Dear friends,
 My colleagues in the English department are forever yammering on about this Shakespeare guy.I’m skeptical. First, he didn’t even know how to spell his own name (“Wm Shakspē”? Really?). Second, he clearly didn’t understand seasonality of the markets. If you listen to Gloucester’s famous declamation in Richard III, you’ll see what I mean:
My colleagues in the English department are forever yammering on about this Shakespeare guy.I’m skeptical. First, he didn’t even know how to spell his own name (“Wm Shakspē”? Really?). Second, he clearly didn’t understand seasonality of the markets. If you listen to Gloucester’s famous declamation in Richard III, you’ll see what I mean:
Now is the winter of our discontent
Made glorious summer by this sun of York;
And all the clouds that lour’d upon our house
In the deep bosom of the ocean buried.
Now are our brows bound with victorious wreaths;
Our bruised arms hung up for monuments;
Our stern alarums changed to merry meetings,
Our dreadful marches to delightful measures.
It’s pretty danged clear that we haven’t had anything “made glorious summer by the sun of [New] York.” By Morningstar’s report, every single category of bond and hybrid fund has lost money over the course of the allegedly “glorious summer.” Seven of the nine domestic equity boxes have flopped around, neither noticeably rising nor falling.
And now, the glorious summer passed, we enter what historically are the two worst months for the stock market. To which I can only reply with three observations (The Pirates are on the verge of their first winning season since 1992! The Steelers have no serious injuries looming over them. And Will’s fall baseball practices are upon us.) and one question:
Is it time to loathe the emerging markets? Again?
Yuh, apparently. A quick search in Google News for “emerging markets panic” turns up 3300 stories during the month of August. They look pretty much like this:
With our preeminent journalists contributing:
Many investors have responded as they usually do, by applying a short-term perspective to a long-term decision. Which is to say, they’re fleeing. Emerging market bond funds saw a $2 billion outflow in the last week of August and $24 billion since late May (Emerging Markets Fund Flows Investors Are Dumping Emerging Markets at an Accelerating Pace, Business Insider, 8/30/13). The withdrawals were indiscriminate, affecting all regions and both local currency and hard currency securities. Equity funds saw $4 billion outflows for the week, with ETFs leading the way down (Emerging markets rout has investors saying one word: sell, Marketwatch, 8/30/13).
In a peculiar counterpoint, Jason Kepler of Investment News claims – using slightly older data – that Mom and pop can’t quit emerging-market stocks. And that’s good (8/27/13). He finds “uncharacteristic resiliency” in retail investors’ behavior. I’d like to believe him. (The News allows a limited number of free article views; if you’d exceeded your limit and hit a paywall, you might try Googling the article title. Or subscribing, I guess.)
We’d like to make three points.
- Emerging markets securities are deeply undervalued
- Those securities certainly could become much more deeply undervalued.
- It’s not the time to be running away.
Emerging markets securities are deeply undervalued
Wall Street Ranter, an anonymous blogger from the financial services industry and sometime contributor to the Observer’s discussion board, shared two really striking bits of valuation data from his blog.
The first, “Valuations of Emerging Markets vs US Stocks” (7/20/13) looks at a PIMCO presentation of the Shiller PE for the emerging markets and U.S., then at how such p/e ratios have correlated to future returns. Shiller adjusts the market’s price/earnings ratio to eliminate the effect of atypical profit margins, since those margins relentlessly regress to the mean over time. There’s a fair amount of research that suggests that the Shiller PE has fair predictive validity; that is, abnormally low Shiller PEs are followed by abnormally high market returns and vice versa.
Here, with Ranter’s kind permission, is one of the graphics from that piece:
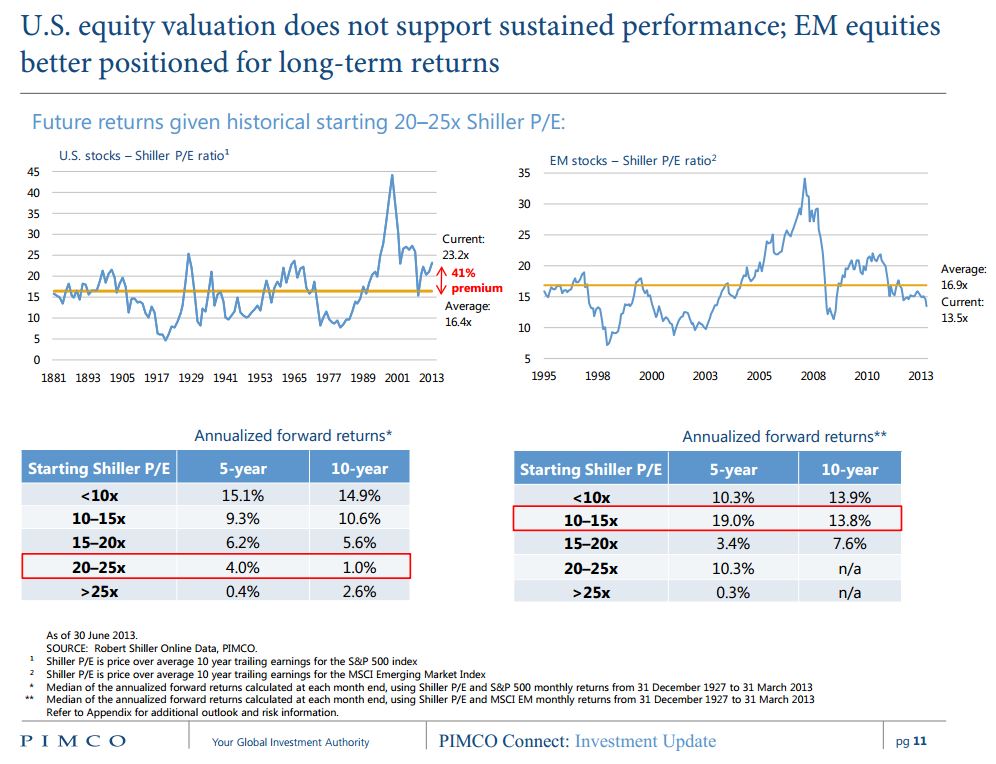
At June 30, 2013 valuations, this suggests that US equities were priced for 4% nominal returns (2-3% real), on average, over the next five years while e.m. equities were priced to return 19% nominal (17% or so real) over the same period. GMO, at month’s end, reached about the same figure for high quality US equities (3.1% real) but a much lower estimate (6.8%) for emerging equities. By GMO’s calculation, emerging equities were priced to return more than twice as much as any other publicly traded asset class.
Based on recent conversations with the folks at GMO, Ranter concludes that GMO suspects that changes in the structure of the Chinese economy might be leading them to overstate likely emerging equity returns. Even accounting for those changes, they remain the world’s most attractive asset class:
While emerging markets are the highest on their 7 year forecast (approx. 7%/year) they are treating it more like 4%/year in their allocations . . . because they believe they need to account for a longer-term shift in the pace of China’s growth. They believe the last 10 years or so have skewed the mean too far upwards. While this reduces slightly their allocation, it still leaves Emerging Markets has one of their highest forecasts (but very close to International Value … which includes a lot of developed European companies).
Ranter offered a second, equally striking graphic in “Emerging Markets Price-to-Book Ratio and Forward Returns (8/9/13).”
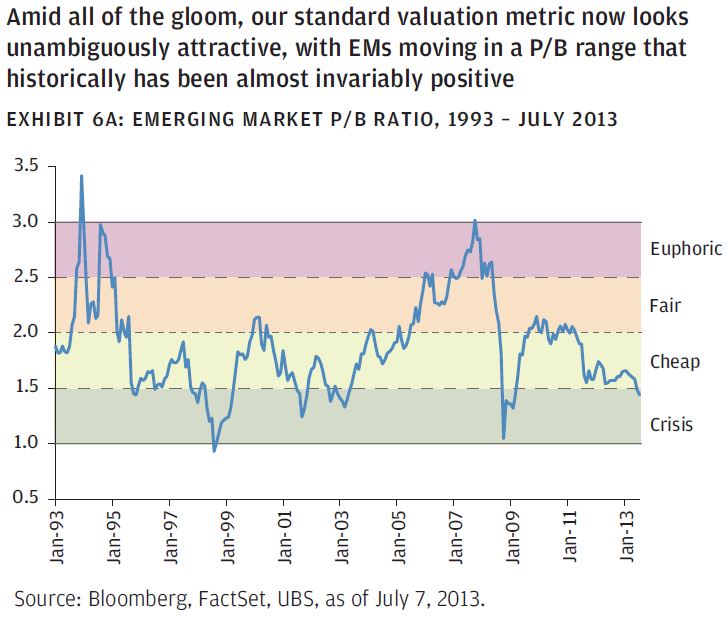
At these levels, he reports, you’d typically expect returns over the following year of around 55%. That data is available in his original article.
In a singularly unpopular observation, Andrew Foster, manager of Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX/SIGIX), one of the most successful and risk-alert e.m. managers (those two attributes are intimately connected), notes that the most-loathed emerging markets are also the most compelling values:
The BRICs have underperformed to such an extent that their aggregate valuation, when compared to the emerging markets as a whole, is as low as it has been in eight years. In other words, based on a variety of valuation metrics (price-to-book value, price-to-prospective-earnings, and dividend yield), the BRICs are as cheap relative to the rest of the emerging markets as they have been in a long time. I find this interesting. . . for the (rare?) subset of investors contemplating a long-term (10-year) allocation to EM, just as they were better off to avoid the BRICs over the past 5 years when they were “hot,” they are likely to be better off over the next 10 years emphasizing the BRICs now they are “not.”
Those securities certainly could become much more deeply undervalued.
The graphic above illustrates the ugly reality that sometimes (late ’98, all of ’08), but not always (’02, ’03, mid ’11), very cheap markets become sickeningly cheap markets before rebounding. Likewise, Shiller PE for the emerging markets occasionally slip from cheap (10-15PE) to “I don’t want to talk about it” (7 PE). GMO mildly notes, “economic reality and investor behavior cause securities and markets to overshoot their fair value.”
