but those books aren’t at the top of their stacks and aren’t the ones in their homes. Jason’s list is replete with titles that I dearly wish I could get my high achieving undergrads to confront (Montaigne’s Essays) but they’re not “easy reads” and they might well be things that won’t speak even to a very bright teenager. Jason writes, “Learning how to think is a lifelong struggle, no matter how intelligent or educated you may be. Books like these will help. The chapter on time in St. Augustine’s Confessions, for instance, which I read 35 years ago, still guides me in understanding why past performance doesn’t predict future success.” Tadas points folks to web services that specialize in long form writing, including Long Reads and The Browser.
Here’s my answer, for what interest that holds:
Marketplace, from American Public Media. The Marketplace broadcast and podcast originate in Los Angeles and boast about 11 million listeners, mostly through the efforts of 500 public radio stations. Marketplace, and its sister programs Marketplace Money and Marketplace Morning Report, are the only shows that I listen to daily. Why? Marketplace starts with the assumption that its listeners are smart and curious, but not obsessed with the day’s (or week’s) market twitches. They help folks make sense of business and finance – personal and otherwise – and they do it in a way that makes you feel more confident of your own ability to make sense of things. The style is lively, engaged and sometimes surprising.
Books, from publishers. I know this seems like a dodge, but it isn’t. At Augustana, I teach about the effects of emerging technologies and on the ways they use us as much as we use them. This goes beyond the creepiness of robots reading my mail (a process Google is now vastly extending) or organizations that can secretly activate my webcam or cellphone. I’m concerned that we’re being rewired for inattention. Neurobiologists make it clear that our brains are very adaptive organs; when confronted with a new demand – whether it’s catching a thrown baseball or navigating the fact of constant connection – it assiduously begins reorganizing itself. We start as novices in the art of managing three email accounts, two calendars, a dozen notification sounds, coworkers we can never quite escape and the ability to continuously monitor both the market and the World Cup but, as our brains rewire, we become experts and finally we become dependent. That is, we get to a state where we need constant input. Teens half wake at night to respond to texts. Adults feel “ghost vibrations” from phones in their pockets. Students check texts 11 times during the average class period. Board members stare quietly at devices on their laps while others present. Dead phones become a source of physical anxiety. Electronic connectedness escapes control and intrudes on driving, meals, sleep, intimacy. In trying never to miss anything, we end up missing everything.
Happily, that same adaptability works in the other direction. Beyond the intrinsic value of encountering an argument built with breadth and depth, the discipline of intentionally disconnecting from boxes and reconnecting with other times and places can rebuild us. It’s a slog at first, just as becoming dependent on your cell phone was, but with the patient willingness to set aside unconnected time each day – 20 minutes at first? one chapter next? – we can begin distancing ourselves from the noise and from the frenetic mistakes it universally engenders.
And now the guys’ complete responses:
Thanks to them all for their generosity and cool leads. I hadn’t looked at either The Browser or The Epicurean Dealmaker before (both look cool) though I’m not quite brave enough to try Feedly just yet for fear of becoming ensnared.
Despite the loud call of a book (Stuff Matters just arrived and is competing with The Diner’s Dictionary and A Year in Provence for my attention), I’ll get back to talking about fund stuff.
Top Developments in Fund Industry Litigation – June 2014
Fund advisors spend a surprising amount of time in court or in avoiding court. We’ve written before about David Smith and FundFox, the only website devoted to tracking the industry’s legal travails. I’ve asked David if he’d share a version of his monthly précis with us and he generously agreed. Here’s his wrap up of the legal highlights from the month just passed.
 For a complete list of developments last month, and for information and court documents in any case, log in at www.fundfox.com. Fundfox is the only intelligence service to focus exclusively on litigation involving U.S.-registered investment companies, their directors and advisers—making it easy to remain specialized and aware in today’s fluid legal environment.
For a complete list of developments last month, and for information and court documents in any case, log in at www.fundfox.com. Fundfox is the only intelligence service to focus exclusively on litigation involving U.S.-registered investment companies, their directors and advisers—making it easy to remain specialized and aware in today’s fluid legal environment.
New Lawsuit
- A new excessive-fee lawsuit alleges that Davis provides substantially the same investment advisory services to subadvised funds for lower fees than its own New York Venture Fund. (Hebda v. Davis Selected Advisers, L.P.)
Settlements
- The court preliminarily approved a $14.95 million settlement of the ERISA class action regarding ING’s receipt of revenue-sharing payments. (Healthcare Strategies, Inc. v. ING Life Ins. & Annuity Co.)
- The court preliminarily approved a $22.5 million settlement of the ERISA class action alleging that Morgan Keegan defendants permitted Regions retirement plans to invest in proprietary RMK Select Funds despite excessive fees. (In re Regions Morgan Keegan ERISA Litig.)
Briefs
- A former portfolio manager filed his opposition to Allianz’s motion to dismiss his breach-of-contract suit regarding deferred compensation under two incentive plans; and Allianz filed a reply brief. (Minn v. Allianz Asset Mgmt. of Am. L.P.)
- BlackRock filed an answer and motion to dismiss an excessive-fee lawsuit alleging that two BlackRock funds charge higher fees than comparable funds subadvised by BlackRock. (In re BlackRock Mut. Funds Advisory Fee Litig.)
- Harbor filed a reply brief in support of its motion to dismiss an excessive-fee lawsuit regarding a subadvised fund. (Zehrer v. Harbor Capital Advisors, Inc.)
Advisor Perspectives launches APViewpoint, a discussion board for advisors
We spent some time at Morningstar chatting with Justin Kermond, a vice president with Advisor Perspectives (AP). We’ve collaborated with AP on other issues over the years, they’re exploring the possibility of using some of our fund-specific work their site and they’ve recently launched a discussion board that’s exclusive to the advisor community. We talked for a while about MFO’s experience hosting a lively (oh so lively) discussion board and what AP might be doing to build on our experience. For the sake of those readers in the advisor community, I asked Justin to share some information about their new discussion community. Here’s his description>
[We] recently launched APViewpoint, a secure discussion forum and “online study group.” APViewpoint enables investment advisers, registered reps, and financial planners to learn from each other by sharing their experiences and knowledge on a wide range of topics of interest to the profession. Current topics of discussion include Thomas Pikkety’s views on inequality; whether small cap and value stocks truly outperform the market; the pros and cons of rebalancing; and the potential transformative effect of robo-advisors. APViewpoint is free to all financial advisors. The site formally launched mid May, 2014 and currently has more than 900 members.
One of APViewpoint’s key differentiators is the participation of more than 40 nationally recognized industry thought leaders, including Bob Veres, Carl Richards, Harold Evensky, Wade Pfau, Doug Short, Michael Kitces, Dan Solin, Michael Edesess, Geoff Considine, Marylin Capelli Dimitroff, Ron Rhoades, Sue Stevens and Advisor Perspectives CEO and editor Robert Huebscher. These thought leaders start and participate in discussions on a variety of topics, and advisors are invited to learn and share their own views, creating a vibrant, highly respectful environment that encourages the free exchange of ideas.
For advisors interested in discussing funds, APViewpoint automatically recognizes mutual fund and ETF symbols mentioned in discussions, permitting users to easily search for conversations about specific products. Users can also create a specific list of funds they wish to “follow,” and be alerted when these funds are mentioned in conversations.
APViewpoint is also designed to foster discussion of the content featured on the Advisor Perspectives web site and weekly newsletter. Every article now features a direct link to an associated discussion on APViewpoint, allowing members to provide spontaneous feedback.
Only advisors can be members of APViewpoint; investors may not join. A multi-step validation process ensures that only advisors are approved, and the content on APViewpoint is not accessible to the general public. This relieves advisors of some of the compliance issues that often restrict their ability to post their thoughts on social media platforms such as Linkedin, where investors can view messages posted in groups where advisors congregate.