Andrew Foster gently dismisses his own predictive powers (“my record on predicting short-term outcomes is very poor”). At the same time, he finds additional cause for short-term concern:
[M]y thinking on the big picture has changed since [early July] because currencies have gotten into the act. I have been worried about this for two years now — and yet even with some sense it could get ugly, it has been hard to avoid mistakes. In my opinion, currency movements are impossible to predict over the short or long term. The only thing that is predictable is that when currency volatility picks up, is likely to overshoot (to the downside) in the short run.
It’s not the time to be running away.
There are two reasons driving that conclusion. First, you’ve already gotten the timing wrong and you’re apt to double your error. The broad emerging markets index has been bumping along without material gain for five years now. If you were actually good at actively allocating your portfolio, you’d have gotten out in the summer of 2007 instead of thinking that five consecutive years of 25%+ gains would go on forever. And you, like the guys at Cook and Bynum, would have foregone Christmas presents in 2008 in order to plow every penny you had into an irrationally, shockingly cheap market. If you didn’t pull it off then, you’re not going to pull it off this time, either.
Second, there are better options here than elsewhere. These remain, even after you adjust down their earnings and adjust them down again, about the best values you’ll find. Ranter grumbles about the thoughtless domestic dash:
Bottom line is I fail to see, on a relative basis, how the US is more tempting looking 5 years out. People can be scared all they want of catching a falling knife…but it’s a lot easier to catch something which is only 5 feet in the air than something that is 10 feet in the air.
If you’re thinking of your emerging markets stake as something that you’ll be holding or building over the next 10-15 years (as I do), it doesn’t matter whether you buy now or in three months, at this level or 7% up or down from here. It will matter if you panic, leave and then refuse to return until the emerging markets feel “safe” to you – typically around the top of the next market cycle.
It’s certainly possible that you’re systemically over-allocated to equities or emerging equities. The current turbulence might well provide an opportunity to revisit your long-term plan, and I’d salute you for it. My argument here is against actions driven by your gut.
Happily, there are a number of first rate options available for folks seeking risk-conscious exposure to the emerging markets. My own choice, discussed more fully below, is Seafarer. I’ve added to my (small investor-sized) account twice since the market began turning south in late spring. I have no idea of whether those dollars with be worth a dollar or eighty cents or a plugged nickel six months from now. My suspicion is that those dollars will be worth more a decade from now having been invested with a smart manager in the emerging markets than they would have been had I invested them in domestic equities (or hidden them away in a 0.01% bank account). But Seafarer isn’t the only “A” level choice. There are some managers sitting on large war chests (Amana Developing World AMDWX), others with the freedom to invest across asset classes (First Trust/Aberdeen Emerging Opportunities FEO) and even some with both (Lazard Emerging Markets Multi-Strategy EMMOX).
To which Morningstar says, “If you’ve got $50 million to spend, we’ve got a fund for you!”
On August 22nd, Morningstar’s Fund Spy trumpeted “Medalist Emerging-Markets Funds Open for Business,” in which they reviewed their list of the crème de la crème emerging markets funds. It is, from the average investor’s perspective, a curious list studded with funds you couldn’t get into or wouldn’t want to pay for. Here’s the Big Picture:
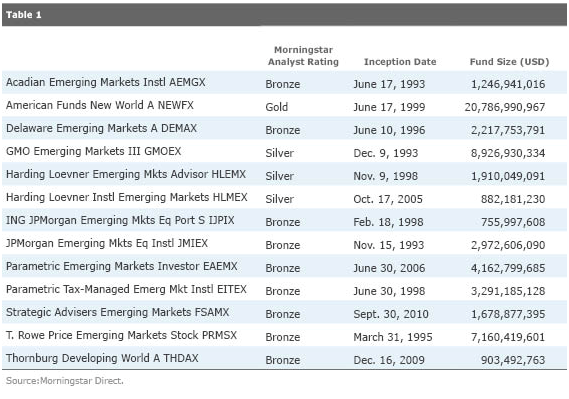
Our take on those funds follows.
|
The medalist …
|
Is perfect for the investor who …
|
|
Acadian EM (AEMGX)
|
Has $2500 and an appreciation of quant funds
|
|
American Funds New World (NEWFX)
|
Wants to pay 5.75% upfront
|
|
Delaware E.M. (DEMAX)
|
Wants to pay 5.75% upfront for a fund whose performance has been inexplicably slipping, year by year, in each of the past five calendar years.
|
|
GMO E.M. III (GMOEX)
|
Has $50,000,000 to open an account
|
|
Harding Loevner E.M. Advisor (HLEMX)
|
Is an advisor with $5000 to start.
|
|
Harding Loevner Inst E.M. (HLMEX)
|
Has $500,000 to start
|
|
ING JPMorgan E.M. Equity (IJPIX)
|
Is not the public, since “shares of the Portfolio are not offered to the public.”
|
|
Parametric E.M. (EAEMX)
|
Has $1000 and somewhat modest performance expectations
|
|
Parametric Tax-Mgd E.M. Inst (EITEX)
|
Has $50,000 and tax-issues best addressed in his e.m. allocation
|
|
Strategic Advisers E.M. (FSAMX)
|
Is likewise not the general public since “the fund is not available for sale to the general public.”
|
|
T. Rowe Price E.M. Stock (PRMSX)
|
Has $2500 and really, really modest performance expectations.
|
|
Thornburg Developing World A (THDAX)
|
Doesn’t mind paying a 4.50% load
|
Our recommendations differ from theirs, given our preference for smaller funds that are actually available to the public. Our shortlist:
Amana Developing World (AMDWX): offers an exceedingly cautious take on an exceedingly risky slice of the world. Readers were openly derisive of Amana’s refusal to buy at any cost, which led the managers to sit on a 50% cash stake while the market’s roared ahead. As those markets began their swoon in 2011, Amana began moving in and disposing of more than half of its cash reserves. Still cash-rich, the fund’s relative performance is picking up and its risks remain very muted.
First Trust/Aberdeen Emerging Opportunity (FEO): one of the first emerging markets balanced funds, it’s performed very well over the long-term and is currently selling at a substantial discount to NAV: 12.6%, about 50% greater than its long-term average. That implies that investors might see something like a 5% arbitrage gain once the current panic abates, above and beyond whatever the market provides.
Grandeur Peak Emerging Markets Opportunities (GPEOX): the Grandeur Peak team has been brilliantly successful both here and at Wasatch. Their intention is to create a single master fund (Global Reach) and six subsidiary funds whose portfolios represent slices of the master profile. Emerging Markets has already cleared the SEC registration procedures but hasn’t launched. The Grandeur Peak folks say two factors are driving the delay. First, the managers want to be able to invest directly in Indian equities which requires registration with that country’s equity regulators. They couldn’t begin the registration until the fund itself was registered in the US. So they’re working through the process. Second, they wanted to be comfortable with the launch of Global Reach before adding another set of tasks. Give or take the market’s current tantrum (one manager describes it as “a taper tantrum”), that’s going well. With luck, but without any guarantees, the fund might be live sometime in Q4.
Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income (SFGIX): hugely talented manager, global portfolio, risk conscious, shareholder-centered and successful.
Wasatch Frontier Emerging Small Countries (WAFMX): one of the very few no-load, retail funds that targets the smaller, more dynamic markets rather than markets with billions of people (India and China) or plausible claim to be developed markets (e.g., Korea). The manager, Laura Geritz, has been exceedingly successful. Frontier markets effectively diversify emerging markets portfolios and the fund has drawn nearly $700 million. The key is that Wasatch is apt to close the fund sooner rather than later.
Snowball’s portfolio
Some number of folks have, reasonably enough, asked whether I invest in all of the funds I profile (uhhh … there have been over 150 of them, so no) or whether I have found The Secret Formula (presumably whatever Nicholas Cage has been looking for in all those movies). The answer is less interesting than the question.
I guess my portfolio construction is driven by three dictums:
- Don’t pretend to be smarter than you are
- Don’t pretend to be braver than you are
- There’s a lot of virtue in doing nothing
Don’t pretend to be smarter than you are. If I knew which asset classes were going to soar and which were going to tank in the next six months or year or two, two things would happen. First, I’d invest in the winners. Second, I’d sell my services to ridiculously rich people and sock them with huge and abusive fees that they’d happily pay. But, I don’t.
As a result, I tend to invest in funds whose managers have a reasonable degree of autonomy about investing across asset classes, rather than ones pigeonholed into a small (style) box. That’s a problem: it makes benchmarking hard, it makes maintaining an asset allocation plan hard and it requires abnormally skilled managers. My focus has been on establishing a strategic objective (“increasing exposure to fast growing economies”) and then spending a lot of time trying to find managers whose strategies I trust, respect and understand.
Don’t pretend to be braver than you are. Stocks have a lot in common with chili peppers. In each case, you get a surprising amount of benefit from a relatively small amount of exposure. In each case, increasing exposure quickly shifts the pleasure/pain balance from pleasantly piquant to moronically painful. Some readers think of my non-retirement asset allocation is surprisingly timid: about 50% stocks, 30% bonds, 20% cash equivalents. They’re not much happier about my 70% equity stake in retirement funds. But, they’re wrong.
T. Rowe Price is one of my favorite fund companies, in part because they treat their investors with unusual respect. I found two Price studies, in 2004 and again in 2010, particularly provocative. Price constructed a series of portfolios representing different levels of stock exposure and looked at how the various portfolios would have played out over the past 50-60 years.
The original study looked at portfolios with 20/40/60/80/100% stocks. The update dropped the 20% portfolio and looked at 0/40/60/80/100%. Below I’ve reproduced partial results for three portfolios. The original 2004 and 2010 studies are available at the T. Rowe Price website.
| |
20% stocks
|
60% stocks
|
100% stocks
|
| |
Conservative mix, 50% bonds, 30% cash
|
The typical “hybrid”
|
S&P 500 index
|
|
Years studied
|
1955-03
|
1949-2009
|
1949-2009
|
|
Average annual return (before inflation)
|
7.4
|
9.2
|
11.0
|
|
Number of down years
|
3
|
12
|
14
|
|
Average loss in a down year
|
-0.5
|
-6.4
|
-12.5
|
|
Standard deviation
|
5.2
|
10.6
|
17.0
|
|
Loss in 2008
|
-0.2*
|
-22.2
|
-37.0
|
|
* based on 20% S&P500, 30% one-year CDs, 50% total bond index
|
Over a 10 year period – reasonable for a non-retirement account – a portfolio that’s 20% stocks would grow from $10,000 to $21,000. A 100% stock portfolio would grow to $28,000. Roughly speaking, the conservative portfolio ends up at 75% of the size of the aggressive one but a pure stock portfolio increases the probability of losing money by 400% (from a 6% chance to 23%), increases the size of your average loss by 2500% (from 0.5% to 12.5%) and triples your volatility. Somewhere in there, it will face the real prospect of a 51% loss, which is the average maximum drawdown for large core stock funds that have been around 20 years or more. Sadly, there’s no way of knowing whether the 51% loss will occur in Year One (where you might have some recovery time) or Year Ten (where you’d be toast).
At 50% equities, I might capture 80% of the market’s gain with 50% of its volatility. If domestic bonds weren’t in such dismal straits, a smaller stock exposure might be justifiable. But they suck so I’m stuck.
There’s a lot of virtue in doing nothing. Our action tends to be a lot more costly than our inaction, so I change my target allocation slowly and change my fund line-up slowly. I’ve held a few retirement plan funds (e.g., Fidelity Low Priced Stock FLPSX) for decades and a number of non-retirement funds since their inception. In general, I’ll only add a fund if it represents an entirely new opportunity set or if it’s replacing an existing fund. On average, I might change out one fund every year or two.
My retirement portfolio is dominated by the providers in Augustana’s 403(b) plan: Fidelity, T. Rowe Price and TIAA-CREF. The college contribution to retirement goes exclusively into TIAA-CREF. CREF Stock accounts for 68%, TIAA Real Estate holds 22% and the rest is in a target-date fund. The Fidelity and Price allocations mirror one another: 33% domestic stock (with a value bias), 33% international stock (with an emerging markets bias) and 33% income (of the eclectic Spectrum Income/Global High Income sort).
My non-retirement portfolio is nine funds and some cash waiting to be deployed.
|
|
|
Portfolio weight
|
What was I, or am I, thinking?
|
|
Artisan Int’l Value
|
ARTKX
|
10%
|
I bought Artisan Int’l (ARTIX) in January 1996 because of my respect for Artisan and Mr. Yockey’s record. I traded-in my ARTIX shares and bought Int’l Value as soon as it launched because of my respect for Artisan, Mr. Samra and O’Keefe’s pedigree and my preference for value investing. Right so far: the fund is top 1% returns for the year-to-date and the trailing 1-, 3-, 5- and 10-year periods. I meditated upon switching to the team’s Global Value Fund (ARTGX) which has comparable returns, more flexibility and fewer assets.
|
|
Artisan Small Value
|
ARTVX
|
8
|
I bought Artisan Small Cap (ARTSX) in the weeks before it closed, also January 1996, for the same reasons I bought ARTIX. And I traded it for Small Cap Value in late 1997 for the same reasons I traded International. That original stake, to which I added regularly, has more than quadrupled in value. The team has been out-of-step with the market lately which, frankly, is what I pay them for. I regret only the need to sell some of my shares about seven years ago.
|
|
FPA Crescent
|
FPACX
|
17
|
Crescent is my surrogate for a hedge fund: Mr. Romick has a strong contrarian streak, the ability to invest in almost anything and a phenomenal record of having done so. If you really wanted to control your asset allocation, this would make it about impossible. I don’t.
|
|
Matthews Asia Strategic Income
|
MAINX
|
6
|
I bought MAINX in the month after the Observer profiled the fund. Matthews is first rate, the arguments for reallocating a portion of my fixed-income exposure from developed to developing markets struck me as sound and Ms. Kong is really sharp.
And it’s working. My holding is still up about 3% while both the world bond group and Aberdeen Asia Bond trail badly. She’s hopeful that pressure of Asian currencies will provoke economic reform and, in the meantime, has the freedom to invest in dollar-denominated bonds.
|
|
Matthews Asian Growth & Income
|
MACSX
|
10
|
I originally bought MACSX while Andrew Foster was manager, impressed by its eclectic portfolio, independent style and excellent risk management. It’s continued to do well after his departure. I sold half of my stake here to invest in Seafarer and haven’t been adding to it in a while because I’m already heavily overweight in Asia. That said, I’m unlikely to reduce this holding either.
|
|
Northern Global Tactical Asset Allocation
|
BBALX
|
13
|
I bought BBALX shortly after profiling it. It’s a fund-of-index-funds whose allocation is set by Northern’s investment policy committee. The combination of very low expenses (0.64%), very low turnover portfolios, wide diversification and the ability to make tactical tilts is very attractive. It’s been substantially above average – higher returns, lower volatility – than its peers since its 2008 conversion.
|
|
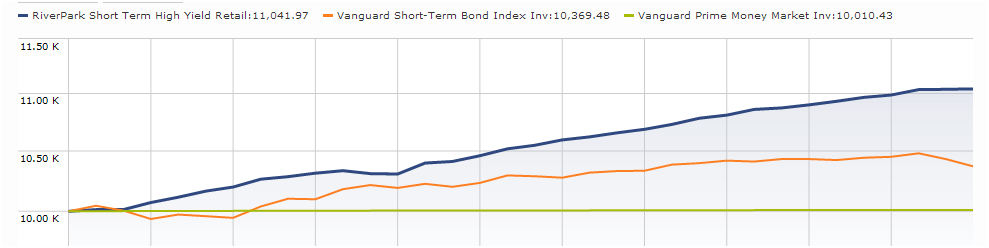
RiverPark Short Term High Yield
|
RPHYX
|
11
|
Misplaced in Morningstar’s “high yield” box, this has been a superb cash management option for me: it’s making 3-4% annually with negligible volatility.
|
|
Seafarer Overseas Growth & Income
|
SFGIX
|
10
|
I’m impressed by Mr. Foster’s argument that many other portions of the developing world are, in 2013, where Asia was in 2003. He believes there are rich opportunities outside Asia and that his experience as an Asia investor will serve him in good stead as the new story rolls out. I’m convinced that having an Asia-savvy manager who has the ability to recognize and make investments beyond the region is prudent.
|
|
T. Rowe Price Spectrum Income
|
RPSIX
|
12
|
This is a fund of income-oriented funds and it serves as the second piece of the cash-management plan for me. I count on it for about 6% returns a year and recognize that it might lose money on rare occasion. Price is steadfastly sensible and investor-centered and I’m quite comfortable with the trade-off.
|
|
Cash
|
|
2
|
This is the holding pool in my Scottrade account.
|
Is anyone likely to make it into my portfolio in 2013-14? There are two candidates:
ASTON/River Road Long-Short (ARLSX). We’ve both profiled the fund and had a conference call with its manager, both of which are available on the Observer’s ARLSX page. I’m very impressed with the quality and clarity of their risk-management disciplines; they’ve left little to chance and have created a system that forces them to act when it’s time. They’ve performed well since inception and have the prospect of outperforming the stock market with a fraction of its risk. If this enters the portfolio, it would likely be as a substitute for Northern Global Tactical since the two serve the same risk-dampening function.
RiverPark Strategic Income (not yet launched). This fund will come to market in October and represents the next step out on the risk-return spectrum from the very successful RiverPark Short Term High Yield (RPHYX). I’ve been impressed with David Sherman’s intelligence and judgment and with RPHYX’s ability to deliver on its promises. We’ll be doing fairly serious inquiries in the next couple months, but the new fund might become a success to T. Rowe Price Spectrum Income.
Sterling Capital hits Ctrl+Alt+Delete
Sterling Capital Select Equity (BBTGX) has been a determinedly bad fund for years. It’s had three managers since 1993 and it has badly trailed its benchmark under each of them. The strategy is determinedly nondescript. They’ve managed to return 3.2% annually over the past 15 years. That’s better – by about 50 bps – than Vanguard’s money market fund, but not by much. Effective September 3, 2013, they’re hitting “reformat.”
The fund’s name changes, to Sterling Capital Large Cap Value Diversified Fund.
The strategy changes, to a “behavioral financed” based system targeting large cap value stocks.
The benchmark changes, to the Russell 1000 Value
And the management team changes, to Robert W. Bridges and Robert O. Weller. Bridges joined the firm in 2008 and runs the Sterling Behavioral Finance Small Cap Diversified Alpha. Mr. Weller joined in 2012 after 15 years at JPMorgan, much of it with their behavioral finance team.
None of which required shareholders’ agreement since, presumably, all aspects of the fund are “non-fundamental.”
One change that they should pursue but haven’t: get the manager to put his own money at risk. The departing manager was responsible for five funds since 2009 and managed to find nary a penny to invest in any of them. As a group, Sterling’s bond and asset allocation team seems utterly uninterested in risking their own money in a lineup of mostly one- and two-star funds. Here’s the snapshot of those managers’ holdings in their own funds:
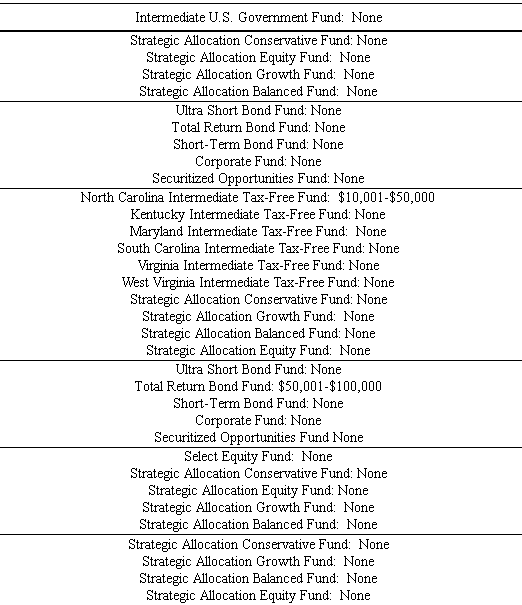
You’ll notice the word “none” appears 32 times. Let’s agree that it would be silly to expect a manager to own tax-free bonds anywhere but in his home jurisdiction. That leaves 26 decisions to avoid their own funds out of a total of 27 opportunities. Most of the equity managers, by contrast, have made substantial personal investments.