Advisors can sign up today at www.apviewpoint.com.
The piece in between the pieces
I’ve always been honored, and more than a little baffled, that folks as sharp as Charles, Chip and Ed have volunteered to freely and continually contribute so much to the Observer and, through us, to you. Perhaps they share my conviction that you’re a lot brighter than you know and that you’re best served by encountering smart folks who don’t always agree and who know that’s just fine.
Our common belief is not that we learn by listening to a smart person with whom we agree (isn’t that the very definition of a smart person? Someone who tells us we’re right?), but to listening to a variety of really first rate people whose perspectives are a bit complicated and whose argument might (gasp!) be more than one screen long.
The problem is that they’re often smarter than we are and often disagree, leaving us with the question “who am I to judge?” That’s at the heart of my day job as a college professor: helping learners get past the simple, frustrated impulse of either (1) picking one side and closing your ears, or (2) closing your ears without picking either.
 One of the best expressions of the problem was offered by Leo Strauss, a 20th century political philosopher and classicist:
One of the best expressions of the problem was offered by Leo Strauss, a 20th century political philosopher and classicist:
To repeat: liberal education consists of listening to the conversation among the greatest minds. But here we are confronted with the overwhelming difficulty that this conversation does not take place without our help – that in fact we must bring about that conversation. The greatest minds utter monologues. We must transform their monologues into a dialogue, their “side by side” into a “together.” The greatest minds utter dialogues even when they write monologues.
Let us face this difficulty, a difficulty so great that it seems to condemn liberal education to an absurdity. Since the greatest minds contradict one another regarding the most important matters, they compel us to judge their monologues; we cannot take on trust what any one of them says. On the other hand, we cannot be notice that we are not competent to be judges. In Liberalism Ancient and Modern (1968)
The two stories that follow are quick attempts to update you on what a couple of first-rate guys have been thinking and doing. The first is Charles’s update on Mebane Faber, co-founder and CIO of Cambria Funds and a prolific writer. The second is my update on Andrew Foster, founder and CIO of Seafarer Funds.
 Meb Faber gets it right in interesting ways
Meb Faber gets it right in interesting ways
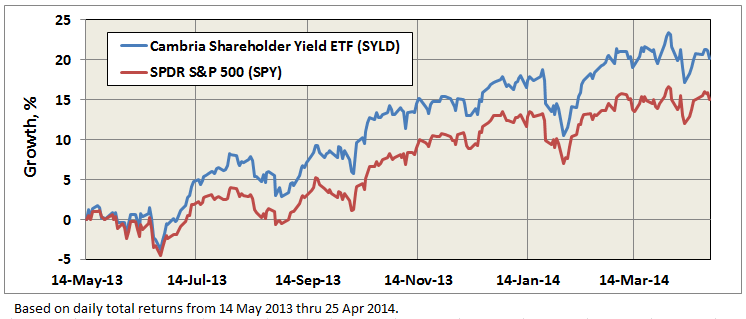
A quick follow-up to our feature on Mebane Faber in the May commentary, entitled “The Existential Pleasure of Engineering Beta.”
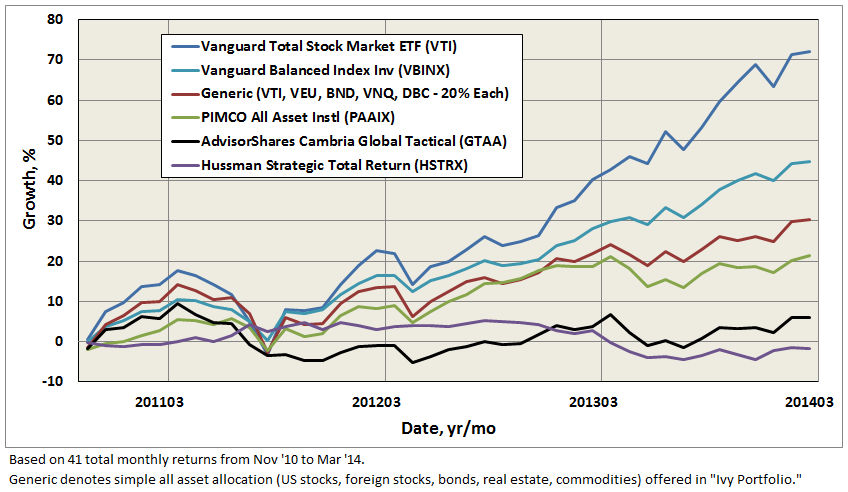
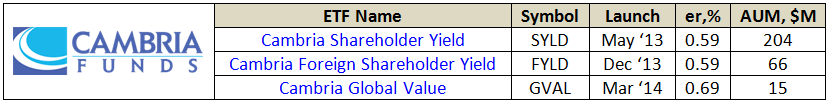
On May 16, Mebane posted on his blog “Skin in the Game – My Portfolio,” which states that he invests 100% of his liquid net worth in his firm’s funds: Global Tactical Hedge Fund (private), Global Value ETF (GVAL), Shareholder Yield ETF (SYLD), Foreign Shareholder Yield ETF (FYLD) – all offered by Cambria Investment Management.
His disclosure meets the “Southeastern Asset Management” rule, as coined and proposed by our colleague Ed Studzinski. It would essentially mandate that all employees of an investment firm limit their investments to funds offered by the firm. Ed proposes such a rule to better attune “investment professionals to what should be their real concern – managing risk with a view towards the potential downside, rather than ignoring risk with other people’s money.”
While Mr. Faber did not specify the dollar amount, he did describe it as “certainly meaningful.” The AdvisorShares SAI dated December 30, 2013, indicated he had upwards of $1M invested in his first ETF, Global Tactical ETF (GTAA), which was one of largest amounts among sub-advisors and portfolio managers at AdvisorShares.
Then, on June 5th, more clarity: “The two parties plan on separating, and Cambria will move on” from sub-advising GTAA and launch its own successor Global Momentum ETF (GMOM) at a full 1% lower expense ratio. Here’s the actual announcement:

Same day, AdvisorShares announced: “After a diligent review and careful consideration, we have decided to propose a change of GTAA’s sub-advisor. At the end of the day, our sole focus remains our shareholders’ best interests…” The updated SAI indicates the planned split is to be effective end of July.

Given the success of Cambria’s own recently launched ETFs, which together represent AUM of $357M or more than 10 times GTAA, the split is not surprising. What’s surprising is that AdvisorShares is not just shuttering GTAA, but chose instead to propose a new sub-advisor, Mark Yusko of Morgan Creek Capital Management.
On the surface, Mr. Yusko and Mr. Faber could not be more different. The former writes 25 page quarterly commentaries without including a single data graph or table. The latter is more likely to give us 25 charts and tables without a single paragraph.
When Mebane does write, it is casual, direct, and easily understood, while Mr. Yusko seems to read from the corporate play book: “We really want to think differently. We really want to embrace alternative strategies. Not alternative investments but alternative strategies. To gain access to the best and brightest. To invest on that global basis. To take advantage of where we see biggest return opportunities around the world.”
When we asked Mebane for a recent photo to use in the May feature, he did not have one and sent us a self-photo taken with his cell phone. In contrast, Mark Yusko offers a professionally produced video introducing himself and his firm, accompanied with scenes of a lovely creek (presumably Morgan’s) and soft music.
Interestingly, Morgan Creek launched its first retail fund last September, aptly named Morgan Creek Tactical Allocation Fund (MAGTX/MIGTX). MAGTX carries a 5.75% front-load with a 2% er. (Gulp.) But, the good news is institutional share class MIGTX waives load on $1M minimum and charges only 1.75% er.
Mr. Yusko says “I don’t mind paying [egregious] fees as long as my net return is really high.” While Mr. Faber made a point during the recent Wine Country Conference that a goal for Cambria is to “disrupt the traditional high fee mutual fund and hedge fund business, mostly through launching ETFs.”