Warren Buffett thinks you’ve come to the right place
Fortune recently published a short article which highlighted a letter that Warren Buffett wrote to the publisher of the Washington Post in 1975. Buffett’s an investor in the Post and was concerned about the long-term consequences of the Post’s defined-benefit pension. The letter covers two topics: the economics of pension obligations in general and the challenge of finding competent investment management. There’s also a nice swipe at the financial services industry, which most folks should keep posted somewhere near their phone or monitor to review as you reflect on the inevitable marketing pitch for the next great financial product.

I particularly enjoy the “initially.” Large money managers, whose performance records were generally parlous, “felt obliged to seek improvement or at least the approach of improvement” by hiring groups “with impressive organizational charts, lots of young talent … and a record of recent performance (pg 8).” Unfortunately, he notes, they found it.
The pressure to look like you were earning your keep led to high portfolio turnover (Buffett warns against what would now be laughably low turnover: 25% per annum). By definition, most professionals cannot be above average but “a few will succeed – in a modest way – because of skill” (pg 10). If you’re going to find them, it won’t be by picking past winners though it might be by understanding what they’re doing and why:

The key: abandon all hope ye who invest in behemoths:

For those interested in Buffett’s entire reflection, Chip’s embedded the following:
Warren Buffett Katharine Graham Letter
And now for something completely different …
We can be certain of some things about Ed Studzinski. As an investor and co-manager of Oakmark Equity & Income (OAKBX), he was consistently successful in caring for other people’s money (as much as $17 billion of it), in part because he remained keenly aware that he was also caring for their futures. $10,000 entrusted to Ed and co-manager Clyde McGregor on the day Ed joined the fund (01 March 2000) would have grown to $27,750 on the day of his departure (31 December 2011). His average competitor (I’m purposefully avoiding “peer” as a misnomer) would have managed $13,900.
As a writer and thinker, he minced no words.
The Equity and Income Fund’s managers have both worked in the investment industry for many decades, so we both should be at the point in our careers where dubious financial-industry innovations no longer surprise us. Such an assumption, however, would be incorrect.
For the past few quarters we have repeatedly read that the daily outcomes in the securities markets are the result of the “Risk On/Risk Off” trade, wherein investors (sic?) react to the most recent news by buying equities/selling bonds (Risk On) or the reverse (Risk Off). As value investors we think this is pure nonsense.
Over the past two years, Ed and I have engaged in monthly conversations that I’ve found consistently provocative and information-rich. It’s clear that he’s been paying active attention for many years to contortions of his industry which he views with equal measures of disdain and alarm.
I’ve prevailed upon Ed to share a manager’s fuss and fulminations with us, as whim, wife and other obligations permit. His first installment, which might also be phrased as the question “Whose skin in the game?” follows.
“Skin in the Game, Part One”
“Virtue has never been as respectable as money.” Mark Twain
One of the more favored sayings of fund managers is that they like to invest with managements with “skin in the game.” This is another instance where the early Buffett (as opposed to the later Buffett) had it right. Managements can and should own stock in their firms. But they should purchase it with their own money. That, like the prospect of hanging as Dr. Johnson said, would truly clarify the mind. In hind sight a major error in judgment was made by investment professionals who bought into the argument that awarding stock options would beneficially serve to align the interests of managements and shareholders. Never mind that the corporate officers should have already understood their fiduciary obligations. What resulted, not in all instances but often enough in the largest capitalization companies, was a class of condottieri such as one saw in Renaissance Italy, heading armies that spent their days marching around avoiding each other, all the while being lavishly paid for the risks they were NOT facing. This sub-set of managers became a new entitled class that achieved great personal wealth, often just by being present and fitting in to the culture. Rather than thinking about truly long-term strategic implications and questions raised in running a business, they acted with a short-duration focus, and an ever-present image of the current share price in the background. Creating sustainable long-term business value rarely entered into the equation, often because they had never seen it practiced.
I understood how much of a Frankenstein’s monster had been created when executive compensation proposals ended up often being the greater part of a proxy filing. A particularly bothersome practice was “reloading” options annually. Over time, with much dilution, these programs transferred significant share ownership to management. You knew you were on to something when these compensation proposals started attracting negative vote recommendations. The calls would initially start with the investor relations person inquiring about the proxy voting process. Once it was obvious that best practices governance indicated a “no” vote, the CFO would call and ask for reconsideration.
How do you determine whether a CEO or CFO actually walks the walk of good capital allocation, which is really what this is all about? One tip-off usually comes from discussions about business strategy and what the company will look like in five to ten years. You will have covered metrics and standards for acquisitions, dividends, debt, share repurchase, and other corporate action. Following that, if the CEO or CFO says, “Why do you think our share price is so low?” I would know I was in the wrong place. My usual response was, “Why do you care if you know what the business value of the company is per share? You wouldn’t sell the company for that price. You aren’t going to liquidate the business. If you did, you know it is worth substantially more than the current share price.” Another “tell” is when you see management taking actions that don’t make sense if building long-term value is the goal. Other hints also raise questions – a CFO leaves “because he wants to enjoy more time with his family.” Selling a position contemporaneously with the departure of a CFO that you respected would usually leave your investors better off than doing nothing. And if you see the CEO or CFO selling stock – “our investment bankers have suggested that I need to diversify my portfolio, since all my wealth is tied up in the company.” That usually should raise red flags that indicate something is going on not obvious to the non-insider.
Are things improving? Options have gone out of favor as a compensation vehicle for executives, increasingly replaced by the use of restricted stock. More investors are aware of the potential conflicts that options awards can create and have a greater appreciation of governance. That said, one simple law or regulation would eliminate many of the potential abuses caused by stock options. “All stock acquired by reason of stock option awards to senior corporate officers as part of their compensation MAY NOT BE SOLD OR OTHERWISE DISPOSED OF UNTIL AFTER THE EXPIRATION OF A PERIOD OF THREE YEARS FROM THE INDIVIDUAL’S LAST DATE OF SERVICE.” Then you might actually see the investors having a better chance of getting their own yachts.
Edward A. Studzinski
If you’d like to reach Ed, click here. An artist’s rendering of Messrs. Boccadoro and Studzinski appears below.
Introducing Charles’ Balcony
 Since his debut in February 2012, my colleague Charles Boccadoro has produced some exceedingly solid, data-rich analyses for us, including this month’s review of the risk/return profiles of the FundX family of funds. One of his signature contributions was “Timing Method Performance Over Ten Decades,” which was widely reproduced and debated around the web.
Since his debut in February 2012, my colleague Charles Boccadoro has produced some exceedingly solid, data-rich analyses for us, including this month’s review of the risk/return profiles of the FundX family of funds. One of his signature contributions was “Timing Method Performance Over Ten Decades,” which was widely reproduced and debated around the web.
We’re pleased to announce that we’ve collected his essays in a single, easy-to-access location. We’ve dubbed it “Charles’ Balcony” and we even stumbled upon this striking likeness of Charles and the shadowy Ed Studzinski in situ. I’m deeply hopeful that from their airy (aerie or eery) perch, they’ll share their sharp-eyed insights with us for years to come.
Observer fund profiles
Each month the Observer provides in-depth profiles of between two and four funds. Our “Most Intriguing New Funds” are funds launched within the past couple years that most frequently feature experienced managers leading innovative newer funds. “Stars in the Shadows” are older funds that have attracted far less attention than they deserve.
Advisory Research Strategic Income (ADVNX): you’ve got to love a 10 month old fund with a 10 year track record and a portfolio that Morningstar can only describe as 60% “other.” AR converted a successful limited partnership into the only no-load mutual fund offering investors substantial access to preferred securities.
Beck, Mack and Oliver Partners (BMPEX): we think of it as “Dodge and Cox without the $50 billion in baggage.” This is an admirably disciplined, focused equity fund with a remarkable array of safeguards against self-inflicted injuries.
FPA Paramount (FPRAX): some see Paramount as a 60-year-old fund that seeks out only the highest-quality mid-cap growth stocks. With a just-announced change of management and philosophy, it might be moving to become a first-rate global value fund (with enough assets under management to start life as one of the group’s most affordable entries).
FundX Upgrader (FUNDX): all investors struggle with the need to refine their portfolios, dumping losers and adding winners. In a follow-up to his data-rich analysis on the possibility of using a simple moving average as a portfolio signal, associate editor Charles Boccadoro investigated the flagship fund of the Upgrader fleet.
Tributary Balanced (FOBAX): it’s remarkable that a fund this consistently good – in the top tier of all balanced funds over the past five-, ten-, and fifteen-year periods and a Great Owl by my colleague Charles’ risk/return calculations – hasn’t drawn more attention. It will be more remarkable if that neglect continues despite the recent return of the long-time manager who beat pretty much everyone in sight.
Elevator Talk #8: Steven Vannelli of GaveKal Knowledge Leaders (GAVAX)
Since the number of funds we can cover in-depth is smaller than the number of funds worthy of in-depth coverage, we’ve decided to offer one or two managers each month the opportunity to make a 200 word pitch to you. That’s about the number of words a slightly-manic elevator companion could share in a minute and a half. In each case, I’ve promised to offer a quick capsule of the fund and a link back to the fund’s site. Other than that, they’ve got 200 words and precisely as much of your time and attention as you’re willing to share. These aren’t endorsements; they’re opportunities to learn more.

Steven Vannelli, Manager
GaveKal Knowledge Leaders (GAVAX) believes in investing only in firms that are committed to being smart, so where did the dumb name come from? GaveKal is a portmanteau formed from the names of the firm’s founders: Charles Gave, Anatole Kaletsky and Louis-Vincent Gave. Happily it changed the fund’s original name from GaveKal Platform Company Fund (named after its European counterpart) to Knowledge Leaders.
GaveKal, headquartered in Hong Kong, started in 2001 as a global economics and asset allocation research firm. Their other investment products (the Asian Balanced Fund – a cool idea which was rechristened Asian Absolute Return – and Greater China Fund) are available to non-U.S. investors as, originally, was Knowledge Leaders. They opened a U.S. office in 2006. In 2010 they deepened their Asia expertise by acquiring Dragonomics, a China-focused research and advisory firm.
Knowledge Leaders has generated a remarkable record in its two-plus years of U.S. operation. They look to invest in “the best among global companies that are tapping a deep reservoir of intangible capital to generate earnings growth,” where “R&D, design, brand and channel” are markers of robust intangible capital. From launch through the end of June, 2013, the fund modestly outperformed the MSCI World Index and did so with two-thirds less volatility. Currently, approximately 30% of the portfolio is in cash, down from 40% earlier in summer.
Manager Steven Vannelli researches intangible capital and corporate performance and leads the fund’s investment team. Before joining GaveKal, he spent a decade at Alexander Capital, a Denver-based investment advisor. Here’s Mr. Vannelli’s 200 words making his case:
We invest in the world’s most innovative companies. Decades of academic research show that companies that invest heavily in innovation are structurally undervalued due to lack of information on innovative activities. Our strategy capitalizes on this market inefficiency.
To find investment opportunities, we identify Knowledge Leaders, or companies with large stores of intangible assets. These companies often operate globally across an array of industries from health care to technology, from consumer to capital goods. We have developed a proprietary method to capitalize a company’s intangible investments, revealing an important, invisible layer of value inherent to intangible-rich companies.
The Knowledge Leaders Strategy employs an active strategy that offers equity-like returns with bond-like risk. Superior risk-adjusted returns with low correlation to market indices make the GaveKal Knowledge Leaders Strategy a good vehicle for investors who seek to maximize their risk and return objectives.
The genesis of the strategy has its origin in the 2005 book, Our Brave New World, by GaveKal Research, which highlights knowledge as a scare asset.
As a validation of our intellectual foundation, in July, the US Bureau of Economic Analysis began to capitalize R&D to measure the contribution of innovation spending on growth of the US economy.
The minimum initial investment on the fund’s retail shares is $2,500. There are also institutional shares (GAVIX) with a $100,000 minimum (though they do let financial advisors aggregate accounts in order to reach that threshold). The fund’s website is clean and easily navigated. It would make a fair amount of sense for you to visit to “Fund Documents” page, which hosts the fund’s factsheet and a thoughtful presentation on intangible capital.
Our earlier Elevator Talks were:
- February 2013: Tom Kerr, Rocky Peak Small Cap Value (RPCSX), whose manager has a 14 year track record in small cap investing and a passion for discovering “value” in the intersection of many measures: discounted cash flows, LBO models, M&A valuations and traditional relative valuation metrics.
- March 2013: Dale Harvey, Poplar Forest Partners (PFPFX and IPFPX), a concentrated, contrarian value stock fund that offers “a once-in-a-generation opportunity to invest with a successful American Funds manager who went out on his own.”
- April 2013: Bayard Closser, Vertical Capital Income Fund (VCAPX), “a closed-end interval fund, VCAPX invests in whole mortgage loans and first deeds of trust. We purchase the loans from lenders at a deep discount and service them ourselves.”
- May 2013: Jim Hillary, LS Opportunity Fund (LSOFX), a co-founder of Marsico Capital Management whose worry that “the quality of research on Wall Street continues to decline and investors are becoming increasingly concerned about short-term performance” led to his faith in “in-depth research and long-term orientation in our high conviction ideas.”
- July 2013: Casey Frazier, Versus Capital Multi-Manager Real Estate Income Fund (VCMRX), a second closed-end interval fund whose portfolio “includes real estate private equity and debt, public equity and debt, and broad exposure across asset types and geographies. We target a mix of 70% private real estate with 30% public real estate to enhance liquidity, and our objective is to produce total returns in the 7 – 9% range net of fees.”
- August 2013: Brian Frank, Frank Value Fund (FRNKX), a truly all-cap value fund with a simple, successful discipline: if one part of the market is overpriced, shop elsewhere.
- August 2013: Ian Mortimer and Matthew Page of Guinness Atkinson Inflation Managed Dividend (GAINX), a global equity fund that pursues firms with “sustainable and potentially rising dividends,” which also translates to firms with robust business models and consistently high return on capital.
Upcoming conference call: A discussion of the reopening of RiverNorth Strategy Income (RNDLX)
 The folks at RiverNorth will host a conference call between the fund’s two lead managers, Patrick Galley of RiverNorth and Jeffrey Gundlach of DoubleLine, to discuss their decision to reopen the fund to new investors at the end of August and what they see going forward (the phrase “fear and loathing” keeps coming up).
The folks at RiverNorth will host a conference call between the fund’s two lead managers, Patrick Galley of RiverNorth and Jeffrey Gundlach of DoubleLine, to discuss their decision to reopen the fund to new investors at the end of August and what they see going forward (the phrase “fear and loathing” keeps coming up).
The call will be: Wednesday, September 18, 3:15pm – 4:15pm CDT
To register, go to www.rivernorthfunds.com/events/
The webcast will feature a Q&A with Messrs. Galley and Gundlach.
RNDLX (RNSIX for the institutional class), which the Observer profiled shortly after launch, has been a very solid fund with a distinctive strategy. Mr. Gundlach manages part of his sleeve of the portfolio in a manner akin to DoubleLine Core Fixed Income (DLFNX) and part with a more opportunistic income strategy. Mr. Galley pursues a tactical fixed-income allocation and an utterly unique closed-end fund arbitrage strategy in his slice. The lack of attractive opportunities in the CEF universe prompted the fund’s initial closure. Emily Deter of RiverNorth reports that the opening “is primarily driven by the current market opportunity in the closed-end fund space. Fixed-income closed-end funds are trading at attractive discounts to their NAVs, which is an opportunity we have not seen in years.” Investment News reported that fixed-income CEFs moved quickly from selling at a 2% premium to selling at a 7% discount.
That’s led Mr. Galley’s move from CEFs from occupying 17% of the portfolio a year ago to 30% today and, it seems, he believes he could pursue more opportunities if he had more cash on hand.
Given RiverNorth’s ongoing success and clear commitment to closing funds well before they become unmanageable, it’s apt to be a good use of your time.
The Observer’s own series of conference calls with managers who’ve proven to be interesting, sharp, occasionally wry and successful, will resume in October. We’ll share details in our October issue.
Funds in Registration
New mutual funds must be registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission before they can be offered for sale to the public. The SEC has a 75-day window during which to call for revisions of a prospectus; fund companies sometimes use that same time to tweak a fund’s fee structure or operating details.
Every day David Welsch, an exceedingly diligent research assistant at the Observer, scours new SEC filings to see what opportunities might be about to present themselves. David tracked down nearly 100 new funds and ETFs. Many of the proposed funds offer nothing new, distinctive or interesting. Some were downright mystifying. (Puerto Rico Shares? Colombia Capped ETF? The Target Duration 2-month ETF?) There were 26 no-load funds or actively-managed ETFs in registration with the SEC this month.
Funds in registration this month won’t be available for sale until, typically, the end of October or early November 2013.
There are probably more interesting products in registration this month than at any time in the seven years we’ve been tracking them. Among the standouts:
Brown Advisory Strategic European Equity Fund which will be managed by Dirk Enderlein of Wellington Management. Wellington is indisputably an “A-team” shop (they’ve got about three-quarters of a trillion in assets under management). Mr. Enderlein joined them in 2010 after serving as a manager for RCM – Allianz Global Investors in Frankfurt, Germany (1999-2009). Media reports described him as “one of Europe’s most highly regarded European growth managers.”
DoubleLine Shiller Enhanced CAPE will attempt to beat an index, Shiller Barclays CAPE® US Sector TR USD Index, which was designed based on decades of research by the renowned Robert Shiller. The fund will be managed by Jeffrey Gundlach and Jeffrey Sherman.
Driehaus Micro Cap Growth Fund, a converted 15 year old hedge fund
Harbor Emerging Markets Equity Fund, which will be sub-advised by the emerging markets team at Oaktree Capital Management. Oaktree’s a first-tier institutional manager with a very limited number of advisory relationships (primarily with Vanguard and RiverNorth) in the mutual fund world.
Meridian Small Cap Growth, which will be the star vehicle for Chad Meade and Brian Schaub, who Meridian’s new owner hired away from Janus. Morningstar’s Greg Carlson described them as “superb managers” who were “consistently successful during their nearly seven years at the helm” of Janus Triton.
Plus some innovative offerings from Northern, PIMCO and T. Rowe Price. Details and the list of all of the funds in registration are available at the Observer’s Funds in Registration page or by clicking “Funds” on the menu atop each page.
Manager Changes
On a related note, we also tracked down a record 85 fund manager changes. Investors should take particular note of Eric Ende and Stephen Geist’s exit from FPA Paramount after a 13 year run. The change is big enough that we’ve got a profile of Paramount as one of the month’s Most Intriguing New Funds.
Updates
 Bretton Fund (BRTNX) is now available through Vanguard. Manager Stephen Dodson writes that after our conference call, several listeners asked about the fund’s availability and Stephen encouraged them to speak directly with Vanguard. Mirabile dictu, the Big V was receptive to the idea.
Bretton Fund (BRTNX) is now available through Vanguard. Manager Stephen Dodson writes that after our conference call, several listeners asked about the fund’s availability and Stephen encouraged them to speak directly with Vanguard. Mirabile dictu, the Big V was receptive to the idea.
Stephen recently posted his most recent letter to his shareholders. He does a nice job of walking folks through the core of his investing discipline with some current illustrations. The short version is that he’s looking for firms with durable competitive advantages in healthy industries whose stocks are selling at a substantial discount. He writes:
There are a number of relevant and defensible companies out there that are easily identifiable; the hard part is finding the rare ones that are undervalued. The sweet spot for us continues to be relevant, defensible businesses at low prices (“cheap compounders”). I continue to spend my waking hours looking for them.