The irony here is that GTAA was founded on the tenants described in Mebane’s first book “The Ivy Portfolio,” which includes attempting to replicate Yale’s endowment success with all-asset strategy using an ETF.
Mr. Yusko’s earned his reputation managing the endowments at Notre Dame and University of North Carolina, helping to transform them from traditional stock/bond/cash portfolios to alternative hedge fund/venture capital/private investment portfolios. But WSJ reports that he was asked to step-down last year as CIO of the $3.5B Endowment Fund, which also attempted to mimic endowments like Yale’s. He actually established the fund in partnership with Salient Partners LP in 2004. “After nearly a decade of working with our joint venture partner in Texas, we found ourselves differing on material aspects of how to best run an endowment portfolio and run the business…” Perhaps with AdvisorShares, Mark Yusko will once again be able to see eye-to-eye.
As for Mebane? We will look forward with interest to the launch of GMOM (a month or two away), his continued insights and investment advice shared generously, and wish him luck in his attempts to disrupt the status quo.
Seafarer gets it right in interesting ways
Why am I not surprised?
Seafarer is an exceedingly independent, exceedingly successful young emerging markets fund run by an exceedingly thoughtful, exceedingly skilled manager (and team). While most funds imply a single goal (“to make our investors rich, rich, rich!”), Seafarer articulated four. In their most recent shareholder letter, Andrew and president Michelle Foster write:
Our abiding goal as an investment adviser is to deliver superior long-term performance to our clients. However, we also noted three ancillary objectives:
- to increase the transparency associated with investment in developing countries;
- to mitigate a portion of the volatility that is inherent to the emerging markets; and
- to deliver lower costs to our clients, over time and with scale.
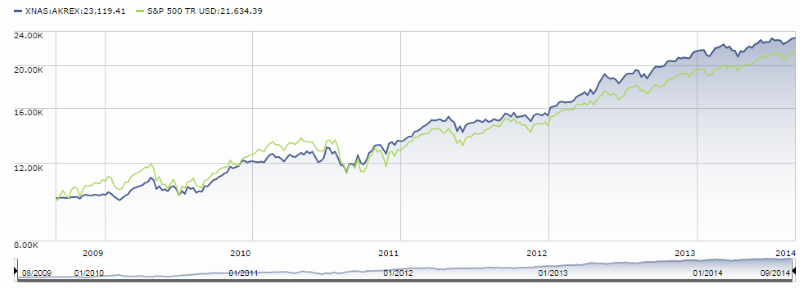
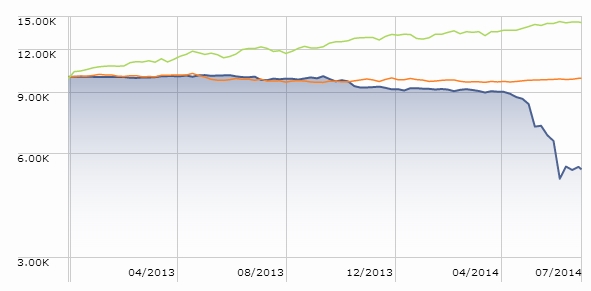
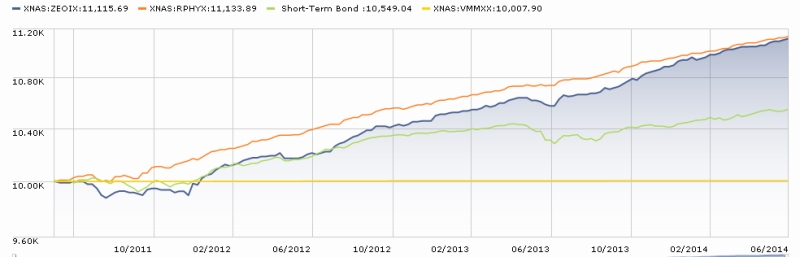
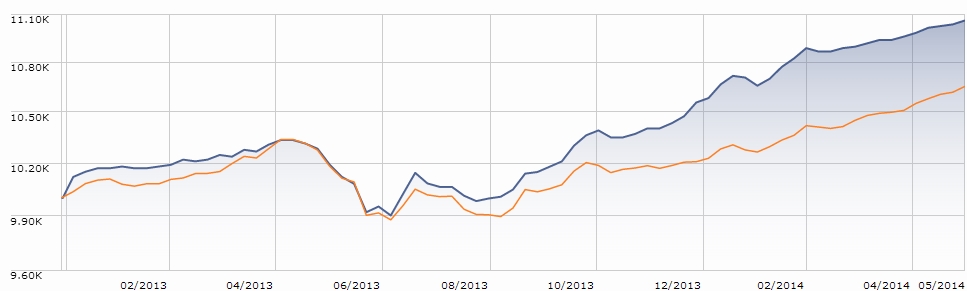
They’ve certainly done a fine job with their “abiding goal.” Here’s the picture, with Seafarer represented by the blue line:
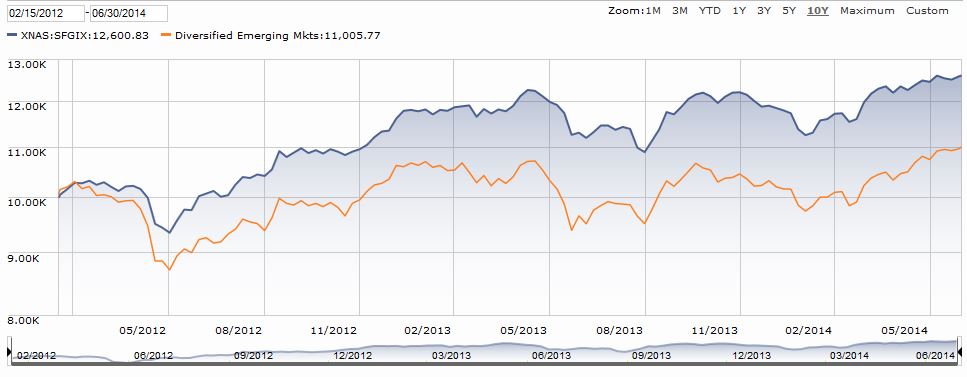
That success is driven, at least in part, by Seafarer’s dogged independence, since you can’t separate yourself from the herd by acting just like it. Seafarer’s median market cap ($4 billion) is one-fifth of its peers’ while still being spread almost evenly across all market capitalizations, it has no exposure at all to some popular countries (Russia: 0) and sectors (commodities: 0), and a simple glance at the portfolio stats (higher price, lower earnings) belies the quality of the holdings.
Four developments worth highlighting just now:
Seafarer’s investment restrictions are being loosened
One can profit from developments in the emerging markets either by investing in firms located there or by investing in firms located here than do business there (for example, BMW’s earnings are increasingly driven by China). Seafarer does both and its original prospectus attempted to give investors a sense of the comparative weights of those two approaches by enunciating guideline ranges: firms located in developed nations might represent 20-50% of the portfolio and developing nations would be 50-80%. Those numeric ranges will disappear with the new prospectus. The advisor’s experience was that it was confusing more investors than it was informing. “I found in practice,” he writes, “that some shareholders were wrongly but understandably interpreting these percentages as precise restrictions, and so we removed the percentage ranges to reduce confusion.”
Seafarer’s gaining more flexibility to add bonds to the portfolio
Currently the fund’s principal investment strategy has it investing in “dividend-paying common stocks, preferred stocks, convertible securities and debt obligations of foreign companies.” Effective August 29, “the Fund may also pursue its investment objective by investing in the debt obligations of foreign governments and their agencies.” Andrew notes that “they help bolster liquidity, yield, and to some extent improve the portfolio’s stability — so we have made this change accordingly. Still, I think it’s unlikely they will become a big part of what we do here at Seafarer.”