Q2 2013 presented slim pickin’s for absolute value investors (Bretton “neither initiated nor eliminated any investments during the quarter”). For all of the market’s disconcerting gyrations this summer, Morningstar calculates that valuations for its Wide Moat and Low Business Uncertainty groups (surrogates for “high quality stocks”) remains just about where they were in June: undervalued by about 4% while junkier stocks remain modestly overvalued.
Patience is hard.
Briefly Noted . . .
Calamos loses another president
James Boyne is resigning as president and chief operating officer of Calamos Investments effective Sept. 30, just eight months after being promoted to president. The firm has decided that they need neither a president nor a chief operating officer. Those responsibilities will be assumed “by other senior leaders” at the firm (see: Black, Gary, below). The preceding president, Nick P. Calamos, decided to “step back” from his responsibilities in August 2012 when, by coincidence, Calamos hired former Janus CEO Gary Black. To describe Black as controversial is a bit like described Rush Limbaugh as opinionated.
They’re not dead yet!
 Back in July, the Board of Caritas All-Cap Growth (CTSAX): “our fund is tiny, expensive, bad, and pursues a flawed investment strategy (long stocks, short ETFs).” Thereupon they reached a sensible conclusion: euthanasia. Shortly after the fund had liquidated all of its securities, “the Board was presented with and reviewed possible alternatives to the liquidation of the Fund that had arisen since the meeting on July 25, 2013.”
Back in July, the Board of Caritas All-Cap Growth (CTSAX): “our fund is tiny, expensive, bad, and pursues a flawed investment strategy (long stocks, short ETFs).” Thereupon they reached a sensible conclusion: euthanasia. Shortly after the fund had liquidated all of its securities, “the Board was presented with and reviewed possible alternatives to the liquidation of the Fund that had arisen since the meeting on July 25, 2013.”
The alternative? Hire Brenda A. Smith, founder of CV Investment Advisors, LLC, to manage the fund. A quick scan of SEC ADV filings shows that Ms. Smith is the principal in a two person firm with 10 or fewer clients and $5,000 in regulated AUM.
(I don’t know more about the firm because they have a one page website.)
At almost the same moment, the same Board gave Ms. Smith charge of the failing Presidio Multi-Strategy Fund (PMSFX), an overpriced long/short fund that executes its strategy through ETFs.
I wish Ms. Smith and her new investors all the luck in the world, but it’s hard to see how a Board of Trustees could, with a straight face, decide to hand over one fund and resuscitate another with huge structural impediments on the promise of handing it off to a rookie manager and declare that both moves are in the best interests of long-suffering shareholders.
Diamond Hill goes overseas, a bit
Effective September 1, 2013, Diamond Hill Research Opportunities Fund (DHROX) gains the flexibility to invest internationally (the new prospectus allows that it “may also invest in non-U.S. equity securities, including equity securities in emerging market countries”) and the SEC filing avers that they “will commence investing in foreign securities.” The fund has 15 managers; I’m guessing they got bored. As a hedge fund (2009-2011), it had a reasonably mediocre record which might have spurred the conversion to a ’40 fund. Which has also had a reasonably mediocre lesson, so points to the management for consistency!
Janus gets more bad news
Janus investors pulled $2.2 billion from the firm’s funds in July, the worst outflows in more than three years. A single investor accounted for $1.3 billion of the leakage. The star managers of Triton and Venture left in May. And now this: they’re losing business to Legg Mason.
The Board of Trustees of Met Investors Series Trust has approved a change of subadviser for the Janus Forty Portfolio from Janus Capital Management to ClearBridge Investments to be effective November 1, 2013 . . . Effective November 1, 2013, the name of the Portfolio will change to ClearBridge Aggressive Growth Portfolio II.
Matthews chucks Taiwan
Matthews Asia China (MCHFX), China Dividend (MCDFX) and Matthews and China Small Companies (MCSMX) have changed their Principal Investment Strategy to delete Taiwan. The text for China Dividend shows the template:
Under normal market conditions, the Matthews China Dividend Fund seeks to achieve its investment objective by investing at least 80% of its net assets, which include borrowings for investment purposes, in dividend-paying equity securities of companies located in China and Taiwan.
To:
Under normal market conditions, the Matthews China Dividend Fund seeks to achieve its investment objective by investing at least 80% of its nets assets, which include borrowings for investment purposes, in dividend-paying equity securities of companies located in China.
A reader in the financial services industry, Anonymous Dude, checked with Matthews about the decision. AD reports
The reason was that the SEC requires that if you list Taiwan in the Principal Investment Strategies portion of the prospectus you have to include the word “Greater” in the name of the fund. They didn’t want to change the name of the fund and since they could still invest up to 20% they dropped Taiwan from the principal investment strategies. He said if the limitation ever became an issue they would revisit potentially changing the name. Mystery solved.
The China Fund currently has nothing investing in Taiwan, China Small is 14% and China Dividend is 15%. And gracious, AD!
T. Rowe tweaks
Long ago, as a college administrator, I was worried about whether the text in a proposed policy statement might one day get us in trouble. I still remember college counsel shaking his head confidently, smiling and saying “Not to worry. We’re going to fuzz it up real good.” One wonders if he works for T. Rowe Price now? Up until now, many of Price’s funds have had relatively detailed and descriptive investment objectives. No more! At least five of Price’s funds propose new language that reduces the statement of investment objectives to an indistinct mumble. T. Rowe Price Growth Stock Fund (PRGFX) goes from
The fund seeks to provide long-term capital growth and, secondarily, increasing dividend income through investments in the common stocks of well-established growth companies.
To
The fund seeks long-term capital growth through investments in stocks.
Similar blandifications are proposed for Dividend Growth, Equity Income, Growth & Income and International Growth & Income.
Wasatch redefines “small cap”
A series of Wasatch funds, Small Growth, Small Value and Emerging Markets Small Cap are upping the size of stocks in their universe from $2.5 billion or less to $3.0 billion or less. The change is effective in November.
Can you say whoa!? Or WOA?
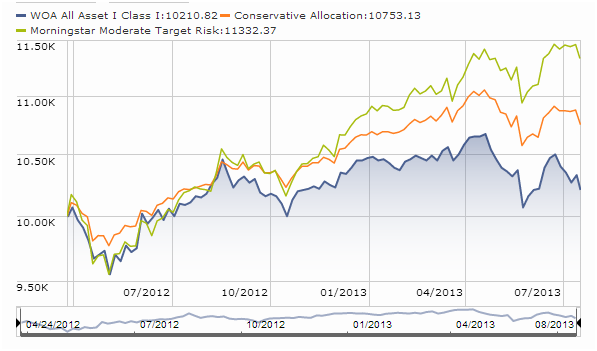
The Board of Trustees of an admittedly obscure little institutional fund, WOA All Asset (WOAIX), has decided that the best way to solve what ails the yearling fund is to get it more aggressive.
The Board approved certain changes to the Fund’s principal investment strategies. The changes will be effective on or about September 3, 2013. . . the changes in the Fund’s strategy will alter the Fund’s risk level from balanced strategy with a moderate risk level to an aggressive risk level.
Here’s the chart of the fund’s performance since inception against conservative and moderate benchmarks. While that might show that the managers just need to fire up the risk machine, I’d also imagine that addressing the ridiculously high expenses (1.75% for an institutional balanced fund) and consistent ability to lag in both up and down months (11 of 16 and counting) might actually be a better move.
WOA’s Trustees, by the way, are charged with overseeing 24 funds. No Trustee has a dollar invested in any of those funds.
SMALL WINS FOR INVESTORS
The Board of Trustees of the Direxion Funds and Rafferty Asset Management have decided to make it cheaper for you to own a bunch of funds that you really shouldn’t own. They’re removed the 25 bps Shareholder Servicing Fee from
- Direxion Monthly S&P 500® Bull 2X Fund
- Direxion Monthly S&P 500® Bear 2X Fund
- Direxion Monthly NASDAQ-100® Bull 2X Fund
- Direxion Monthly Small Cap Bull 2X Fund
- Direxion Monthly Small Cap Bear 2X Fund
- Direxion Monthly Emerging Markets Bull 2X Fund
- Direxion Monthly Latin America Bull 2X Fund
- Direxion Monthly China Bull 2X Fund
- Direxion Monthly Commodity Bull 2X Fund
- Direxion Monthly 7-10 Year Treasury Bull 2X Fund
- Direxion Monthly 7-10 Year Treasury Bear 2X Fund
- Dynamic HY Bond Fund and
- U.S. Government Money Market Fund.
Because Eaton Vance loves you, they’ve decided to create the opportunity for investors to buy high expense “C” class shares of Eaton Vance Bond (EVBCX). The new shares will add a 1.00% back load for sales held less than a year and a 1.70% expense ratio (compared to 0.7 and 0.95 for Institutional and A, respectively).
The Fairholme Fund (FAIRX) reopened to new investors on August 19, 2013. The other Fairholme family funds, not so much.
The Advisor Class shares of Forward Select Income Fund (FSIMX) reopened to new investors at the end of August.
The Board of Directors of the Leuthold Global Industries Fund (LGINX) has agreed to reduce the Fund’s expense cap from 1.85% to 1.60%.
JacksonPark Capital reduced the minimum initial investment on Oakseed Opportunity Institutional shares (SEDEX) from $1 million to $10,000. Given the 18% lower fees on the institutional class (capped at 1.15% versus 1.40% for retail shares), reasonably affluent retail investors ought to seriously consider pursuing the institutional share class. That said, Oakseed’s minimum investment for the retail shares, as low as $100 for accounts set up with an AIP, are awfully reasonable.
RiverNorth DoubleLine Strategic Income (RNDLX/RNSIX) reopened to new investors at the end of August. Check the “upcoming conference calls” feature, above, for more details.
Westcore Blue Chip Dividend Fund (WTMVX ) lowered the expense ratio on its no-load retail shares from 1.15% to 0.99%, effective September 1. They also changed from paying distributions annually to paying them quarterly. It’s a perfectly agreeable, mild-mannered little fund: stable management, global diversified, reasonable expenses and very consistently muted volatility. You do give up a fair amount of upside for the opportunity to sleep a bit more quietly at night.