Seafarer’s expenses are dropping (again)
Effective September 1, the expense ratio on retail shares drops from 1.49% to 1.25% and the management fee – the money the advisor actually gets to keep – drops from 0.85% to 0.75%. Parallel declines occur in the Institutional shares.
Given their choice, Seafarer would scoot more investors into its lower cost institutional shares but agreements with major distributions (think “Schwab”) keep them from reducing the institutional minimum. That said, the current shareholder letter actually lists three ways that investors might legally dodge the $100k minimum and lower their expenses. Those are details in the final six paragraphs of the shareholder letter. If you’re a large individual investor or a smaller advisor, you might want to check out the possibilities.
Active management is working!
Seafarer’s most recent conference call was wide-ranging. For those unable to listen in (sadly, the mp3 isn’t available), the slide deck offers some startling information. Here’s my favorite slide:
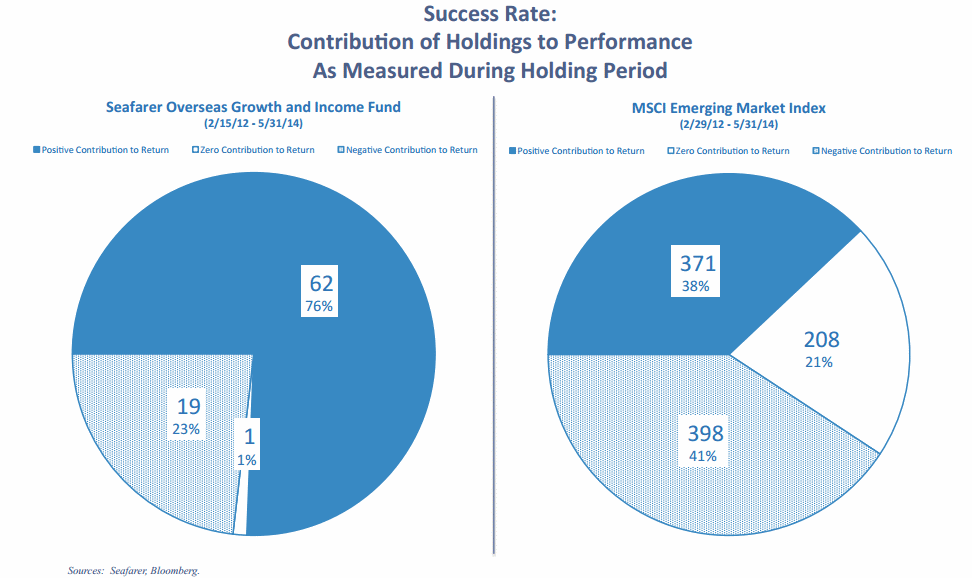
Dark blue: stocks the make money for the portfolio. White: break-even. Light blue: losers (“negative contributors”). If you buy a broad-based EM index, exactly 38% of the stocks in your fund actually make you money. If you buy Seafarer, that proportion doubles.
That strikes me as incredibly cool. Also consistent with my suspicion (and Andrew’s research) that indexes are often shockingly careless constructs.
Observer Fund Profiles
Each month the Observer provides in-depth profiles of between two and four funds. Our “Most Intriguing New Funds” are funds launched within the past couple years that most frequently feature experienced managers leading innovative newer funds. “Stars in the Shadows” are older funds that have attracted far less attention than they deserve.
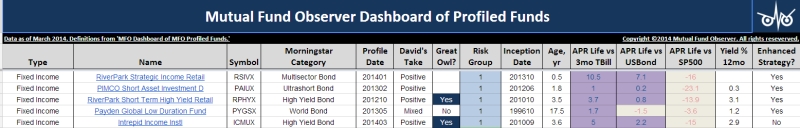
This month: fixed income investing from A to Z (or zed).
Artisan High Income (ARTFX): Artisan continues to attract highly-talented young managers with promises of integrity, autonomy and support. The latest emigrant is Bryan Krug, formerly the lead manager of the four star, $10 billion Ivy High Income fund. Mr. Krug is a careful risk manager who invests in a mix of high-yield bonds and secured and unsecured loans. And yes, he does know what everybody is saying about the high yield market.
Zeo Strategic Income (ZEOIX): Manager Venk Reddy has been honing his craft in private partnerships for years now as the guy who put the “hedging” in hedge funds but he aspires to more. He wanted to get out and pursue his own vision. In Latin, EXEO is pronounced “ek-zeo” and means something like “I’m outta here.” And so he left the world of high alpha for the land of low beta. Mr. Reddy is a careful risk manager who invests in an unusually compact portfolio of short term high-yield bonds and secured loans designed to produce consistent, safe inflation-beating returns for investors looking for “cash” that’s not trash.
Launch Alert: Touchstone Sands Emerging Markets Growth Fund
In May, 2014, Touchstone Investments launched the Touchstone Sands Capital Emerging Markets Growth Fund, sub-advised by Sands Capital Management. Sands Capital, with about $42 billion in AUM, has maintained an exclusive focus on growth-oriented equity investing since 1992. They began investing in the emerging markets in 2006 as part of their Global Growth strategy then launched a devoted EM strategy at the very end of 2012. Over time they’ve added resources to allow their EM team to handle ever greater responsibilities.
The EM composite has done exceedingly well since launch, substantially outperforming the standard EM index in both 2013 and 2014. The more important factor is that there are rational decisions which increase the prospect that the strategy’s success with be repeated in the fund. At base, there are good places to be in emerging markets and bad places to be.
Good places: small firms that tap into the growing affluence of the EMs and the emergence of their middle class.
Bad places: large firms that are state-owned or state-controlled that are economically tied to the slow-growing developed world. Banks, telecoms, and energy companies are pretty standard examples.
Structurally, indexes and many funds that benchmark themselves against the indexes tend to over-invest in the bad places because they are, well, big. Cap-weighted means buy whatever’s big, corrupt and inefficient or not.
Steve Owens of Touchstone talked with me about Sands’ contrasting approach to EM investing:
Sands Capital’s investment philosophy is based on a belief that over time, common stock prices will reflect the earnings power and growth of the underlying businesses. Sands Capital utilizes the same six investment criteria to evaluate all current and potential business investments across its [three] strategies.
Sands Capital has found many innovative and distinctive businesses that are similar to those which the firm has historically invested in its developed market portfolios. Sands Capital seeks dominant franchises that are taking market share in a growing business space, while generating significant free cash flow to self-fund their growth. Sands Capital tends to avoid most commodity-based companies, state-owned enterprises or companies that are highly leveraged with opaque balance sheets (i.e. many Utilities and Financials). It seeks to avoid emerging market businesses that are levered to developed market demand rather than local consumption.
This process results in a benchmark agnostic, high active share, all-cap portfolio of 30-50 businesses which tends to behave differently from traditional Emerging Market indices. Sands Capital opportunistically invests in Frontier Market Equities when it finds a great business opportunity.
Sands other funds are high growth, low turnover four- and five-star funds, now closed to new investors. The new fund is apt to be likewise. The minimum initial investment in the retail class is $2500, reduced to $1000 for IRAs. The expenses are capped at 1.49%. Here’s the fund’s homepage.
Sands will likely join Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income and Dreihaus Emerging Markets Small Cap Growth Fund on the short list of still-open EM funds that we keep a close eye on. Investors who are more cautious but still interested in enhanced EM exposure should watch Amana Developing World as well.
Funds in Registration
The summer doldrums continue with only nine new no-load funds in registration. The most interesting might be an institutional fund from T. Rowe Price which focuses on frontier markets. Given Price’s caution, the launch of this fund seems to signal the fact that the frontier markets are now mainstream investments.