CLOSINGS (and related inconveniences)
American Beacon Stephens Small Cap Growth Fund (STSGX) will close to new investors, effective as of September 16, 2013. The no-class share class has returned 11.8% while its peers made 9.3% and it did so with lower volatility. The fund is closing at a still small $500 million.
Neither high fees nor mediocre performance can dim the appeal of AQR Multi-Strategy Alternative Fund (ASANX/ASAIX). The fund has drawn $1.5 billion and has advertised the opportunity for rich investors (the minimum runs between $1 million and $5 million) to rush in before the doors swing shut at the end of September. It’s almost always a bad sign that a fund feels the need to close and the need to put up a flashing neon sign six weeks ahead.
Morgan Stanley Institutional Global Franchise (MSFAX) will close to new investors on Nov. 29, 2013. The current management team came on board four years ago (June 2009) and have posted very good risk-adjusted returns since then. Investors might wonder why a large cap global fund with a small asset base needs to close. The answer is that the mutual fund represents just the tip of the iceberg; this team actually manages almost $17 billion in this strategy, so the size of the separate accounts is what’s driving the decision.
OLD WINE, NEW BOTTLES
At the end of September Ariel International Equity Fund (AINTX) becomes Ariel International Fund and will no longer be required to invest at least 80% of its assets in equities. At the same time, Ariel Global Equity Fund (AGLOX) becomes Ariel Global Fund. The advisor avers that it’s not planning on changing the funds’ investment strategies, just that it would be nice to have the option to move into other asset classes if conditions dictate.
Effective October 30, Guggenheim U.S. Long Short Momentum Fund (RYAMX) will become plain ol’ Guggenheim Long-Short Fund. In one of those “why bother” changes, the prospectus adds a new first sentence to the Strategy section (“invest, under normal circumstances, at least 80% of its assets in long and short equity or equity-like securities”) but maintains the old “momentum” language in the second and third sentences. They’ll still “respond to the dynamically changing economy by moving its investments among different industries and styles” and “allocates investments to industries and styles according to several measures of momentum. “ Over the past five years, the fund has been modestly more volatile and less profitable than its peers. As a result, they’ve attracted few assets and might have decided, as a marketing matter, that highlighting a momentum approach isn’t winning them friends.
As of October 28, the SCA Absolute Return Fund (SCARX) will become the Granite Harbor Alternative Fund and it will no longer aim to provide “positive absolute returns with less volatility than traditional equity markets.” Instead, it’s going for the wimpier “long-term capital appreciation and income with low correlation” to the markets. SCA Directional Fund (SCADX) will become Granite Harbor Tactical Fund but will no longer seek “returns similar to equities with less volatility.” Instead, it will aspire to “long term capital appreciation with moderate correlation to traditional equity markets.”
Have you ever heard someone say, “You know, what I’m really looking for is a change for a moderate correlation to the equity markets”? No, me neither.
Thomas Rowe Price, Jr. (the man, 1898-1983) has been called “the father of growth investing.” It’s perhaps then fitting that T. Rowe Price (the company) has decided to graft the word “Growth” into the names of many of its funds effective November 1.
T. Rowe Price Institutional Global Equity Fund becomes T. Rowe Price Institutional Global Focused Growth Equity Fund. Institutional Global Large-Cap Equity Fund will change its name to the T. Rowe Price Institutional Global Growth Equity Fund. T. Rowe Price Global Large-Cap Stock Fund will change its name to the T. Rowe Price Global Growth Stock Fund.
Effective October 28, 2013, USB International Equity Fund (BNIEX) gets a new name (UBS Global Sustainable Equity Fund), new mandate (invest globally in firms that pass a series of ESG screens) and new managers (Bruno Bertocci and Shari Gilfillan). The fund’s been a bit better under the five years of Nick Irish’s leadership than its two-star rating suggests, but not by a lot.
Off to the dustbin of history
There were an exceptionally large number of funds giving up the ghost this month. We’ve tracked 26, the same as the number of new no-load funds in registration and well below the hundred or so new portfolios of all sorts being launched. I’m deeply grateful to The Shadow, one of the longest-tenured members of our discussion board, for helping me to keep ahead of the flood.
American Independence Dynamic Conservative Plus Fund (TBBIX, AABBX) will liquidate on or about September 27, 2012.
Dynamic Canadian Equity Income Fund (DWGIX) and Dynamic Gold & Precious Metals Fund (DWGOX), both series of the DundeeWealth Funds, are slated for liquidation on September 23, 2013. Dundee bumped off Dynamic Contrarian Advantage Fund (DWGVX) and announced that it was divesting itself of three other funds (JOHCM Emerging Markets Opportunities Fund JOEIX, JOHCM International Select Fund JOHIX and JOHCM Global Equity Fund JOGEX), which are being transferred to new owners.
Equinox Commodity Strategy Fund (EQCAX) closed to new investors in mid-August and will liquidate on September 27th.
 The Evolution Funds face extinction! Oh, the cruel irony of it.
The Evolution Funds face extinction! Oh, the cruel irony of it.
Evolution Managed Bond (PEMVX) Evolution All-Cap Equity (PEVEX), Evolution Market Leaders (PEVSX) and Evolution Alternative Investment (PETRX) have closed to all new investment and were scheduled to liquidate by the end of September. Given their disappearance from Morningstar, one suspects the end came more quickly than we knew.
Frontegra HEXAM Emerging Markets Fund (FHEMX) liquidates at the end of September.
The Northern Lights Board of Trustees has concluded that “based on, among other factors, the current and projected level of assets in the Fund and the belief that it would be in the best interests of the Fund and its shareholders to discontinue the Hundredfold Select Global Fund (SFGPX).”
Perhaps the “other factors” would be the fact that Hundredfold trailed 100% of its peers over the past three- and five-year periods? The manager was unpaid and quite possibly the fund’s largest shareholder ($50-100k in a $2M fund). His Hundredfold Select Equity (SFEOX) is almost as woeful as the decedent, but Hundredfold Select Alternative (SFHYX) is in the top 1% of its peer group for the same period that the others are bottom 1%. That raises the spectre that luck, rather than skill, might be involved.
JPMorgan is cleaning house: JPMorgan Credit Opportunities Fund (JOCAX), JPMorgan Global Opportunities Fund (JGFAX) and JPMorgan Russia Fund (JRUAX) are all gone as of October 4.
John Hancock intends to merge John Hancock High Income (JHAQX) into John Hancock High Yield (JHHBX). I’m guessing at the fund tickers because the names in the SEC filing don’t quite line up with the Morningstar ones.
Legg Mason Esemplia Emerging Markets Long-Short Fund (SMKAX) will be terminated on October 1, 2013. Let’s see: hard-to-manage strategy, high risk, high expenses, high front load, no assets . . . sounds like Legg.
Leuthold Asset Allocation Fund (LAALX) is merging into Leuthold Core Investment Fund (LCORX). The Board of Directors approved a proposal for the Leuthold Asset Allocation to be acquired by the Leuthold Core, sometime in October 2013. Curious. LAALX, with a quarter billion in assets, modestly lags LCORX which has about $600 million. Both lag more mild-mannered funds such as Northern Global Tactical Asset Allocation (BBALX) and Vanguard STAR (VGSTX) over the course of LAALX’s lifetime. This might be less a story about LAALX than about the once-legendary Leuthold Core. Leuthold’s funds are all quant-driven, based on an unparalleled dataset. For years Core seemed unstoppable: between 2003 and 2008, it finished in the top 5% of its peer group four times. But for 2009 to now, it has trailed its peers every year and has bled $1 billion in assets. In merging the two, LAALX investors get a modestly less expensive fund with modestly better performance. Leuthold gets a simpler administrative structure.
I halfway admire the willingness of Leuthold to close products that can’t distinguish themselves in the market. Clean Tech, Hedged Equity, Undervalued & Unloved, Select Equities and now Asset Allocation have been liquidated.
MassMutual Premier Capital Appreciation Fund (MCALX) will be liquidated, but not until January 24, 2014. Why?
New Frontiers KC India Fund (NFIFX) has closed and began the process of liquidating their portfolio on August 26th. They point to “difficult market conditions in India.” The fund’s returns were comparable to its India-focused peers, which is to say it lost about 30% in 18 months.
Nomura Partners India Fund (NPIAX), Greater China Fund (NPCAX) and International Equity Fund (NPQAX) will all be liquidated by month’s end.
Nuveen Quantitative Enhanced Core Equity (FQCAX) is slated, pending inevitable shareholder approval, to disappear into Nuveen Symphony Low Volatility Equity Fund (NOPAX, formerly Nuveen Symphony Optimized Alpha Fund)
Oracle Mutual Fund (ORGAX) has “due to the relatively small size of the fund” underwent the process of “orderly dissolution.” Due to the relatively small size? How about, “due to losing 49.5% of our investors’ money over the past 30 months, despite an ongoing bull market in our investment universe”? To his credit, the advisor’s president and portfolio manager went down with the ship: he had something between $500,000 – $1,000,000 left in the fund as of the last SAI.
Quantitative Managed Futures Strategy Fund (QMFAX) will “in the best interests of the Fund and its shareholders” redeem all outstanding shares on September 15th.
The directors of the United Association S&P 500 Index Fund (UASPX/UAIIX) have determined that it’s in their shareholders’ best interest to liquidate. Uhhh … I don’t know why. $140 million in assets, low expenses, four-star rating …
Okay, so the Oracle Fund didn’t seem particularly oracular but what about the Steadfast Fund? Let’s see: “steadfast: firmly loyal or constant, unswerving, not subject to change.” VFM Steadfast Fund (VFMSX) launched less than one year ago and gone before its first birthday.
In Closing . . .
Interesting stuff’s afoot. We’ve spoken with the folks behind the surprising Oberweis International Opportunities Fund (OBIOX), which was much different and much more interesting that we’d anticipated. Thanks to “Investor” for poking us about a profile. In October we’ll have one. RiverPark Strategic Income is set to launch at the end of the month, which is exciting both because of the success of the other fund (the now-closed RiverPark Short Term High Yield Fund RPHYX) managed by David Sherman and Cohanzick Asset Management and because Sherman comes across as such a consistently sharp and engaging guy. With luck, I’ll lure him into an extended interview with me and a co-conspirator (the gruff but lovable Ed Studzinski, cast in the role of a gruff but lovable curmudgeon who formerly managed a really first-rate mutual fund, which he did).