Manager Changes
Fifty-six funds underwent partial or total manager changes this month, a substantial number that’s a bit below recent peaks. One change in particular piqued Chip’s curiosity. As you know, our esteemed technical director also tracks industry-wide manager changes. She notes, with some perplexity, that Wilmington Multi-Manager Alternative might well be renamed Wilmington Ever-changing Manager Alternative fund. She writes:
Normally, writing up the manager changes is relatively straight-forward. This month, one caught my eye. The Wilmington Multi-Manager Alternatives Fund (WRAAX) turned up with a manager change for the third month in a row. A quick check of the data shows that the fund has had 42 managers since its inception in 2012. Twenty-eight of them are no longer with the fund.
|
Year
|
Managers ending their tenure at WRAAX
|
|
2012
|
5
|
|
2013
|
18
|
|
2014 to date
|
5
|
The fund currently sports 14 managers but they also dismiss about 14 managers a year. Our recommendation to the current crew: keep your resumes polished and your bags packed.
We’d be more sympathetic to the management churn if it resulted in superior returns for the fund’s investors, but we haven’t seen that yet. $10,000 invested in the fund at launch would have swollen to $10,914 today. In the average multialternatives fund, it would be $10,785. That’s a grand total of $129 in excess returns generated by almost constant staff turnover.
By way of an alternative, rather than paying a 5% load and 2.84% expenses here in order to hedge yourself, you might consider Vanguard Balanced Index (VBINX). The world’s dullest fund charges 0.24% and would have turned your $10,000 into $13,611.
Briefly Noted . . .
Special thanks, as always, to The Shadow for independently tracking down 14 or 15 fund changes this month, sometimes posting changes just before the fund companies realize they’re going to make them. That’s spooky-good.
SMALL WINS FOR INVESTORS
American Century Equity Income Fund (TWEIX) reopens to new investors on August 1. The folks on the discussion board react with three letters (WTF) and one question: Why? The fund’s assets have risen just a bit since the closure while its performance has largely been mediocre.
On July 1, 2014, ASTON/LMCG Emerging Markets Fund (ALEMX) reduced its expense ratio from 1.65% to 1.43% on its retail “N” shares and from 1.40% down to 1.18% on its institutional shares. The fund has had a tough first year. The fund returned about 9% over the past 12 months while its peers made 15%. A lower expense ratio won’t solve all that, but it’s a step in the right direction.
CCM Alternative Income (CCMNX) is lowering its investment minimum from $100,000 to $1,000. While the Morningstar snapshot of the fund trumpets expenses of 0.00%, they’re actually capped at 1.60%.
|
Morningstar’s clarification:
Our website shows the expense ratio from the fund’s annual report, not a fund’s prospectus. The 1.60% expense ratio is published in the fund’s prospectus.
Thanks for the quick response.
|
Effective June 23, 2014, Nuveen converted all of their funds’ “B” shares into “A” shares.
We should have mentioned this earlier: Effective May 7, 2014, Persimmon Long/Short (LSEAX/LSEIX) agreed to reduce its management fee from 2.50% to 1.99%. This is really a small win since the resulting total expense ratio remains around 3.25% and the fund sports a 5% sales load. Meaning no disrespect to the doubtless worthy folks behind the fund, but I’m baffled at how they expect to gain traction in the market with such structurally high expenses.
Good news for all Lutherans out there! For the month of August 2014 only, the sales load on the “A” shares of Thrivent Growth and Income Plus Fund (TEIAX), Thrivent Balanced Income Plus Fund (AABFX), Thrivent Diversified Income Plus Fund (AAHYX), Thrivent Opportunity Income Plus Fund (AAINX), and Thrivent Municipal Bond Fund (AAMBX) will be temporarily waived. Bad news for all Lutherans out there: other than Diversified Income, these really aren’t very good.
CLOSINGS (and related inconveniences)
As of August 1, 2014, AMG Managers Skyline Special Equities Fund (SKSEX) will close to new investors. In the nature of such things, the fund’s blistering performance in 2013 (up 51.6%) drew in a rush of eager new money. The newbies are now enjoying the fund’s bottom 10% performance YTD and might well soon head out again for greener pastures. These are, doubtless, folks who should have read Erma Bombeck’s classic The Grass Is Always Greener over the Septic Tank (1976) rather than watching CNBC.
As of July 11, 2014, Columbia Acorn Emerging Markets Fund (CAGAX) is closing to new investors. The fund reached the half billion plateau well before it reached its third birthday, driven by a surge in performance that began in May 2012.
On July 8, 2014, the $1.3 billion Franklin Biotechnology Discovery Fund (FBDIX) is closed to new folks as well.
The Board of Trustees approved the imposition of a 2% redemption fee on shares of the Hotchkis & Wiley High Yield Fund (HWHAX) that are redeemed or exchanged in 90 days or less. Given the fact that high yield is hot and overpriced (those two do go together), it strikes me as a good thing that H&W are trying to slow folks down a bit.
Any guesses about why Morningstar codes half of the H&W funds as “Hotchkis and Wiley” and the other half as “Hotchkis & Wiley”? It really goofs up my attempts to search the danged database.
|
A reply from Morningstar:
For all Hotchkis & Wiley funds, Morningstar has been in the process of replacing “and” with “&” in accordance with the cover page of the fund’s prospectus. You should see this reflected on Morningstar.com in the next day or two.
The consistency will be greatly appreciated.
|
OLD WINE, NEW BOTTLES
I’ve placed this note here because I hadn’t imagined the need for a section named “Coups and Other Uprisings.” Effective August 1, Forward Endurance Long/Short Fund (FENRX) becomes a new fund. The name changes (to Forward Equity Long/Short), the mandate changes, fees drop by 25 bps, it ceases to be “non-diversified” and the management team changes (the earlier co-manager left on one week’s notice in May, two new in-house guys are … well, in).
The old mandate was “to identify trends that may have a disruptive impact on and result in significant changes to global business markets, including new technology developments and the emergence of new industries.” The less disruptive new strategy is “to position the Fund in the stronger performing sectors using a proprietary relative strength model and in high conviction fundamental ideas.”
Other than for a few minutes in the spring of 2014, they were actually doing a pretty solid job.
On July 7, 2014, the Direxion Monthly Commodity Bull 2X Fund (DXCLX) will be renamed as Direxion Monthly Natural Resources Bull 2X Fund, with a corresponding change to the underlying index.
At the beginning of September, Dreyfus Select Managers Long/Short Equity Fund (DBNAX) becomes Dreyfus Select Managers Long/Short Fund. I’m deeply grateful for Dreyfus’s wisdom in choosing to select managers rather than randomly assigning them. Thanks, guy!
On October 1, 2014, SunAmerica High Yield Bond Fund (SHNAX) becomes SunAmerica Flexible Credit Fund, and that simultaneously make “certain changes to their principal investment strategy and techniques.” In particular, they won’t have to invest in high yield bonds if they don’t wanna. That good because, as a high yield bond fund, they’ve pretty much trail the pack by 50-100 bps over most trailing time periods.
At the end of July, the $300 million Vice Fund (VICEX) becomes the Barrier Fund. It’s a nice fund run by a truly good person, Gerry Sullivan. The new mandate does, however, muddy things a bit. First, the fund only commits to investing at least 25% of assets to its traditional group of alcohol, tobacco, gaming and defense (high barrier-to-entry) stocks but it’s not quite clear where else the money would go, or why. And the fund will reserve for itself the power to short and use options.
OFF TO THE DUSTBIN OF HISTORY
Apparently diversification isn’t working for everybody. Diversified Risk Parity Fund (DRPAX/DRPIX) will “cease operations, close and redeem all outstanding shares” on July 30, 2014. ASG Diversifying Strategies Fund (DSFAX) is slated to be liquidated about a week later, on August 8. The omnipresent Jason Zweig has a thoughtful essay of the fund’s liquidation, “When hedging cuts both ways.” At base, the ASG product was a hedge-like fund that … well, would actually hedge a portfolio. Investors loved the theory but were impatient with the practice:
If you want an investment that can do well when stocks and bonds do badly, a liquid-alt fund can do that for you. But you will have nobody but yourself to blame when stocks and bonds do well and you get annoyed at your alternative fund for underperforming. That is what it is supposed to do.