 MFO returns to Morningstar! Morningstar is hosting their annual ETF Invest Conference in Chicago, from October 2 – 4. While, on whole, we’d rather drop by their November conference in Milan, Italy it was a bit pricey and I couldn’t get a dinner reservation at D’O before early February 2014 so we decided to pass it up. While the ETF industry seems to be home to more loony ideas and regrettable business practices than most, it’s clear that the industry’s maturing and a number of ETF products offer low cost access to sensible strategies, some in areas where there are no tested active managers. The slow emergence of active ETFs blurs the distinction with funds and Morningstar does seem do have arranged both interesting panels (skeptical though I am, I’ll go listen to some gold-talk on your behalf) and flashy speakers (Austan Goolsbee among them). With luck, I’ll be able to arrange a couple of face-to-face meetings with Chicago-based fund management teams while I’m in town. If you’re going to be at the conference, feel free to wave. If you’d like to chat, let me know.
MFO returns to Morningstar! Morningstar is hosting their annual ETF Invest Conference in Chicago, from October 2 – 4. While, on whole, we’d rather drop by their November conference in Milan, Italy it was a bit pricey and I couldn’t get a dinner reservation at D’O before early February 2014 so we decided to pass it up. While the ETF industry seems to be home to more loony ideas and regrettable business practices than most, it’s clear that the industry’s maturing and a number of ETF products offer low cost access to sensible strategies, some in areas where there are no tested active managers. The slow emergence of active ETFs blurs the distinction with funds and Morningstar does seem do have arranged both interesting panels (skeptical though I am, I’ll go listen to some gold-talk on your behalf) and flashy speakers (Austan Goolsbee among them). With luck, I’ll be able to arrange a couple of face-to-face meetings with Chicago-based fund management teams while I’m in town. If you’re going to be at the conference, feel free to wave. If you’d like to chat, let me know.
 If you shop Amazon, please do remember to click on the Observer’s link and use it. If you click on it right now, you can bookmark it or set it as a homepage and then you won’t forget. The partnership with Amazon generates about $20/day which, while modest, allows us to reliably cover all of our “hard” expenses and underwrites the occasional conference coverage. If you’d prefer to consider other support options, that’s great. Just click on “support us” on the top menu bar. But the Amazon thing is utterly painless for you.
If you shop Amazon, please do remember to click on the Observer’s link and use it. If you click on it right now, you can bookmark it or set it as a homepage and then you won’t forget. The partnership with Amazon generates about $20/day which, while modest, allows us to reliably cover all of our “hard” expenses and underwrites the occasional conference coverage. If you’d prefer to consider other support options, that’s great. Just click on “support us” on the top menu bar. But the Amazon thing is utterly painless for you.
The Sufi poet Attar records the fable of a powerful king who asks assembled wise men to create a ring that will make him happy when he is sad, and vice versa. After deliberation the sages hand him a simple ring with the words “This too will pass.” That’s also true of whatever happens to the market and your portfolio in September and October.
Be brave and we’ll be with you in a month!


 My colleagues in the English department are forever yammering on about this Shakespeare guy.I’m skeptical. First, he didn’t even know how to spell his own name (“Wm Shakspē”? Really?). Second, he clearly didn’t understand seasonality of the markets. If you listen to Gloucester’s famous declamation in Richard III, you’ll see what I mean:
My colleagues in the English department are forever yammering on about this Shakespeare guy.I’m skeptical. First, he didn’t even know how to spell his own name (“Wm Shakspē”? Really?). Second, he clearly didn’t understand seasonality of the markets. If you listen to Gloucester’s famous declamation in Richard III, you’ll see what I mean:








 Since his debut in February 2012, my colleague Charles Boccadoro has produced some exceedingly solid, data-rich analyses for us, including this month’s review of the risk/return profiles of the FundX family of funds. One of his signature contributions was “
Since his debut in February 2012, my colleague Charles Boccadoro has produced some exceedingly solid, data-rich analyses for us, including this month’s review of the risk/return profiles of the FundX family of funds. One of his signature contributions was “

 Back in July, the Board of Caritas All-Cap Growth (CTSAX): “our fund is tiny, expensive, bad, and pursues a flawed investment strategy (long stocks, short ETFs).” Thereupon they reached a sensible conclusion: euthanasia. Shortly after the fund had liquidated all of its securities, “the Board was presented with and reviewed possible alternatives to the liquidation of the Fund that had arisen since the meeting on July 25, 2013.”
Back in July, the Board of Caritas All-Cap Growth (CTSAX): “our fund is tiny, expensive, bad, and pursues a flawed investment strategy (long stocks, short ETFs).” Thereupon they reached a sensible conclusion: euthanasia. Shortly after the fund had liquidated all of its securities, “the Board was presented with and reviewed possible alternatives to the liquidation of the Fund that had arisen since the meeting on July 25, 2013.”

 The Evolution Funds face extinction! Oh, the cruel irony of it.
The Evolution Funds face extinction! Oh, the cruel irony of it. MFO returns to Morningstar! Morningstar is hosting their annual ETF Invest Conference in Chicago, from October 2 – 4. While, on whole, we’d rather drop by their November conference in Milan, Italy it was a bit pricey and I couldn’t get a dinner reservation at D’O before early February 2014 so we decided to pass it up. While the ETF industry seems to be home to more loony ideas and regrettable business practices than most, it’s clear that the industry’s maturing and a number of ETF products offer low cost access to sensible strategies, some in areas where there are no tested active managers. The slow emergence of active ETFs blurs the distinction with funds and Morningstar does seem do have arranged both interesting panels (skeptical though I am, I’ll go listen to some gold-talk on your behalf) and flashy speakers (Austan Goolsbee among them). With luck, I’ll be able to arrange a couple of face-to-face meetings with Chicago-based fund management teams while I’m in town. If you’re going to be at the conference, feel free to wave. If you’d like to chat, let me know.
MFO returns to Morningstar! Morningstar is hosting their annual ETF Invest Conference in Chicago, from October 2 – 4. While, on whole, we’d rather drop by their November conference in Milan, Italy it was a bit pricey and I couldn’t get a dinner reservation at D’O before early February 2014 so we decided to pass it up. While the ETF industry seems to be home to more loony ideas and regrettable business practices than most, it’s clear that the industry’s maturing and a number of ETF products offer low cost access to sensible strategies, some in areas where there are no tested active managers. The slow emergence of active ETFs blurs the distinction with funds and Morningstar does seem do have arranged both interesting panels (skeptical though I am, I’ll go listen to some gold-talk on your behalf) and flashy speakers (Austan Goolsbee among them). With luck, I’ll be able to arrange a couple of face-to-face meetings with Chicago-based fund management teams while I’m in town. If you’re going to be at the conference, feel free to wave. If you’d like to chat, let me know.

 Everybody’s talking about long/short funds. Google chronicles 273,000 pages that use the phrase. Bloomberg promises “a comprehensive list of long/short funds worldwide.” Morningstar, Lipper and U.S. News plunk nearly a hundred funds into a box with that label. (Not the same hundred funds, by the way. Not nearly.) Seeking Alpha offers up the “best and less long/short funds 2013.”
Everybody’s talking about long/short funds. Google chronicles 273,000 pages that use the phrase. Bloomberg promises “a comprehensive list of long/short funds worldwide.” Morningstar, Lipper and U.S. News plunk nearly a hundred funds into a box with that label. (Not the same hundred funds, by the way. Not nearly.) Seeking Alpha offers up the “best and less long/short funds 2013.”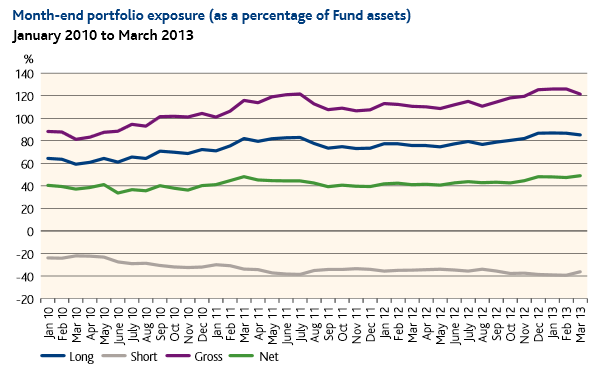
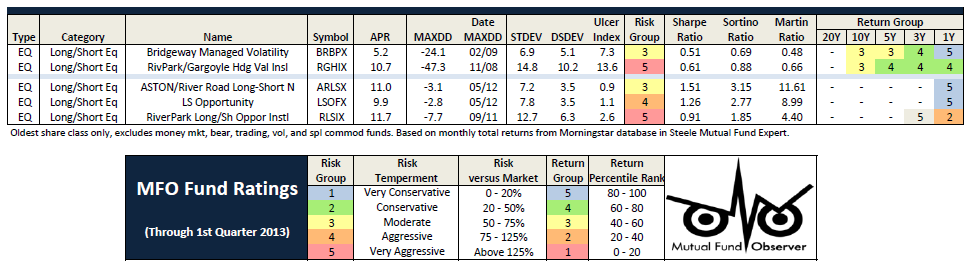

 The Healthy Debate
The Healthy Debate Versus Capital Multi-Manager Real Estate Income Fund is a closed-end interval fund. That means that you can buy Versus shares any day that the market is open, but you only have the opportunity to sell those shares once each quarter. The advisor has the option of meeting some, all or none of a particular quarter’s redemption requests, based on cash available and the start of the market.
Versus Capital Multi-Manager Real Estate Income Fund is a closed-end interval fund. That means that you can buy Versus shares any day that the market is open, but you only have the opportunity to sell those shares once each quarter. The advisor has the option of meeting some, all or none of a particular quarter’s redemption requests, based on cash available and the start of the market.