If you can’t accept that, maybe you should just keep some of your money in cash.
Dreyfus is giving up on a variety of its funds: one bad hedge-y fund Global Absolute Return (DGPAX, which has returned absolutely nothing since launch), one perfectly respectable hedge-y fund, Satellite Alpha (DSAAX), with under a million in assets and the B and I of the BRICs: India (DIIAX) and Brazil (DBZAX) are all being liquidated in late August.
Driehaus Mid Cap Growth Fund (DRMGX) has closed to new investors and will liquidate at the end of August. It’s not a very distinguished fund but it’s undistinguished in an unDriehaus way. Normally Driehaus funds are high vol / high return, which is sometimes their undoing.
Got a call into Fidelity on this freak show: Strategic Advisers® U.S. Opportunity Fund (FUSOX) is about to be liquidated. It’s a four star fund with $5.5 billion in assets. Low expenses. Top tier long-term returns. Apparently that makes it a candidate for closure. Manager Robert Vick left on June 4th, ahead of his planned retirement at the end of June. (Note to Bob: states with cities named Portland are really lovely places to spend your later years!). On June 6 they appointed two undertakers new managers to “oversee all activities relating to the fund’s liquidation and will manage the day-to-day operations of the fund until the final liquidation.” Wow. Fund Mortician.
Special note to Morningstar: tell your programmers to stop including the ® symbol in fund names. It makes it impossible to search for the fund since the ® is invisible, there’s no way to type it in the search box and the search will fail unless you type it.
|
Replay from Morningstar:
Thanks for your feedback about using the ® symbol in fund names on Morningstar.com. Again, this is a reflection of what is published in the annual reports, but I’ve shared your feedback with our team, which has already been working on a project to standardize the display of trademark symbols in Morningstar products.
|
JPMorgan International Realty Fund (JIRAX) experiences “liquidation and dissolution” on July 31, 2014
The $100 million Nationwide Enhanced Income Fund (NMEAX) and the $73 million Nationwide Short Duration Bond Fund (MCAPX)are both, simultaneously, merging into $300 million Nationwide Highmark Short Term Bond Fund (NWJSX). The Enhanced Duration shareholders must approve the move but “[s]hareholders of the Short Duration Bond Fund are not required, and will not be requested, to approve the Merger.” No timetable yet.
Legg Mason’s entire lineup of tiny, underperforming, overcharged retirement date funds (Legg Mason Target Retirement 2015 – 50 and Retirement Fund) “are expected to cease operations during the fourth quarter of 2014.”
Payden Tax Exempt Bond Fund (PYTEX) will be liquidated on July 22. At $6.5 million and an e.r. of 0.65%, the fund wasn’t generating enough income to pay its postage bills much less its manager.
On June 11, the Board of the Plainsboro China Fund (PCHFX) announced that the fund had closed and that it would be liquidated on the following day. Curious. The fund had under $2 million in assets, but top 1% returns over the past 12 months. The manager, Yang Xiang, used to be a portfolio manager for Harding Loevner. On whole, the “liquidated immediately and virtually without notice” sounds rather more like the Plainsboro North Korea Fund (JONGX).
RPg Emerging Market Sector Rotation Fund (EMSAX/EMSIX) spins out for the last time on July 30, 2014.
Royce Focus Value Fund (RYFVX) will be liquidated at the end of July “because it has not attracted and maintained assets at a sufficient level for it to be viable.” Whitney George, who runs seven other funds for Royce, isn’t likely even to notice that it’s gone.
SunAmerica GNMA Fund (GNMAX) is slated to merge into SunAmerica U.S. Government Securities Fund (SGTAX), a bit sad for shareholders since SGTAX seems the weaker of the two.
Voya doesn’t merge funds. They disappear them. And when some funds disappear, others are survivors. On no particular date, Voya Core Equity Research Fund disappears while Voya Large Cap Value Fund (IEDAX) survives. Presumably at the same time, Voya Global Opportunities Fund but Voya Global Equity Dividend Fund (IAGEX) doesn’t.
With the retirement of Matthew E. Megargel, Wellington Management’s resulting decision to discontinue its U.S. multi-cap core equity strategy. That affects some funds subadvised by Wellington.
William Blair Commodity Strategy Long/Short Fund (WCSNX)has closed and will liquidate on July 24, 2014. It’s another of the steadily shrinking cadre of managed futures funds, a “can’t fail” strategy backed by scads of research, modeling and backtested data. Oops.
In Closing . . .
A fund manager shared this screen cap from his browser:
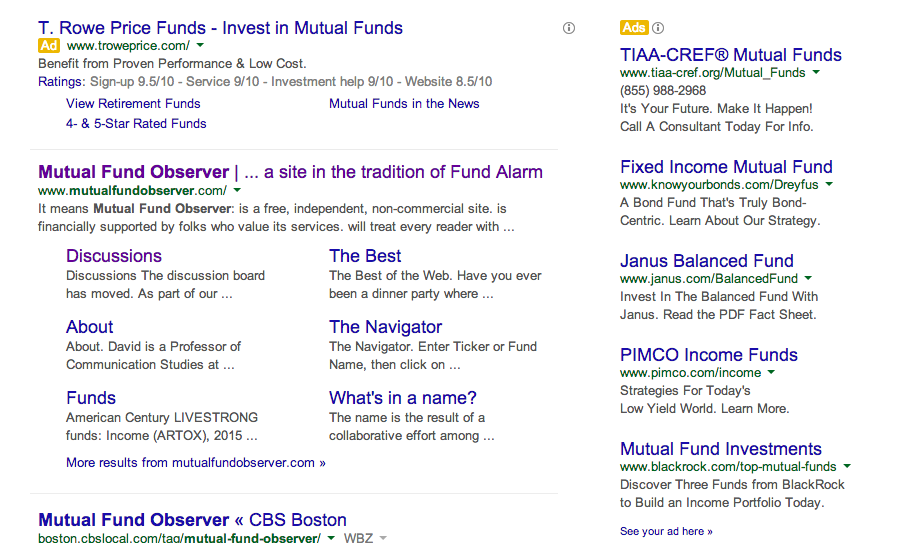
It appears that T. Rowe is looking over us! I guess if I had to pick someone to be sitting atop up, they’d surely make the short list. The manager speculates that Price might have bought the phrase “Mutual Fund Observer” as one they want to associate with in Google search results. Sort of affirming if true, but no one knows for sure.
See ya in August!





 Recovery Time
Recovery Time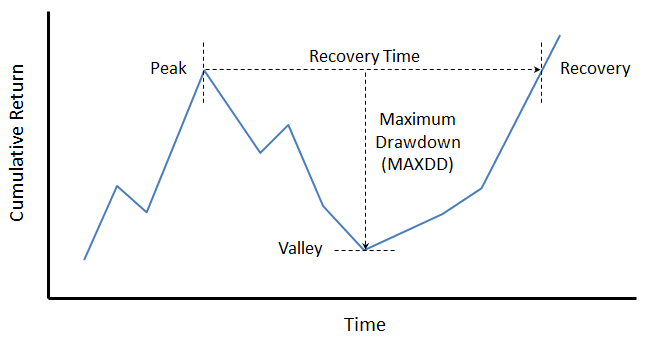
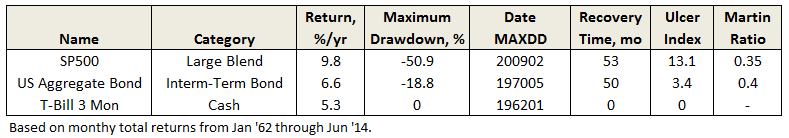
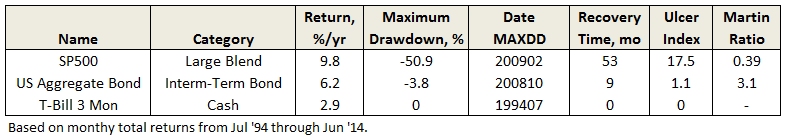
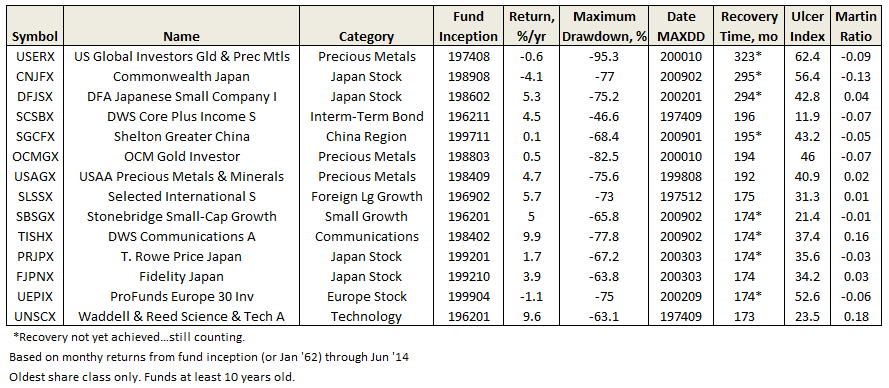
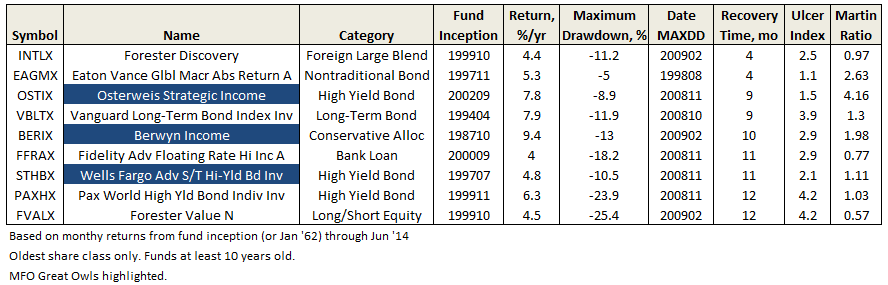
 Flash Geeks and Other Vagaries of Life …..
Flash Geeks and Other Vagaries of Life …..
 Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more. Mr. Cunnane manages Advisory Research MLP & Energy Infrastructure Fund which started life as a Fiduciary Asset Management Company (FAMCO) fund until the complex was acquired by Advisory Research. He’d been St. Louis-based FAMCO’s chief investment officer for 15 years. He’s the CIO for the MLP & Energy Infrastructure team and chair of AR’s Risk Management Committee. He also manages two closed-end funds which also target MLPs: the Fiduciary/Claymore MLP Opportunity Fund (FMO) and the Nuveen Energy MLP Total Return Fund (JMF). Here are his 200 words (and one picture) on why you might consider INFRX:
Mr. Cunnane manages Advisory Research MLP & Energy Infrastructure Fund which started life as a Fiduciary Asset Management Company (FAMCO) fund until the complex was acquired by Advisory Research. He’d been St. Louis-based FAMCO’s chief investment officer for 15 years. He’s the CIO for the MLP & Energy Infrastructure team and chair of AR’s Risk Management Committee. He also manages two closed-end funds which also target MLPs: the Fiduciary/Claymore MLP Opportunity Fund (FMO) and the Nuveen Energy MLP Total Return Fund (JMF). Here are his 200 words (and one picture) on why you might consider INFRX: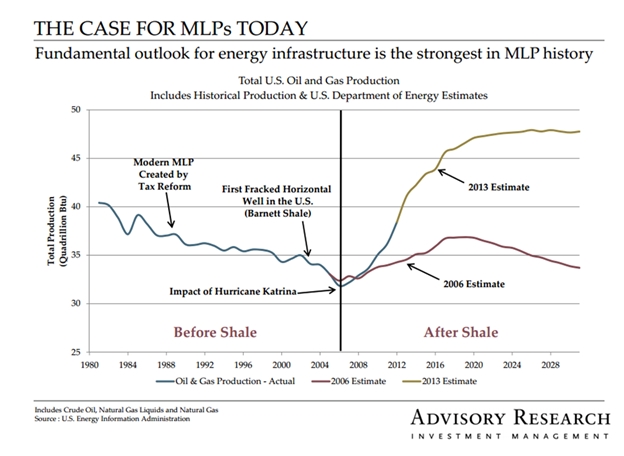
 Here’s a major vote of confidence: Effective August 1, 2014, John Neff and Thomas Saberhagen were named as co-portfolio managers for the
Here’s a major vote of confidence: Effective August 1, 2014, John Neff and Thomas Saberhagen were named as co-portfolio managers for the  Citing “the lack of investment opportunities” and “high current cash levels” occasioned by the five year run-up in global stock prices, Tweedy Browne announced the impending soft close of Tweedy, Browne Global Value II (TBCUX). TBCUX is an offshoot of Tweedy, Browne Global Value (TBGVX) with the same portfolio and managers but Global Value often hedges its currency exposure while Global Value II does not. The decision to close TBCUX makes sense as a way to avoid “diluting our existing shareholders’ returns in this difficult environment” since the new assets were going mostly to cash. Will Browne planned “to reopen the Fund when new idea flow improves and larger amounts of cash can be put to work in cheap stocks.”
Citing “the lack of investment opportunities” and “high current cash levels” occasioned by the five year run-up in global stock prices, Tweedy Browne announced the impending soft close of Tweedy, Browne Global Value II (TBCUX). TBCUX is an offshoot of Tweedy, Browne Global Value (TBGVX) with the same portfolio and managers but Global Value often hedges its currency exposure while Global Value II does not. The decision to close TBCUX makes sense as a way to avoid “diluting our existing shareholders’ returns in this difficult environment” since the new assets were going mostly to cash. Will Browne planned “to reopen the Fund when new idea flow improves and larger amounts of cash can be put to work in cheap stocks.” Thanks, as always, go to The Shadow – an incredibly vigilant soul and long tenured member of the Observer’s discussion community for his contributions to this section. Really, very little gets past him and that gives me a lot more confidence in saying that we’ve caught of all of major changes hidden in the ocean of SEC filings.
Thanks, as always, go to The Shadow – an incredibly vigilant soul and long tenured member of the Observer’s discussion community for his contributions to this section. Really, very little gets past him and that gives me a lot more confidence in saying that we’ve caught of all of major changes hidden in the ocean of SEC filings.
 My son Will, still hobbled after dropping his iPad on a toe, has taken to wincing every time we approach the mall. It’s festooned with “back to school sale! Sale! sale!” banners which seem, somehow, to unsettle him.
My son Will, still hobbled after dropping his iPad on a toe, has taken to wincing every time we approach the mall. It’s festooned with “back to school sale! Sale! sale!” banners which seem, somehow, to unsettle him.
 feel free to resort to PayPal or the USPS. It all helps and it’s all detailed on our
feel free to resort to PayPal or the USPS. It all helps and it’s all detailed on our 




 For a complete list of developments last month, and for information and court documents in any case, log in at
For a complete list of developments last month, and for information and court documents in any case, log in at  One of the best expressions of the problem was offered by Leo Strauss, a 20th century political philosopher and classicist:
One of the best expressions of the problem was offered by Leo Strauss, a 20th century political philosopher and classicist:








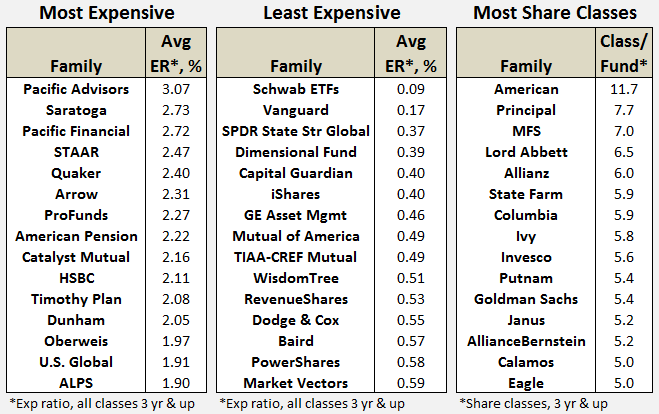
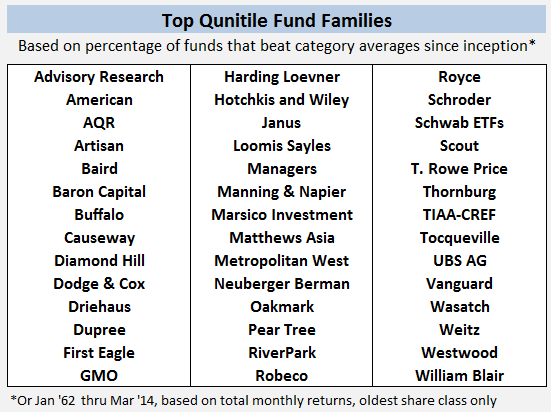
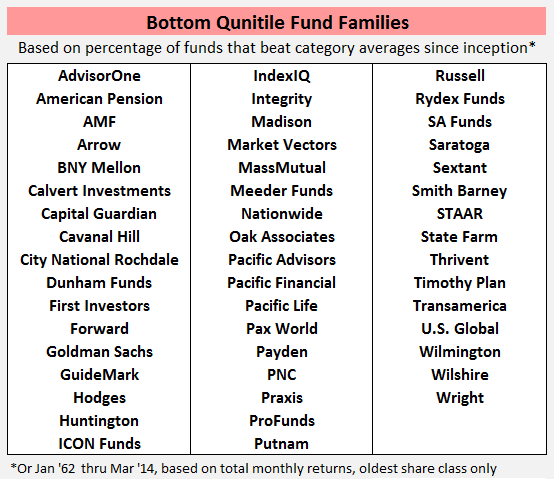
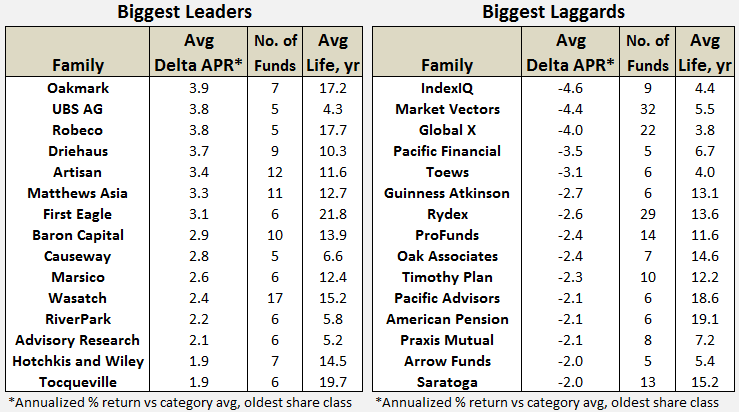













 It’s been that kind of month. Oh so very much that kind of month. In addition to teaching four classes and cheering Will on through 11 baseball games, I’ve spent much of the past six weeks buying a new (smaller, older but immaculate) house and beginning to set up a new household. It was a surprisingly draining experience, physically, psychologically and mentally. Happily I had the guidance and support of family and friends throughout, and I celebrated the end of April with 26 signatures, eight sets of initials, two attorneys, one large and one moderately-large check, and the arrival of a new set of keys and a new garage door clicker. All of which slightly derailed my focus on the world of funds. Fortunately the indefatigable Charles came to the rescue with …
It’s been that kind of month. Oh so very much that kind of month. In addition to teaching four classes and cheering Will on through 11 baseball games, I’ve spent much of the past six weeks buying a new (smaller, older but immaculate) house and beginning to set up a new household. It was a surprisingly draining experience, physically, psychologically and mentally. Happily I had the guidance and support of family and friends throughout, and I celebrated the end of April with 26 signatures, eight sets of initials, two attorneys, one large and one moderately-large check, and the arrival of a new set of keys and a new garage door clicker. All of which slightly derailed my focus on the world of funds. Fortunately the indefatigable Charles came to the rescue with …
 The folks are MFWire did a nice, nearly snarky story on The Mario’s most recent payday. (
The folks are MFWire did a nice, nearly snarky story on The Mario’s most recent payday. (

 I’ve been asked to provide the keynote address at the Cohen Client Conference, August 20 – 21, 2014. The conference, in Milwaukee, is run by Cohen Fund Audit Services. This will be Cohen’s third annual client conference. Last year’s version, in Cleveland OH, drew about 100 clients from 23 states.
I’ve been asked to provide the keynote address at the Cohen Client Conference, August 20 – 21, 2014. The conference, in Milwaukee, is run by Cohen Fund Audit Services. This will be Cohen’s third annual client conference. Last year’s version, in Cleveland OH, drew about 100 clients from 23 states. Cohen offers the conference as a way of helping fund professionals – directors, compliance officers, tax and accounting guys, operating officers and the occasional curious hedge fund manager –develop both professional competence and connections within the fund community. Which is to say, the Cohen folks promised that there would be both serious engagement – staff presentations, panels by industry experts, audience interaction – and opportunities for fellowshipping. (My first, unworthy impulse is to drive a bunch of compliance officers over to Horny Goat Brewing, buy a round or two, then get them to admit that they’re making stuff up as they go.)
Cohen offers the conference as a way of helping fund professionals – directors, compliance officers, tax and accounting guys, operating officers and the occasional curious hedge fund manager –develop both professional competence and connections within the fund community. Which is to say, the Cohen folks promised that there would be both serious engagement – staff presentations, panels by industry experts, audience interaction – and opportunities for fellowshipping. (My first, unworthy impulse is to drive a bunch of compliance officers over to Horny Goat Brewing, buy a round or two, then get them to admit that they’re making stuff up as they go.) We’ll also spend three full days in and around the Morningstar Investment Conference, June 18 – 20, in Chicago. We try to divide our time there into thirds: interviewing fund managers and talking to fund reps, listening to presentations by famous guys, and building our network of connections by spending time with readers, friends and colleagues. If you’d like to connect with us somewhere in the bowels of McCormick Place,
We’ll also spend three full days in and around the Morningstar Investment Conference, June 18 – 20, in Chicago. We try to divide our time there into thirds: interviewing fund managers and talking to fund reps, listening to presentations by famous guys, and building our network of connections by spending time with readers, friends and colleagues. If you’d like to connect with us somewhere in the bowels of McCormick Place,  Especially for the benefit of the 6000 first-time readers we see each month, if you’re inclined to support the Observer, the easiest way is to use the Observer’s Amazon link. The system is simple, automatic, and painless. We receive an amount equivalent to about 7% of the value of almost anything you purchase through our Amazon link (used books, Kindle downloads, groceries, sunscreen, power tools, pool toys …). You might choose to set it as a bookmark or, in my case, you might choose to have one of your tabs open in Amazon whenever you launch your browser. Some purchases generate a dime, some generate $10-12 and all help keep the lights on!
Especially for the benefit of the 6000 first-time readers we see each month, if you’re inclined to support the Observer, the easiest way is to use the Observer’s Amazon link. The system is simple, automatic, and painless. We receive an amount equivalent to about 7% of the value of almost anything you purchase through our Amazon link (used books, Kindle downloads, groceries, sunscreen, power tools, pool toys …). You might choose to set it as a bookmark or, in my case, you might choose to have one of your tabs open in Amazon whenever you launch your browser. Some purchases generate a dime, some generate $10-12 and all help keep the lights on!